The Worlds Remaining Communist Countries: Economic Performance and Challenges
The worlds remaining communist countries and how theyre faring economically – The world’s remaining communist countries and how they’re faring economically is a topic that continues to spark debate and intrigue. While communism has undergone significant transformations and adaptations over the decades, its presence persists in a handful of nations, each with its unique story to tell.
These countries, often facing immense political and economic pressures, have navigated a complex path, striving to balance ideological principles with the realities of a globalized world. This exploration delves into the diverse experiences of these nations, examining their economic performance, the factors that shape their development, and the social and political implications of their chosen path.
From the vast expanse of China to the smaller states of Cuba and North Korea, these countries offer a fascinating case study in the evolution of communism and its adaptability in the face of global trends. We’ll examine their economic models, the role of government intervention, and the impact of external forces on their development.
Furthermore, we’ll explore the social and political landscapes of these nations, considering the implications of their economic choices on their citizens’ lives. This exploration seeks to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the world’s remaining communist countries and their economic journeys.
Defining “Communist” Countries Today: The Worlds Remaining Communist Countries And How Theyre Faring Economically
In today’s global landscape, defining a country as “communist” presents a significant challenge. The term “communist” has evolved over time, encompassing various ideologies and political systems, making it difficult to apply a singular definition across different contexts. Furthermore, many countries that once identified as communist have undergone significant transformations, blurring the lines between communist and non-communist states.
The Evolution of Communist Ideologies
Communist ideologies have undergone a complex evolution since their inception in the 19th century. The core tenets of communism, such as the abolition of private property and the establishment of a classless society, have been interpreted and implemented in diverse ways throughout history.
- Marxist-Leninist Communism:This ideology, based on the works of Karl Marx and Vladimir Lenin, emphasizes the role of a vanguard party in leading the proletariat to revolution and establishing a socialist state. This model was adopted by the Soviet Union and its allies during the Cold War.
- Maoist Communism:This ideology, developed by Mao Zedong, emphasized the importance of peasant revolution and the role of the peasantry in achieving communism. Maoist China adopted a distinct path to communism, emphasizing self-reliance and agricultural collectivization.
