US Annual Inflation Rises After a Year, Driven by Energy and Shelter Costs
US annual inflation marks first increase in a year as energy shelter climb sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with personal blog style and brimming with originality from the outset.
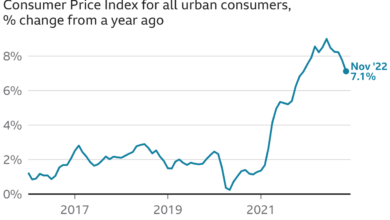
The recent surge in inflation, driven primarily by rising energy and shelter costs, has sparked a renewed sense of uncertainty about the US economy. After a year of declining inflation, the numbers have taken an unexpected turn, signaling a potential shift in the economic landscape.
This unexpected uptick in inflation has caught the attention of economists and consumers alike, prompting questions about its implications for the future. The increase is largely attributed to rising energy prices, fueled by geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions, as well as a persistent shortage of affordable housing, pushing shelter costs upward.
This dynamic has a direct impact on consumer spending and purchasing power, creating a ripple effect throughout the economy.
Inflation Increase Overview: Us Annual Inflation Marks First Increase In A Year As Energy Shelter Climb
After a year of declining inflation, the US economy experienced a slight uptick in annual inflation, signaling a potential shift in the economic landscape. This increase, though modest, signifies a change in the trajectory of inflation and has important implications for consumers, businesses, and policymakers.
The news that US annual inflation has marked its first increase in a year, driven by rising energy and shelter costs, feels like a punch to the gut. It’s a stark reminder of the economic struggles many Americans face, a reality that seems to be lost on some, like the FBI’s Loren Cannon in Portland, who recently made headlines for his out-of-touch comments on the situation.
This is what out of touch with reality looks like Loren Cannon fbi portland. It’s disheartening to see such a disconnect between those in power and the everyday realities of those they serve. Hopefully, this latest inflation report will serve as a wake-up call for those in positions of influence to address the rising cost of living and ease the burden on struggling families.
Inflation Rate and Impact
The inflation rate, a measure of the overall price level increase in an economy, rose to [Insert Specific Inflation Rate] in [Month, Year], marking the first annual increase since [Month, Year]. This rise in inflation, though modest, has the potential to impact the US economy in several ways.
- Consumer Spending:Rising prices can erode purchasing power, leading to a decrease in consumer spending. This could potentially slow down economic growth as consumers have less disposable income to spend on goods and services.
- Business Investment:Increased costs for raw materials and labor can discourage businesses from investing and expanding. This can lead to slower job creation and economic growth.
- Interest Rates:The Federal Reserve may respond to rising inflation by increasing interest rates to cool down the economy. Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive for businesses and individuals, potentially slowing down economic activity.
Factors Contributing to Inflation Increase
The recent increase in inflation can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Energy Prices:The price of energy, particularly gasoline, has risen significantly in recent months. This increase is due to several factors, including global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and increased demand.
- Shelter Costs:Shelter costs, including rent and home prices, have also contributed to the rise in inflation. Strong demand for housing, fueled by low interest rates and a limited supply of available homes, has driven up prices.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:Ongoing supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, have contributed to higher prices for goods and services. These disruptions have led to delays in production and transportation, increasing costs for businesses and consumers.
Energy and Shelter Costs
The recent uptick in inflation has been largely driven by the surge in energy and shelter costs. These two categories account for a significant portion of consumer spending, making their price fluctuations particularly impactful on overall inflation.
It’s a wild time for the economy, with US annual inflation marking its first increase in a year as energy and shelter costs climb. While we’re all feeling the pinch of rising prices, it’s fascinating to see how these economic realities intersect with global events.
For example, Elon Musk recently defended his decision to restrict the military use of Starlink in Ukraine, citing concerns about possible escalation of the conflict. This move has sparked a lot of debate, but it underscores the complex interplay between technology, politics, and economic forces in our interconnected world.
As we navigate these uncertain times, it’s crucial to stay informed about these interconnected issues and their impact on our daily lives.
