Twenty-Eight Kidney Complications After COVID-19 Vaccination
Twenty eight types of kidney complications reported following covid 19 vaccination – Twenty-Eight Kidney Complications After COVID-19 Vaccination: This phrase might sound alarming, but it’s crucial to understand the full picture. While rare, these complications have been reported following vaccination, raising concerns about potential side effects. Understanding these complications is essential for both medical professionals and the public, allowing us to make informed decisions about vaccination and manage any potential risks effectively.
This blog post delves into the twenty-eight types of kidney complications reported after COVID-19 vaccination, exploring their nature, frequency, and potential causes. We’ll examine the available research, discuss risk factors, and explore clinical management strategies. Our aim is to shed light on this complex issue, providing valuable insights for anyone seeking to understand the potential connection between COVID-19 vaccination and kidney health.
Overview of Kidney Complications and COVID-19 Vaccination
Kidney complications are conditions that affect the kidneys’ ability to function properly. These complications can range from mild to severe, and can have a significant impact on overall health. While COVID-19 vaccination is generally safe and effective, there have been reports of kidney complications following vaccination.
It is important to understand the potential link between these events, as it can help healthcare providers identify and manage these complications effectively.
Understanding the Potential Link
It is crucial to understand the potential link between COVID-19 vaccination and kidney complications to ensure that individuals receive the appropriate care and support. The significance of this understanding lies in:* Early Detection and Intervention:By recognizing the potential association, healthcare providers can be more vigilant in monitoring patients for early signs of kidney complications following vaccination.
This allows for prompt diagnosis and timely intervention, potentially mitigating the severity of the complications.
The news of twenty-eight types of kidney complications reported following the COVID-19 vaccination is concerning, but it’s crucial to remember that correlation doesn’t equal causation. Just like this is the 1 reason why 65 businesses fail in the first 10 years and many founders still dont get it , a lack of proper research and analysis can lead to hasty conclusions.
We need to delve deeper into the potential links between the vaccine and these kidney complications to understand the true nature of the relationship.
Risk Assessment and Management
Understanding the link helps healthcare professionals assess the individual risk factors for developing kidney complications after vaccination. This information can be used to tailor treatment plans and preventative measures to minimize potential complications.
Public Health Awareness
Raising awareness about the potential link between vaccination and kidney complications can empower individuals to be more proactive in monitoring their health and seeking medical attention if needed. This can contribute to better patient outcomes and reduce the overall burden of kidney complications.
Types of Kidney Complications Reported: Twenty Eight Types Of Kidney Complications Reported Following Covid 19 Vaccination
Following COVID-19 vaccination, various kidney complications have been reported, ranging from mild and transient to severe and life-threatening. While most individuals experience no kidney-related issues after vaccination, understanding the potential complications is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike.
Kidney Complications Reported Following COVID-19 Vaccination
A comprehensive understanding of the reported kidney complications following COVID-19 vaccination is essential for informed decision-making and effective management. The following table categorizes these complications based on their nature and severity, providing insights into their descriptions, reported frequency, and potential causes.