- Eurocommunism:This ideology emerged in the 1970s and sought to adapt communist principles to Western democracies. Eurocommunist parties aimed to achieve socialist goals through parliamentary means rather than revolution.
Identifying Remaining Communist Countries
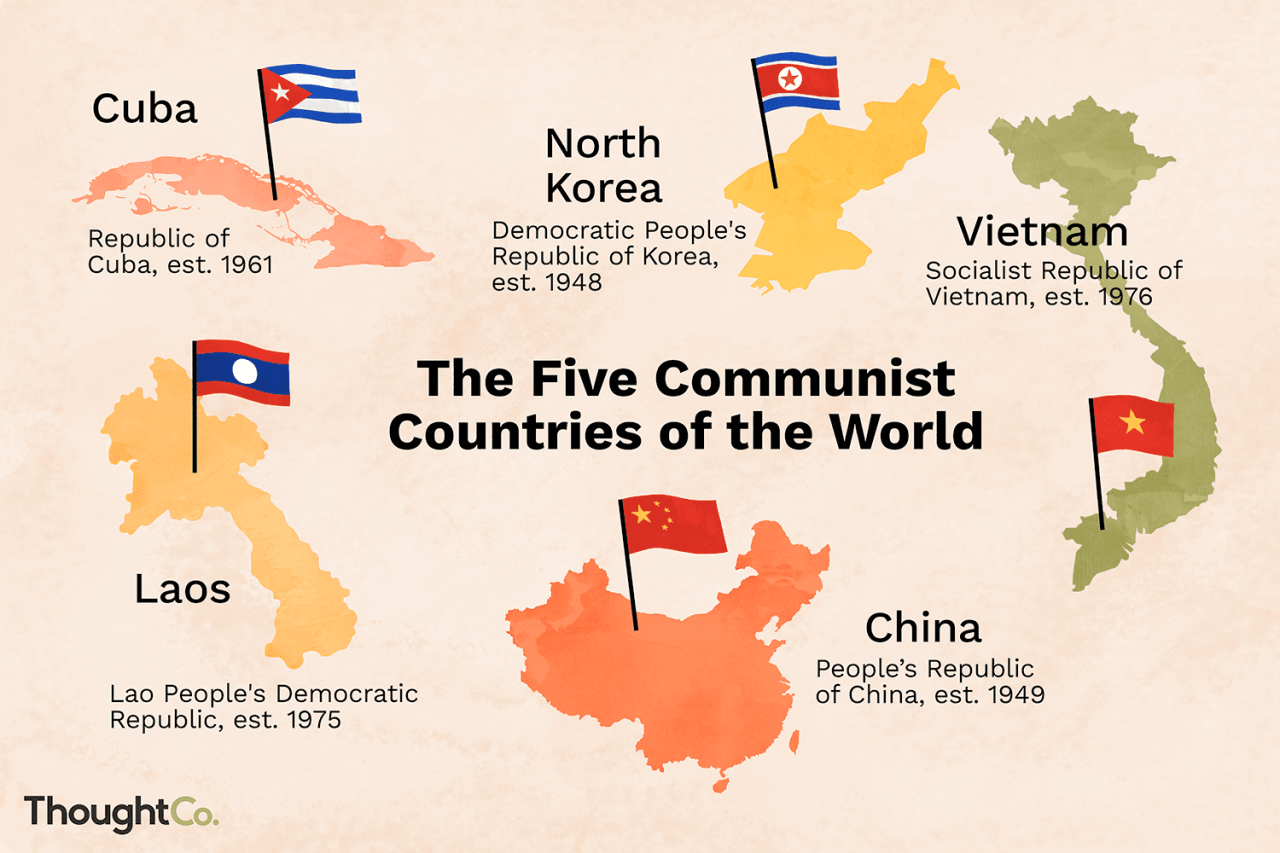
While the Cold War ended decades ago, and the global landscape has shifted significantly, a handful of countries still maintain communist political systems and economic models. Understanding these countries and their unique paths to development is crucial for comprehending the current global political and economic order.
This section will explore the remaining communist countries, delving into their historical contexts, political systems, economic models, and notable features.
Remaining Communist Countries, The worlds remaining communist countries and how theyre faring economically
The following table lists the countries currently considered communist, along with key information about their political systems and economic models:
| Country Name | Governing Party | Economic Model | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Chinese Communist Party (CCP) | Socialist market economy | World’s second-largest economy, rapid economic growth, state-led capitalism, increasing market liberalization, social control and censorship, growing wealth inequality. |
| Cuba | Communist Party of Cuba | Centralized planned economy | Single-party state, state-controlled economy, limited private enterprise, reliance on tourism and remittances, social welfare programs, political repression. |
| Laos | Lao People’s Revolutionary Party (LPRP) | Centrally planned economy with market elements | Single-party state, limited political freedom, reliance on agriculture and natural resources, economic reforms, growing foreign investment. |
| North Korea | Workers’ Party of Korea (WPK) | Command economy | Hereditary dictatorship, strict political control, closed economy, reliance on military and nuclear programs, widespread poverty and human rights abuses. |
| Vietnam | Communist Party of Vietnam | Socialist-oriented market economy | Single-party state, economic reforms, rapid economic growth, growing middle class, limited political freedom, state control over key industries. |
Economic Performance of Communist Countries

The economic performance of communist countries varies greatly, and their economic systems have undergone significant transformations in recent decades. While some countries have achieved notable economic growth, others face persistent challenges, such as low productivity, corruption, and limited access to capital.
This section delves into the economic performance of communist countries, examining their growth rates, development indicators, and the challenges and opportunities they face.
