COVID-19 Antibody Supplies Still Limited After a Year
Supplies still limited more than a year after monoclonal antibodies authorized for treating covid 19 – More than a year after monoclonal antibodies were authorized for treating COVID-19, the reality is that supplies remain limited. This ongoing issue has left many patients struggling to access this potentially life-saving treatment, highlighting the complex challenges faced by healthcare systems in the fight against the pandemic.
Monoclonal antibodies, essentially lab-made versions of the body’s natural defenses, can help neutralize the virus and prevent severe illness. However, production, distribution, and logistical hurdles have created a persistent bottleneck, impacting the accessibility of this critical treatment for COVID-19 patients.
Monoclonal Antibodies
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented unprecedented challenges to healthcare systems worldwide. While vaccines have been instrumental in mitigating the severity of the disease, there remains a critical need for effective treatments, particularly for individuals who are at high risk of severe illness or those who are unable to receive vaccines.
Monoclonal antibodies have emerged as a promising therapeutic option, offering a lifeline to those battling COVID-19.
The Role of Monoclonal Antibodies in Treating COVID-19
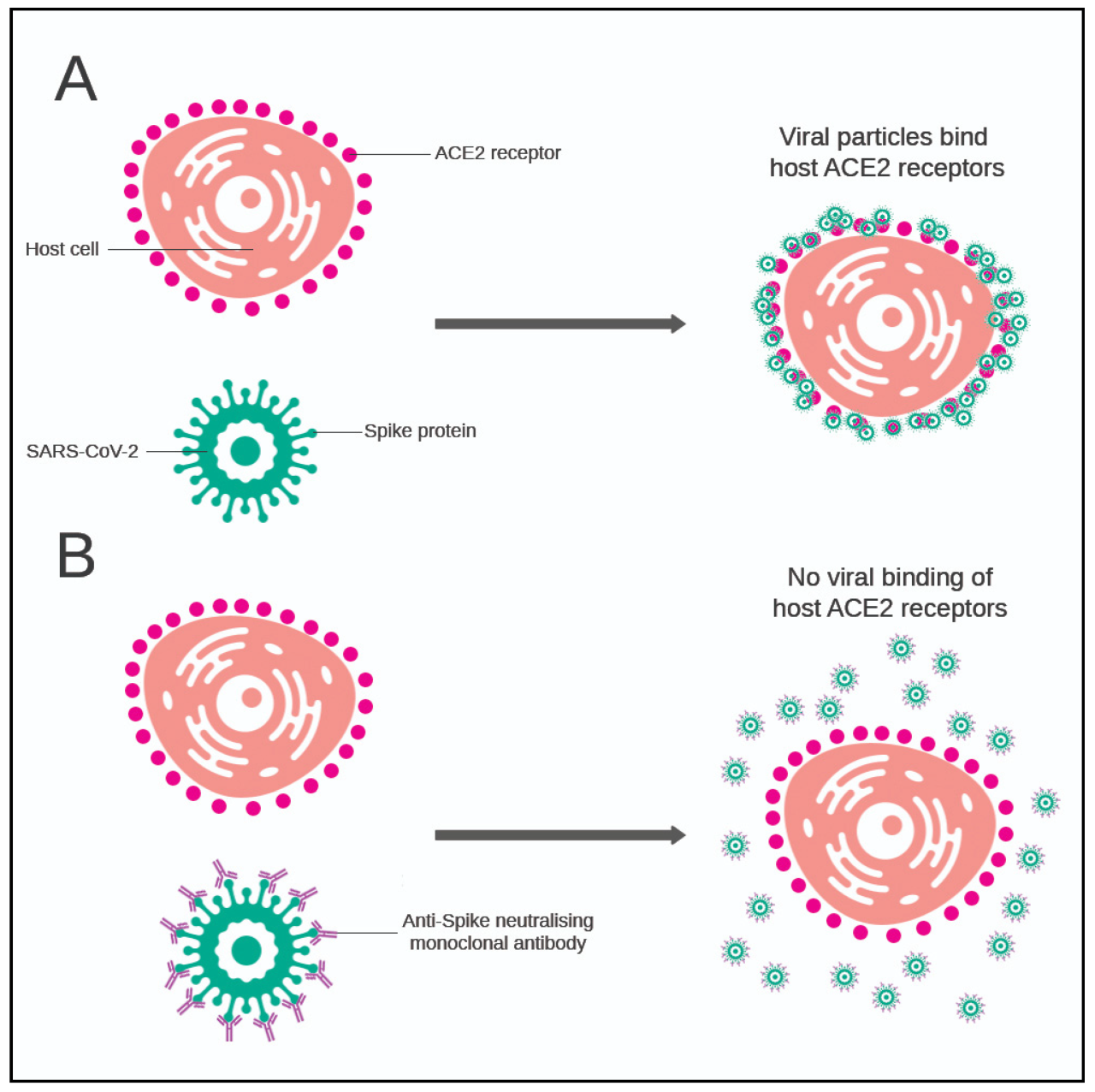
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that mimic the body’s natural immune response to fight off infections. They are designed to target specific proteins on the surface of viruses, such as the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
By binding to these proteins, monoclonal antibodies can block the virus from entering healthy cells, preventing infection and reducing the severity of illness.
