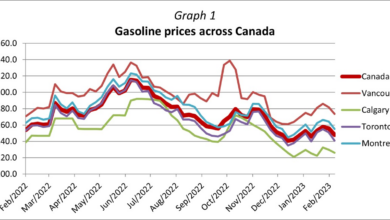
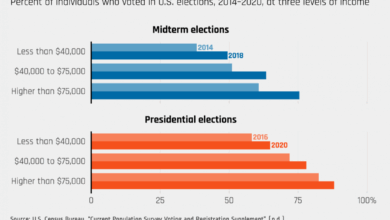
Top Economist Warns: Regulators Face Mission Impossible Amid Inflation, Recession Risks
Top economist warns regulators face mission impossible amid inflation recession risks – Top Economist Warns: Regulators Face Mission Impossible Amid Inflation, Recession Risks sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with personal blog style and brimming with originality from the outset.
In an increasingly complex economic landscape, where inflation and recession risks loom large, a prominent economist has issued a stark warning: regulators are facing an almost impossible task in navigating this treacherous terrain.
The economist highlights the unprecedented challenges posed by the current economic climate, characterized by surging inflation, slowing growth, and the specter of a potential recession. These factors are creating a perfect storm, making it incredibly difficult for regulators to strike the delicate balance between controlling inflation and fostering economic growth.
Inflation and Recession: Top Economist Warns Regulators Face Mission Impossible Amid Inflation Recession Risks
The global economy is currently grappling with a double whammy: soaring inflation and the looming threat of recession. These intertwined forces pose significant challenges to policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike.
Inflation: A Persistent Threat, Top economist warns regulators face mission impossible amid inflation recession risks
Inflation, a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, has been a major concern in recent years. The surge in inflation has been attributed to a confluence of factors, including supply chain disruptions, surging energy prices, and strong consumer demand fueled by government stimulus measures.
The impact of inflation is felt across various sectors, leading to higher prices for everyday essentials, such as food, energy, and housing. This erosion of purchasing power can significantly impact household budgets and strain consumer confidence.
It’s hard to focus on the economic turmoil when news like 9 boxes of biden documents taken from boston office not reviewed for classified materials keeps popping up. While the top economist’s warning about regulators facing a mission impossible amid inflation recession risks is certainly serious, it’s hard to ignore the political drama unfolding.
Maybe the economy will be the least of our worries if we’re not careful!
The Regulator’s Role

Regulators play a crucial role in navigating the complex economic landscape, particularly during periods of heightened uncertainty. They have a range of responsibilities and tools at their disposal to address economic challenges, but the current environment presents unique difficulties.
Balancing Inflation Control and Economic Growth
Regulators face the delicate task of balancing inflation control and economic growth. These two objectives often conflict, requiring careful consideration of the potential trade-offs. The primary tool for controlling inflation is raising interest rates. This makes borrowing more expensive, slowing economic activity and reducing demand.
However, aggressive rate hikes can also stifle investment and job creation, potentially leading to a recession.
Potential Trade-offs and Unintended Consequences
The actions of regulators can have unintended consequences, requiring careful analysis and adjustments. For instance, raising interest rates to curb inflation might lead to a decrease in investment, potentially hindering long-term economic growth. Similarly, loosening monetary policy to stimulate economic activity could fuel inflation, eroding purchasing power and creating uncertainty.
It’s a tough time for the economy, with a top economist warning regulators face an uphill battle against inflation and recession risks. And while they grapple with these complex issues, the government seems to be moving in a different direction, with President Biden ordering up more socialist government initiatives.
It remains to be seen how these policies will impact the already delicate economic landscape, but one thing is clear: the road ahead is fraught with uncertainty.
Examples of Regulatory Actions and Their Impact
- Monetary Policy:Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the US, use interest rate adjustments to influence the money supply and inflation. Raising rates can slow down economic activity and curb inflation, but it can also lead to a recession.
Lowering rates can stimulate economic growth, but it can also fuel inflation.
- Fiscal Policy:Governments use fiscal policy, such as tax cuts or increased spending, to influence economic activity. Stimulating spending can boost demand and growth, but it can also increase government debt and potentially lead to higher inflation.
- Regulation of Financial Markets:Regulators can influence the stability of financial markets by setting rules and oversight for banks and other financial institutions. Stronger regulation can reduce risk and prevent financial crises, but it can also increase the cost of borrowing and hinder economic growth.
Navigating Uncertainty
The current economic environment is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty. Regulators must carefully monitor economic data, analyze potential risks, and adjust their policies accordingly. They must also communicate clearly with the public about their decisions and the rationale behind them, fostering confidence and stability.
Policy Options and Their Effectiveness
Regulators face a daunting task in navigating the current economic landscape, characterized by both inflation and recession risks. The choices they make will have significant consequences for individuals, businesses, and the overall economy. This section examines the key policy options available to regulators, exploring their potential effectiveness in mitigating these risks.
