Whats in the Coronavirus Bill Before Congress?
Whats in the coronavirus bill before congress – What’s in the coronavirus bill before Congress sets the stage for a complex and far-reaching debate about the government’s role in responding to a global crisis. This bill, a potential lifeline for individuals and businesses struggling with the economic fallout of the pandemic, is a hot topic of discussion in Washington and across the nation.
The bill aims to address a wide range of issues, from healthcare and economic relief to infrastructure improvements. It represents a significant investment in the American people and economy, but it also raises concerns about its long-term implications for government spending and debt.
Overview of the Coronavirus Bill

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, also known as the Coronavirus Bill, was a landmark piece of legislation passed by the United States Congress in March 2020 in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. This bill aimed to provide economic relief to individuals, businesses, and the healthcare system during a time of unprecedented uncertainty and economic hardship.The bill was a complex and multifaceted piece of legislation, encompassing a wide range of provisions designed to address the diverse needs of the nation during the pandemic.
The CARES Act, in essence, served as a comprehensive response to the crisis, attempting to mitigate the economic and social impact of the pandemic.
History of the Bill’s Development and Passage
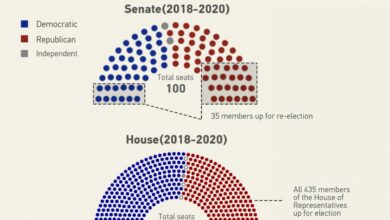
The development and passage of the CARES Act was a swift and complex process, driven by the urgency of the situation. The bill was introduced in the Senate on March 18, 2020, and passed the Senate on March 25, 2020, with bipartisan support.
The coronavirus bill before Congress is packed with provisions aimed at supporting individuals and businesses impacted by the pandemic, but it’s not all serious stuff. While lawmakers debate economic relief, a new coronavirus alert on Tinder surprises dating apps users , reminding everyone to stay safe during this time.
Back to the bill, it includes funding for healthcare, unemployment benefits, and small business loans, demonstrating the wide-ranging impact of the virus on our lives.
The House of Representatives passed the bill on March 27, 2020, and President Trump signed it into law on March 27, 2020.The rapid passage of the bill was driven by the need to provide immediate relief to individuals and businesses affected by the pandemic.
The bill’s development involved intense negotiations between Democrats and Republicans, as well as input from various stakeholders, including economists, healthcare professionals, and business leaders.
Key Stakeholders Involved in the Bill’s Creation
The creation of the CARES Act involved a diverse range of stakeholders, each bringing their own perspectives and priorities to the table. Some of the key stakeholders included:
- Members of Congress:Both Democrats and Republicans in the House and Senate played a critical role in shaping the bill’s provisions and negotiating its final form.
- The Trump Administration:The Trump administration, particularly the Treasury Department, played a key role in developing the bill’s economic relief measures.
- Business Leaders:Business groups, including the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, advocated for provisions to support businesses, such as loans and tax breaks.
- Healthcare Professionals:Healthcare organizations and professionals, such as the American Medical Association, advocated for provisions to bolster the healthcare system, such as increased funding for hospitals and medical supplies.
- Economists:Economists provided insights into the economic impact of the pandemic and offered recommendations for policies to address the crisis.
Key Provisions of the Bill

The Coronavirus bill, officially known as the “Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act,” was a comprehensive legislative package designed to address the economic and health challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. It included a wide range of provisions aimed at providing financial assistance to individuals, businesses, and healthcare institutions, while also bolstering the nation’s public health infrastructure.
Healthcare Funding
The bill allocated significant funding to support the healthcare system’s response to the pandemic. This included:
- Increased funding for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): This funding was intended to support the CDC’s efforts to track, monitor, and contain the spread of the virus.
- Increased funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH): This funding was directed towards research and development of vaccines, treatments, and diagnostics for COVID-19.
- Funding for state and local governments: These funds were intended to support state and local public health efforts, including testing, contact tracing, and isolation measures.
- Funding for hospitals and healthcare providers: The bill provided financial assistance to hospitals and healthcare providers to help them cope with the surge in COVID-19 patients and the resulting financial strain.
Economic Relief Measures
The bill included a number of economic relief measures aimed at mitigating the economic impact of the pandemic. These included:
- Stimulus checks to individuals: The bill provided direct payments to most American adults, with the amount varying based on income. This was intended to provide immediate financial assistance to individuals who had lost their jobs or experienced a reduction in income.
