Why Japan Appeared to Avoid a Mass Coronavirus Outbreak
Why japan appears to have avoided a mass coronavirus outbreak – Why Japan Appeared to Avoid a Mass Coronavirus Outbreak is a question that has intrigued many. While other nations grappled with devastating waves of COVID-19, Japan seemed to weather the storm with relatively fewer cases and deaths. This resilience, however, wasn’t just a matter of luck.
It was a combination of factors, from a proactive and culturally-influenced response to a robust public health system and unique social norms.
This blog delves into the key elements that likely contributed to Japan’s success, exploring its early and aggressive actions, its existing public health infrastructure and awareness, the impact of cultural practices, and the effectiveness of its testing and data collection strategies.
We’ll also examine government policies, demographics, and the strength of its healthcare system.
Early and Aggressive Action: Why Japan Appears To Have Avoided A Mass Coronavirus Outbreak
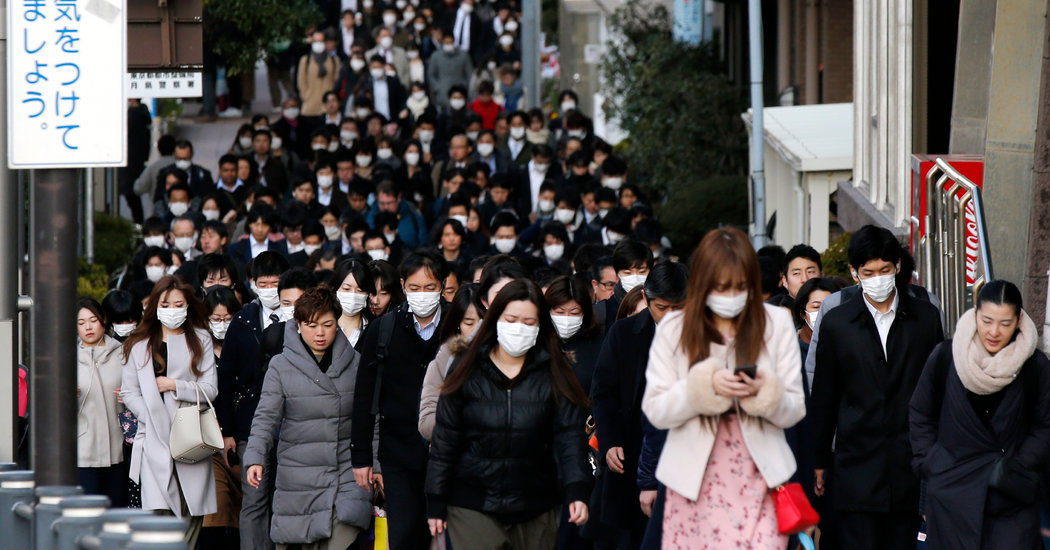

Japan’s early and decisive response to the COVID-19 outbreak played a significant role in mitigating the severity of the pandemic within its borders. This proactive approach involved a combination of travel restrictions, widespread testing, and robust contact tracing, implemented swiftly and effectively.
Japan’s success in containing the coronavirus has been attributed to factors like early detection, aggressive testing, and a culture of mask-wearing. But it’s also worth considering the role of their strong healthcare system, which has been built over decades of investment.
It’s a stark contrast to the situation in the US, where healthcare costs are skyrocketing and many Americans are struggling to afford basic care. As marc thiessen the actual cost of bernie sanders spending plans is terrifying , the financial strain on our healthcare system is a serious concern.
Perhaps Japan’s success with COVID-19 is a reminder of the importance of prioritizing healthcare, even if it means making tough choices about spending.
Travel Restrictions
Japan’s initial response to the COVID-19 outbreak was marked by early and stringent travel restrictions. On January 30, 2020, the Japanese government imposed a travel ban on foreign nationals who had recently visited Wuhan, China, the epicenter of the outbreak.
This swift action aimed to prevent the influx of infected individuals from entering the country.
- Early Ban on Foreign Nationals from Wuhan:This restriction was imposed on January 30, 2020, demonstrating Japan’s proactive approach to containing the spread of the virus.
- Expansion of Travel Restrictions:As the outbreak escalated, Japan expanded its travel restrictions to include other affected regions in China and later to other countries experiencing significant outbreaks.
- Quarantine Measures:Individuals arriving from affected regions were subject to mandatory quarantine periods, further limiting the potential for virus transmission.
These early travel restrictions, while disruptive, proved to be a crucial component in delaying the spread of COVID-19 in Japan.
Testing and Contact Tracing
Japan’s approach to testing and contact tracing was also characterized by its early and aggressive nature. Recognizing the importance of identifying infected individuals quickly, the government implemented a comprehensive testing strategy.
- Widespread Testing:Japan’s testing strategy emphasized widespread testing, aiming to identify infected individuals early in the course of their illness. This approach, while requiring significant resources, proved effective in identifying and isolating cases, thereby limiting transmission.
- Contact Tracing:Japan’s contact tracing system, known for its meticulousness, involved the identification and isolation of individuals who had come into contact with confirmed cases. This rigorous process helped to break chains of transmission and prevent further spread of the virus.
Japan’s commitment to testing and contact tracing, while demanding significant resources and coordination, proved to be a key factor in its success in mitigating the pandemic.
Cultural Factors
Cultural factors also played a role in shaping Japan’s response to the COVID-19 outbreak. Japanese society is known for its strong sense of social responsibility and deference to authority, which contributed to the effectiveness of government measures.
- Social Norms:Japan’s social norms, such as wearing masks in public when feeling unwell, facilitated compliance with public health recommendations. This ingrained practice helped to reduce the spread of the virus.