| Type of Kidney Complications | Description | Reported Frequency | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) | Sudden decline in kidney function, characterized by a decrease in urine output and an increase in blood creatinine levels. | Rare | Immune-mediated response, direct viral infection, or pre-existing kidney conditions exacerbated by the vaccine. |
| Glomerulonephritis | Inflammation of the glomeruli, the tiny filtering units in the kidneys. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and damage to the glomeruli. |
| Interstitial Nephritis | Inflammation of the interstitial tissue surrounding the nephrons, the functional units of the kidneys. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and damage to the interstitial tissue. |
| Tubulointerstitial Nephritis | Inflammation of the tubules and interstitial tissue of the kidneys. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and damage to the tubules and interstitial tissue. |
| Nephrotic Syndrome | A condition characterized by proteinuria (protein in the urine), hypoalbuminemia (low albumin levels in the blood), edema (swelling), and hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol levels). | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to damage to the glomeruli and increased protein leakage into the urine. |
| Kidney Stones | Solid masses that form in the kidneys due to an accumulation of minerals and salts. | Rare | Possible changes in fluid balance or electrolyte levels due to the vaccine, potentially contributing to stone formation. |
| Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) | Infection of the urinary tract, including the bladder, urethra, and kidneys. | Rare | Possible immune suppression associated with the vaccine, potentially increasing susceptibility to UTIs. |
| Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) | A rare but serious condition that causes damage to the red blood cells, kidneys, and blood vessels. | Very Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to the destruction of red blood cells and kidney damage. |
| Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) | A rare blood disorder characterized by a shortage of platelets, abnormal blood clotting, and damage to the blood vessels. | Very Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to the formation of blood clots in the small blood vessels of the kidneys. |
| Kidney Failure | A severe condition where the kidneys are unable to filter waste products from the blood effectively. | Very Rare | Severe complications from other kidney conditions, such as AKI or HUS, leading to kidney failure. |
| Proteinuria | Presence of protein in the urine, indicating damage to the kidneys. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to increased protein leakage into the urine. |
| Hematuria | Presence of blood in the urine, indicating damage to the kidneys or urinary tract. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and damage to the kidneys or urinary tract. |
| Microscopic Hematuria | Presence of microscopic amounts of blood in the urine, detectable only through laboratory testing. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and damage to the kidneys or urinary tract. |
| Elevated Creatinine Levels | Increased levels of creatinine in the blood, indicating impaired kidney function. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to damage to the kidneys and decreased creatinine clearance. |
