Unreal Hawaii: Zero Coronavirus Tests, Waiting on CDC Kits
Unreal hawaii has tested exactly zero people for coronavirus still waiting for test kits from the cdc – Unreal Hawaii: Zero Coronavirus Tests, Waiting on CDC Kits – it’s a headline that sounds more like a satirical news piece than reality. Yet, here we are, with the Aloha State facing a critical shortage of testing kits, leaving them unable to effectively assess the spread of COVID-19 within their borders.
This situation has left Hawaii grappling with a multitude of challenges, from understanding the true scope of the virus to implementing effective public health measures. The implications are far-reaching, affecting not only the health and safety of residents but also the state’s vital tourism industry.
The lack of testing is a major roadblock in Hawaii’s fight against the virus. Without reliable data on infection rates, it’s impossible to make informed decisions about public health measures. This leaves Hawaii vulnerable to outbreaks, as the true extent of the virus’s spread remains shrouded in uncertainty.
The state’s dependence on the CDC for testing kits has also exposed a critical vulnerability in its pandemic preparedness strategy.
The State of Testing in Hawaii
Hawaii’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been met with mixed reactions, particularly regarding the state’s initial approach to testing. The statement “unreal Hawaii has tested exactly zero people for coronavirus” highlights the significant challenges the state faced in the early stages of the outbreak.
It’s mind-boggling that Hawaii, a state so reliant on tourism, has tested exactly zero people for coronavirus. They’re still waiting for test kits from the CDC, which seems incredibly slow considering the urgency of the situation. Meanwhile, the news is filled with reports like this one trump furious americans infected with coronavirus flew back to us without his permission report , which only adds to the growing sense of unease.
It’s crucial that Hawaii gets its testing procedures in place ASAP, especially with the potential for infected travelers coming in from other parts of the world.
This lack of testing, while initially a reflection of limited resources and testing kit availability, had crucial implications for understanding the spread of the virus and implementing effective public health measures.
Challenges in Accessing Testing Kits
The initial lack of widespread testing in Hawaii was primarily attributed to the scarcity of testing kits. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) initially struggled to provide sufficient kits to states, leading to delays and limited testing capacity across the nation.
Hawaii, like many other states, faced difficulties in acquiring the necessary resources to conduct large-scale testing.
The Role of the CDC in Providing Testing Resources
The CDC played a crucial role in developing and distributing testing kits, but the initial supply was insufficient to meet the demands of states like Hawaii. The agency faced challenges in producing and distributing kits quickly enough, contributing to the delays experienced by states in ramping up testing efforts.
As the pandemic evolved, the CDC collaborated with private laboratories and expanded testing capacity, but the initial lack of resources had a significant impact on the ability to monitor and contain the virus in Hawaii.
Impact on Public Health

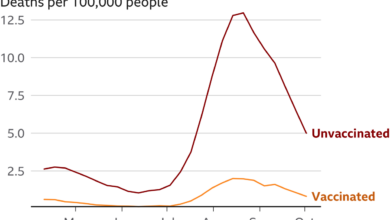
The limited availability of COVID-19 testing in Hawaii poses a significant threat to public health, potentially hindering efforts to control the spread of the virus and protect the community. Without accurate data on the prevalence of the virus, it becomes challenging to make informed decisions regarding public health measures and resource allocation.
Risks Associated with Limited Testing Data
Limited testing data can lead to an underestimation of the true number of COVID-19 cases in Hawaii. This lack of accurate data can have several detrimental consequences for public health:
- Misguided Public Health Measures:Without reliable data, policymakers might implement ineffective or overly restrictive measures, leading to unnecessary economic disruptions or public anxiety.
- Delayed Response to Outbreaks:The delayed identification of outbreaks due to limited testing can allow the virus to spread unchecked, potentially overwhelming healthcare resources and leading to a surge in hospitalizations and fatalities.
- Underestimation of Mortality Rate:The true mortality rate of COVID-19 in Hawaii might be higher than estimated due to undetected cases, making it difficult to assess the true impact of the virus on the population.
Challenges of Contact Tracing and Containment, Unreal hawaii has tested exactly zero people for coronavirus still waiting for test kits from the cdc
Effective contact tracing is crucial for breaking the chain of transmission and preventing further spread of the virus. However, limited testing significantly hampers contact tracing efforts:
- Difficulty Identifying Contacts:Without widespread testing, individuals who are infected but asymptomatic or have mild symptoms might go undetected, making it challenging to identify and isolate their contacts.
- Delayed Isolation and Quarantine:The delayed identification of infected individuals due to limited testing can lead to a delay in isolation and quarantine measures, allowing the virus to spread further within the community.
- Reduced Effectiveness of Containment Strategies:The lack of comprehensive testing data can undermine the effectiveness of containment strategies, making it difficult to target resources and interventions to areas with the highest risk of transmission.
