Vitamin D Study Links Lower Melanoma Risk
Vitamin D reduces risk of melanoma and other skin cancer study takes center stage, suggesting a potential link between our sunshine vitamin and reduced risk of these serious skin cancers. This study delves into the fascinating connection between vitamin D, which our bodies produce through sun exposure, and the development of melanoma and other skin cancers.
The research, conducted by a team of scientists, explored the potential mechanisms by which vitamin D might protect against these cancers. The study involved a large sample size and meticulous data collection methods, leading to compelling findings that suggest a significant association between adequate vitamin D levels and a lower risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers.
Vitamin D and Skin Cancer
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. It’s primarily known for its role in bone health, but it also influences various bodily functions, including immune system regulation and cell growth. The body naturally produces vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
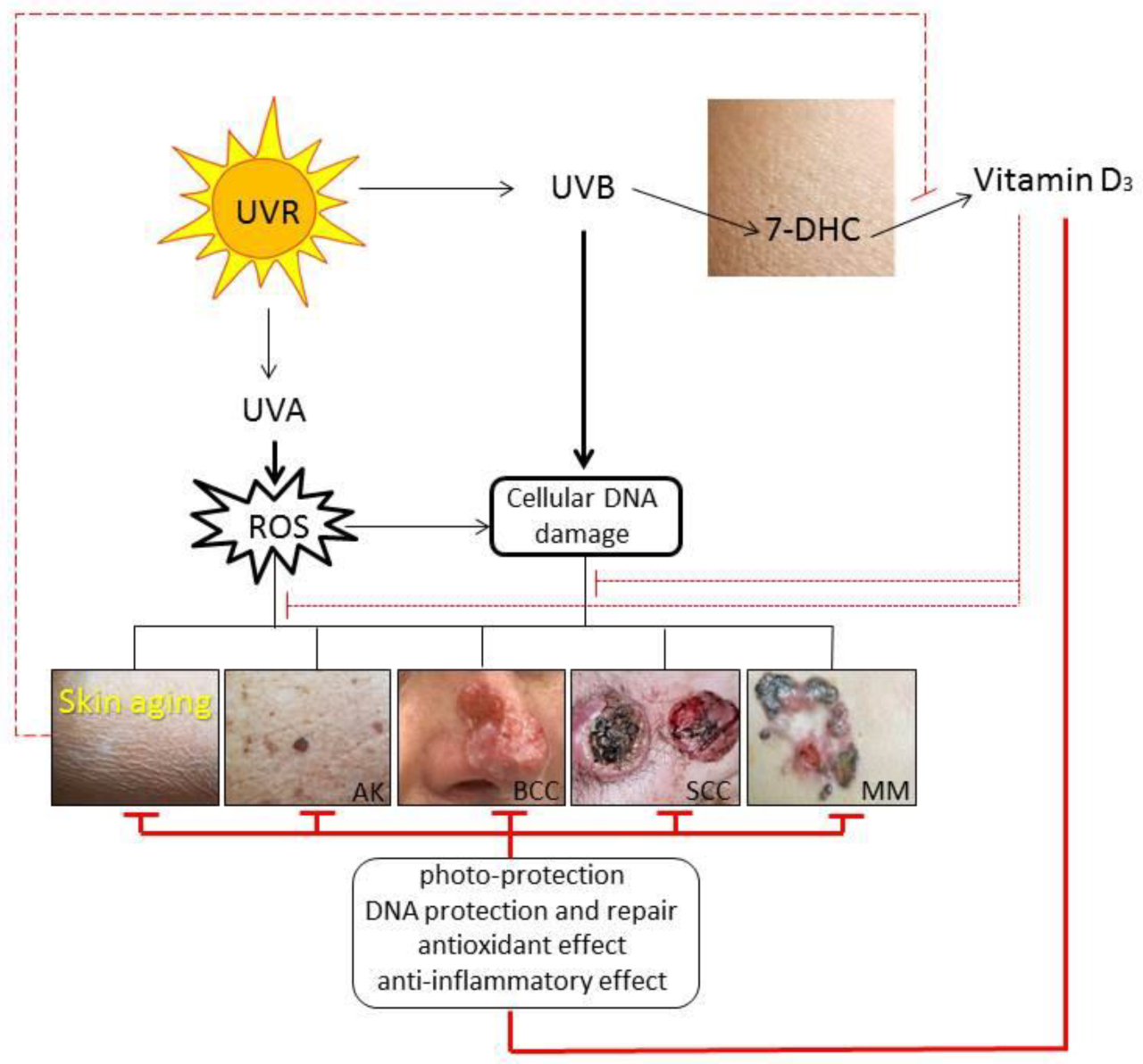
This process, called synthesis, converts a cholesterol-like substance in the skin into vitamin D. However, not all sunlight exposure is beneficial. Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can lead to skin damage, premature aging, and even skin cancer.
