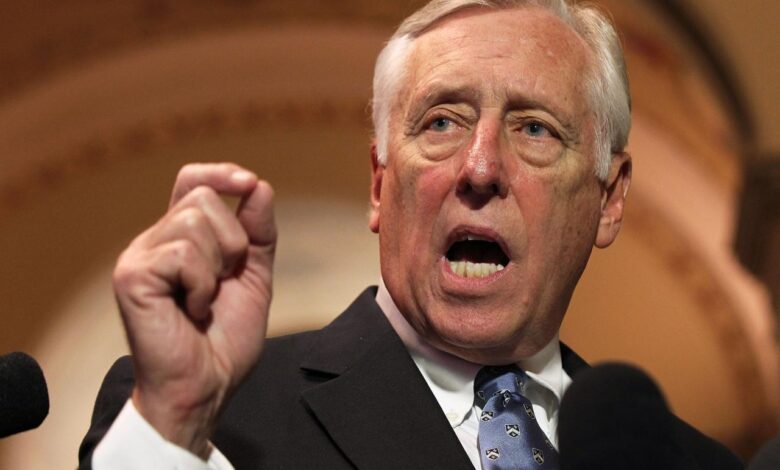
House to Move on Stimulus, but Payroll Tax Cut Rejected
House to move on coronavirus related stimulus package but hoyer says payroll tax cut a nonstarter, this statement throws the spotlight on a major political clash within the ongoing efforts to combat the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic. The House is pushing forward with a stimulus package aimed at providing relief to struggling individuals and businesses, but a key element of the package – a payroll tax cut – has been met with strong opposition from House Speaker Hoyer.
This clash highlights the complex and multifaceted nature of the debate surrounding economic recovery, raising questions about the effectiveness of different stimulus measures and the political will to navigate these challenges.
The proposed stimulus package includes a range of provisions designed to address various economic needs, such as direct payments to individuals, extended unemployment benefits, and aid to small businesses. The rationale behind the House’s decision to move forward with the package is rooted in the urgency to provide immediate relief and support long-term economic recovery.
The package aims to stimulate growth, create jobs, and prevent further economic hardship in the wake of the pandemic.
Stimulus Package Debate

The House of Representatives is poised to vote on a new coronavirus-related stimulus package, aiming to provide much-needed relief to individuals and businesses struggling amid the ongoing pandemic. This proposed package, however, faces significant hurdles, including opposition from some lawmakers and uncertainty about its effectiveness.
Key Provisions and Funding Sources
The proposed stimulus package encompasses a range of measures designed to address the economic fallout from the pandemic. Key provisions include direct payments to individuals, extended unemployment benefits, funding for small businesses, and support for healthcare providers. The package is expected to be financed through a combination of borrowing and increased taxes on corporations and high-income earners.
Rationale for the Stimulus Package
The House’s decision to move forward with the stimulus package is driven by concerns about the ongoing economic hardship and the potential for a protracted recession. The pandemic has led to widespread job losses, business closures, and a sharp decline in consumer spending.
Proponents argue that the stimulus package is necessary to prevent a further economic downturn and provide much-needed relief to struggling Americans.
Perspectives on the Stimulus Package
The proposed stimulus package has generated considerable debate, with proponents and opponents offering contrasting views. Supporters argue that the package is essential to stimulate economic activity, create jobs, and provide financial assistance to those in need. They highlight the urgent need for government intervention to mitigate the economic impact of the pandemic.Opponents, however, raise concerns about the potential for excessive government spending and the long-term implications for the national debt.
They argue that the stimulus package may not be effective in achieving its intended goals and could lead to unintended consequences, such as inflation or increased dependence on government assistance.
The House is pushing forward with a coronavirus-related stimulus package, but it seems a payroll tax cut is off the table for now, with Speaker Hoyer calling it a “nonstarter.” Meanwhile, in a separate development, a judge has ordered Attorney General Barr to show him the unredacted Mueller report, a move that could shed more light on the investigation.
This decision, though seemingly unrelated, could influence the overall political climate, potentially affecting the trajectory of the stimulus package discussions as well.
Potential Impact of the Stimulus Package
The potential impact of the stimulus package on the economy and individuals is a subject of ongoing debate. Proponents argue that the package will provide much-needed relief to individuals and businesses, boost consumer spending, and stimulate economic growth. They point to historical examples of government stimulus measures that have successfully mitigated economic downturns.Opponents, however, express concerns about the potential for the stimulus package to exacerbate existing economic problems, such as inflation or a decline in the value of the dollar.
