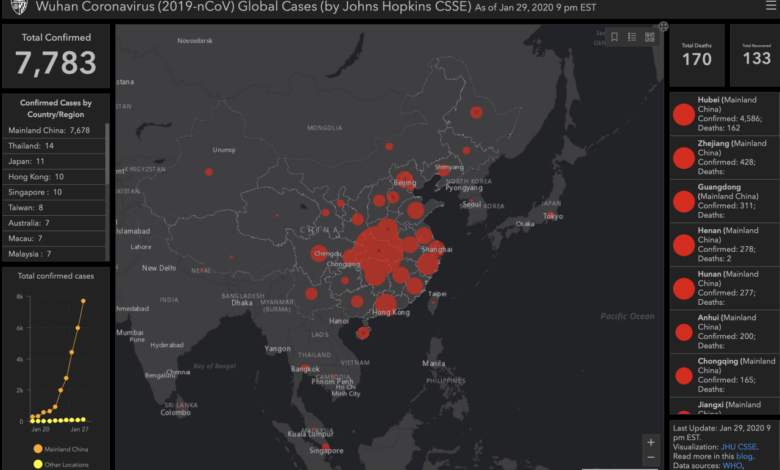
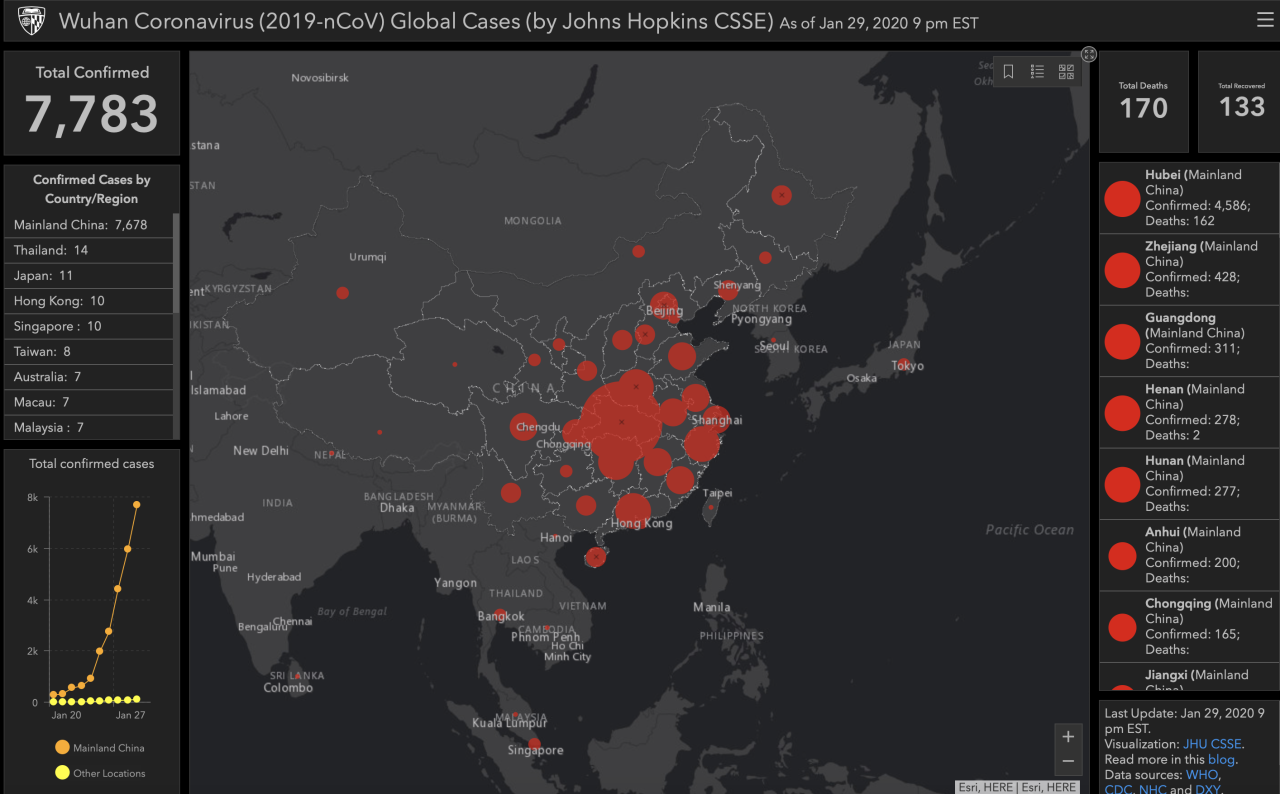
WHO Declares Coronavirus Outbreak a Global Health Emergency
World health organization declares coronavirus outbreak a global health emergency – WHO Declares Coronavirus Outbreak a Global Health Emergency – these words sent shockwaves around the world in early 2020, marking a pivotal moment in the fight against a rapidly spreading pandemic. The declaration, a serious call to action, signified the global community’s recognition of the unprecedented threat posed by the novel coronavirus.