| Elevated Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Levels | Increased levels of BUN in the blood, indicating impaired kidney function. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to damage to the kidneys and decreased BUN clearance. |
| Decreased Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) | Reduced rate of blood filtration by the kidneys, indicating impaired kidney function. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to damage to the glomeruli and decreased GFR. |
| Kidney Transplant Rejection | Rejection of a transplanted kidney by the recipient’s immune system. | Rare | Possible immune response to the vaccine, potentially leading to rejection of the transplanted kidney. |
| Kidney Cyst Formation | Development of fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys. | Rare | Possible immune response to the vaccine, potentially contributing to the formation of kidney cysts. |
| Kidney Cancer | Uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the kidneys. | Very Rare | No direct link established between COVID-19 vaccination and kidney cancer, but further research is needed. |
| Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) | A genetic disorder characterized by the growth of multiple cysts in the kidneys. | Rare | No direct link established between COVID-19 vaccination and PKD, but further research is needed. |
| Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA) | A disorder that affects the kidneys’ ability to regulate acid-base balance in the body. | Rare | Possible immune response to the vaccine, potentially affecting the kidneys’ acid-base regulation. |
| Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (NDI) | A condition characterized by the inability of the kidneys to concentrate urine. | Rare | Possible immune response to the vaccine, potentially affecting the kidneys’ ability to concentrate urine. |
| Kidney Pain | Pain in the area of the kidneys, potentially caused by inflammation or other kidney-related issues. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and pain in the kidneys. |
| Kidney Swelling | Swelling in the area of the kidneys, potentially caused by inflammation or fluid retention. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and swelling in the kidneys. |
| Kidney Dysfunction | Impaired kidney function, potentially leading to a decrease in urine output and an increase in waste products in the blood. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to damage to the kidneys and impaired function. |
| Kidney Damage | Injury or deterioration of kidney tissue, potentially leading to impaired kidney function. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and damage to the kidneys. |
| Kidney Disease | A broad term encompassing various conditions that affect the kidneys, including AKI, glomerulonephritis, and nephrotic syndrome. | Rare | Immune-mediated response to the vaccine, leading to inflammation and damage to the kidneys, potentially progressing to kidney disease. |
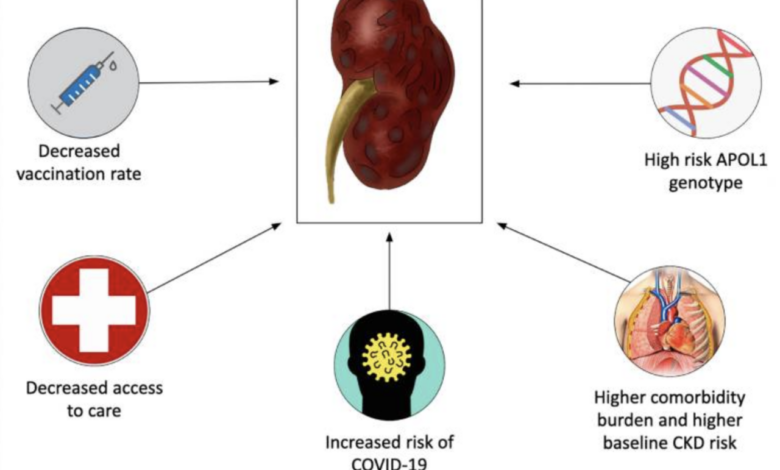
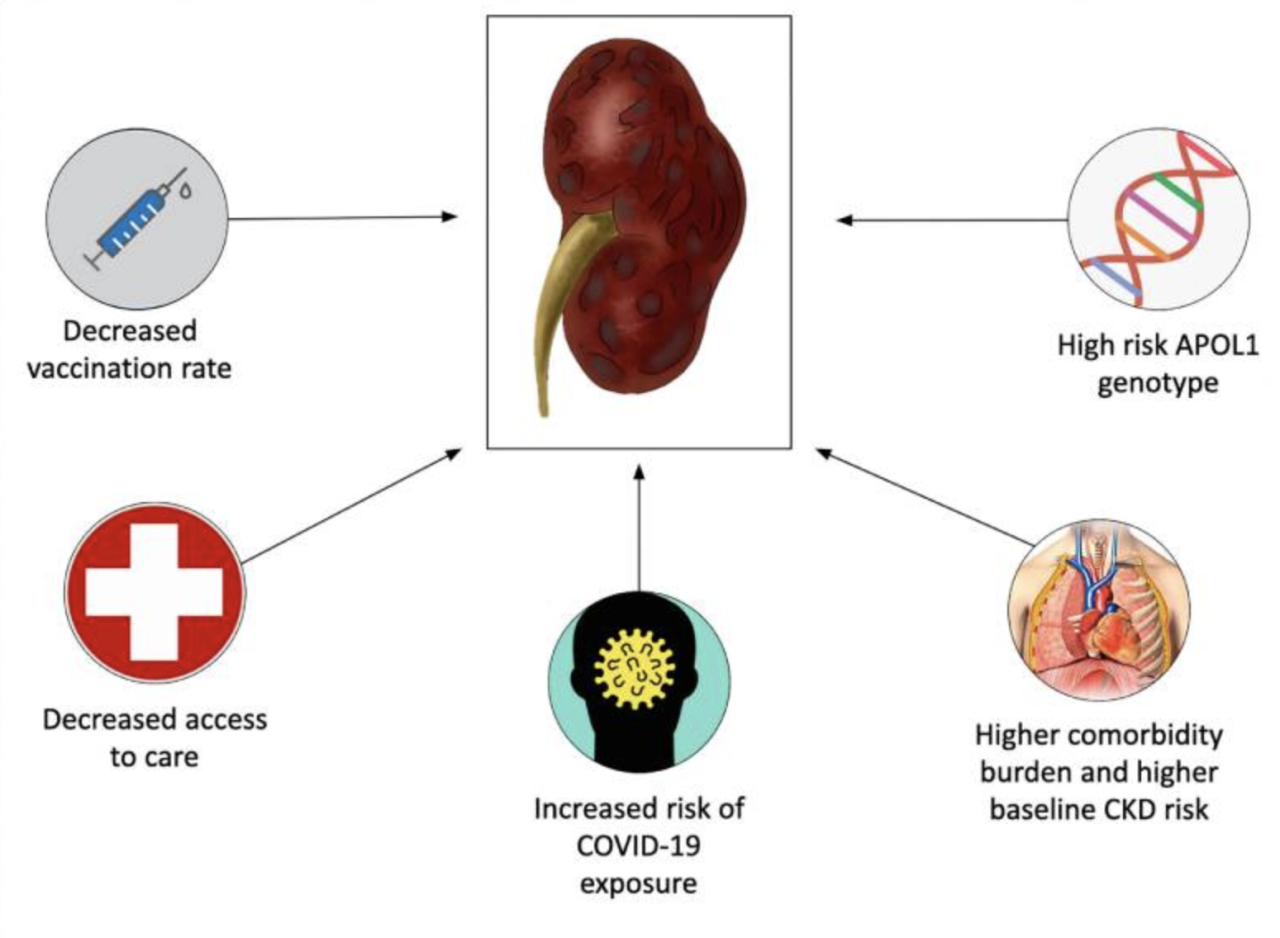
Risk Factors and Contributing Factors
While the COVID-19 vaccines are generally safe and effective, a small number of individuals have reported kidney complications following vaccination. Understanding the potential risk factors associated with these complications is crucial for informed decision-making and early intervention.Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing kidney complications after vaccination.
