Unemployment Rate Spike Triggers SAHM Rule, Signaling US Recession?
Unemployment rate spike triggers sahm rule indicator signaling potential us recession – Unemployment Rate Spike Triggers SAHM Rule, Signaling US Recession? This is a question on the minds of many economists and financial experts as we navigate the current economic landscape. The recent spike in unemployment, coupled with the activation of the SAHM (Stock-to-Flow) rule, a leading indicator of potential recessions, has sent alarm bells ringing.
These intertwined factors are fueling speculation about a looming recession in the United States.
Understanding the factors behind the rising unemployment rate and the significance of the SAHM rule is crucial to grasping the potential implications for individuals, businesses, and the overall economy. This analysis delves into the details of these economic indicators, their historical context, and the potential consequences of a recession.
We’ll also explore the economic policies that might be implemented to address the situation and discuss the impact on various sectors of the US economy.
Unemployment Rate Spike
The recent spike in the unemployment rate has sent shockwaves through the economy, raising concerns about a potential recession. This increase, though seemingly sudden, is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Understanding the causes and consequences of this rise is crucial for navigating the economic landscape.
Factors Contributing to the Unemployment Rate Spike
The recent spike in the unemployment rate can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including:
- Rising Interest Rates:The Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes, aimed at curbing inflation, have slowed economic growth, leading to job losses in sectors sensitive to interest rate changes, such as housing and manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:Ongoing supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the war in Ukraine and the COVID-19 pandemic, have impacted businesses’ ability to operate efficiently, leading to layoffs and reduced hiring.
- Recessionary Fears:Growing concerns about a recession, driven by inflation and geopolitical uncertainty, have caused businesses to become more cautious about hiring, leading to a slowdown in job creation.
- Automation and Technological Advancements:Automation and technological advancements continue to reshape the labor market, leading to job displacement in some sectors and a need for workers with new skills in others.
Historical Data and Comparison to Previous Trends
While the current unemployment rate spike is concerning, it’s important to consider it in the context of historical trends. Comparing the current spike to previous ones can provide valuable insights:
- Magnitude of the Spike:The current spike in unemployment is relatively moderate compared to the sharp increases seen during the Great Recession (2007-2009) and the COVID-19 pandemic (2020).
- Duration of the Spike:It remains to be seen how long the current unemployment rate spike will persist. Previous spikes have lasted for varying durations, influenced by factors like government policies and the pace of economic recovery.
- Sectoral Impact:The current spike is affecting certain sectors more than others, such as technology and retail, reflecting the evolving nature of the economy and the impact of specific economic trends.
Potential Consequences of the Rising Unemployment Rate
A rising unemployment rate can have significant consequences for individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole:
- Increased Economic Strain:Job losses lead to reduced income, impacting consumer spending and overall economic growth.
- Social Unrest:Rising unemployment can fuel social unrest and dissatisfaction, as people struggle to make ends meet.
- Reduced Tax Revenue:Fewer employed individuals translate to lower tax revenue for governments, potentially impacting public services and infrastructure development.
- Deflationary Pressures:High unemployment can lead to deflationary pressures, as businesses lower prices to compete for fewer customers.
SAHM Rule Indicator
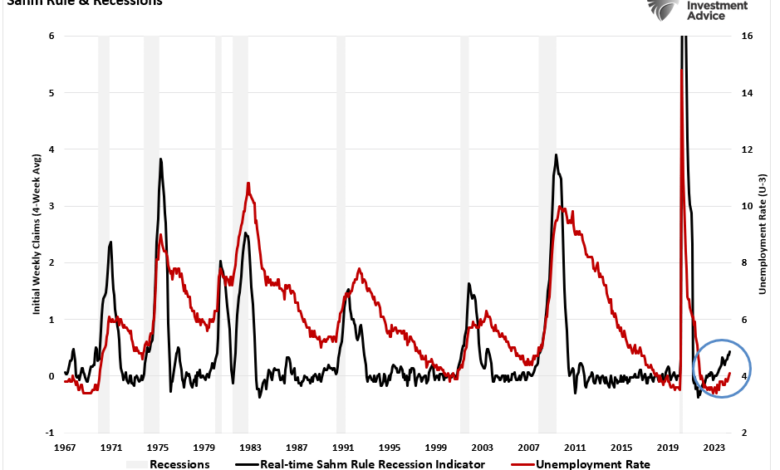
The SAHM rule indicator, named after its creator, Robert J. Shiller, is a rule of thumb used to predict potential recessions in the US economy. This indicator is based on the observation that the US economy has historically experienced a recession whenever the unemployment rate has risen by a certain amount within a specific time frame.
The SAHM Rule Indicator Calculation
The SAHM rule is calculated by tracking the three-month moving average of the unemployment rate. When this moving average rises by 0.5 percentage points or more from its previous peak, the SAHM rule indicator signals a potential recession.