Economic Growth Rates
Economic growth rates in communist countries have varied significantly over time. Some countries, such as China and Vietnam, have experienced remarkable economic growth, while others, such as Cuba and North Korea, have lagged behind.
- Chinahas been a leading example of rapid economic growth, averaging over 10% per year for several decades. This growth has been driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Massive investments in infrastructure and manufacturing
- Opening up to foreign investment and trade
- A large and growing workforce
- Vietnamhas also achieved impressive economic growth, averaging over 7% per year in recent decades. This growth has been fueled by:
- A focus on export-oriented industries
- A young and dynamic workforce
- Strong government policies promoting economic development
- Cubahas experienced a more modest economic growth rate, averaging around 2% per year in recent decades. This growth has been constrained by:
- The US embargo
- A lack of investment
- Inefficient state-owned enterprises
- North Koreahas experienced very low economic growth, averaging around 1% per year in recent decades. This low growth has been attributed to:
- A highly centralized and inefficient economic system
- International sanctions
- A lack of access to technology and capital
Development Indicators
Development indicators, such as life expectancy, literacy rates, and per capita income, provide a broader perspective on the economic and social progress of communist countries.
- Chinahas made significant progress in improving its development indicators. Life expectancy has increased dramatically, literacy rates have risen, and per capita income has grown substantially.
- Vietnamhas also experienced significant improvements in its development indicators, particularly in terms of reducing poverty and improving access to education and healthcare.
- Cubahas a relatively high life expectancy and literacy rate, but its per capita income remains low due to the US embargo and economic inefficiencies.
- North Koreahas low development indicators, with low life expectancy, limited access to education and healthcare, and a very low per capita income.
Challenges and Opportunities
Communist countries face a number of challenges in achieving sustainable economic growth, including:
- Corruption: Corruption can undermine economic growth by distorting markets, discouraging investment, and creating an uneven playing field for businesses.
- Lack of innovation: Some communist countries struggle with a lack of innovation, which can hinder their ability to compete in the global economy.
- Limited access to capital: Access to capital is essential for economic growth, but many communist countries face restrictions on foreign investment and limited access to domestic capital markets.
However, communist countries also have opportunities for economic growth, including:
- A large and growing workforce: Many communist countries have a large and growing workforce, which can be a source of competitive advantage in labor-intensive industries.
- Natural resources: Some communist countries possess significant natural resources, such as oil, gas, and minerals, which can be a source of economic growth.
- Government support for economic development: Communist governments can play a significant role in promoting economic development by investing in infrastructure, education, and technology.
Factors Influencing Economic Performance
The economic performance of communist countries is influenced by a complex interplay of internal and external factors. These factors can have a significant impact on economic growth, development, and the overall well-being of the population.
Economic Policies
Communist countries typically implement a range of economic policies aimed at achieving specific goals, such as centralized planning, state ownership of key industries, and social welfare programs. These policies can have both positive and negative effects on economic performance.
- Centralized Planning:This involves the government setting production targets, allocating resources, and determining prices. While it can promote economic stability and social equality, it can also lead to inefficiencies and a lack of innovation.
- State-Owned Enterprises:These are businesses owned and operated by the government. While they can provide essential services and contribute to economic growth, they can also be susceptible to corruption and mismanagement.
- Social Welfare Programs:These programs provide social safety nets for citizens, such as healthcare, education, and pensions. While they can improve social well-being, they can also be costly and strain government resources.
Government Intervention in the Economy
The level and nature of government intervention in the economy play a crucial role in shaping economic performance.
- State-Owned Enterprises:The extent to which state-owned enterprises dominate key sectors of the economy can influence economic efficiency and innovation. For example, in China, the government has increasingly allowed private businesses to operate in sectors that were previously dominated by state-owned enterprises.
- Resource Management:Government control over natural resources can impact economic growth and sustainability. For example, in Venezuela, government control over oil reserves has led to economic instability and corruption.
