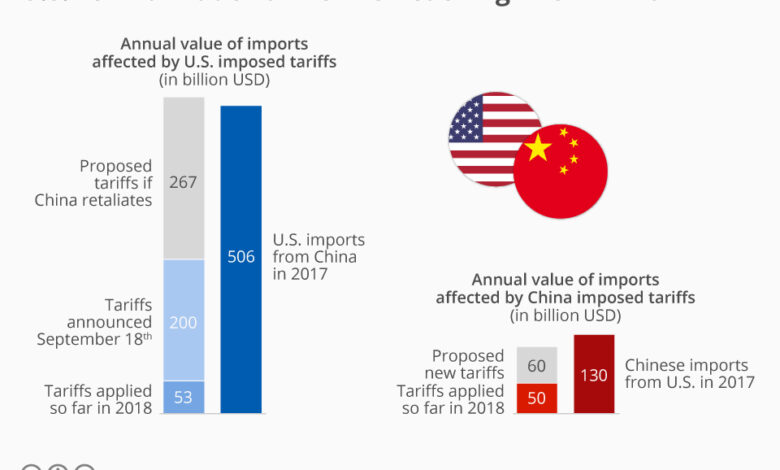
Trumps China Tariffs Yield $150 Billion
Trumps china tariffs yield 150 billion – Trump’s China tariffs yield $150 billion, a figure that raises eyebrows and sparks debate. The impact of these tariffs, implemented during the Trump administration, reverberates through the US and Chinese economies, affecting businesses, consumers, and the global trade landscape. While some argue that these tariffs were a necessary step to address trade imbalances, others contend that they have had unintended consequences, hindering economic growth and straining relations between the two superpowers.
This article delves into the complex ramifications of these tariffs, examining their impact on both countries and exploring the long-term implications for the global economy.
The US imposed tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods, ranging from electronics and furniture to agricultural products. These tariffs, intended to protect American businesses and create a more level playing field, resulted in higher prices for consumers and businesses alike. Meanwhile, China retaliated with tariffs on American goods, leading to a trade war that impacted both economies.
Impact of Tariffs on the US Economy
The imposition of tariffs on goods imported from China has had a significant impact on the US economy, affecting both businesses and consumers. While the tariffs were intended to protect American industries and reduce the trade deficit, they have also resulted in increased costs for businesses and consumers, as well as potential disruptions to supply chains.
The news about Trump’s China tariffs yielding $150 billion is certainly interesting, but it seems like the legal drama surrounding the former president continues to escalate. Just this week, Trump filed a motion seeking to prevent the DOJ from accessing Mar-a-Lago records until a special master is appointed, as reported by Mol News Net. It’s hard to say whether these legal battles will have any impact on the economic impact of his China tariffs, but it’s certainly a story worth following.
Effects on US Businesses and Consumers
The tariffs have directly impacted US businesses and consumers by raising prices for imported goods. These increased costs have been passed on to consumers, leading to higher prices for a wide range of products, including clothing, electronics, and furniture. For businesses, the tariffs have added to their operating expenses, making it more challenging to compete in the market. Some businesses have even had to reduce their operations or lay off workers due to the increased costs.
The news about Trump’s China tariffs yielding $150 billion is interesting, but I’m more focused on the potential legal battles brewing over COVID-19 mandates. It seems like a lawyer is warning that lawsuits are coming for entities that don’t change their mandates after the CDC updates its guidance. This article highlights the potential legal challenges ahead, which could have significant implications for businesses and institutions.
Back to the tariffs, it’s important to remember that the impact of these measures is still being debated and analyzed, and we’ll need to see how they play out in the long run.
Impact of Tariffs on US Inflation and Employment
Tariffs have contributed to inflation in the US economy. The increased prices for imported goods have pushed up the overall price level, impacting consumer spending and potentially leading to economic slowdowns. While the impact on employment is complex, some studies have shown that tariffs can lead to job losses in industries that rely heavily on imported goods. However, other studies have suggested that tariffs could potentially create jobs in protected industries.
Impact of Tariffs on the US Trade Deficit with China
The tariffs were intended to reduce the US trade deficit with China. While they have had some impact on reducing the trade deficit, the effect has been relatively modest. Other factors, such as the global economic environment and the strength of the US dollar, have also played a significant role in the trade deficit.