They argue that the package may not be effective in addressing the underlying causes of the economic downturn and could lead to unintended consequences.
Payroll Tax Cut
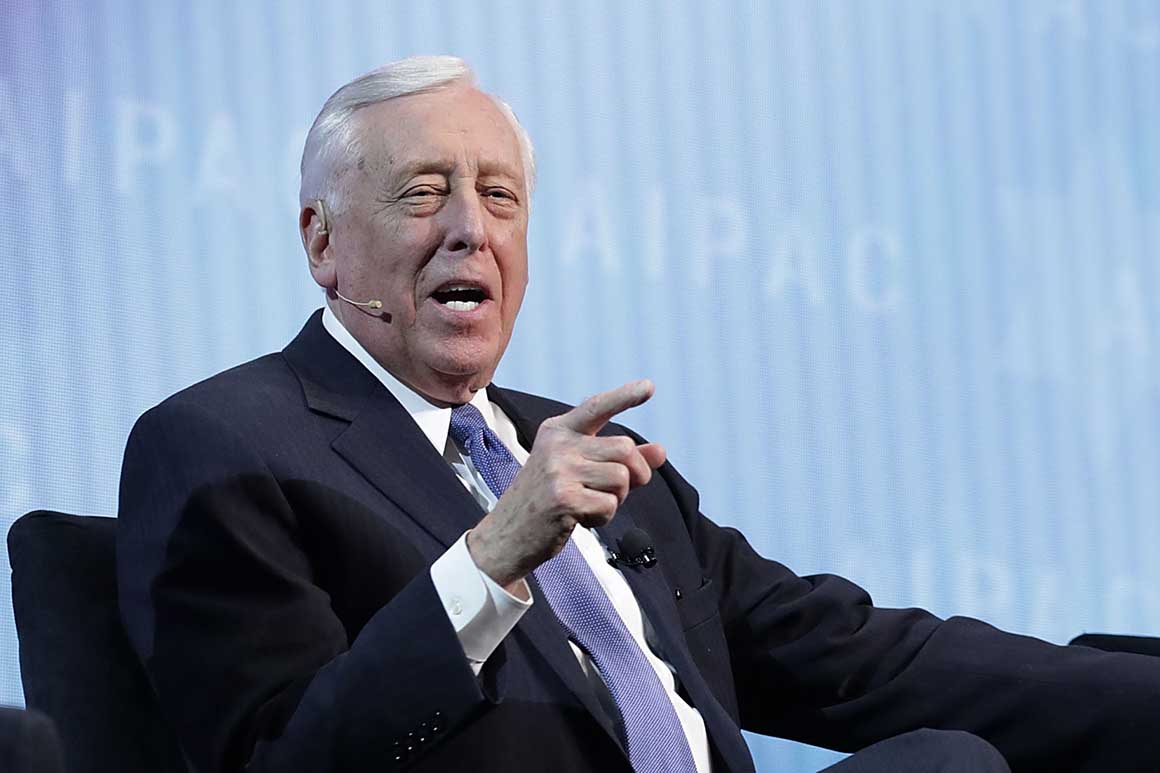

House Speaker Steny Hoyer has firmly stated that a payroll tax cut is a “nonstarter” in the current negotiations for a coronavirus-related stimulus package. His stance reflects concerns about the effectiveness of such a measure and its potential to exacerbate existing economic disparities.
Hoyer’s Reasons for Rejecting a Payroll Tax Cut
Hoyer argues that a payroll tax cut would disproportionately benefit high-income earners, while offering limited relief to low- and middle-income individuals who are most vulnerable to the economic fallout of the pandemic. He emphasizes that direct payments, expanded unemployment benefits, and support for small businesses are more effective ways to stimulate the economy and provide targeted assistance to those in need.
Economic Effects of a Payroll Tax Cut vs. Other Stimulus Measures
A payroll tax cut would put more money in the pockets of workers, but its impact on consumer spending and economic growth is uncertain. Some economists argue that it could lead to increased savings rather than spending, while others believe it could boost demand and stimulate the economy.
However, the effectiveness of a payroll tax cut depends on factors such as the size of the cut, the duration of the program, and the overall economic climate. Direct payments, on the other hand, provide a more immediate and targeted form of stimulus, ensuring that money reaches those who need it most.
Similarly, expanded unemployment benefits offer vital financial support to workers who have lost their jobs due to the pandemic. These measures have a more direct and predictable impact on consumer spending and economic activity.