The virus, which originated in Wuhan, China, had already begun to spread rapidly, infecting thousands and causing widespread fear and uncertainty.
This declaration, issued by the World Health Organization (WHO), triggered a cascade of events, prompting countries to implement stringent measures to contain the virus. From travel restrictions and border closures to social distancing guidelines and lockdowns, the world grappled with the unprecedented challenge of a global pandemic.
The declaration served as a wake-up call, urging governments, health organizations, and individuals to act decisively and collaboratively to mitigate the spread of the virus and protect public health.
The WHO’s Declaration
On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak of the novel coronavirus, later named COVID-19, a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). This declaration was a significant moment in the global response to the pandemic, signaling the seriousness of the situation and prompting international collaboration to contain its spread.The WHO’s declaration of a PHEIC is a serious measure, reserved for public health events that pose a significant risk to other countries and require an international coordinated response.
It’s hard to believe that while the World Health Organization declared the coronavirus outbreak a global health emergency, a tragic incident occurred right here in Chicago. A mail carrier was killed on her route, a stark reminder of the dangers we face every day , even amidst global crises.
It’s a sobering reminder that life goes on, even as we grapple with unprecedented challenges like the coronavirus pandemic.
The declaration triggered a cascade of actions from various stakeholders, including governments, international organizations, and individuals, aiming to curb the pandemic’s trajectory.
Timeline of Events Leading to the Declaration
The declaration was not a sudden decision, but rather a culmination of events that unfolded rapidly over several weeks. Here’s a timeline of key events leading up to the WHO’s PHEIC declaration:
- December 31, 2019:China reported a cluster of pneumonia cases of unknown cause in Wuhan, Hubei province.
- January 7, 2020:The Chinese authorities identified the novel coronavirus as the cause of the outbreak.
- January 11, 2020:The first case outside of China was confirmed in Thailand.
- January 20, 2020:The WHO convened an Emergency Committee to assess the situation and advise on whether a PHEIC should be declared.
- January 23, 2020:Wuhan was placed under lockdown, effectively restricting travel in and out of the city.
- January 30, 2020:The WHO declared the outbreak a PHEIC, citing the rapid spread of the virus and the potential for global impact.
Criteria for PHEIC Declaration, World health organization declares coronavirus outbreak a global health emergency
The WHO’s decision to declare a PHEIC was based on a set of criteria, including:
- The severity of the public health event:The COVID-19 outbreak was characterized by rapid spread, a high number of cases, and a significant mortality rate.
- The potential for international spread:The virus was already detected in multiple countries outside China, indicating its ability to spread globally.
- The potential for international disruption:The outbreak had the potential to disrupt global travel, trade, and economies.
- The need for a coordinated international response:The declaration triggered a coordinated response from the international community, including sharing information, research, and resources to combat the pandemic.
“The decision to declare a Public Health Emergency of International Concern is not taken lightly and is based on the best available evidence. The WHO’s declaration is a call to action for all countries to take urgent measures to prevent further spread of the virus and to protect their populations.”Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General
Global Impact of the Coronavirus Outbreak

The COVID-19 pandemic, originating in Wuhan, China, in late 2019, rapidly transformed into a global health crisis, leaving an indelible mark on every facet of human life. The virus’s swift and widespread dissemination, coupled with its unprecedented nature, triggered a cascade of economic, social, and political repercussions that continue to reverberate across the world.
Global Spread and Infection Rates
The virus’s global spread was characterized by its rapid and geographically diverse transmission. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020, as cases were reported in every continent except Antarctica.