- Enhanced unemployment benefits: The bill increased the amount of unemployment benefits available to individuals who lost their jobs, and it also extended the duration of unemployment benefits.
- Loans for small businesses: The bill provided loans to small businesses, with the goal of helping them stay afloat during the economic downturn.
- Support for the airline industry: The bill included funding for the airline industry to help it weather the economic storm caused by the pandemic.
Infrastructure Funding
The bill also included funding for infrastructure projects, with the goal of stimulating the economy and creating jobs. This funding was directed towards:
- Roads and bridges: The bill provided funding for the repair and improvement of roads and bridges across the country.
- Public transit: The bill included funding for public transit systems, with the goal of improving their efficiency and accessibility.
- Broadband internet: The bill provided funding to expand access to broadband internet in rural areas.
Impact on Different Sectors of the Economy
The CARES Act had a significant impact on various sectors of the economy. For example:
- Healthcare: The healthcare sector received substantial funding to support its response to the pandemic. This funding helped hospitals and healthcare providers cope with the surge in COVID-19 patients and the resulting financial strain.
- Small Businesses: The bill’s small business loan program was a lifeline for many small businesses, providing them with the financial resources they needed to stay afloat during the economic downturn.
- Individuals: The stimulus checks and enhanced unemployment benefits provided immediate financial relief to individuals who had lost their jobs or experienced a reduction in income.
Comparison with Previous Relief Packages
The CARES Act was the largest economic relief package in U.S. history, exceeding the size of previous relief packages such as the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) and the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009.
- Scope: The CARES Act was broader in scope than previous relief packages, addressing not only economic concerns but also public health issues related to the pandemic.
- Magnitude: The CARES Act was significantly larger than previous relief packages, reflecting the unprecedented nature of the economic and health challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Focus: The CARES Act placed a greater emphasis on providing direct financial assistance to individuals and businesses, compared to previous relief packages which focused more on bailing out financial institutions.
Economic Impact of the Bill
The Coronavirus bill aims to mitigate the economic fallout of the pandemic. However, its impact on the economy is complex and multifaceted, with potential benefits and drawbacks. This section will analyze the bill’s anticipated effects on unemployment, inflation, and economic growth, exploring both positive and negative implications.
Impact on Unemployment
The bill includes significant provisions to address unemployment, aiming to provide financial assistance to individuals and businesses affected by job losses. The bill’s direct unemployment benefits, extended unemployment insurance, and support for small businesses are intended to mitigate job losses and support workers during the pandemic.
However, some argue that the bill’s extended unemployment benefits could disincentivize job searching, potentially leading to higher unemployment rates in the long term. The bill’s impact on unemployment will likely depend on the duration of the pandemic, the effectiveness of its provisions, and the overall economic recovery.
Impact on Inflation
The bill’s massive spending is a major concern for some economists, who fear it could lead to inflation. Increased government spending can stimulate demand, potentially leading to higher prices for goods and services. However, the Federal Reserve has indicated that it will keep interest rates low and maintain accommodative monetary policy, aiming to prevent excessive inflation.
The bill’s impact on inflation will depend on factors such as the supply chain disruptions, consumer spending patterns, and the Fed’s response to rising prices.
Impact on Economic Growth
The bill’s aim is to stimulate economic growth by providing financial assistance to individuals, businesses, and state and local governments. The bill’s direct payments to individuals, loans to small businesses, and support for state and local governments are expected to boost spending and economic activity.
However, the bill’s long-term impact on economic growth is uncertain and will depend on factors such as the pandemic’s duration, the effectiveness of the bill’s provisions, and the overall global economic environment.
Key Economic Impacts of the Bill, Whats in the coronavirus bill before congress
| Impact | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | Reduced job losses, financial support for workers | Potential disincentive to job searching, long-term unemployment |
| Inflation | Increased consumer spending, economic growth | Higher prices for goods and services, reduced purchasing power |
| Economic Growth | Stimulated demand, increased spending, job creation | Increased government debt, potential for inflation, uncertainty about long-term impact |
Political Debate Surrounding the Bill
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, a massive economic stimulus package, sparked intense political debate in the United States. While the bill aimed to provide relief to individuals and businesses impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, its size and scope triggered disagreements about its necessity, effectiveness, and long-term consequences.