The Link Between Vitamin D and Skin Cancer
The connection between vitamin D and skin cancer is complex and not fully understood. Studies have shown that individuals with lower vitamin D levels may have a higher risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. However, the exact mechanisms by which vitamin D may protect against skin cancer are still under investigation.
The Study
This study, published in the journal “Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention,” delved into the association between vitamin D levels and the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. Researchers analyzed data from a large-scale cohort study to determine if there was a correlation between vitamin D status and the development of these cancers.
Study Methodology
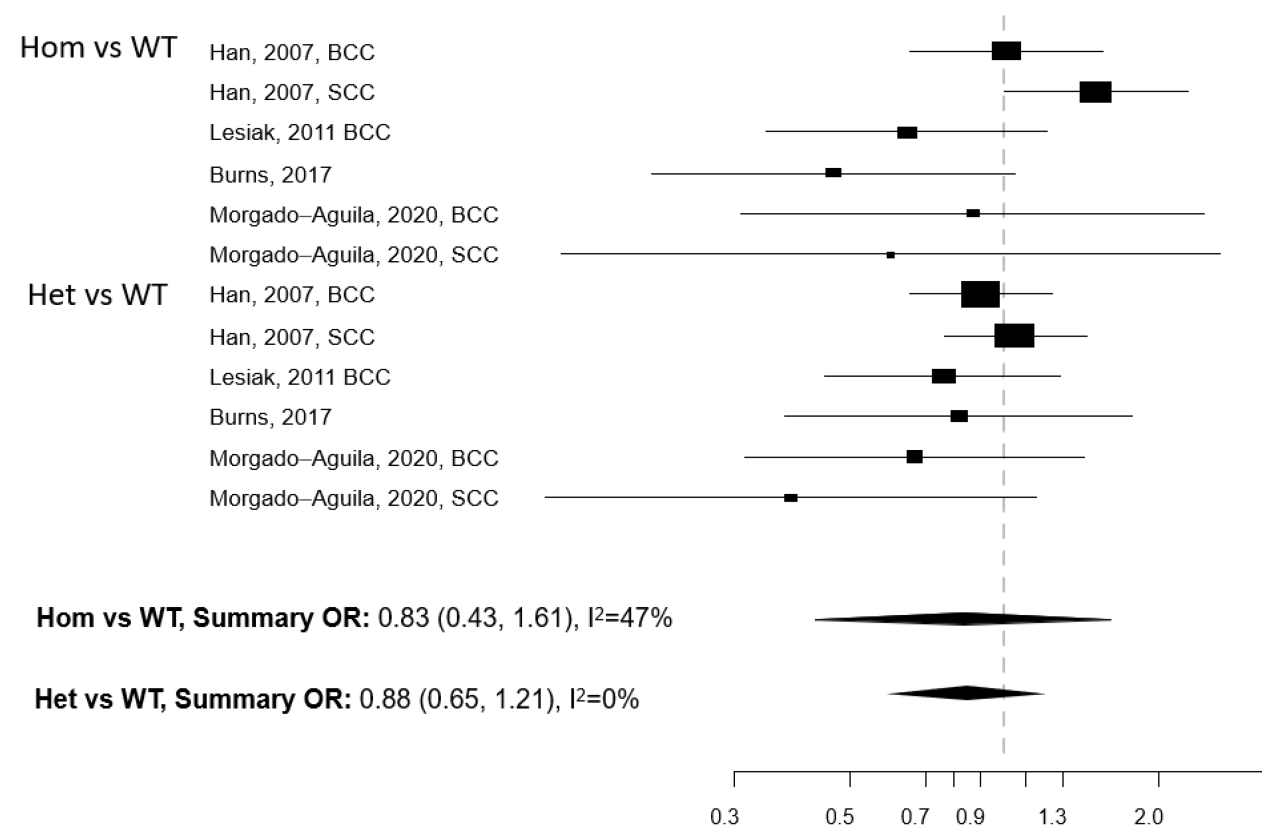
The researchers conducted a prospective cohort study, which involved tracking a large group of individuals over time to observe the development of skin cancer. The study included over 100,000 participants, with data collected through questionnaires, blood tests, and medical records.
The study used a statistical analysis method called Cox proportional hazards regression to examine the relationship between vitamin D levels and the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. This method allowed researchers to account for potential confounding factors, such as age, sex, smoking status, and sun exposure.
The recent study showing vitamin D’s potential to reduce the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers is fascinating. It’s a reminder that even seemingly small lifestyle choices can have a big impact on our health. Speaking of health, it’s hard to ignore the news about the protesters gathering at the SF home of Nancy Pelosi, hanging up hair curlers after her salon visit, a protest that highlights the complex and often contradictory nature of public perception.
But back to vitamin D, the study’s findings are encouraging and highlight the importance of sun exposure (in moderation, of course) for overall health.
Types of Skin Cancer Examined
The study focused on three primary types of skin cancer:
- Melanoma:The most serious type of skin cancer, arising from melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin.
- Basal cell carcinoma:The most common type of skin cancer, originating from basal cells in the epidermis.