These include pre-existing kidney conditions, certain medical treatments, and individual characteristics.
It’s mind-boggling to think about the twenty-eight types of kidney complications reported following COVID-19 vaccination. While we focus on the physical impact, it’s also important to consider how these events might influence our educational system. Take a look at 7 facts about the state of edtech in schools to see how technology is being used to adapt to these evolving challenges.
Returning to the kidney complications, understanding their causes and potential long-term effects is crucial for ensuring proper healthcare access and education for those affected.
Pre-existing Kidney Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions are generally considered at higher risk for developing complications after vaccination. This is because their kidneys may be more susceptible to damage or dysfunction.
Pre-existing kidney conditions can significantly increase the risk of developing kidney complications following COVID-19 vaccination.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD):Individuals with CKD, characterized by a gradual decline in kidney function, are more vulnerable to vaccine-induced kidney complications.
- Kidney Failure:People undergoing dialysis or with end-stage kidney failure may experience a higher risk of complications due to their compromised kidney function.
- Kidney Transplant:Individuals who have received a kidney transplant may be more susceptible to complications as their immune systems are suppressed.
Other Contributing Factors
Beyond pre-existing kidney conditions, several other factors can contribute to the development of kidney complications after vaccination.
The news about twenty-eight types of kidney complications reported following COVID-19 vaccination is concerning, especially given the ongoing debate about the vaccine’s long-term effects. It’s a stark reminder that even with the best intentions, unintended consequences can arise. This reminds me of the recent analysis of Big Oil’s windfall profits , which raises questions about the industry’s role in contributing to climate change while simultaneously benefiting from it.
Both situations highlight the complex ethical and societal dilemmas we face in navigating a rapidly changing world, and it’s crucial to approach these issues with a critical and nuanced perspective, considering all potential outcomes.
- Age:Older adults, particularly those over 65, may have a higher risk of experiencing kidney complications. This is because their kidneys may have declined in function with age.
- Underlying Medical Conditions:Individuals with conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and autoimmune diseases may be more susceptible to vaccine-induced kidney complications. These conditions can put extra stress on the kidneys.
- Certain Medications:Some medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain antibiotics, can have a negative impact on kidney function and may increase the risk of complications.
- Previous Infections:Individuals who have recently had a severe infection, including COVID-19, may be more prone to developing kidney complications after vaccination.
Clinical Management and Treatment
The clinical management of individuals experiencing kidney complications following COVID-19 vaccination focuses on early detection, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment strategies to mitigate the severity of complications and promote recovery.