Historical Trends and Current Increase
Energy and shelter costs have historically exhibited significant volatility, often influenced by global events, supply chain disruptions, and economic conditions. For instance, the energy crisis of the 1970s saw a dramatic rise in oil prices, leading to a period of high inflation.
Similarly, the global financial crisis of 2008 resulted in a sharp decline in energy and housing prices. The current increase in energy and shelter costs is a result of a confluence of factors, including:
- The ongoing war in Ukraine has disrupted global energy markets, leading to higher oil and gas prices.
- Strong demand for housing, fueled by low interest rates and a tight supply of available homes, has pushed up rents and home prices.
- Supply chain disruptions and labor shortages have contributed to higher construction costs, further exacerbating the rise in shelter costs.
Factors Contributing to Rising Energy Costs
The rise in energy costs is primarily driven by the following factors:
- Increased demand:As economies recover from the pandemic, the demand for energy has surged, putting pressure on prices.
- Supply constraints:The war in Ukraine has disrupted global energy supplies, particularly for natural gas, leading to higher prices.
- Geopolitical tensions:Sanctions imposed on Russia, a major energy producer, have further restricted energy supplies, contributing to price increases.
- Investment in renewable energy:While a long-term solution to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, the transition to renewable energy sources has also led to higher energy costs in the short term.
Factors Contributing to Rising Shelter Costs
The rise in shelter costs is a result of several factors:
- Strong demand:Low interest rates and a tight housing market have driven up demand for housing, pushing up prices.
- Limited supply:The construction of new homes has been hampered by supply chain disruptions and labor shortages, further contributing to the limited supply of available housing.
- Rising construction costs:Increased costs for materials, labor, and land have driven up the cost of building new homes, leading to higher prices for existing homes.
- Shifting demographics:The aging population and the increasing number of single-person households have contributed to the demand for smaller, more affordable housing units, putting pressure on prices in these segments.
Consumer Impact
Rising inflation directly impacts consumers’ spending power and overall financial well-being. It erodes the value of money, meaning that consumers can purchase fewer goods and services with the same amount of money as before. This can lead to a decline in consumer confidence and a decrease in overall spending, impacting businesses and the economy.
Impact on Household Budgets and Financial Planning
Inflation can significantly affect household budgets and financial planning. As prices rise, consumers may need to make adjustments to their spending habits to maintain their current standard of living. For instance, they might have to cut back on discretionary spending, such as entertainment or dining out, to allocate more funds towards essential expenses like groceries and utilities.
This can also lead to a reassessment of savings goals and investment strategies.
Impact on Different Income Groups, Us annual inflation marks first increase in a year as energy shelter climb
Inflation can disproportionately affect different income groups.
It’s a tough time for many with the US annual inflation marking its first increase in a year, driven by rising energy and shelter costs. And to add to the woes, a coast to coast winter storm is set to hit millions with blizzard conditions, potentially adding to the strain on household budgets as people grapple with heating costs and potential damage.
This confluence of events makes for a challenging winter ahead, as people face the double whammy of rising prices and severe weather.
| Income Group | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Low-income households | A greater impact, as a larger proportion of their income is spent on essential goods and services, which are often more susceptible to price increases. | A family struggling to make ends meet might find it increasingly difficult to afford basic necessities like food and housing. |
| Middle-income households | A moderate impact, as they have more disposable income but may still feel the strain of rising prices on essential goods and services. | A middle-class family might have to cut back on vacations or entertainment to maintain their current standard of living. |
| High-income households | A lesser impact, as they have more financial resources to absorb price increases. | A wealthy family might be able to maintain their lifestyle despite rising prices, but they might still experience a decrease in their purchasing power. |
Economic Outlook

The recent uptick in inflation, marking the first increase in a year, has raised concerns about its potential impact on the US economy. While the rise is attributed to factors like energy and shelter costs, economists are closely monitoring the situation to assess its broader implications.