The SAHM rule is calculated as follows:
SAHM Rule Indicator = (Current 3-month moving average of unemployment rate)
The recent spike in the unemployment rate, triggering the Sahm Rule indicator and signaling a potential US recession, is a stark reminder of the fragility of our economy. It’s a harsh reality that hits close to home when you read stories like chicago mail carrier killed on her route.
These tragedies highlight the human cost of economic instability, making the potential recession all the more concerning.
(Previous peak of the 3-month moving average of unemployment rate)
If SAHM Rule Indicator ≥ 0.5, then the indicator signals a potential recession.
The recent spike in the unemployment rate, triggering the Sahm Rule indicator, has many economists worried about a potential US recession. While this economic uncertainty looms, a federal judge has just struck down California’s “one gun a month” law in a ruling that could have significant implications for gun control across the country.
It’s a strange juxtaposition, but perhaps this is a sign of the times – a volatile economic landscape paired with a renewed focus on individual rights.
Current Status of the SAHM Rule Indicator
As of [insert date], the SAHM rule indicator has [insert current status, e.g., not triggered, triggered, or close to triggering]. This means that [insert interpretation based on the current status, e.g., the unemployment rate has not risen sufficiently to signal a recession, the unemployment rate has risen by 0.5 percentage points or more, or the unemployment rate is nearing the threshold for triggering the indicator].
Reliability of the SAHM Rule Indicator
The SAHM rule indicator has been a reliable predictor of past recessions. For example, in [insert historical example, e.g., the 2008 financial crisis], the SAHM rule indicator triggered several months before the official recession began. However, it’s important to note that the indicator is not a perfect predictor, and it has occasionally provided false signals.
For instance, in [insert historical example, e.g., the 1990s recession], the SAHM rule indicator did not trigger before the recession began.
Potential US Recession
The recent spike in the unemployment rate, coupled with the activation of the Sahm Rule indicator, has ignited concerns about a potential US recession. These signals, while not definitive, warrant careful consideration and analysis of key economic indicators to assess the likelihood and potential impact of such an economic downturn.
Key Economic Indicators Suggesting a Potential Recession
The economic health of a nation is reflected in a range of indicators, some of which are considered leading indicators, providing early signals of potential economic shifts. A significant decline in these indicators can signal an impending recession.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP):A decline in GDP for two consecutive quarters is often used as a traditional definition of a recession.
- Consumer Confidence:A sharp drop in consumer confidence can indicate a decrease in spending, which can lead to a slowdown in economic activity.
- Manufacturing Activity:A decline in manufacturing activity, as measured by the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), can indicate a weakening in the production sector.
- Inflation:While high inflation can sometimes be a sign of a healthy economy, persistent high inflation can erode consumer purchasing power and lead to economic instability.
- Interest Rates:The Federal Reserve often raises interest rates to combat inflation. However, aggressive rate hikes can also slow economic growth and potentially trigger a recession.
Relationship Between Unemployment Rate Spike and SAHM Rule Indicator
The Sahm Rule, developed by economist Claudia Sahm, identifies a potential recession by observing a specific decline in the three-month moving average of the unemployment rate. The rule states that if the three-month moving average of the unemployment rate rises by 0.5 percentage points or more from its low point over the previous year, it signals a recession.
The recent spike in the unemployment rate, triggering the SAHM Rule indicator, suggests a potential shift in the economic landscape. This spike indicates a loss of jobs, which can lead to decreased consumer spending and further economic slowdown. The combination of these indicators reinforces the possibility of a recession.
Potential Impact of a Recession on US Economy
A recession can have a significant impact on various sectors of the US economy, leading to:
- Increased Unemployment:As businesses struggle, layoffs and job losses become more common, leading to higher unemployment rates.
- Reduced Consumer Spending:With job insecurity and reduced income, consumers tend to cut back on spending, impacting retail sales and other industries.
- Slowed Economic Growth:A recession can lead to a significant slowdown in economic growth, as businesses invest less and consumer spending declines.
- Financial Market Volatility:Recessions can create uncertainty in financial markets, leading to increased volatility in stock prices and other investments.
- Impact on Housing Market:A recession can lead to a decline in home values and reduced demand for housing, affecting the real estate industry.
Expert Opinions and Forecasts
While the recent economic indicators have raised concerns about a potential recession, expert opinions and forecasts vary. Some economists believe that the US economy is resilient and can weather the current challenges, while others express more cautious views. The likelihood and timing of a recession depend on various factors, including the severity of the current economic challenges, the effectiveness of policy responses, and global economic conditions.
The Federal Reserve is closely monitoring economic indicators and is prepared to adjust monetary policy as needed to address potential risks. It is important to stay informed about economic developments and to consult with financial professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Economic Policies and Responses
The recent spike in the unemployment rate, coupled with the SAHM rule indicator signaling a potential recession, has triggered a wave of concern among economists and policymakers. To combat these economic challenges, the government may implement a range of policies aimed at stimulating growth and reducing unemployment.