- Social Welfare Programs:The design and implementation of social welfare programs can impact the overall level of economic inequality and social well-being. For example, Cuba’s universal healthcare system has been praised for its effectiveness, but the country’s economy has struggled to provide a high standard of living for all citizens.
The economic landscape of the world’s remaining communist countries is a complex tapestry, with varying degrees of success and struggle. While some, like Vietnam, have embraced market reforms and experienced significant growth, others, like Cuba, continue to grapple with economic challenges.
Meanwhile, the political landscape in the United States continues to be dominated by the ongoing legal battles stemming from the Mueller probe, with recent developments seeing former President Trump threaten lawsuits over the investigation and criticize prosecutors in the Roger Stone case.
As these legal battles unfold, the world watches to see how they will impact the future of American politics, while the communist countries continue to navigate their own unique paths towards economic development.
External Factors
Economic performance can be influenced by a variety of external factors, such as global trade, foreign investment, and political stability.
- Global Trade:The level of access to international markets and the terms of trade can significantly impact economic growth. For example, Vietnam has benefited from its integration into the global economy through trade agreements and foreign investment.
- Foreign Investment:Foreign investment can provide much-needed capital and technology, but it can also come with risks, such as exploitation of labor and environmental damage. For example, China’s rapid economic growth has been fueled by foreign investment, but the country has faced criticism for its environmental record.
It’s fascinating to see how the remaining communist countries are navigating the global economic landscape. While some, like Cuba, are struggling to maintain their socialist model, others, like China, have embraced market reforms to achieve remarkable growth. The political climate in the US, however, seems far removed from these economic realities, as evidenced by the recent Trump energized after Dems debate melee takes rally blitz to Colorado news.
Whether this focus on domestic politics will impact US foreign policy and its approach to communist countries remains to be seen, but it’s a question worth pondering as we witness the ongoing evolution of global economic power dynamics.
- Political Stability:Political instability can disrupt economic activity and deter foreign investment. For example, North Korea’s political isolation and economic sanctions have severely hampered its economic development.
Social and Political Implications
Communist economic policies have far-reaching consequences, impacting social structures, political systems, and individual lives. The impact of these policies on economic performance, in turn, shapes social welfare, income inequality, and human rights, ultimately influencing political stability in these countries.
Social Welfare and Income Inequality
The impact of economic performance on social welfare and income inequality in communist countries is a complex issue. While communist ideology emphasizes social equality, the reality is often different.
- State Control and Social Welfare:Communist governments often prioritize state control over the economy, leading to centralized planning and distribution of resources. This can result in varying levels of social welfare depending on the efficiency and effectiveness of government programs.
- Income Inequality and Social Stratification:Despite the goal of eliminating class distinctions, income inequality can persist in communist countries. While the gap between the richest and poorest may be smaller than in capitalist economies, social stratification can still exist based on factors like access to education, healthcare, and political influence.
- Examples:China, for instance, has experienced rapid economic growth but also significant income inequality. While the government has implemented policies to address this issue, such as poverty alleviation programs, challenges remain.
Human Rights and Political Stability
The relationship between economic performance and human rights, as well as political stability, is intricate and often debated.
- Economic Growth and Political Repression:Some argue that economic growth in communist countries can lead to increased political repression. As countries develop, governments may feel pressure to maintain control and suppress dissent to ensure stability.
- Economic Stagnation and Social Unrest:Conversely, economic stagnation or decline can fuel social unrest and instability. People may become disillusioned with the government’s policies and demand change, potentially leading to political upheaval.
- Human Rights and Economic Performance:The impact of economic performance on human rights is multifaceted. While economic growth can sometimes lead to improvements in living standards and social welfare, it may also result in the erosion of individual freedoms and civil liberties if governments prioritize economic development over human rights.
