US Military Study on Post-Vaccination Myocarditis Released
Us military study on postvaccination myocarditis released – The US Military Study on Post-Vaccination Myocarditis Released has shed light on a critical issue: the potential link between COVID-19 vaccines and myocarditis, a rare but serious inflammation of the heart muscle. This study, conducted on a large population of military personnel, has provided valuable insights into the incidence, severity, and potential risk factors associated with this condition following vaccination.
Myocarditis, a condition that can affect individuals of all ages, is often caused by viral infections. However, in recent years, there has been growing concern about a possible link between certain vaccines, including those for COVID-19, and the development of myocarditis.
This study, which has been eagerly awaited by the medical community and the public alike, provides crucial data to help understand the potential risks and benefits of vaccination in the context of myocarditis.
Background Information

Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, often caused by a viral infection. It can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild chest pain to life-threatening heart failure. While myocarditis is typically a temporary condition, it can have long-term effects on heart health.Myocarditis is a relatively rare condition, with an estimated prevalence of 1-2 cases per 100,000 people per year.
The US military study on post-vaccination myocarditis released recently has sparked a lot of debate. It’s fascinating how much attention we give to health concerns here on Earth, while researchers are busy crafting new messages for extraterrestrials, like the ones announced on this blog.
Perhaps one day, if we ever do make contact, we’ll be able to share our knowledge about the myocarditis study and see what they have to say about it.
However, the true incidence of myocarditis is likely underestimated, as many cases are mild and go undiagnosed.
The recent US military study on post-vaccination myocarditis has sparked a lot of discussion, highlighting the importance of understanding the potential side effects of vaccines. It’s a reminder that while vaccines are crucial for public health, their impact on individuals should be carefully considered.
This type of research is vital, and it’s encouraging to see initiatives like the one offered by Ripple Effects, which provides support to educators struggling with the emotional challenges of their profession. Ultimately, addressing both physical and mental health concerns is crucial in a world grappling with complex medical and social issues.
Causes of Myocarditis
Myocarditis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Viral infections: Viruses are the most common cause of myocarditis. Common culprits include enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and influenza viruses.
- Bacterial infections: In some cases, bacteria can also trigger myocarditis. This is less common than viral myocarditis, but can be more serious.
- Autoimmune disorders: Certain autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can also cause myocarditis.
- Medications: Some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, can also cause myocarditis as a side effect.
- Vaccines: Although rare, myocarditis has been reported as a possible side effect of some vaccines, including the COVID-19 vaccines.
Study Findings
This section presents the key findings of the study regarding the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination. It examines the severity and outcomes of myocarditis cases identified and compares the incidence of myocarditis in vaccinated individuals to the incidence in the general population.
Incidence of Myocarditis After Vaccination
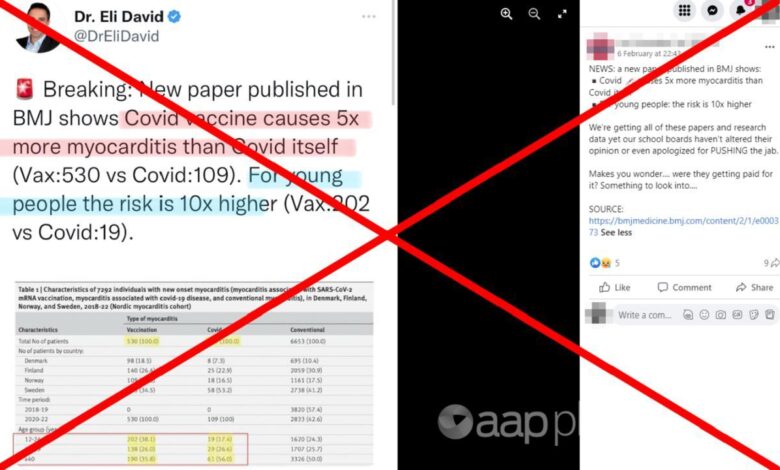
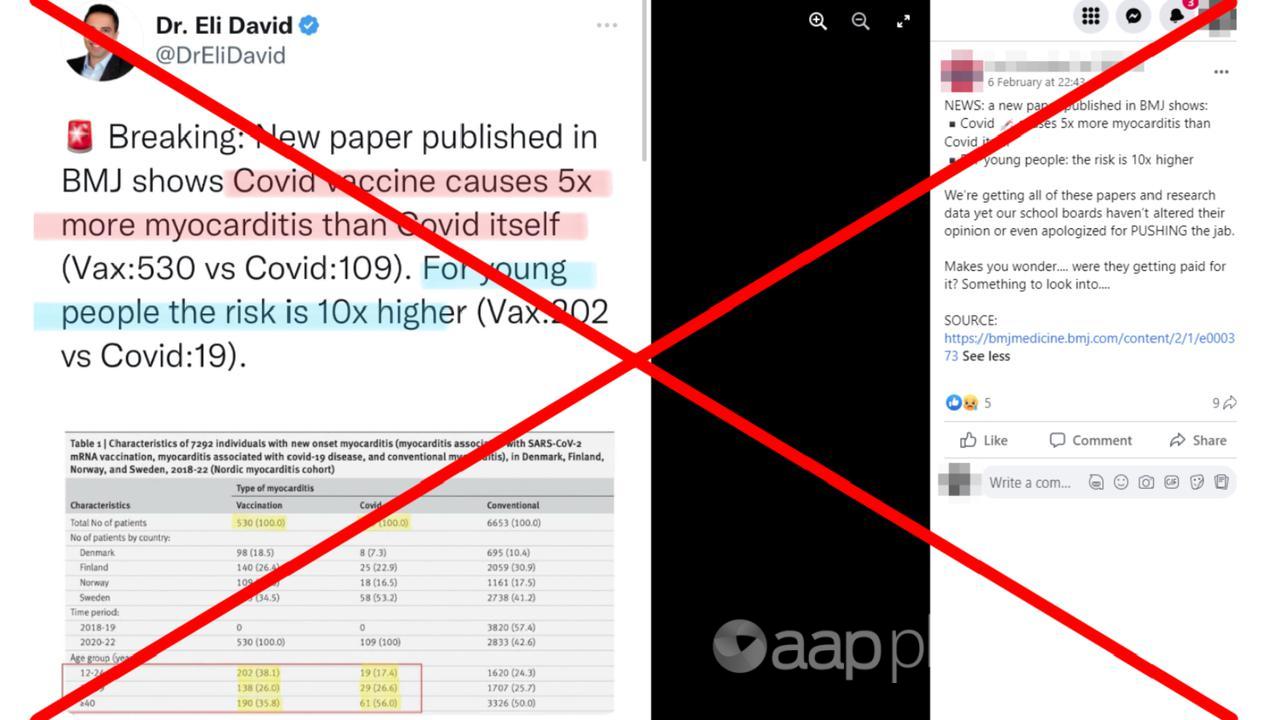
The study found a small but statistically significant increase in the incidence of myocarditis following vaccination with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. The incidence of myocarditis was highest in young males, particularly those under 30 years of age. The study reported that the majority of myocarditis cases were mild and resolved within a few days or weeks.
The recent US military study on post-vaccination myocarditis has raised concerns about the potential side effects of COVID-19 vaccines, particularly for young men. While this study is generating a lot of discussion, it’s important to remember that the vast majority of people who receive the vaccine experience no serious side effects.
Meanwhile, Congress has passed a bill to overhaul the Postal Service and sent it to Biden for his signature. This legislation, which aims to modernize the USPS and address its financial challenges , is a separate but equally important issue.