Impact of Tariffs on the Chinese Economy
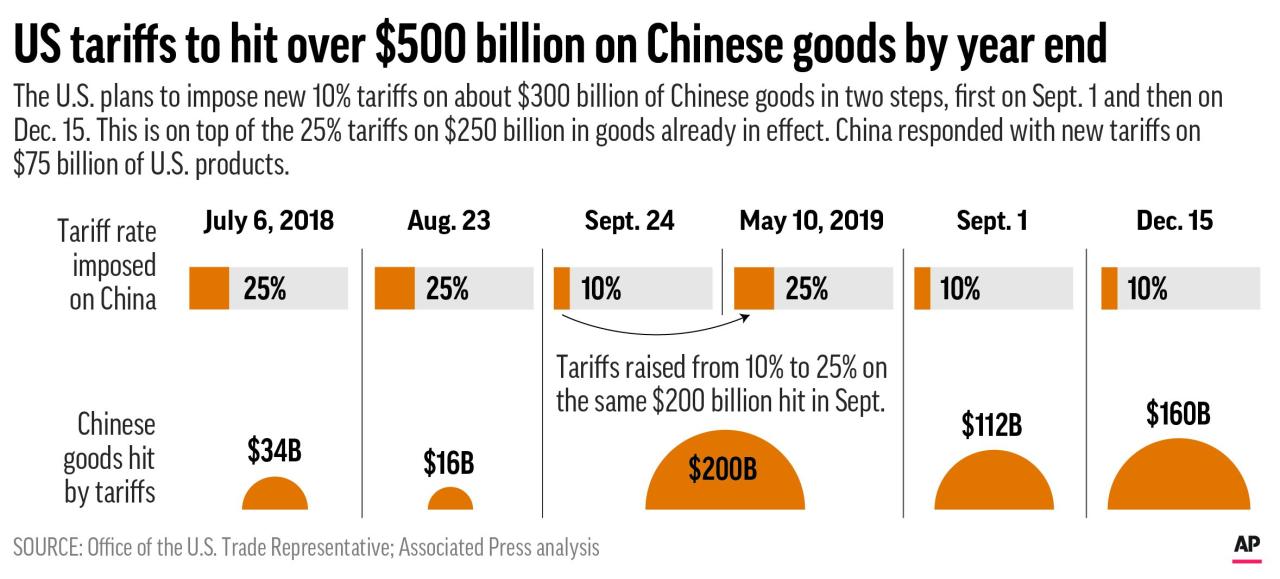
The US-China trade war, marked by significant tariffs imposed by both sides, has had a considerable impact on the Chinese economy. These tariffs have directly affected Chinese businesses and consumers, impacting various sectors and influencing overall economic growth.
The news of Trump’s China tariffs yielding $150 billion was a big deal, but it’s been overshadowed by the recent resignation of Dr. Fauci. Fauci’s resignation has been met with mixed reactions, but Rep. Buddy Carter believes it’s good news for America. While the impact of the tariffs is still being debated, it’s clear that the political landscape is shifting, and the implications for the future are significant.
Effects on Chinese Businesses and Consumers
The tariffs imposed by the US have led to increased costs for Chinese businesses, particularly those exporting goods to the US. These businesses have faced several challenges:
- Increased production costs: Tariffs have raised the cost of raw materials and finished goods, leading to higher production expenses for Chinese businesses.
- Reduced competitiveness: The tariffs have made Chinese products less competitive in the US market, leading to reduced demand and sales.
- Shifting supply chains: Some Chinese businesses have been forced to shift their production facilities to other countries to avoid tariffs, disrupting supply chains and potentially impacting employment.
- Reduced consumer spending: Higher prices for imported goods from the US have led to reduced consumer spending in China, affecting the domestic economy.
Impact on Chinese GDP Growth and Employment
While the exact impact of the tariffs on Chinese GDP growth and employment is difficult to quantify precisely, several studies and reports have shed light on the potential effects.
- Reduced GDP growth: The tariffs have contributed to a slowdown in Chinese economic growth, with estimates suggesting a reduction of 0.5% to 1% in GDP growth.
- Job losses: The tariffs have led to job losses in sectors heavily reliant on exports to the US, particularly in manufacturing and agriculture.