- Trust in Authority:High levels of trust in government and public health officials contributed to the public’s willingness to follow guidelines and regulations. This trust was essential for the successful implementation of containment measures.
Japan’s cultural context, with its emphasis on social responsibility and trust in authority, provided a fertile ground for the successful implementation of public health measures.
Japan’s success in containing the coronavirus outbreak, despite its initial struggles, is a testament to its strong public health infrastructure and cultural norms. While the world watched in shock as the virus spread rapidly in other countries, Japan’s proactive approach, including widespread testing and contact tracing, helped to slow the spread.
It’s interesting to note that this success comes at a time when Chris Matthews, a well-known commentator, has been absent from MSNBC’s primary coverage after facing allegations of sexism on air, chris matthews absent from msnbcs primary coverage after sexism allegations on air slip ups.
It’s a stark contrast between a nation’s public health triumphs and the downfall of a prominent media personality, both unfolding in the midst of a global crisis.
Public Health Infrastructure and Awareness
Japan’s success in containing the COVID-19 outbreak can be attributed, in part, to its robust public health infrastructure and high levels of public health awareness. These factors played a crucial role in mitigating the spread of the virus and preventing a large-scale outbreak.
Public Health Infrastructure, Why japan appears to have avoided a mass coronavirus outbreak
Japan’s public health infrastructure is considered one of the strongest in the world. It has a well-established healthcare system, comprehensive public health surveillance, and a network of community health centers. This infrastructure has been instrumental in Japan’s response to the pandemic.
- Healthcare System:Japan has a universal healthcare system that provides access to quality medical care for all citizens. This ensures that people can access testing and treatment without financial barriers, which is crucial for containing outbreaks. Japan has a high density of doctors and hospital beds compared to many other developed countries.
- Public Health Surveillance:Japan has a sophisticated public health surveillance system that tracks infectious diseases and other health threats. This system allows authorities to quickly identify and respond to outbreaks, including the COVID-19 pandemic. This surveillance system includes mandatory reporting of infectious diseases by healthcare providers and the use of electronic health records to track patient movements and potential contacts.
- Community Health Centers:Japan has a network of community health centers that provide a range of services, including health education, screenings, and vaccinations. These centers play a vital role in promoting public health awareness and providing access to healthcare services, particularly in rural areas.
While Japan’s success in containing the virus is still being debated, it’s interesting to note that many early US coronavirus patients have fully recovered, as reported by health officials in this article. This recovery rate, coupled with Japan’s proactive testing and contact tracing, may contribute to their apparent avoidance of a widespread outbreak.
Public Health Awareness and Hygiene Practices
Prior to the pandemic, Japan had a high level of public health awareness and hygiene practices. This was influenced by factors such as cultural norms, public health campaigns, and the experience of past outbreaks.
- Cultural Norms:Japanese culture emphasizes cleanliness and hygiene, which has contributed to a strong public health ethos. This is evident in practices like frequent handwashing, wearing masks during flu season, and maintaining social distancing in crowded spaces.
- Public Health Campaigns:Japan has a long history of public health campaigns promoting healthy behaviors, such as handwashing, vaccination, and proper nutrition. These campaigns have raised awareness about the importance of public health and helped to build a culture of prevention.
- Experience of Past Outbreaks:Japan has experienced several outbreaks of infectious diseases in the past, including SARS and avian influenza. These experiences have highlighted the importance of early detection, isolation, and public health measures.
Comparison with Other Countries
Japan’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been praised for its effectiveness. Several factors contributed to its success, including:
- Early and Aggressive Action:Japan acted quickly to contain the virus, implementing travel restrictions, contact tracing, and testing.
- Strong Public Health Infrastructure:Japan’s robust public health infrastructure, including its healthcare system, surveillance, and community health centers, provided a solid foundation for its response.
- High Public Health Awareness:Japan’s high levels of public health awareness and hygiene practices facilitated compliance with public health measures.
- Cultural Factors:Japan’s cultural norms, such as respect for authority and a sense of collective responsibility, contributed to the effectiveness of its response.
Cultural Practices and Social Norms

Japan’s cultural practices and social norms have been suggested as potential factors contributing to its relatively low number of COVID-19 cases compared to other developed nations. These factors, ingrained in Japanese society for centuries, may have played a role in shaping individual behavior and facilitating public health measures.
Mask-Wearing and Bowing
Mask-wearing in Japan has been common practice for decades, primarily driven by concerns over seasonal allergies, air pollution, and the common cold. This pre-existing cultural norm likely facilitated the widespread adoption of masks during the pandemic. Additionally, the traditional Japanese custom of bowing as a form of greeting, which minimizes physical contact, may have also contributed to reducing transmission.
Collectivism and Community
Japan’s strong sense of collectivism and community fosters a sense of social responsibility, encouraging individuals to prioritize the well-being of the group over individual needs. This cultural value may have motivated people to comply with public health guidelines, such as social distancing and quarantine measures, to protect their communities.
Comparison to Other Countries
Compared to Western cultures that often prioritize individualism, Japan’s collectivist ethos may have made it easier to implement stringent public health measures and encourage social compliance. In countries with a stronger emphasis on individual freedom, resistance to restrictions and government interventions may have been more pronounced, potentially contributing to higher infection rates.
Final Summary
Japan’s experience with the pandemic highlights the complex interplay of factors that can influence a nation’s response. While its success is undeniable, it’s crucial to remember that no country is immune to the unpredictable nature of a global health crisis.
Understanding the factors that contributed to Japan’s relative success, however, offers valuable insights for navigating future challenges.