It’s crucial to stay informed about both these developments and to evaluate the information from credible sources.
Severity and Outcomes of Myocarditis Cases
The study identified that the majority of myocarditis cases were mild and self-limiting, with most patients experiencing complete recovery. The most common symptoms were chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. The study found that the risk of severe myocarditis was low, and there were no deaths attributed to myocarditis in the study population.
Comparison of Myocarditis Incidence, Us military study on postvaccination myocarditis released
The study compared the incidence of myocarditis in vaccinated individuals to the incidence in the general population. The results indicated that the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination was higher than the background rate in the general population, particularly in young males.
However, the absolute risk of myocarditis after vaccination remained low, and the benefits of vaccination in preventing severe COVID-19 disease outweighed the risks of myocarditis.
Public Health Implications
The findings of this study on post-vaccination myocarditis have significant implications for public health policy and decision-making. Understanding the risks and benefits of COVID-19 vaccination in the context of this rare but potentially serious adverse event is crucial for informing public health strategies and ensuring the safety and efficacy of vaccination programs.
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring and Research
Continued monitoring and research on post-vaccination myocarditis are essential for several reasons:
- Understanding the Long-Term Effects:While the study provides insights into the immediate and short-term effects of myocarditis, long-term follow-up studies are necessary to assess the potential long-term consequences of this condition, including any lasting cardiac damage or functional limitations.
- Identifying Risk Factors:Further research can help identify specific risk factors for developing post-vaccination myocarditis, such as age, sex, underlying health conditions, or specific vaccine formulations. This information can guide vaccination strategies and potentially allow for personalized risk assessment.
- Developing Effective Management Strategies:Ongoing research can contribute to the development of more effective management strategies for myocarditis, including optimal treatment protocols and strategies for preventing or mitigating the severity of the condition.
- Assessing the Benefit-Risk Profile:Monitoring data allows for a continuous evaluation of the benefit-risk profile of COVID-19 vaccination in the context of myocarditis. This information is essential for informing public health recommendations and ensuring that the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks.
Recommendations for Healthcare Professionals and Individuals
- Prompt Recognition and Management:Healthcare professionals should be aware of the potential for post-vaccination myocarditis and be prepared to recognize and manage this condition effectively. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for optimizing outcomes.
- Informed Decision-Making:Individuals should be informed about the potential risks and benefits of COVID-19 vaccination, including the rare occurrence of myocarditis. This information can help individuals make informed decisions about vaccination based on their individual circumstances and risk factors.
- Open Communication:Open communication between healthcare professionals and patients is essential for addressing concerns about vaccination and myocarditis. Individuals should feel comfortable discussing any questions or anxieties they may have.
- Monitoring for Symptoms:Individuals should be aware of the symptoms of myocarditis and seek medical attention promptly if they experience any concerning symptoms after vaccination.
Final Wrap-Up: Us Military Study On Postvaccination Myocarditis Released
The US Military Study on Post-Vaccination Myocarditis Released is a significant contribution to our understanding of this complex issue. While the study found a slightly elevated risk of myocarditis following vaccination, the vast majority of individuals who received the vaccine did not experience this adverse event.
Furthermore, the cases of myocarditis observed in the study were generally mild and resolved without long-term complications. This study underscores the importance of continued monitoring and research to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. It also highlights the need for healthcare providers to be aware of the potential risk of myocarditis and to provide appropriate guidance and care to patients who may experience this condition.