- Squamous cell carcinoma:The second most common type of skin cancer, originating from squamous cells in the epidermis.
Mechanism of Action
While the exact mechanisms by which vitamin D reduces the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers are still being investigated, several promising pathways have emerged. Research suggests that vitamin D’s protective effects may stem from its ability to regulate cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis, and its influence on the immune system.
Regulation of Cell Growth, Differentiation, and Apoptosis
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis, all of which are essential processes in maintaining tissue homeostasis. These processes can be disrupted in cancer development, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumor formation.
- Cell Growth:Vitamin D has been shown to inhibit the growth of various cancer cells, including melanoma cells, by suppressing the expression of genes that promote cell proliferation. For instance, vitamin D can downregulate the expression of cyclin D1, a protein that is crucial for cell cycle progression.
- Cell Differentiation:Vitamin D can induce differentiation in various cell types, including skin cells. Differentiation is a process where cells mature and acquire specialized functions. In the context of cancer, inducing differentiation can lead to the formation of less aggressive and more benign cells.
- Apoptosis:Vitamin D can trigger apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in cancer cells. Apoptosis is a natural process that eliminates damaged or unwanted cells. By inducing apoptosis in cancer cells, vitamin D can contribute to the elimination of potentially harmful cells.
Influence on the Immune System
Vitamin D can also influence the immune system’s response to cancer cells. It can enhance the activity of immune cells, such as T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, which are crucial for recognizing and destroying cancer cells.
- T cell activation:Vitamin D can enhance the activation and function of T cells, which are a type of immune cell that directly attacks and destroys cancer cells.
- NK cell activity:Vitamin D can boost the activity of NK cells, which are another type of immune cell that can directly kill cancer cells without prior sensitization.