It seems like the House is deadlocked on a coronavirus stimulus package, with Democrats and Republicans at odds over a payroll tax cut. While the political wrangling continues, it’s hard not to be reminded of the escalating tensions in Europe, where Putin could make a move to absorb Belarus, Europe’s last dictatorship, according to experts.
Perhaps a global crisis like this could inspire a more unified approach to the pandemic in the US, but it’s hard to be optimistic when our own political landscape is so fractured.
Political Implications of Hoyer’s Position
Hoyer’s stance on a payroll tax cut has significant political implications, as it highlights the divide between Democrats and Republicans on how to address the economic crisis. Republicans have advocated for a payroll tax cut as a key component of their stimulus plan, arguing that it would boost economic growth and provide much-needed relief to businesses and workers.
However, Democrats have largely rejected this proposal, arguing that it would be ineffective and exacerbate income inequality. This clash of priorities could hinder negotiations and delay the passage of a much-needed stimulus package. The political deadlock could also lead to further polarization and gridlock, making it difficult to address other pressing issues facing the nation.
Potential Alternatives to a Payroll Tax Cut
Hoyer has indicated support for a range of alternative stimulus measures, including direct payments, expanded unemployment benefits, support for small businesses, and increased funding for healthcare and education. These measures aim to provide targeted relief to those most affected by the pandemic while also stimulating the economy.
For example, direct payments could be targeted to low- and middle-income households, ensuring that the money reaches those who need it most. Expanded unemployment benefits could provide a safety net for workers who have lost their jobs, allowing them to maintain their standard of living and contribute to the economy.
Support for small businesses could help them stay afloat during the pandemic, preserving jobs and contributing to economic recovery. While these alternative measures have their own advantages and disadvantages, they offer a more targeted and effective approach to stimulating the economy and providing relief to those in need.
The Role of the Coronavirus Pandemic in Shaping Stimulus Measures

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the global economy, triggering widespread economic disruptions and necessitating unprecedented government interventions. Stimulus packages, designed to mitigate the economic fallout of the pandemic, have played a crucial role in supporting businesses, workers, and consumers.
Understanding the pandemic’s influence on the design and implementation of these measures is essential for evaluating their effectiveness and informing future economic policy responses.
Economic Challenges Posed by the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has posed numerous economic challenges, affecting businesses, workers, and consumers alike. The pandemic led to widespread business closures, supply chain disruptions, and a sharp decline in consumer spending. Businesses faced significant challenges in adapting to the changing economic landscape, while workers experienced job losses, reduced hours, and wage cuts.
The House is moving forward with a coronavirus-related stimulus package, but the Democrats and Republicans are still at odds over the details. Speaker Nancy Pelosi has said that a payroll tax cut is a nonstarter, while President Trump, in a recent rally in South Carolina, accused the Democrats of politicizing the coronavirus and insisted that the country is “totally prepared”.
The House’s proposed stimulus package is likely to face further hurdles in the Senate, where Republicans have already expressed reservations about some of the provisions.
Consumers, facing uncertainty and reduced income, cut back on discretionary spending, leading to a further decline in economic activity.
Influence of the Pandemic on Stimulus Measures
The pandemic’s unprecedented nature has significantly influenced the design and implementation of stimulus packages. The need for immediate relief, coupled with the uncertain duration of the pandemic, has prompted policymakers to adopt measures aimed at providing short-term support while also laying the groundwork for long-term economic recovery.
The stimulus packages have been designed to address the specific challenges posed by the pandemic, such as providing financial assistance to businesses, supporting unemployed workers, and stimulating consumer spending.
Effectiveness of Previous Stimulus Measures
Previous stimulus measures have had a mixed impact on mitigating the economic impact of the pandemic. While some measures, such as the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) and enhanced unemployment benefits, have been successful in providing immediate relief, others, such as the payroll tax cut, have been less effective.
The effectiveness of stimulus measures has also been influenced by factors such as the speed and scale of implementation, the targeting of specific groups, and the overall economic environment.