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy, controlled by central banks, aims to influence the economy by adjusting interest rates and the money supply. In times of high inflation, central banks typically raise interest rates to make borrowing more expensive, thus slowing down economic activity and reducing demand.
This can help curb inflation but also risks pushing the economy into a recession. Conversely, during periods of recession, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment, boosting economic growth. The effectiveness of monetary policy depends on various factors, including the severity of inflation, the state of the economy, and the responsiveness of businesses and consumers to interest rate changes.
Historical Examples
- The Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes in the early 1980s under Paul Volcker successfully brought down high inflation but led to a deep recession.
- The European Central Bank’s response to the 2008 financial crisis involved cutting interest rates to near zero and implementing quantitative easing, which helped stabilize the economy but was criticized for its limited impact on inflation.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy refers to the government’s use of spending and taxation to influence the economy. During periods of inflation, governments can reduce spending or raise taxes to curb demand and slow economic growth. Conversely, during recessions, they can increase spending or cut taxes to stimulate demand and boost economic growth.
It’s a tough time to be a regulator, with a top economist warning of a “mission impossible” situation amid inflation and recession risks. The economic landscape feels as volatile as the health one, with recent studies like this one linking the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine to heart inflammation adding another layer of uncertainty.
Navigating these complex challenges requires a delicate balance of action and caution, and it’s clear that the road ahead will be fraught with difficult decisions.
Historical Examples
- The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, enacted in response to the Great Recession, involved substantial government spending on infrastructure, education, and tax cuts, which helped stabilize the economy.
- The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act in the United States, which reduced taxes for businesses and individuals, aimed to stimulate economic growth, but its effectiveness in mitigating inflation remains a subject of debate.
Supply-Side Policies
Supply-side policies focus on increasing the productive capacity of the economy by addressing factors that constrain economic growth, such as labor shortages, regulatory burdens, or inadequate infrastructure. These policies can help mitigate inflation by increasing the supply of goods and services, thereby reducing price pressures.
Historical Examples
- The Reagan administration’s supply-side policies in the 1980s, which included tax cuts and deregulation, aimed to boost economic growth, but their effectiveness in curbing inflation is debated.
- The 1990s economic boom in the United States is often attributed to technological advancements and deregulation, which increased productivity and contributed to low inflation.
Other Policy Options
Regulators have other tools at their disposal, including:
- Price controls: Setting maximum prices for certain goods and services can help control inflation but can lead to shortages and distortions in the market.
- Wage and price guidelines: Encouraging businesses and workers to moderate wage and price increases can help curb inflation but can be difficult to enforce.
- Targeted interventions: Addressing specific factors contributing to inflation, such as energy price spikes, can help mitigate inflationary pressures but may not be a comprehensive solution.
Economic Outlook and Uncertainty
The top economist’s warning about regulators facing a mission impossible amid inflation and recession risks underscores the challenging economic landscape. While the current economic outlook remains uncertain, several key factors could influence the trajectory of inflation and recession risks.
Factors Influencing Inflation and Recession Risks
The current economic outlook is characterized by a complex interplay of factors that make predicting future economic developments difficult.
- Persistent Inflation:Inflation remains stubbornly high, fueled by supply chain disruptions, strong consumer demand, and the war in Ukraine. While central banks are aggressively raising interest rates to combat inflation, the effectiveness of these measures in curbing price increases remains uncertain.
- Slowing Economic Growth:Global economic growth is slowing, as rising interest rates and inflation weigh on consumer spending and business investment. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has downgraded its global growth forecasts, highlighting the risks of a recession in major economies.
- Geopolitical Tensions:The ongoing war in Ukraine has disrupted global energy and food markets, adding to inflationary pressures and contributing to economic uncertainty. The conflict also raises concerns about potential spillover effects on other regions.
- Labor Market Dynamics:The labor market remains strong, with low unemployment rates and robust job creation. However, rising wages and labor shortages could further fuel inflationary pressures, leading to a wage-price spiral.
Uncertainty Surrounding Future Economic Developments
The level of uncertainty surrounding future economic developments is high. The interplay of these factors creates a complex and unpredictable economic environment, making it challenging to forecast the future trajectory of inflation and recession risks.
“The current economic environment is unlike anything we have seen in decades. We are facing a perfect storm of inflation, slowing growth, and geopolitical uncertainty.”[Name of economist]
Final Conclusion
The economist’s warning serves as a stark reminder of the precarious state of the global economy and the immense pressure on regulators to make the right decisions. The choices they make will have a profound impact on businesses, consumers, and the overall health of the economy.
It’s a situation where even the most seasoned economic minds are grappling with uncertainty and the potential for unintended consequences. The future remains uncertain, and the ability of regulators to navigate this complex landscape will be crucial in determining the ultimate outcome of this economic crisis.