Tax Day is Monday: Deadlines, Extensions, and Refunds
Tax day is monday what to know about deadlines extensions and refunds – Tax Day is Monday, and for many of us, that means scrambling to get our returns filed on time. But with deadlines, extensions, and the potential for a refund, there’s a lot to consider. This year, let’s navigate the tax landscape together and make sure we’re all on the right track.
The IRS offers various options for filing your taxes, including online, by mail, or through a professional tax preparer. Each method has its pros and cons, so it’s important to weigh your options carefully. Whether you’re a seasoned filer or a first-timer, understanding the basics of tax day is essential for avoiding penalties and maximizing your refund.
Tax Day Basics
Tax Day is the annual deadline for individuals and businesses to file their federal income tax returns with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It’s a significant date because it determines whether you owe the government money or receive a refund.
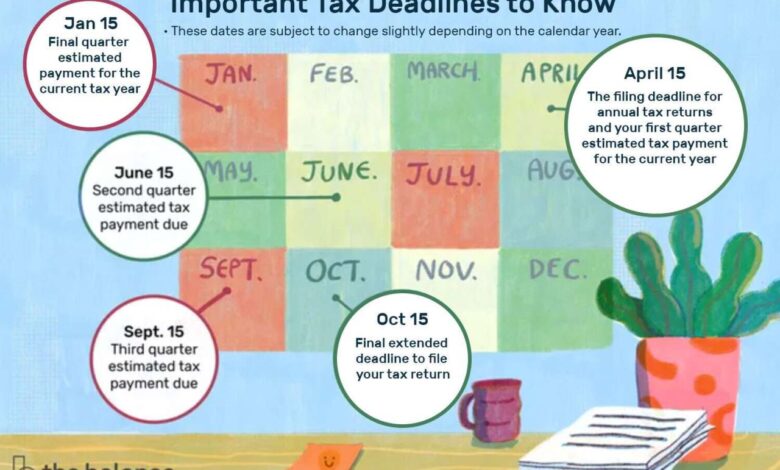
This year, Tax Day is April 18, 2023. This is because April 15th falls on a Saturday, and Emancipation Day is observed on Monday, April 17th in Washington, D.C.
Penalties for Late Filing or Non-Payment
Failing to file your tax return by the deadline or not paying your taxes on time can result in penalties. The IRS charges penalties for late filing and late payment.The late filing penalty is typically 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that your return is late.
This penalty can be up to 25% of your unpaid taxes. However, there are exceptions to this penalty, such as if you have a reasonable cause for filing late.The late payment penalty is 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that your taxes are late.
Tax Day is Monday, April 17th, and while it’s definitely a stressful time for many, it’s important to remember that you’re not alone. There are resources available to help you understand deadlines, extensions, and even refunds. For example, you can find helpful information on the IRS website.
It’s also worth noting that amidst the news about tax season, there’s been a concerning development – a possible noose was found near a CIA facility, leading to a warning from the agency director. c i a director issues warning after possible noose is found near facility.
But let’s get back to taxes – remember, you can file an extension if you need more time, and there are even ways to get a refund. Don’t let the stress of Tax Day get you down, there’s help available!
This penalty is capped at 25% of your unpaid taxes.
It is important to note that the penalties for late filing and late payment can be combined, meaning you could potentially be charged a total of 50% of your unpaid taxes.
Filing Deadlines and Extensions
Tax Day is right around the corner, and it’s crucial to understand the deadlines and options available to you. While the standard deadline is typically April 15th, there are variations depending on your specific circumstances and the forms you need to file.
Tax Day is Monday, and it’s crunch time for filing your taxes. While you’re figuring out deadlines, extensions, and potential refunds, don’t forget about the importance of daily organization. You can boost your productivity and success by opening the five key documents outlined in this helpful article 5 documents you should open every day to maximize your success with templates.
These templates will help you stay on top of your finances and make sure you’re ready for next year’s tax season!
This section delves into the complexities of tax filing deadlines and the process of obtaining an extension.
Different Filing Deadlines
The deadline for filing your federal income tax return is usually April 15th. However, certain situations can affect this deadline. For example, if April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is automatically extended to the next business day.
Tax Day is Monday, April 17th, and while you’re busy filing your returns and trying to figure out if you’re getting a refund, it’s also important to stay informed about your health. Recent news suggests the CDC may have hidden findings of a possible link between COVID vaccines and tinnitus , which is a condition causing ringing in the ears.
This information, if true, could be important for those who have received the vaccine and are experiencing this symptom. So, while you’re focusing on taxes, don’t forget to prioritize your health and stay informed about potential side effects of vaccines.
The following are some common scenarios and their corresponding deadlines:
- Taxpayers living or working abroad:They have until June 15th to file their taxes.
- Military personnel serving outside the U.S.:They have an automatic extension of up to 180 days after returning to the U.S.
- Victims of natural disasters:The IRS may grant extensions for taxpayers affected by natural disasters.
Obtaining a Tax Filing Extension, Tax day is monday what to know about deadlines extensions and refunds
If you need more time to prepare your tax return, you can request an extension to file. This extension grants you an additional six months to file your return, but it does not extend the deadline for paying your taxes.The process for requesting an extension is relatively simple:
- File Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
- Include your name, address, Social Security number, and estimated tax liability on the form.