Early Detection and Diagnosis, Twenty eight types of kidney complications reported following covid 19 vaccination
Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for effective management of kidney complications. Prompt identification allows for timely intervention, potentially preventing further damage and improving patient outcomes.
- Comprehensive Medical History and Physical Examination:A thorough medical history, including vaccination details and any pre-existing kidney conditions, is essential. A physical examination helps assess vital signs and identify any signs of kidney dysfunction, such as edema, hypertension, or altered urine output.
- Laboratory Tests:Blood tests, such as serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and electrolytes, are vital for assessing kidney function. Urine tests, including urinalysis and proteinuria assessment, can help identify kidney damage or inflammation.
- Imaging Studies:Ultrasound imaging of the kidneys can help visualize the size, structure, and blood flow within the kidneys. Other imaging techniques, such as CT scans or MRI, may be used to evaluate the kidneys and surrounding structures in more detail, depending on the suspected complication.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for kidney complications following vaccination vary depending on the specific type and severity of the complication.
- Supportive Care:This includes managing symptoms like fluid overload, electrolyte imbalances, and hypertension. It may involve medication adjustments, fluid restriction, and monitoring vital signs.
- Medications:Depending on the underlying cause, medications may be prescribed to address specific complications. For example, diuretics can help reduce fluid overload, while antihypertensives can manage high blood pressure.
- Dialysis:In cases of severe kidney failure, dialysis may be necessary to filter the blood and remove waste products.
- Kidney Transplantation:In rare and severe cases, kidney transplantation may be considered as a long-term solution for end-stage kidney failure.
Public Health Implications
The reported kidney complications following COVID-19 vaccination raise significant public health concerns. While the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks for the vast majority of individuals, it’s crucial to understand and address these potential complications to ensure vaccine safety and maintain public trust.
Strategies for Mitigating Potential Risks and Promoting Vaccine Safety
A multi-pronged approach is essential to mitigate potential risks and promote vaccine safety:
- Enhanced Surveillance and Monitoring:Continuously monitor vaccine safety through robust surveillance systems that capture and analyze reports of adverse events. This involves collaborations between healthcare providers, regulatory agencies, and researchers to identify emerging trends and patterns.
- Early Detection and Intervention:Implement strategies for early detection of potential kidney complications. This includes educating healthcare professionals about the possible signs and symptoms, promoting prompt referral to specialists, and ensuring timely access to appropriate diagnostic tests and treatment.
- Risk Factor Assessment and Management:Identify and manage risk factors associated with kidney complications. This involves comprehensive assessment of individuals’ medical history, pre-existing conditions, and potential interactions with medications.
- Targeted Communication and Education:Provide clear and accurate information about the potential risks and benefits of COVID-19 vaccination. This includes addressing common misconceptions and anxieties related to kidney complications, ensuring informed decision-making, and promoting open communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- Research and Innovation:Continuously invest in research to better understand the mechanisms underlying these complications. This includes investigating the specific types of vaccines, potential contributing factors, and developing strategies for prevention and management.
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring and Research
Ongoing monitoring and research are essential for:
- Early Detection and Intervention:Identifying emerging patterns and trends in kidney complications to facilitate early detection and intervention, improving patient outcomes.
- Risk Factor Identification and Management:Gaining a deeper understanding of the risk factors associated with kidney complications, allowing for targeted risk assessment and management strategies.
- Treatment Development:Developing new and improved treatments for kidney complications related to COVID-19 vaccination, improving patient outcomes and minimizing long-term consequences.
- Public Trust and Confidence:Building public trust and confidence in vaccination by demonstrating a commitment to transparency, ongoing monitoring, and continuous improvement in vaccine safety.
Final Summary
While the connection between COVID-19 vaccination and kidney complications is still being investigated, understanding these potential risks is crucial for both individuals and public health. Early detection, proper clinical management, and ongoing research are essential for mitigating risks and ensuring vaccine safety.
By staying informed and engaging in open dialogue, we can navigate this complex issue responsibly and make informed decisions about our health and well-being.