- Increased unemployment: The job losses caused by the tariffs have contributed to a rise in unemployment in China, impacting the livelihoods of many workers.
Impact on China’s Trade Surplus with the US
The tariffs have had a significant impact on China’s trade surplus with the US, leading to a reduction in the surplus.
- Reduced exports: The tariffs have reduced the volume of Chinese exports to the US, leading to a decrease in the trade surplus.
- Increased imports: The tariffs have also led to an increase in US imports from other countries, further reducing the trade surplus.
- Shifting trade patterns: The tariffs have prompted Chinese businesses to seek alternative export markets, leading to a shift in trade patterns and a potential decrease in reliance on the US market.
Alternative Trade Policies: Trumps China Tariffs Yield 150 Billion
Tariffs, while a tool to protect domestic industries and potentially increase government revenue, are not the only option for influencing trade. A range of other trade policies exist, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for navigating the complex world of international trade.
Comparison of Trade Policy Options
Comparing tariffs with other trade policy options, such as free trade agreements, requires understanding their distinct characteristics and potential outcomes. Free trade agreements, for instance, aim to eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers between participating countries, fostering increased trade and economic integration. Here’s a table comparing the potential benefits and drawbacks of various trade policy options:
| Trade Policy | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Tariffs |
|
|
| Free Trade Agreements |
|
|
| Quotas |
|
|
| Subsidies |
|
|
| Non-Tariff Barriers |
|
|
Alternative Policies to Address Trade Imbalances
Trade imbalances, where a country imports more goods and services than it exports, can be a source of economic concern. While tariffs are sometimes used to address these imbalances, alternative policies can be more effective and less disruptive to global trade. Here are some alternative policies that could be implemented to address trade imbalances:
- Promote domestic economic growth and competitiveness. By fostering a strong domestic economy, countries can increase exports and reduce the need for imports. This can be achieved through policies that encourage investment, innovation, and productivity.
- Reduce government spending and debt. High government spending and debt can lead to inflation and a weaker currency, making imports more expensive and exports less competitive. Fiscal discipline can help to stabilize the economy and improve trade balance.
- Improve infrastructure and education. Investing in infrastructure and education can enhance productivity and competitiveness, leading to increased exports and a more balanced trade. This can also attract foreign investment and create jobs.
- Negotiate free trade agreements. Free trade agreements can reduce trade barriers and increase trade volume, potentially leading to a more balanced trade relationship.
- Address currency manipulation. Some countries manipulate their currencies to gain an unfair advantage in trade. International cooperation is needed to address this issue and ensure a level playing field for all countries.
Long-Term Implications of the Tariffs
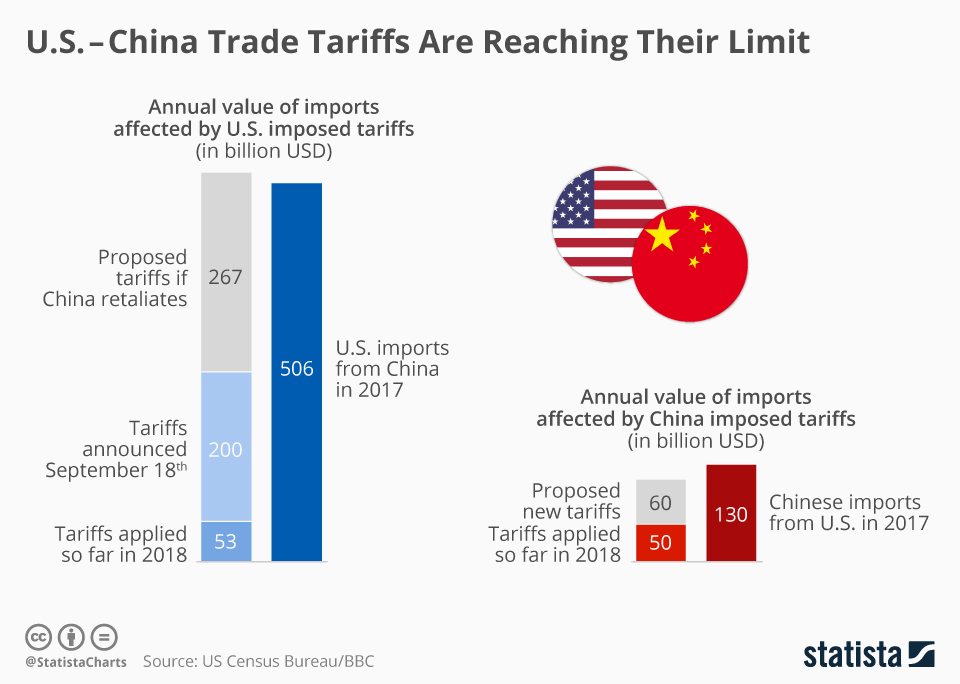
The tariffs imposed by the US on Chinese goods have had a significant impact on the global economy and have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the immediate economic effects. While the short-term effects have been widely discussed, the long-term implications of these tariffs are still unfolding and warrant careful consideration.