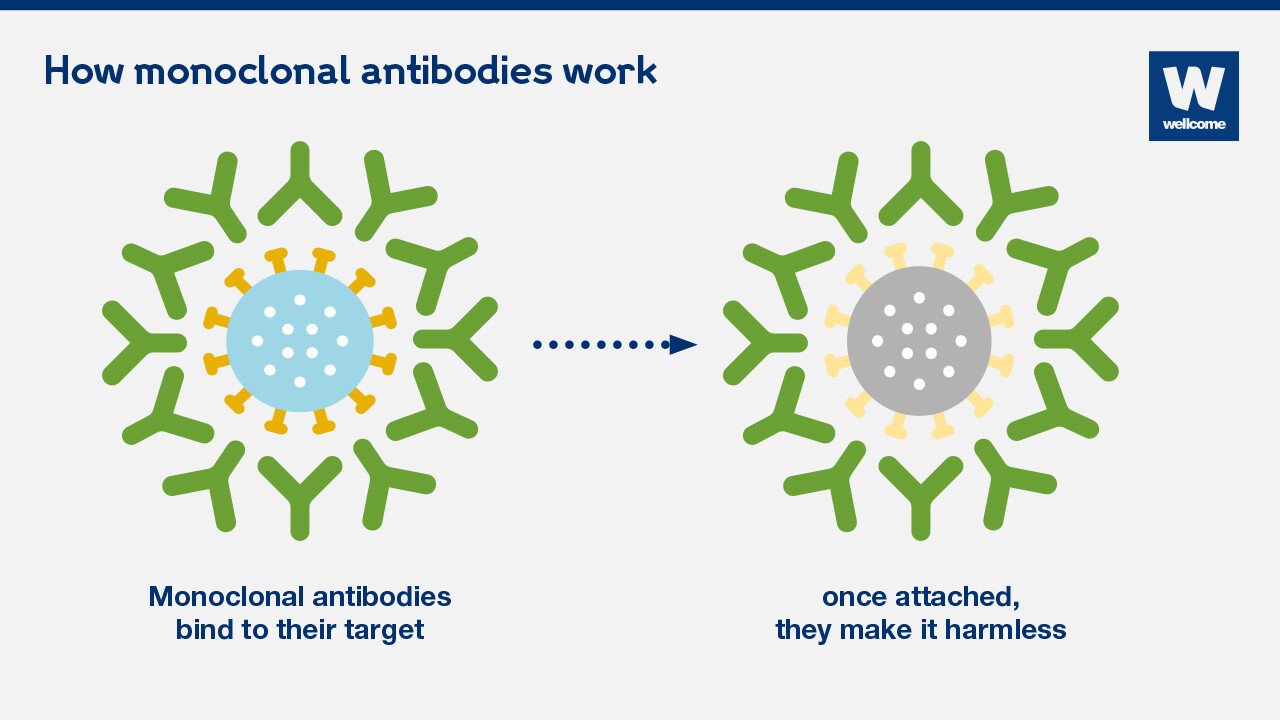
How Monoclonal Antibodies Work
Monoclonal antibodies work by targeting the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This protein is crucial for the virus to enter human cells. When monoclonal antibodies bind to the spike protein, they block the virus from attaching to and entering cells, effectively preventing infection.
It’s frustrating to see that supplies of monoclonal antibodies, a vital treatment for COVID-19, are still limited more than a year after they were authorized. This is especially concerning given the recent news about the condition of the LA deputies attacked in a patrol car, new details on condition of la deputies attacked in patrol car huge reward offered for info on triggerman , and the need for effective treatments for those who may contract the virus.
It’s critical that we prioritize access to these therapies, especially for vulnerable populations.
This mechanism is similar to how vaccines work, but instead of stimulating the body to produce its own antibodies, monoclonal antibodies are directly administered.
Effectiveness of Monoclonal Antibodies in Reducing Hospitalization and Death
Clinical trials and real-world data have demonstrated the effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies in reducing hospitalization and death in high-risk COVID-19 patients. Studies have shown that early treatment with monoclonal antibodies can significantly reduce the risk of hospitalization by up to 70% and decrease the risk of death by up to 85% in individuals who are at high risk of severe illness.
This makes monoclonal antibodies a valuable tool in managing the pandemic, particularly for vulnerable populations.