Potential Economic Policies
A variety of economic policies can be employed to address the rising unemployment rate and recessionary concerns. These policies are designed to stimulate economic activity, increase demand, and create jobs.
- Fiscal Policy:The government can use fiscal policy to influence the economy through changes in government spending and taxes. In a recession, expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government spending or reducing taxes to boost aggregate demand. This can involve infrastructure projects, tax breaks for businesses, or direct payments to individuals.
- Monetary Policy:The central bank, in this case, the Federal Reserve, can influence the money supply and interest rates through monetary policy. During a recession, the Fed can lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending, and it can also purchase government bonds to inject liquidity into the financial system.
- Job Training and Education Programs:Investing in job training and education programs can equip workers with the skills needed to find employment in a changing economy. This can include vocational training, apprenticeships, and programs to help workers transition into new industries.
- Support for Small Businesses:Small businesses are often the backbone of the economy and can be particularly vulnerable during recessions. Government policies to support small businesses, such as loan programs, grants, and tax breaks, can help them stay afloat and contribute to economic recovery.
Effectiveness of Past Economic Policies
Historical data shows that economic policies have been effective in mitigating recessions in the past. For example, during the Great Recession of 2008-2009, the government implemented a combination of fiscal and monetary policies, including the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 and quantitative easing by the Federal Reserve.
These policies helped to stabilize the economy and prevent a deeper recession.
The recent spike in the unemployment rate, triggering the Sahm Rule indicator, has many economists worried about a potential US recession. This economic uncertainty comes at a time when Congress is showing bipartisan support for the postal service reform bill , which could provide some much-needed stability to the economy.
It remains to be seen whether this bill will be enough to offset the potential recessionary pressures, but its passage is a positive sign that lawmakers are taking steps to address the challenges facing the US economy.
Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing economic policies in the current context presents both challenges and opportunities.
- Political Challenges:The effectiveness of economic policies can be hindered by political gridlock and partisan divisions. For example, disagreements over the size and scope of government spending or tax cuts can delay the implementation of necessary measures.
- Economic Uncertainty:The current economic climate is characterized by a high degree of uncertainty, making it difficult to predict the effectiveness of specific policies. Factors such as global trade tensions, rising inflation, and the ongoing pandemic can create unpredictable economic conditions.
- Long-Term Sustainability:While short-term measures may provide immediate relief, it is crucial to consider the long-term sustainability of economic policies. Excessive government spending or overly loose monetary policy can lead to higher inflation or increased national debt.
- Technological Disruption:The rapid pace of technological change is creating new economic opportunities but also presents challenges. Policies aimed at promoting innovation and reskilling the workforce will be crucial to navigate these changes.
Consequences of Inaction or Delayed Action, Unemployment rate spike triggers sahm rule indicator signaling potential us recession
Failure to address the rising unemployment rate and recessionary concerns could have severe consequences for the economy and society.
- Prolonged Recession:Delaying action could lead to a deeper and longer recession, resulting in greater job losses, business closures, and a decline in living standards.
- Increased Inequality:Recessions often disproportionately affect low-income households and marginalized communities. Inaction could exacerbate existing inequalities and create long-term social and economic challenges.
- Erosion of Confidence:A lack of decisive action can erode confidence in the economy and financial markets, leading to reduced investment and slower growth.
- Political Instability:Economic hardship can fuel social unrest and political instability, creating challenges for policymakers and threatening the stability of democratic institutions.
Impact on Individuals and Businesses
A recession, marked by a significant decline in economic activity, can have profound and wide-ranging consequences for individuals and businesses alike. While recessions are a normal part of the economic cycle, their impact can be disruptive and challenging, requiring careful planning and adaptation to navigate the turbulent waters.
Impact on Individuals
A recession can significantly impact individuals’ financial well-being, leading to job losses, reduced income, and increased financial strain.
- Job Losses:One of the most immediate and devastating effects of a recession is job losses. As businesses struggle to stay afloat, they may resort to layoffs or hiring freezes, leaving individuals unemployed and facing the daunting task of finding new employment in a challenging job market.
- Reduced Income:Even if individuals retain their jobs, recessions often lead to reduced income. Businesses may implement pay cuts or reduce working hours to cut costs, impacting individuals’ ability to meet their financial obligations.
- Increased Financial Strain:Reduced income coupled with rising costs of living, such as food, housing, and healthcare, can lead to increased financial strain. Individuals may find themselves struggling to make ends meet, facing difficulties in paying bills, and potentially accumulating debt.
Impact on Businesses
Recessions can have a significant impact on businesses, leading to reduced profits, layoffs, and even business closures.