- File the form by the original tax deadline.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Filing for an Extension
While a tax filing extension can provide much-needed breathing room, it’s essential to weigh the benefits and drawbacks before deciding.
Benefits:
- More time to gather necessary documents and prepare your return:This can be especially helpful if you have complex tax situations or need to gather information from multiple sources.
- Avoid penalties for late filing:Filing an extension prevents penalties for late filing, but you may still be subject to penalties for late payment if you don’t pay your taxes by the original deadline.
Drawbacks:
- You still need to pay your taxes by the original deadline:An extension only gives you more time to file, not to pay. Failure to pay your taxes by the original deadline could result in penalties and interest.
- Extension doesn’t eliminate potential audit risk:The IRS can still audit your return even if you file an extension.
Understanding Refunds

Getting a tax refund is often seen as a bonus, but it’s important to understand that a refund doesn’t necessarily mean you’ve done your taxes perfectly. It simply means you’ve overpaid your taxes throughout the year. Let’s delve into the factors that influence the size of your refund and explore different ways to receive it.
Factors Influencing Refund Size
The amount of your tax refund is determined by several factors, including:
- Withholdings:The amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck throughout the year directly impacts your refund. If your employer withholds too much, you’ll likely receive a larger refund. Conversely, if you withhold too little, you might owe the government come tax time.
- Tax Credits:Tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the Child Tax Credit, directly reduce your tax liability, potentially increasing your refund.
- Deductions:Deductions, such as the standard deduction or itemized deductions, can lower your taxable income, leading to a smaller tax bill and potentially a larger refund.
- Taxable Income:The more you earn, the more taxes you generally owe, potentially resulting in a smaller refund.
Refund Receipt Methods
You have several options for receiving your tax refund:
- Direct Deposit:This is the most common and convenient method. You provide your bank account information on your tax return, and the IRS deposits your refund directly into your account.
- Check:If you don’t choose direct deposit, you’ll receive your refund by mail in the form of a check.
Reasons for Smaller Refunds
Here are some common reasons why you might receive a smaller refund than expected:
- Changes in Withholdings:If you changed jobs or your income increased significantly, your employer might have adjusted your withholdings, leading to a smaller refund.
- Reduced Tax Credits:Tax credit eligibility can change from year to year, potentially reducing your refund if you no longer qualify for the full amount.
- Increased Deductions:If you used the standard deduction in the past and now choose to itemize, your deductions might be lower, resulting in a smaller refund.
- Tax Law Changes:Changes in tax laws can affect your refund, even if you haven’t made any changes to your personal situation.
Tax Tips for Different Life Stages
Your tax obligations and opportunities change throughout your life. From student loans to retirement planning, understanding how to navigate tax rules at different stages can save you money and maximize your financial well-being.
Students
Students often have unique tax considerations, including income from part-time jobs, scholarships, and student loans.
- Tuition and Fees Deduction:This deduction allows you to reduce your taxable income by up to $4,000 for qualified education expenses. This includes tuition, fees, and course materials.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit:This credit is available for the first four years of post-secondary education and is worth up to $2,500 per student. To qualify, you must meet certain income requirements and be enrolled at least half-time.
- Student Loan Interest Deduction:You can deduct up to $2,500 in interest paid on qualified student loans. This deduction is phased out for taxpayers with higher incomes.
Tax planning can help students minimize their tax burden and potentially save money on education expenses.
New Parents
New parents face a variety of tax-related issues, including child tax credits, dependent care expenses, and college savings plans.
- Child Tax Credit:This credit is worth up to $2,000 per qualifying child under the age of 17. The credit is fully refundable, meaning you can receive a portion of it back even if you owe no taxes.
- Dependent Care Credit:This credit helps offset the cost of childcare expenses for qualifying dependents. The amount of the credit depends on your income and the amount of care expenses you incur.
- 529 College Savings Plans:These plans allow you to save for future college expenses tax-free. Contributions to 529 plans may be tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified education expenses are tax-free.
Strategic tax planning can help new parents maximize their tax benefits and save for their children’s future education.
Retirees
Retirement brings its own set of tax considerations, including income from Social Security, pensions, and retirement accounts.
- Standard Deduction vs. Itemized Deductions:Retirees often have lower incomes and may benefit from taking the standard deduction instead of itemizing. However, if you have significant medical expenses or other deductible expenses, itemizing may be more advantageous.
- Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs):If you have traditional IRAs or 401(k)s, you are required to take minimum distributions starting at age 72. These distributions are taxable as ordinary income.
- Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies:Retirees can use tax-efficient withdrawal strategies to minimize their tax liability. For example, you may want to withdraw from Roth IRAs first, as withdrawals from these accounts are tax-free.
Tax planning is essential for retirees to ensure they are taking advantage of available tax breaks and minimizing their tax burden.
Closing Summary: Tax Day Is Monday What To Know About Deadlines Extensions And Refunds
Tax Day can be a stressful time, but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By understanding the deadlines, extensions, and refund process, you can file your taxes confidently and avoid any surprises. Remember, there are resources available to help you along the way, so don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance if needed.
Happy filing!