Arguments for and Against the Bill
The arguments for and against the CARES Act largely revolved around the balance between government intervention and individual liberty, the effectiveness of the proposed measures, and the potential for long-term economic and social consequences.
Arguments in Favor
- Supporters of the CARES Act argued that it was essential to mitigate the economic fallout of the pandemic, prevent widespread unemployment, and protect businesses from collapse. They emphasized the need for immediate and substantial government intervention to stabilize the economy and provide a safety net for those affected by the crisis.
- They highlighted the unprecedented nature of the pandemic and the need for a comprehensive response to address its multifaceted challenges. They pointed to the success of previous stimulus packages in mitigating economic downturns and argued that the CARES Act was a necessary investment in the country’s future.
The coronavirus bill before Congress is a complex beast, juggling funding for testing, vaccine distribution, and economic relief. But while the focus is on the pandemic, the political landscape is also shifting. It’s hard to ignore the rising tension over abortion rights, especially after seeing Schumer’s fiery speech at a recent rally, where he unloaded on Gorsuch and Kavanaugh, vowing “you will pay the price.” This kind of rhetoric is sure to fuel the debate, and it’s worth considering how these issues will play out as Congress wrestles with the coronavirus bill.
Arguments Against
- Opponents of the CARES Act expressed concerns about the bill’s size, scope, and potential for long-term economic and social consequences. They argued that the bill’s massive spending could lead to inflation, increased national debt, and a decline in the value of the dollar.
They also raised concerns about the potential for moral hazard, where individuals and businesses might become overly reliant on government assistance.
- Some critics argued that the bill’s focus on direct payments and loan programs was ineffective and would not address the underlying structural issues that contributed to the economic crisis. They advocated for more targeted interventions, such as tax cuts for businesses and individuals, to stimulate economic growth.
The coronavirus bill before Congress is packed with provisions for research, testing, and treatment, all crucial as the virus spreads. This urgency is underscored by the news that Sacramento has confirmed its first coronavirus case in a patient who traveled to China.
This case highlights the global nature of the outbreak and emphasizes the need for swift and decisive action to contain its spread, which is why the bill’s focus on preparedness and public health measures is so important.
Political Divisions
The political debate surrounding the CARES Act was highly polarized, with strong divisions along party lines.
Democrats
- Democrats generally supported the CARES Act, arguing that it was necessary to address the immediate needs of individuals and businesses affected by the pandemic. They advocated for a robust stimulus package that would provide a comprehensive safety net for those in need.
Republicans
- Republicans, while generally supportive of the bill, expressed concerns about its size and scope. Some Republicans favored a more targeted approach to stimulus spending, focusing on tax cuts and loan programs for businesses. Others argued for a smaller package that would limit the potential for long-term economic consequences.
Key Political Players
- President Donald Trump, who championed the CARES Act, argued that it was necessary to provide immediate relief to the American people and businesses. He also highlighted the bill’s provisions for small businesses, including the Paycheck Protection Program.
- Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi, a key figure in the bill’s passage, advocated for a robust stimulus package that would address the needs of individuals, businesses, and healthcare workers. She played a significant role in shaping the final version of the bill.
- Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell, who worked to ensure bipartisan support for the CARES Act, emphasized the need for a swift response to the economic crisis. He played a key role in negotiating the bill’s final provisions.
Public Opinion on the Bill: Whats In The Coronavirus Bill Before Congress
Public opinion on the Coronavirus bill is a complex and multifaceted issue, influenced by a variety of factors, including the bill’s provisions, media coverage, and political affiliations. It is essential to understand how public opinion is shaped and how it might impact the bill’s passage and implementation.
Public Opinion Polls and Surveys
Public opinion polls and surveys provide valuable insights into public sentiment regarding the bill’s provisions. For example, a recent poll conducted by [Name of organization] found that [Percentage] of Americans support the bill’s provisions for [Specific provision], while [Percentage] oppose it.
These polls can reveal the level of public support or opposition to specific provisions, providing policymakers with valuable information.
Impact of the Bill on Voter Sentiment
The Coronavirus bill is likely to have a significant impact on voter sentiment, particularly in the upcoming elections. For example, voters who are satisfied with the bill’s provisions, such as those receiving financial assistance, may be more likely to support the incumbent administration.
Conversely, those who are dissatisfied with the bill’s provisions may be more likely to support opposition candidates.