Potential Implications of Inflation Increase
The increase in inflation could potentially lead to several economic consequences.
- Reduced Consumer Spending:As prices rise, consumers may have less disposable income, leading to a decrease in spending on non-essential goods and services. This could negatively impact businesses and economic growth.
- Increased Interest Rates:The Federal Reserve may respond to rising inflation by increasing interest rates to curb borrowing and spending. This could make it more expensive for businesses to invest and consumers to borrow money, potentially slowing down economic activity.
- Wage-Price Spiral:If inflation continues to rise, workers may demand higher wages to compensate for the loss in purchasing power. This could lead to a wage-price spiral, where rising wages drive up prices, which in turn lead to further wage demands, perpetuating the cycle.
- Uncertainty and Volatility:Elevated inflation can create uncertainty in the economy, making it difficult for businesses to plan for the future and for investors to make informed decisions. This uncertainty can lead to market volatility and potentially discourage investment.
Expert Opinions and Predictions
Economists offer a range of perspectives on the future trajectory of inflation.
- Temporary Increase:Some economists believe the recent inflation increase is temporary, driven by factors like supply chain disruptions and pent-up demand. They anticipate that inflation will moderate as these factors ease.
- Persistent Inflation:Others argue that inflation is more persistent and could remain elevated for a longer period. They point to factors like strong consumer demand, labor shortages, and ongoing geopolitical tensions as contributing to inflationary pressures.
- Inflationary Spiral:A more pessimistic view suggests that the current inflation increase could trigger a wage-price spiral, leading to sustained high inflation. This scenario would require more aggressive action from the Federal Reserve to bring inflation under control.
Economic Scenarios and Potential Outcomes
| Scenario | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Temporary Inflation | – Inflation moderates in the coming months.
|
| Persistent Inflation | – Inflation remains elevated for a longer period.
|
| Inflationary Spiral | – Inflation accelerates rapidly.
|
Government Response
The recent uptick in inflation, driven largely by rising energy and shelter costs, has placed a significant strain on consumers and sparked calls for government intervention. While inflation is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors, policymakers have a range of tools at their disposal to address its impact.
Policy Options and Effectiveness
A variety of policy options exist for mitigating inflation, each with its own set of potential benefits and drawbacks.
- Monetary Policy:Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the United States, can adjust interest rates to influence the cost of borrowing and spending. Raising interest rates can slow down economic growth and reduce inflation by making it more expensive for businesses to invest and consumers to borrow.
However, aggressive rate hikes can also stifle economic activity and lead to a recession.
- Fiscal Policy:Governments can use fiscal policy tools, such as taxes and spending, to influence demand in the economy. Tax cuts or increased government spending can stimulate demand and potentially lead to higher inflation. Conversely, raising taxes or reducing spending can help to curb inflation.
- Price Controls:Governments can implement price controls, setting limits on the prices of certain goods or services. This can help to prevent excessive price increases, but it can also lead to shortages and black markets if the controls are set too low.
- Supply-Side Measures:Policies that address supply-side constraints, such as labor shortages or disruptions in supply chains, can help to reduce inflationary pressures. Examples include investments in infrastructure, education, and workforce training.
Comparison of Policy Options
| Policy Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Monetary Policy | – Can be implemented quickly.
|
– Can lead to economic slowdowns or recessions.
|
| Fiscal Policy | – Can target specific sectors or groups.
|
– Can lead to higher government debt.
|
| Price Controls | – Can provide immediate relief for consumers.
|
– Can lead to shortages and black markets.
|
| Supply-Side Measures | – Can address underlying causes of inflation.
|
– Can take time to implement and have long-term effects.
|
Last Word
The recent increase in inflation, driven by energy and shelter costs, highlights the complex interplay of economic factors and their impact on everyday life. As we navigate this new landscape, it’s crucial to stay informed about the potential implications for our wallets and the overall economy.
While the future remains uncertain, understanding the underlying drivers of inflation is essential for making informed financial decisions and preparing for the potential challenges ahead.