- Examples:Cuba’s economic difficulties have contributed to social unrest and limited political freedoms. On the other hand, Vietnam’s economic reforms have been accompanied by a degree of political liberalization, though human rights concerns remain.
Political Stability and Economic Performance
Political stability is crucial for sustained economic growth and development in communist countries.
It’s fascinating to see how the world’s remaining communist countries are faring economically, especially in the face of global challenges. China, often seen as a model for communist economic success, has faced its own share of difficulties, most recently with the ongoing pandemic.
The transparency of China’s official coronavirus numbers has been called into question, as seen in the recent article chinas coronavirus numbers dont add up and the white house doesnt believe them , and this raises questions about the true impact of the virus on the country’s economic trajectory.
Whether or not these concerns are justified, they highlight the complexities of navigating economic challenges within a communist system, particularly when facing a global crisis.
- Stability and Investment:Political stability attracts foreign investment, fosters domestic entrepreneurship, and encourages economic activity. A stable political environment provides predictability and confidence for businesses and investors.
- Instability and Economic Uncertainty:Conversely, political instability can deter investment, disrupt economic activity, and create uncertainty. Political turmoil can lead to economic downturns and hinder development.
- Examples:North Korea’s political isolation and instability have severely hampered its economic development. In contrast, China’s relatively stable political environment has contributed to its economic rise.
Future Prospects and Challenges
The long-term economic prospects of communist countries are intertwined with their ability to adapt to the globalized and interconnected world. While some communist countries have experienced periods of economic growth, they face significant challenges in achieving sustainable development and improving living standards for their citizens.
Economic Prospects and Challenges
The future economic prospects of communist countries are a complex issue, influenced by various factors, including:* Global Economic Trends:The global economic landscape is constantly evolving, and communist countries must navigate these changes effectively. The rise of emerging economies, technological advancements, and geopolitical shifts all impact their economic performance.
Domestic Reforms
The success of communist countries in the future depends heavily on their willingness and ability to implement necessary economic and political reforms. This includes fostering a more open and competitive market environment, promoting innovation, and improving governance.
Resource Dependence
Many communist countries heavily rely on natural resources for economic growth. Fluctuations in global commodity prices and environmental concerns pose significant risks to their economic stability.
Integration with Global Markets
Integrating into the global economy offers opportunities for communist countries to access new markets, attract foreign investment, and learn from other countries’ experiences. However, it also presents challenges related to competition, trade imbalances, and potential loss of economic sovereignty.
Strategies for Economic Development and Modernization
Communist countries can adopt various strategies to foster economic development and modernization:* Diversification of the Economy:Moving away from a reliance on natural resources and developing new industries, such as manufacturing, technology, and services, is crucial for sustainable growth.
Investment in Human Capital
Investing in education, healthcare, and skills development is essential to enhance productivity and competitiveness.
Technological Innovation
Embracing technological advancements, such as automation and artificial intelligence, can help communist countries improve efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in the global market.
Strengthening Institutions
Establishing robust institutions, including a transparent legal system, independent judiciary, and strong regulatory framework, is vital for attracting foreign investment and promoting a level playing field for domestic businesses.
Promoting Entrepreneurship
Fostering a culture of entrepreneurship and innovation can stimulate economic growth and create new jobs.
Improving Infrastructure
Investing in transportation, energy, and communication infrastructure is essential for facilitating trade, attracting investment, and improving the quality of life for citizens.
Conclusion
The world’s remaining communist countries present a complex and dynamic landscape, with each nation navigating its own unique path. Their economic performance is shaped by a combination of internal policies, external factors, and historical context. While some have achieved impressive economic growth, others face significant challenges in achieving sustainable development and improving the lives of their citizens.
As the world continues to evolve, the future of these nations will depend on their ability to adapt, innovate, and address the complex economic and social challenges they face. The journey of these countries provides a valuable lens through which to examine the broader themes of globalization, economic development, and the evolving role of ideology in the 21st century.