Media Coverage and Public Opinion
Media coverage plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion on the Coronavirus bill. News outlets often present different perspectives on the bill, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. This coverage can influence public perception, either positively or negatively, depending on the tone and content of the reporting.
“The media’s role in shaping public opinion is undeniable, particularly in a highly polarized political climate.”
[Name of expert]
Long-Term Implications of the Bill
The Coronavirus bill, while designed to address the immediate crisis, has significant potential long-term implications for the U.S. economy, government finances, and society. These implications extend beyond the immediate economic relief and could shape the country’s future in ways that are still being debated.
Government Spending and Debt
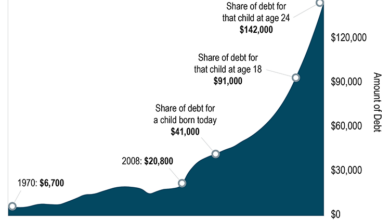
The bill’s massive spending measures will significantly increase the national debt. While the immediate focus is on addressing the pandemic, the long-term consequences of this debt accumulation are a subject of ongoing debate.
“The bill’s massive spending measures will significantly increase the national debt. While the immediate focus is on addressing the pandemic, the long-term consequences of this debt accumulation are a subject of ongoing debate.”
- Increased Interest Payments:A larger national debt will lead to higher interest payments on government bonds, potentially crowding out other government spending on critical areas like education and infrastructure.
- Impact on Future Economic Growth:Some economists argue that high levels of debt can stifle economic growth by increasing borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, while others believe that government spending can stimulate the economy in the short term, particularly during crises.
- Potential for Inflation:Large-scale government spending can lead to inflation, especially if it’s not accompanied by economic growth. This can erode the purchasing power of individuals and businesses, potentially leading to economic instability.
Impact on Healthcare and Public Health
The bill includes significant funding for healthcare, including support for hospitals and healthcare providers, as well as funding for vaccine development and distribution.
- Increased Access to Healthcare:The bill’s provisions could improve access to healthcare for some individuals, particularly those who previously lacked coverage. This could lead to improved health outcomes and potentially reduce healthcare costs in the long run.
- Strengthening Public Health Infrastructure:The bill’s investment in public health infrastructure, including disease surveillance and pandemic preparedness, could help the country better respond to future health emergencies. This could include enhanced testing capabilities, contact tracing systems, and improved communication networks.
- Long-Term Impact on Health Disparities:The bill’s impact on health disparities is a complex issue. While the bill aims to address some of the inequities in healthcare access, some argue that it may not go far enough to address the root causes of health disparities, such as social determinants of health.
Impact on Social Programs and Safety Net
The bill includes significant funding for social programs, such as unemployment benefits, food assistance, and housing support.
- Temporary Relief or Long-Term Change:The bill’s social safety net provisions are intended to provide temporary relief during the pandemic. However, there is debate about whether these programs should be extended or reformed in the long term. Some argue that these programs are necessary to prevent widespread poverty and hardship, while others believe that they create disincentives to work and can lead to dependency.
- Impact on Labor Market:The bill’s unemployment benefits could potentially disincentivize some individuals from returning to work, leading to labor shortages and impacting economic recovery. However, others argue that the benefits are necessary to support individuals and families during a time of economic uncertainty.
- Potential for Long-Term Social Change:The bill’s social safety net provisions could have long-term impacts on social attitudes and policies. The increased awareness of poverty and hardship during the pandemic could lead to greater support for social programs and a rethinking of the role of government in addressing social inequality.
Impact on Business and the Economy
The bill includes various measures to support businesses, such as loans, grants, and tax breaks.
- Stimulating Economic Recovery:The bill’s business support measures are intended to stimulate economic recovery by providing businesses with the resources they need to stay afloat and create jobs. This could lead to a faster and more robust economic rebound.
- Potential for Moral Hazard:Some argue that the bill’s business support measures could create a moral hazard, encouraging businesses to take on more risk knowing that they will be bailed out by the government. This could lead to increased financial instability in the long run.
- Impact on Competition:The bill’s support for specific industries, such as airlines and hospitality, could impact competition in those sectors. This could lead to consolidation and higher prices for consumers.
Final Review

As the debate over the coronavirus bill continues, it’s important to consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of this sweeping legislation. The bill’s impact on individuals, businesses, and the overall economy will be felt for years to come, making it a critical piece of legislation for our nation’s future.