The pandemic’s impact varied significantly across regions, with some countries experiencing far more severe outbreaks than others. For example, as of January 2023, the United States had the highest number of confirmed cases, followed by India and Brazil. However, infection rates also varied widely within countries, with densely populated urban areas often experiencing higher rates of transmission than rural areas.
Economic Consequences
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a global economic recession, the most severe since the Great Depression. The pandemic’s impact on the economy was multifaceted, including:
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The pandemic led to widespread disruptions in global supply chains, as factories closed and transportation networks were disrupted. This resulted in shortages of essential goods, including medical supplies, food, and other consumer products.
- Business Closures and Job Losses:The pandemic forced businesses to close temporarily or permanently, resulting in widespread job losses. This was particularly acute in industries such as tourism, hospitality, and retail, which were heavily impacted by travel restrictions and social distancing measures.
- Financial Market Volatility:The pandemic caused significant volatility in financial markets, as investors reacted to the uncertainty surrounding the outbreak. This led to sharp declines in stock prices and increased volatility in currency markets.
Social Consequences
The pandemic had profound social consequences, including:
- Social Distancing and Isolation:Governments around the world implemented social distancing measures, including lockdowns, to slow the spread of the virus. This led to widespread social isolation, as people were encouraged to stay home and avoid contact with others.
- Mental Health Challenges:The pandemic’s social and economic impacts contributed to increased stress, anxiety, and depression. The isolation, uncertainty, and fear associated with the pandemic took a toll on mental health worldwide.
- Disparities in Access to Healthcare:The pandemic highlighted existing disparities in access to healthcare, with marginalized communities often experiencing disproportionate impacts. This was due to factors such as poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and underlying health conditions.
Political Consequences
The pandemic also had significant political consequences, including:
- Government Responses:Governments around the world implemented a range of measures to manage the pandemic, including lockdowns, travel restrictions, and mask mandates. These measures were often controversial, with some arguing that they were too restrictive and others arguing that they were necessary to protect public health.
- Political Polarization:The pandemic contributed to political polarization in many countries, as people disagreed on the best way to manage the crisis. This was particularly evident in countries with divided political systems.
- International Cooperation:The pandemic highlighted the importance of international cooperation in addressing global health threats. However, it also exposed challenges to international collaboration, such as differing priorities and approaches to managing the crisis.
Country-Specific Responses and Outcomes
Countries around the world implemented a range of strategies to manage the COVID-19 outbreak, with varying degrees of success. Some countries, such as South Korea and Taiwan, were able to effectively contain the virus through a combination of early detection, aggressive testing, and contact tracing.
Others, such as the United States and Brazil, experienced far more severe outbreaks, with high rates of infection and mortality.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has been a global crisis unlike any other in recent history, and its impact has been felt in every corner of the world. The pandemic has exposed the vulnerabilities of our interconnected world and highlighted the need for greater international cooperation to address future health threats.”
Public Health Measures and Responses
The global response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been characterized by a wide range of public health measures aimed at containing the spread of the virus and mitigating its impact. These measures have been implemented at various levels, from individual actions to national and international policies, and have evolved over time as scientific understanding of the virus and its transmission has progressed.
The World Health Organization’s declaration of the coronavirus outbreak as a global health emergency was a stark reminder of the fragility of our world. While we grappled with the immediate threat of a pandemic, news of the Buffalo shooting brought a different kind of fear and trauma to the forefront, especially for African Americans, as experts like those featured in this article point out.
The pandemic and the shooting, though seemingly disparate events, both underscored the importance of community, resilience, and the urgent need for social change.
Key Public Health Measures
Public health measures have been crucial in the fight against COVID-19, and these measures have been implemented across the globe. These strategies have been designed to break the chain of transmission, protect vulnerable populations, and manage the healthcare system’s burden.
- Travel Restrictions:Governments worldwide imposed travel restrictions, including border closures and quarantine requirements, to limit the importation and spread of the virus. This was particularly important in the early stages of the pandemic when understanding of the virus was limited.
- Quarantine:Individuals suspected of having COVID-19 or who had been in contact with infected individuals were placed under quarantine to prevent further transmission. This involved isolating individuals at home or in designated facilities for a specific period.
- Social Distancing:Measures aimed at reducing close contact between individuals, such as maintaining physical distance, avoiding large gatherings, and working from home, have been critical in reducing transmission. Social distancing has been implemented in various forms, including lockdowns and stay-at-home orders.