Importance of Testing for Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection of COVID-19 is crucial for timely treatment and improved patient outcomes. Testing plays a vital role in facilitating early detection:
- Prompt Medical Attention:Testing allows individuals with suspected COVID-19 to seek medical attention promptly, enabling early intervention and potentially preventing severe complications.
- Targeted Treatment:Early detection through testing allows healthcare providers to administer appropriate treatment and support based on individual patient needs and medical history.
- Reduced Transmission Risk:Testing helps identify infected individuals, allowing them to isolate themselves and reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
Economic and Social Implications

The limited availability of COVID-19 testing in Hawaii has significant implications for the state’s economy and social fabric. The lack of testing can hinder efforts to contain the virus, leading to potential economic repercussions and social disruptions.
It’s crazy to think that Hawaii has tested exactly zero people for coronavirus and is still waiting for test kits from the CDC. The whole situation seems like a bad dream, especially when you consider that China’s coronavirus numbers don’t add up, and the White House doesn’t believe them, as you can read here.
Hawaii’s lack of testing is a major concern, as it could mean that the virus is spreading undetected. We need to get testing kits out there and start getting a handle on this situation.
Impact on Tourism Industry
The tourism industry, a cornerstone of Hawaii’s economy, is particularly vulnerable to the impact of limited testing. Tourists, concerned about potential exposure to the virus, may be hesitant to travel to Hawaii if they are unsure of the testing availability and procedures.
This uncertainty can lead to a decline in tourist arrivals, impacting hotels, restaurants, transportation services, and other businesses reliant on tourism revenue. For example, a study by the Hawaii Tourism Authority estimated that the state lost $2.5 billion in tourism revenue in 2020 due to the pandemic.
Impact on Business Operations and Public Gatherings
Limited testing can also affect businesses and public gatherings in various ways. Businesses may struggle to maintain operations if employees are unable to get tested and confirmed negative, leading to potential closures or disruptions. Public gatherings, such as concerts, festivals, and sporting events, may face restrictions or cancellations due to concerns about potential virus spread.
The lack of testing can create uncertainty and anxiety among businesses and the public, hindering economic activity and social interaction.
Impact on Public Trust and Community Safety
Limited testing can erode public trust in the government’s ability to manage the pandemic. The lack of readily available testing may lead to skepticism about the accuracy of official data and public health messaging. This can hinder efforts to encourage public compliance with health guidelines and promote community safety.
For instance, a recent poll by the University of Hawaii found that a significant percentage of residents expressed distrust in the government’s handling of the pandemic due to limited testing availability.
Impact on Public Health Messaging and Awareness
Limited testing can hinder public health messaging and awareness efforts. Without reliable testing data, it becomes challenging to accurately assess the spread of the virus, identify potential hotspots, and implement effective public health interventions. This can lead to a lack of awareness about the true extent of the pandemic, potentially undermining efforts to encourage preventive measures like mask-wearing, social distancing, and vaccination.
Comparison with Other States
Hawaii’s testing situation has been a point of concern, particularly in the early stages of the pandemic. It’s important to compare Hawaii’s approach to testing with other states to understand the factors contributing to these differences and identify potential best practices.
Factors Contributing to Differences in Testing Capacity and Availability
The testing capacity and availability in different states have been influenced by various factors, including:
- State-level policies and strategies: Different states have adopted varying approaches to testing, ranging from proactive testing programs to more reactive measures. Some states have prioritized testing for specific groups, such as healthcare workers or residents of long-term care facilities, while others have adopted a more universal approach.
- Availability of testing resources: The availability of testing resources, such as test kits, laboratory capacity, and trained personnel, has been a critical factor in determining the scale of testing efforts. States with greater access to these resources have been able to conduct more tests, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the pandemic’s spread.
- Population density and demographics: Population density and demographic factors, such as the age distribution and health status of the population, can influence the demand for testing and the effectiveness of testing strategies. States with higher population densities or older populations may experience a greater need for testing.
- Economic factors: The economic resources available to states have also played a role in their ability to invest in testing infrastructure and programs. States with stronger economies have been able to allocate more funds for testing, while states facing budget constraints may have had to prioritize other public health initiatives.
Best Practices and Strategies Employed by Other States
Several states have adopted best practices and strategies to address testing challenges during the pandemic. Some examples include:
- Drive-through testing sites: Many states have implemented drive-through testing sites to increase accessibility and convenience for individuals seeking testing. These sites have allowed for rapid testing without requiring individuals to enter a healthcare facility, minimizing the risk of exposure to the virus.
- Mobile testing units: Mobile testing units have been deployed to reach underserved communities and areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. These units have been particularly effective in rural areas and communities with high concentrations of vulnerable populations.
- Partnerships with private labs: States have partnered with private laboratories to expand testing capacity and shorten turnaround times for test results. These partnerships have allowed states to leverage the expertise and resources of private labs to increase the volume and efficiency of testing.
It’s surreal to think that Hawaii, a state known for its tourism and idyllic beaches, has tested exactly zero people for coronavirus. They’re still waiting for test kits from the CDC, while meanwhile, the political landscape is heating up with Bernie Sanders’ surge shaking up the Democratic establishment.