Supply Chain Challenges
More than a year after monoclonal antibodies were authorized for treating COVID-19, access to these vital therapies remains limited for many patients. While the development of these treatments marked a significant step forward in combating the pandemic, persistent supply chain challenges have hindered their widespread availability.
This ongoing issue highlights the complexities of producing and distributing these essential medical products.
Production Challenges
Manufacturing monoclonal antibodies presents several challenges that contribute to limited supply. The production process is intricate and requires specialized facilities and expertise. The following are some of the key production hurdles:
- Complex Manufacturing Process:Monoclonal antibodies are produced using complex cell culture techniques, requiring highly specialized equipment and controlled environments. This process is time-consuming and can be susceptible to disruptions, impacting production capacity.
- Raw Material Availability:The production of monoclonal antibodies relies on a range of raw materials, including cell lines, media, and reagents. Shortages or delays in procuring these materials can significantly impact production timelines.
- Scaling Up Production:Meeting the demand for monoclonal antibodies requires scaling up production significantly. This can be challenging due to the complex nature of the manufacturing process and the need for additional specialized equipment and personnel.
Distribution and Logistical Hurdles
Distribution and logistical challenges further compound the supply issue. Getting these treatments to patients in a timely manner requires efficient distribution networks and coordinated efforts:
- Cold Chain Requirements:Monoclonal antibodies require strict temperature control during storage and transportation. Maintaining the cold chain throughout the distribution process is crucial to ensure the efficacy of the treatment.
- Limited Storage Capacity:Hospitals and clinics often have limited storage capacity for these medications, further complicating distribution and creating challenges for managing inventory levels.
- Accessibility and Equity:Ensuring equitable access to monoclonal antibodies for all patients, regardless of location or socioeconomic status, is a major challenge. This requires robust distribution systems and addressing potential disparities in access.
The Impact of Limited Supply on Patients: Supplies Still Limited More Than A Year After Monoclonal Antibodies Authorized For Treating Covid 19
The limited availability of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for treating COVID-19 has had a significant impact on patients, hindering their access to potentially life-saving treatment and creating challenges for healthcare providers. The shortage has resulted in delays, denials of treatment, and inequities in access, raising concerns about the effectiveness and fairness of the healthcare system.
Delays and Denials of Treatment, Supplies still limited more than a year after monoclonal antibodies authorized for treating covid 19
The scarcity of mAbs has forced many patients to face delays and denials of treatment, leaving them vulnerable to severe COVID-19 complications. The situation has been particularly challenging for patients in rural areas or those with limited access to healthcare resources.
“My father was diagnosed with COVID-19 in December 2021 and his condition quickly worsened. We tried to get him mAb treatment, but there was a shortage, and we were told there was a waiting list. By the time he received the treatment, his condition had deteriorated significantly,”
It’s frustrating to see that monoclonal antibodies, a crucial treatment for COVID-19, remain in short supply more than a year after authorization. Meanwhile, the lack of visitor logs for Biden’s house, where classified documents were found, as reported here , raises serious questions about security.
This situation makes me wonder if we’re truly prioritizing public health and national security, or if we’re just playing catch-up with a pandemic and its aftermath.
shared a concerned daughter, highlighting the challenges faced by patients in accessing timely treatment.
Disparities in Access
The limited supply of mAbs has also exacerbated existing disparities in access to healthcare. Patients in underserved communities, particularly those with lower socioeconomic status, have been disproportionately affected by the shortage. Factors such as limited transportation, lack of insurance, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure contribute to these disparities.
“It is disheartening to see how the mAb shortage has disproportionately impacted communities of color and those with lower socioeconomic status. They are more likely to face delays and denials of treatment, exacerbating existing health inequities,”
It’s frustrating to see that supplies of monoclonal antibodies, a crucial treatment for COVID-19, are still limited over a year after their authorization. While we grapple with this healthcare issue, it’s equally concerning to hear that China is rapidly advancing its space capabilities, according to a recent warning from a US Space Force general.
This kind of rapid development raises questions about resource allocation and prioritization, particularly when vital medical treatments are still in short supply.
stated a healthcare advocate, emphasizing the urgent need to address these disparities.
Alternative Treatments and Strategies
While monoclonal antibodies remain a valuable tool in the fight against COVID-19, their limited supply necessitates exploring alternative treatments and strategies. This section delves into other available treatment options and strategies for improving the supply of monoclonal antibodies.
Other Available Treatments
The availability of alternative treatments for COVID-19 is crucial, particularly when monoclonal antibodies are scarce. These treatments can provide therapeutic benefits and manage the disease’s severity.
- Antiviral Medications:Antiviral medications like Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) and remdesivir have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the severity of COVID-19, particularly in high-risk individuals. These medications work by interfering with the virus’s replication process, preventing its spread within the body.