Potential Long-Term Economic and Political Consequences
The tariffs have the potential to reshape the global economic landscape and lead to long-term economic and political consequences. Here are some key considerations:
- Increased Costs and Inflation: The tariffs have increased the cost of goods for American consumers, contributing to inflation and potentially reducing consumer spending power. This could lead to a decrease in overall economic activity and potentially slow down economic growth.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The tariffs have disrupted global supply chains, leading to delays and uncertainties in the production and delivery of goods. This has forced businesses to find alternative suppliers, which can be costly and time-consuming. Furthermore, businesses may be hesitant to invest in new projects or expand operations, as the trade environment remains uncertain.
- Trade Wars and Retaliation: The tariffs have sparked a trade war between the US and China, with both countries imposing retaliatory tariffs on each other’s goods. This tit-for-tat escalation can lead to further trade restrictions and economic instability. It could also damage diplomatic relations and create a more adversarial environment between the two countries.
- Geopolitical Shifts: The tariffs have also fueled geopolitical tensions between the US and China. Both countries are increasingly vying for global economic and political dominance, and the trade war has become a proxy battleground for this competition. The tariffs have also led to a reassessment of global trade alliances, as countries try to navigate the new trade landscape and find ways to mitigate the risks associated with the US-China trade war.
Impact of Tariffs on Global Trade Patterns, Trumps china tariffs yield 150 billion
The tariffs have already begun to shift global trade patterns, as businesses seek to diversify their supply chains and reduce their reliance on China. This could lead to a more fragmented global economy, with regional trade blocs emerging and potentially reducing the interconnectedness of the global marketplace.
- Reshoring and Nearshoring: Businesses are increasingly considering reshoring their production back to the US or nearshoring to other countries in the Americas or Europe. This could lead to job creation in these regions, but it also raises concerns about the potential for higher production costs and increased reliance on specific regions.
- Rise of Alternative Trade Partners: The tariffs have encouraged countries to seek alternative trade partners, such as India, Vietnam, and Mexico. This could lead to a shift in global trade flows, as businesses look for new sources of supply and markets for their products.
- Increased Trade Protectionism: The tariffs have set a precedent for trade protectionism, which could encourage other countries to adopt similar measures. This could lead to a more fragmented global trade system, with higher barriers to trade and reduced economic growth.
Potential Future Scenarios for US-China Trade Relations
The long-term implications of the tariffs for US-China trade relations are uncertain and depend on a variety of factors, including the political climate in both countries, the willingness of both sides to compromise, and the global economic outlook. Here are some potential scenarios:
- De-escalation and Cooperation: The US and China could reach a trade agreement that addresses some of the key issues, such as intellectual property rights and market access. This would lead to a de-escalation of the trade war and potentially foster greater cooperation between the two countries.
- Continued Trade War: The trade war could continue, with both sides imposing further tariffs and retaliatory measures. This would likely lead to a further decline in trade between the two countries and potentially a more adversarial relationship.
- Economic Decoupling: The US and China could decouple their economies, with each country pursuing its own economic interests and reducing their reliance on each other. This would likely lead to a more fragmented global economy and could potentially have a significant impact on global growth.
The impact of Trump’s China tariffs on the US and Chinese economies is a complex and multifaceted issue. While the tariffs have yielded $150 billion in revenue for the US, they have also had significant economic and political consequences. The long-term effects of these tariffs remain uncertain, but it is clear that they have reshaped the global trade landscape and left a lasting impact on US-China relations.
As we move forward, it is crucial to carefully consider the potential consequences of trade policies and strive for a more stable and mutually beneficial global economic order.