Comparison of Stimulus Measures
The following table compares and contrasts different stimulus measures implemented during the pandemic:
| Measure | Intended Effect | Target Audience | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) | Provide forgivable loans to small businesses to cover payroll and other expenses | Small businesses | Potential for fraud and misuse, limited access for certain businesses |
| Enhanced Unemployment Benefits | Provide additional unemployment benefits to laid-off workers | Unemployed workers | Potential for disincentivizing job search, potential for fraud |
| Stimulus Checks | Provide direct payments to individuals and families to stimulate consumer spending | Individuals and families | Potential for leakage into savings, potential for unintended consequences |
| Payroll Tax Cut | Reduce payroll taxes for employers and employees to stimulate economic activity | Employers and employees | Limited impact on consumer spending, potential for increased government debt |
The Future of Economic Policy in the Context of the Pandemic: House To Move On Coronavirus Related Stimulus Package But Hoyer Says Payroll Tax Cut A Nonstarter
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound and lasting impact on the global economy. While the immediate crisis has eased in many countries, the long-term economic implications are still unfolding, posing significant challenges for policymakers. This section will delve into the ongoing economic challenges, the need for continued policy support, and key policy priorities for addressing these challenges.
Ongoing Economic Challenges
The pandemic has left a trail of economic challenges, including the potential for inflation, supply chain disruptions, and labor shortages. These challenges are interconnected and can exacerbate each other, creating a complex economic landscape.
- Inflation:The pandemic-induced supply chain disruptions and increased demand have led to rising prices for goods and services. This has eroded consumer purchasing power and fueled concerns about a sustained period of inflation.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The pandemic has exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to shortages of essential goods and materials. These disruptions have driven up costs and created uncertainty for businesses.
- Labor Shortages:The pandemic has led to a decline in labor force participation, driven by factors such as health concerns, childcare responsibilities, and early retirements. This has created a tight labor market, leading to higher wages and difficulty filling job vacancies.
Long-Term Economic Implications, House to move on coronavirus related stimulus package but hoyer says payroll tax cut a nonstarter
The pandemic’s long-term economic implications are significant and multifaceted. The pandemic has accelerated existing trends, such as the rise of e-commerce and the shift towards remote work. It has also highlighted the importance of social safety nets and the need for greater economic resilience.
- Increased Inequality:The pandemic has disproportionately affected low-income households and marginalized communities, exacerbating existing inequalities. This has raised concerns about the need for policies to address income disparities and promote economic inclusion.
- Structural Changes:The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of new technologies and business models, leading to structural changes in the economy. This has implications for labor markets, skills development, and the role of government in supporting economic transformation.
- Geopolitical Tensions:The pandemic has highlighted the importance of global cooperation in addressing shared challenges. However, it has also led to increased geopolitical tensions, which could pose risks to the global economy.
Key Policy Priorities
Addressing the ongoing economic challenges and mitigating the long-term implications of the pandemic requires a comprehensive policy response. This response should prioritize:
- Continued Policy Support:Governments need to continue providing targeted support to households and businesses, particularly those most affected by the pandemic. This could include extending unemployment benefits, providing financial assistance to small businesses, and investing in job training programs.
- Infrastructure Investments:Investing in infrastructure projects, such as transportation, energy, and broadband, can create jobs, boost economic growth, and enhance the long-term competitiveness of the economy.
- Workforce Development Programs:The pandemic has highlighted the need for workers to adapt to changing labor market demands. Investing in education, training, and upskilling programs can help workers acquire the skills they need to succeed in a rapidly evolving economy.
- Addressing Inequality:Policies aimed at reducing income disparities and promoting economic inclusion are essential for building a more resilient and equitable economy. This could include expanding access to affordable housing, healthcare, and childcare.
- Strengthening Global Cooperation:Addressing global challenges, such as climate change and pandemics, requires international cooperation. Governments need to work together to promote global economic stability and address shared threats.
Flowchart Illustrating Interconnectedness of Economic Policy Choices
[ Flowchart Description:The flowchart illustrates the interconnectedness of various economic policy choices and their potential impact on different sectors of the economy. The flowchart begins with a central node labeled “Economic Policy Choices.” From this node, branches extend to different policy areas, such as fiscal policy, monetary policy, and regulatory policy.
Each policy area is further divided into specific policy options, such as tax cuts, interest rate adjustments, and environmental regulations. The flowchart then shows the potential impact of these policy choices on various sectors of the economy, including households, businesses, and the environment.
For example, tax cuts can stimulate consumer spending, while interest rate adjustments can affect investment and borrowing costs. The flowchart highlights the complex web of interactions between economic policy choices and their potential consequences for different sectors of the economy.]
Epilogue
The debate over the stimulus package and the rejection of the payroll tax cut underscore the complex and politically charged nature of economic policy during a crisis. While the House moves forward with its own proposal, the future of the stimulus package and the ultimate shape of economic recovery remain uncertain.
The pandemic has fundamentally reshaped the economic landscape, requiring innovative solutions and a willingness to compromise to navigate the challenges ahead.