With Nevada’s caucus just around the corner, it’s hard to say whether the focus on public health or political drama will dominate the news cycle in the coming days. But one thing’s for sure, Hawaii’s lack of testing is a concerning reminder of the challenges we face in responding to this global pandemic.
- Public-private partnerships: Some states have established public-private partnerships to develop and deploy innovative testing solutions. These partnerships have brought together the resources and expertise of government agencies, private companies, and academic institutions to address the challenges of testing.
Lessons Learned from Other States’ Experiences
The experiences of other states have provided valuable lessons for managing testing during a pandemic:
- Early and aggressive testing is crucial: Early and aggressive testing is essential to identify cases, track the spread of the virus, and implement timely public health interventions. States that have prioritized testing have been more successful in controlling the pandemic.
- Testing should be accessible and convenient: Testing should be accessible to all individuals, regardless of their insurance status or socioeconomic background. Convenient testing options, such as drive-through testing sites and mobile testing units, are essential to encourage individuals to get tested.
- Rapid turnaround times for test results are critical: Rapid turnaround times for test results are crucial for effective contact tracing and isolation of infected individuals. States have sought to shorten turnaround times through partnerships with private labs and investments in laboratory capacity.
- Data sharing and collaboration are essential: Effective data sharing and collaboration between states, local governments, and public health agencies are essential for a coordinated response to the pandemic. Data sharing allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the virus’s spread and helps to inform public health decisions.
Future Strategies for Testing: Unreal Hawaii Has Tested Exactly Zero People For Coronavirus Still Waiting For Test Kits From The Cdc
Hawaii’s current testing situation underscores the urgent need for a comprehensive strategy to increase testing capacity and ensure equitable access to testing for all residents. This will require a multifaceted approach that addresses both immediate and long-term needs.
Increasing Testing Capacity
Hawaii needs to significantly expand its testing capacity to meet the demands of a growing population and potential surges in cases. This involves increasing the number of testing sites, procuring sufficient testing supplies, and expanding the workforce responsible for conducting and processing tests.
- Establish more testing sites:Expanding the number of testing sites across the islands, including mobile testing units in underserved communities, will increase accessibility for residents.
- Streamline the procurement of testing supplies:Secure a reliable and consistent supply chain for testing kits, reagents, and other necessary materials to avoid shortages. This could involve partnering with manufacturers, securing government funding, or establishing a state-level stockpile.
- Expand the testing workforce:Train additional healthcare professionals, laboratory technicians, and administrative staff to manage the increased testing volume. This could involve utilizing existing resources like medical schools and community colleges, offering incentives for professionals to work in testing, or exploring partnerships with private laboratories.
Overcoming Challenges in Accessing Testing Kits
Challenges in accessing testing kits have hampered Hawaii’s ability to effectively monitor and contain the spread of the virus. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensuring timely and accurate testing for all residents.
- Reduce reliance on the CDC:Explore alternative sources for testing kits, such as private manufacturers or state-level production facilities, to minimize delays and ensure a steady supply.
- Increase transparency and communication:Provide clear and timely information to the public about testing availability, eligibility criteria, and the process for obtaining tests. This will reduce confusion and facilitate access to testing.
- Develop a centralized testing coordination system:Establish a centralized system for managing testing requests, scheduling appointments, and tracking results. This will streamline the process and reduce wait times for testing.
Investing in Infrastructure and Resources
Investing in infrastructure and resources is critical to supporting widespread testing in Hawaii. This includes allocating funds for laboratory expansion, data management systems, and public health workforce development.
- Expand laboratory capacity:Invest in new equipment, technology, and personnel to increase the processing capacity of existing laboratories and establish new testing facilities.
- Develop robust data management systems:Invest in technology to effectively collect, analyze, and share testing data to inform public health decisions and track the spread of the virus.
- Strengthen the public health workforce:Provide training and resources to public health professionals to effectively manage testing programs, conduct contact tracing, and implement public health interventions.
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships can play a vital role in expanding testing access and improving the efficiency of testing programs. These partnerships can leverage the expertise and resources of both sectors to overcome challenges and achieve shared goals.
- Collaborate with private laboratories:Partner with private laboratories to increase testing capacity, share resources, and streamline the testing process.
- Engage with technology companies:Work with technology companies to develop innovative solutions for testing, data management, and communication.
- Seek support from philanthropic organizations:Engage with philanthropic organizations to secure funding for testing infrastructure, workforce development, and community outreach.
Last Recap
The situation in Hawaii underscores the importance of robust testing infrastructure, not just for individual states but for the entire nation. The pandemic has exposed the fragility of our public health systems and the need for proactive measures to ensure we are prepared for future outbreaks.
While Hawaii is currently facing a challenging situation, it’s not without hope. With a concerted effort to increase testing capacity and secure access to resources, Hawaii can navigate this crisis and protect its residents and economy.