- Supportive Care:Supportive care plays a vital role in managing COVID-19 symptoms and preventing complications. This may involve oxygen therapy, ventilation, and managing underlying conditions like diabetes or heart disease. Supportive care aims to maintain vital functions and improve patient outcomes.
Effectiveness and Accessibility of Alternative Treatments
Comparing the effectiveness and accessibility of alternative treatments to monoclonal antibodies is essential for informing treatment decisions.
- Antiviral Medications:Antiviral medications like Paxlovid and remdesivir have shown significant efficacy in reducing hospitalization and death, particularly in high-risk individuals. However, their availability can be limited due to production constraints and supply chain issues.
- Supportive Care:Supportive care is readily accessible and plays a crucial role in managing COVID-19 symptoms and complications. However, its effectiveness may vary depending on the severity of the illness and the individual’s health status.
Strategies for Improving Monoclonal Antibody Supply
Addressing the limited supply of monoclonal antibodies requires comprehensive strategies that focus on increasing production capacity and streamlining distribution.
- Expanding Production Capacity:Increasing production capacity can be achieved through various means, including expanding existing manufacturing facilities, partnering with other pharmaceutical companies, and streamlining regulatory processes. Government incentives and support can also play a crucial role in accelerating production.
- Streamlining Distribution:Optimizing the distribution process can ensure timely and efficient delivery of monoclonal antibodies to patients in need. This may involve establishing regional distribution centers, coordinating with healthcare providers, and utilizing data analytics to predict demand and allocate resources effectively.
Looking Ahead
The ongoing supply constraints for monoclonal antibodies, despite their authorization over a year ago, highlight the need for a more robust and adaptable approach to developing and distributing these crucial treatments. Looking ahead, research and innovation are crucial to overcome these challenges and ensure that monoclonal antibodies become a reliable and accessible treatment option for COVID-19 and other infectious diseases.
Future Breakthroughs in Monoclonal Antibody Development
The development of monoclonal antibodies is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research focusing on improving their efficacy, safety, and accessibility.
- Next-Generation Monoclonal Antibodies:Scientists are exploring novel antibody formats, such as bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates, that can target multiple parts of a virus or enhance their therapeutic effects. For instance, bispecific antibodies could simultaneously bind to two different epitopes on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, potentially increasing their neutralizing potency and reducing the risk of viral escape mutations.
- Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies:Researchers are actively searching for monoclonal antibodies that can neutralize a wider range of viral variants, including emerging strains. This could provide a more durable and effective treatment option against future outbreaks and pandemics. For example, the development of broadly neutralizing antibodies against influenza virus has been a major focus of research, with promising results for future universal flu vaccines.
- Personalized Medicine:The field of personalized medicine is also influencing the development of monoclonal antibodies. This involves tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup and specific immune responses. This could lead to more targeted and effective therapies with fewer side effects.
The Role of Research and Innovation in Addressing Supply Challenges
Addressing the supply chain challenges for monoclonal antibodies requires a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Streamlining Production Processes:Improving manufacturing efficiency and scaling up production capacity are critical to meeting the demand for monoclonal antibodies. This involves optimizing fermentation processes, developing novel purification techniques, and utilizing advanced bioreactors.
- Developing Alternative Production Methods:Exploring alternative production methods, such as cell-free protein synthesis or plant-based expression systems, could provide more flexible and scalable manufacturing options. For instance, plant-based production systems have been explored for producing therapeutic proteins, offering potential for cost-effective and large-scale manufacturing of monoclonal antibodies.
- Investing in Research and Development:Continued investment in research and development is crucial for advancing the science of monoclonal antibody development and improving their accessibility. This includes funding for clinical trials, preclinical research, and the development of new technologies.
Long-Term Impact of Monoclonal Antibodies on the Treatment of COVID-19 and Other Infectious Diseases
Monoclonal antibodies are poised to play a significant role in the future of infectious disease treatment. Their potential impact includes:
- Preventing Severe Disease:Monoclonal antibodies have demonstrated effectiveness in preventing severe COVID-19, particularly in high-risk individuals. Their widespread availability could reduce hospitalizations and deaths, especially in vulnerable populations.
- Treating Existing Infections:Monoclonal antibodies can be used to treat existing COVID-19 infections, particularly in the early stages of the disease. This could help to reduce viral load and prevent the progression of illness.
- Expanding Treatment Options for Other Infectious Diseases:The success of monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 has spurred research into their potential for treating other infectious diseases, including influenza, HIV, and malaria. This could lead to new and effective therapies for a wide range of illnesses.
Closing Notes
The ongoing shortage of monoclonal antibodies underscores the need for continued research and innovation to improve the availability and accessibility of this vital treatment. As we navigate the evolving landscape of the pandemic, finding solutions to these supply chain challenges is crucial to ensuring that all patients have access to the best possible care.