- Reduced Profits:During a recession, consumer spending typically declines, leading to a reduction in demand for goods and services. This can result in lower sales and reduced profits for businesses, making it difficult to maintain profitability and sustain operations.
- Layoffs:To mitigate the impact of reduced profits, businesses may resort to layoffs, reducing their workforce to cut costs. This can result in job losses for employees and disrupt the flow of operations.
- Business Closures:In severe recessions, businesses that are unable to adapt to the changing economic conditions may be forced to close their doors. This can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, leading to further job losses and economic hardship.
Strategies for Individuals and Businesses
Individuals and businesses can adopt strategies to mitigate the potential negative effects of a recession.
Strategies for Individuals
- Build an Emergency Fund:Having an emergency fund can provide a financial safety net during a recession. It can help cover essential expenses during periods of unemployment or reduced income.
- Reduce Spending:During a recession, it’s crucial to review spending habits and identify areas where costs can be reduced. This may involve cutting back on non-essential expenses or exploring alternative options for goods and services.
- Increase Savings:Saving more money during periods of economic stability can provide a cushion during a recession. This can help individuals weather the storm and avoid taking on unnecessary debt.
- Upskill or Reskill:In a recession, individuals may need to acquire new skills or update existing ones to remain competitive in the job market. This can increase employability and open up new career opportunities.
Strategies for Businesses
- Diversify Revenue Streams:Businesses can mitigate the impact of a recession by diversifying their revenue streams. This can reduce dependence on a single market or product and provide more stability during economic downturns.
- Cut Costs:Businesses can reduce expenses by implementing cost-cutting measures, such as streamlining operations, negotiating better prices with suppliers, and reducing non-essential spending.
- Invest in Innovation:Investing in research and development, product innovation, or process improvements can help businesses stay ahead of the competition and maintain their market share during a recession.
- Build Strong Customer Relationships:Cultivating strong relationships with customers can help businesses retain customers and build loyalty during challenging economic times.
Examples of Successful Navigation
Individuals and businesses have successfully navigated past recessions by adopting various strategies.
- Individuals:Many individuals have successfully navigated past recessions by taking advantage of government assistance programs, seeking new employment opportunities, and reducing their expenses.
- Businesses:Companies such as Amazon and Netflix have thrived during recessions by adapting to changing consumer needs and investing in innovation. Amazon, for example, expanded its online presence and delivery services, while Netflix capitalized on the growing demand for streaming entertainment.
Ultimate Conclusion: Unemployment Rate Spike Triggers Sahm Rule Indicator Signaling Potential Us Recession
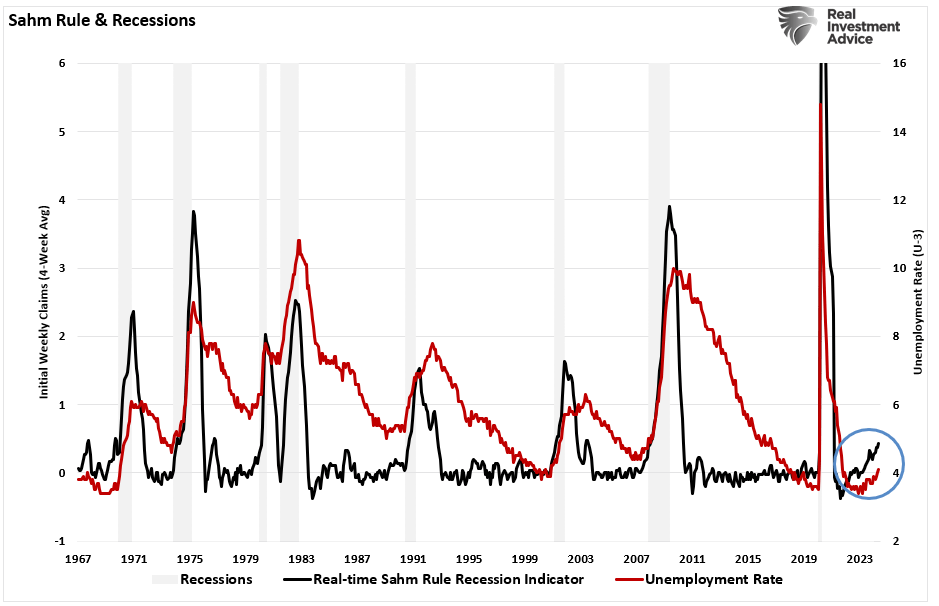
The current economic climate presents a complex and uncertain landscape. While the unemployment rate spike and the SAHM rule indicator point to potential recessionary pressures, it’s important to remember that economic forecasts are not always accurate. The government’s response to the situation, along with the resilience of individuals and businesses, will play a significant role in determining the ultimate outcome.
As we navigate these uncharted waters, it’s essential to stay informed, be prepared, and adapt to the evolving economic landscape.