- Testing Strategies:Extensive testing has been essential for identifying infected individuals, isolating them, and tracing their contacts. Testing strategies have evolved over time, with the development of more accurate and rapid tests.
- Mask Wearing:The use of face masks has been widely adopted as a measure to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets, which can carry the virus. Mask-wearing recommendations have varied across countries and contexts, with some mandating their use in public spaces.
- Vaccination:The development and deployment of COVID-19 vaccines have been a major breakthrough in the fight against the pandemic. Vaccination programs have been implemented globally, with the aim of achieving herd immunity and reducing the severity of disease.
Challenges and Successes of Public Health Measures
The implementation of public health measures has faced numerous challenges, including:
- Public Compliance:Ensuring public compliance with measures such as social distancing and mask-wearing has been a major challenge, with varying levels of adherence across different populations.
- Economic Impacts:Public health measures have had significant economic impacts, leading to business closures, job losses, and disruptions to supply chains. Balancing public health concerns with economic considerations has been a complex issue for governments.
- Equity and Access:The availability and accessibility of public health measures, such as testing, treatment, and vaccines, have varied significantly across different regions and populations, highlighting existing health inequities.
- Evolving Scientific Understanding:The scientific understanding of the virus and its transmission has evolved over time, leading to adjustments in public health recommendations and measures.
Despite these challenges, public health measures have achieved significant successes:
- Reduced Transmission:Public health measures, particularly social distancing and mask-wearing, have been effective in reducing the spread of the virus, leading to a decline in infection rates and hospitalizations.
- Protection of Vulnerable Populations:Measures such as vaccination programs have helped protect vulnerable populations, such as older adults and those with underlying health conditions, from severe illness and death.
- Development of New Tools:The pandemic has spurred the development of new tools and technologies, such as rapid diagnostic tests and antiviral treatments, which have enhanced the response to the virus.
Comparison of Approaches Across Countries
Different countries have adopted a range of approaches to managing the COVID-19 outbreak, reflecting variations in their political systems, cultural contexts, and resource availability.
- Lockdowns:Some countries, such as China and Australia, implemented strict lockdowns early in the pandemic, which were successful in containing the spread of the virus. However, lockdowns have also had significant economic and social consequences.
- Targeted Measures:Other countries, such as Sweden, adopted a more targeted approach, focusing on measures such as social distancing and hygiene recommendations, while avoiding strict lockdowns. This approach has been criticized for its higher death toll but has also been praised for its minimal impact on economic activity.
- Vaccination Strategies:Countries have also differed in their vaccination strategies, with some prioritizing universal vaccination while others have focused on vaccinating high-risk groups first. The effectiveness of vaccination strategies has been influenced by factors such as vaccine availability, vaccine hesitancy, and logistical challenges.
The global response to the COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the importance of a coordinated and comprehensive approach to public health emergencies. Public health measures, while challenging to implement, have been crucial in mitigating the impact of the virus and protecting populations.
The ongoing evolution of the virus and the emergence of new variants will continue to pose challenges, requiring ongoing adaptation and innovation in public health responses.
Scientific Research and Development
The global health emergency triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic ignited an unprecedented surge in scientific research and development. The scientific community, fueled by a sense of urgency and global collaboration, embarked on a mission to understand the virus, develop diagnostic tests, and create vaccines.
Understanding the Virus
The initial focus of scientific research was to understand the virus itself. Researchers around the world worked tirelessly to sequence the virus’s genome, identify its structure, and understand its mechanisms of transmission and infection. This knowledge was crucial for developing effective diagnostic tests and vaccines.
Diagnostic Tests
The development of accurate and rapid diagnostic tests was critical for controlling the spread of the virus. Scientists developed a variety of tests, including PCR tests, antigen tests, and antibody tests, each with its own strengths and limitations. The availability of reliable diagnostic tests allowed for early detection of infected individuals, enabling isolation and contact tracing measures to curb transmission.
Vaccine Development
The race to develop a safe and effective vaccine against COVID-19 was perhaps the most remarkable scientific achievement of the pandemic. Scientists from different countries collaborated, sharing data and resources to accelerate the development process. Multiple vaccine candidates were developed using different technologies, including mRNA vaccines, viral vector vaccines, and protein subunit vaccines.