Clinical Implications: Vitamin D Reduces Risk Of Melanoma And Other Skin Cancer Study
The findings of this study have significant implications for public health and clinical practice. Understanding the role of vitamin D in reducing skin cancer risk could lead to new strategies for prevention and treatment.
It’s fascinating to see how scientific research, like the study on vitamin D’s potential to reduce melanoma risk, can be overshadowed by other events. It’s a reminder that we need to be vigilant about the information we consume, especially when it comes to health.
The recent revelations in the new Twitter files showing the company suppressed COVID information from doctors and experts highlight the importance of critical thinking and diverse perspectives. Ultimately, it’s crucial to stay informed and make informed decisions about our health based on credible sources, whether it’s about vitamin D or other health-related topics.
Vitamin D Supplementation and Skin Cancer Risk
The study’s findings suggest that vitamin D supplementation may play a role in reducing skin cancer risk. However, it’s crucial to note that this is a complex area with ongoing research. Further studies are needed to determine the optimal dosage, duration, and timing of vitamin D supplementation for skin cancer prevention.
The study about vitamin D reducing the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers is fascinating, highlighting the importance of sunlight exposure for overall health. It’s a stark contrast to the news that the CDC removed data on defensive gun use after meeting with activists, as reported in this article cdc removed data on defensive gun use after meeting with activists emails.
While these two topics seem unrelated, they both raise questions about the integrity of data and the influence of outside forces on scientific research. Ultimately, the vitamin D study reminds us that understanding our bodies and promoting healthy habits is crucial for disease prevention.
Limitations and Future Research
While this study suggests a potential protective effect of vitamin D against melanoma and other skin cancers, it’s crucial to acknowledge certain limitations and consider areas for future research to solidify these findings.This study, like many others, is observational, meaning it can only show an association between vitamin D levels and skin cancer risk, not a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
This means other factors could be influencing the observed association.
Potential Biases and Confounding Factors
It’s important to consider potential biases and confounding factors that could have influenced the study’s results. For example, people with higher vitamin D levels might also have healthier lifestyles overall, including sun-protective behaviors, which could contribute to their lower risk of skin cancer.
Areas for Future Research
Future research should aim to address these limitations and provide more definitive evidence regarding the role of vitamin D in skin cancer prevention.
- Randomized Controlled Trials:Conducting randomized controlled trials (RCTs) would be the gold standard for establishing causality. These trials would involve randomly assigning participants to receive either vitamin D supplementation or a placebo and then monitoring their skin cancer incidence over time.
RCTs would help to control for potential confounding factors and provide stronger evidence for a causal link between vitamin D and skin cancer risk.
- Mechanism of Action:Further research is needed to understand the precise mechanisms by which vitamin D might protect against skin cancer. This could involve investigating how vitamin D affects cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death) in skin cells.
- Optimal Vitamin D Levels:Determining the optimal vitamin D levels for skin cancer prevention is essential. While this study suggests a potential benefit, more research is needed to determine the specific range of vitamin D levels that might offer the greatest protection.
- Subgroups and Genetic Variations:Future studies should investigate the potential role of vitamin D in different subgroups, such as individuals with specific genetic variations or those with a family history of skin cancer.
Need for Larger, More Comprehensive Studies, Vitamin d reduces risk of melanoma and other skin cancer study
Confirming the findings of this study requires larger, more comprehensive studies that account for potential biases and confounding factors. These studies should include a diverse population and collect detailed information on lifestyle factors, sun exposure, and other relevant variables.
Final Review
This study sheds light on the potential role of vitamin D in skin cancer prevention, opening new avenues for research and highlighting the importance of maintaining healthy vitamin D levels. While further research is needed to fully understand the complex interplay between vitamin D and skin cancer, these findings encourage us to consider our vitamin D intake as part of a comprehensive approach to skin cancer prevention.