International Collaboration
International collaboration was essential for the rapid progress made in research and development. The World Health Organization (WHO) played a central role in coordinating research efforts, sharing information, and facilitating access to resources. Scientists from different countries shared their expertise and data, leading to a collective effort to address the global health crisis.
Long-Term Health Effects
The pandemic also brought to light the long-term health effects associated with COVID-19. A significant proportion of individuals who contracted the virus experienced persistent symptoms, known as “long COVID.” Ongoing research is focused on understanding the mechanisms behind these long-term effects and developing strategies for managing and treating them.
Research Efforts to Address Long-Term Health Effects
Researchers are investigating a range of potential factors contributing to long COVID, including:
- Persistent inflammation
- Immune system dysregulation
- Organ damage
- Mental health issues
This research is crucial for developing effective treatments and support services for individuals experiencing long COVID.
The Role of the WHO
The World Health Organization (WHO) played a crucial role in coordinating the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Its responsibilities encompassed providing leadership, guidance, and support to countries worldwide to effectively manage the outbreak.
It’s hard to believe that it’s been two years since the World Health Organization declared the coronavirus outbreak a global health emergency. It feels like a lifetime ago! But, as we emerge from the pandemic, life is slowly returning to normal, and what better way to celebrate than with the return of the iconic Easter Parade in New York City, a vibrant spectacle of extravagant bonnets and festive spirits.
It’s a reminder that even in the face of global challenges, we can still find joy and beauty in the simple things, and that the human spirit is resilient and capable of overcoming even the most daunting obstacles.
WHO’s Responsibilities and Actions
The WHO’s primary responsibilities during the COVID-19 pandemic included:
- Surveillance and Monitoring:The WHO established a global surveillance system to track the spread of the virus, collect data on cases, and monitor the emergence of new variants. This data was essential for understanding the pandemic’s trajectory and guiding public health interventions.
- Information Sharing and Communication:The WHO disseminated accurate and timely information about the virus, its transmission, and prevention measures to the public, healthcare professionals, and governments. This communication was crucial for building trust and promoting public health awareness.
- Technical Guidance and Support:The WHO provided technical guidance to countries on managing the outbreak, including recommendations on testing, treatment, isolation, contact tracing, and vaccination. This support helped countries implement effective public health measures and strengthen their healthcare systems.
- Coordination and Collaboration:The WHO facilitated collaboration between countries, international organizations, and research institutions to share knowledge, resources, and best practices. This coordination was vital for ensuring a unified global response to the pandemic.
- Research and Development:The WHO supported research and development efforts to understand the virus, develop diagnostics, treatments, and vaccines. This research was essential for finding effective solutions to combat the pandemic.
Challenges Faced by the WHO
The WHO faced several challenges in managing the COVID-19 crisis, including:
- Political Interference:The WHO’s response to the pandemic was often hampered by political interference from certain countries, which hindered its ability to provide impartial guidance and support.
- Resource Constraints:The WHO faced significant resource constraints, which limited its ability to fully implement its response plan. This shortage of funding impacted its capacity to provide technical assistance and support to countries in need.
- Misinformation and Disinformation:The spread of misinformation and disinformation about the virus and the pandemic created confusion and undermined public health efforts. The WHO had to combat these false narratives to ensure the public received accurate information.
- Global Inequality:The pandemic highlighted the existing global inequalities in access to healthcare and resources. The WHO struggled to address these disparities and ensure equitable access to vaccines and treatments.
Impact of the WHO on Public Health Policies and Strategies
The WHO’s efforts during the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted public health policies and strategies worldwide. Examples include:
- Promotion of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions:The WHO’s recommendations on non-pharmaceutical interventions, such as handwashing, physical distancing, and mask-wearing, were widely adopted by countries and became a cornerstone of public health strategies.
- Development of Vaccination Strategies:The WHO played a critical role in coordinating the global vaccination effort, including the development of the COVAX facility, which aimed to ensure equitable access to vaccines for all countries.
- Advocacy for Global Health Security:The pandemic highlighted the importance of global health security and the need for stronger international cooperation. The WHO advocated for increased investment in pandemic preparedness and response systems.
Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness: World Health Organization Declares Coronavirus Outbreak A Global Health Emergency
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a stark reminder of the vulnerability of global health systems to infectious disease outbreaks. While the world has made significant progress in tackling many infectious diseases, the pandemic exposed weaknesses in our preparedness and response capabilities.
By examining the lessons learned from the global response to the outbreak, we can strengthen our global health systems and improve our ability to mitigate the impact of future pandemics.
Key Lessons Learned
The global response to the COVID-19 pandemic has provided valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities associated with managing infectious disease outbreaks. Some of the key lessons learned include:
- Early Detection and Response:The importance of early detection and rapid response to outbreaks cannot be overstated. Delays in identifying and responding to the COVID-19 outbreak allowed the virus to spread rapidly, resulting in a global pandemic.
- Strengthening Surveillance Systems:Effective surveillance systems are essential for detecting outbreaks early and tracking their spread. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for robust surveillance systems that can identify and monitor emerging infectious diseases.
- Global Cooperation and Coordination:The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the critical role of international cooperation and coordination in managing global health emergencies. Effective collaboration between countries, international organizations, and other stakeholders is essential for sharing information, coordinating responses, and ensuring equitable access to resources.
- Public Health Measures:Public health measures, such as social distancing, mask-wearing, and hand hygiene, played a crucial role in slowing the spread of COVID-19. The pandemic highlighted the importance of implementing these measures effectively and consistently.
- Communication and Transparency:Clear, consistent, and transparent communication is essential for building public trust and ensuring effective public health responses. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of providing accurate and timely information to the public, while addressing concerns and misconceptions.
- Equitable Access to Resources:Ensuring equitable access to resources, including vaccines, treatments, and diagnostics, is critical for mitigating the impact of outbreaks. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed significant disparities in access to resources, highlighting the need for a more equitable global health system.
Implications for Future Pandemic Preparedness
The lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic have significant implications for future pandemic preparedness. These include:
- Investment in Public Health Infrastructure:Strengthening public health infrastructure, including surveillance systems, laboratory capacity, and workforce development, is essential for early detection, rapid response, and effective management of future outbreaks.
- Development of Pandemic Response Plans:Countries should develop comprehensive pandemic response plans that Artikel clear roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and resource allocation mechanisms. These plans should be regularly reviewed and updated based on evolving scientific knowledge and emerging threats.
- Stockpiling of Essential Supplies:Ensuring adequate stockpiles of essential medical supplies, such as personal protective equipment, ventilators, and antiviral medications, is crucial for responding to future outbreaks effectively.
- Research and Development:Continued investment in research and development is essential for developing new vaccines, treatments, and diagnostics for emerging infectious diseases.
- Strengthening International Collaboration:Fostering strong international collaboration and coordination mechanisms is essential for sharing information, coordinating responses, and ensuring equitable access to resources during future outbreaks.
- Public Education and Awareness:Raising public awareness about infectious diseases and promoting healthy behaviors, such as vaccination, hand hygiene, and social distancing, is crucial for preventing and mitigating the impact of future outbreaks.
Recommendations for Strengthening Global Health Systems
Strengthening global health systems to mitigate the impact of future outbreaks requires a multi-faceted approach. Key recommendations include:
- Increase Funding for Public Health:Investing in public health infrastructure, surveillance systems, and research is crucial for improving preparedness and response capabilities.
- Strengthen International Collaboration:Fostering stronger international collaboration and coordination mechanisms, such as the WHO, is essential for sharing information, coordinating responses, and ensuring equitable access to resources.
- Promote Equitable Access to Resources:Ensuring equitable access to vaccines, treatments, and diagnostics is critical for mitigating the impact of outbreaks, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
- Invest in Research and Development:Continued investment in research and development is essential for developing new vaccines, treatments, and diagnostics for emerging infectious diseases.
- Enhance Public Health Communication:Clear, consistent, and transparent communication is essential for building public trust and ensuring effective public health responses.
- Address Health Inequities:Addressing health inequities, such as poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and social determinants of health, is essential for strengthening global health systems and reducing vulnerability to outbreaks.
Last Recap
The WHO’s declaration of a global health emergency was a critical step in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. It galvanized global efforts to combat the virus, highlighting the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of international cooperation. The lessons learned from this pandemic will shape future responses to emerging health threats, emphasizing the need for robust public health systems, early detection and response mechanisms, and ongoing scientific research and development.
As we move forward, the collective memory of this global crisis serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of preparedness, collaboration, and resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges.