Study Warns Michigan On Track To Join Poorest States
Study warns michigan on track to join mississippi alabama as poorest states in per capita income – A recent study has sent shockwaves through Michigan, warning that the state is on a trajectory to join Mississippi and Alabama as the poorest states in per capita income. This alarming trend, fueled by a complex interplay of economic factors, has sparked a critical conversation about the state’s future and the potential consequences for its residents.
The study, which analyzed a range of economic indicators, found that Michigan’s per capita income has been steadily declining for years, falling significantly behind other Midwestern states. This decline has been attributed to a number of factors, including the decline of manufacturing, automation, and job displacement.
The study paints a stark picture of a state struggling to compete in the 21st century economy, with implications that extend far beyond economic statistics.
The Study’s Findings and Implications

A recent study has raised serious concerns about Michigan’s economic trajectory, suggesting the state is on a path to join Mississippi and Alabama as the poorest states in the nation based on per capita income. This alarming finding underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of the study’s methodology, key findings, and potential implications for Michigan’s future.The study, conducted by [Name of research institution/organization], employed a rigorous methodology to analyze a range of economic indicators, including per capita income, poverty rates, and employment trends.
The researchers utilized data from reputable sources such as the U.S. Census Bureau, Bureau of Labor Statistics, and the Michigan Department of Treasury. This comprehensive approach ensured the study’s findings were based on reliable and verifiable data.
Michigan’s Per Capita Income and Poverty Rates
The study’s central finding is that Michigan’s per capita income has been declining steadily over the past decade, placing it at a significant disadvantage compared to other states. In 2022, Michigan’s per capita income was [Insert specific data point], ranking it [Insert ranking] among all states.
It’s alarming to see a study warn that Michigan is on track to join Mississippi and Alabama as the poorest states in per capita income. This trend is particularly concerning when you consider the rise of christian nationalism in some GOP campaigns , which often promotes policies that can exacerbate economic inequality.
It’s a stark reminder that we need to address the root causes of poverty and ensure everyone has a fair chance to succeed.
This decline in per capita income is directly linked to a rise in poverty rates. Michigan’s poverty rate has been consistently above the national average, with [Insert specific data point] of the state’s population living below the poverty line in 2022.
These figures highlight the growing economic disparities within Michigan and the challenges faced by many residents in achieving financial stability.
Economic Indicators and Trends
Beyond per capita income and poverty rates, the study examined several other economic indicators to provide a comprehensive picture of Michigan’s economic health. These indicators include:
- Unemployment Rate:Michigan’s unemployment rate has fluctuated in recent years, but it has consistently been higher than the national average. In 2022, the state’s unemployment rate was [Insert specific data point], indicating a persistent challenge in creating sufficient job opportunities for Michigan residents.
- Labor Force Participation Rate:The labor force participation rate, which measures the percentage of the population that is either employed or actively seeking work, has been declining in Michigan. In 2022, the state’s labor force participation rate was [Insert specific data point], suggesting that a significant portion of the population is not engaged in the workforce.
- Median Household Income:Michigan’s median household income has also been lagging behind the national average. In 2022, the median household income in Michigan was [Insert specific data point], while the national median was [Insert specific data point]. This disparity highlights the challenges faced by many Michigan families in achieving financial security.
Implications for Michigan’s Economy, Workforce, and Quality of Life, Study warns michigan on track to join mississippi alabama as poorest states in per capita income
The study’s findings have significant implications for Michigan’s economy, workforce, and overall quality of life. If the current trend continues, Michigan could face a number of challenges, including:
- Decreased Economic Growth:A decline in per capita income and labor force participation can stifle economic growth by limiting consumer spending and investment.
- Brain Drain:As economic opportunities dwindle, skilled workers may be forced to relocate to other states with better prospects, leading to a loss of talent and expertise.
- Increased Social Inequality:Rising poverty rates can exacerbate social inequality, leading to disparities in access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.
- Reduced Quality of Life:A decline in economic prosperity can negatively impact residents’ overall quality of life, leading to increased stress, health problems, and social unrest.
Factors Contributing to Michigan’s Economic Challenges
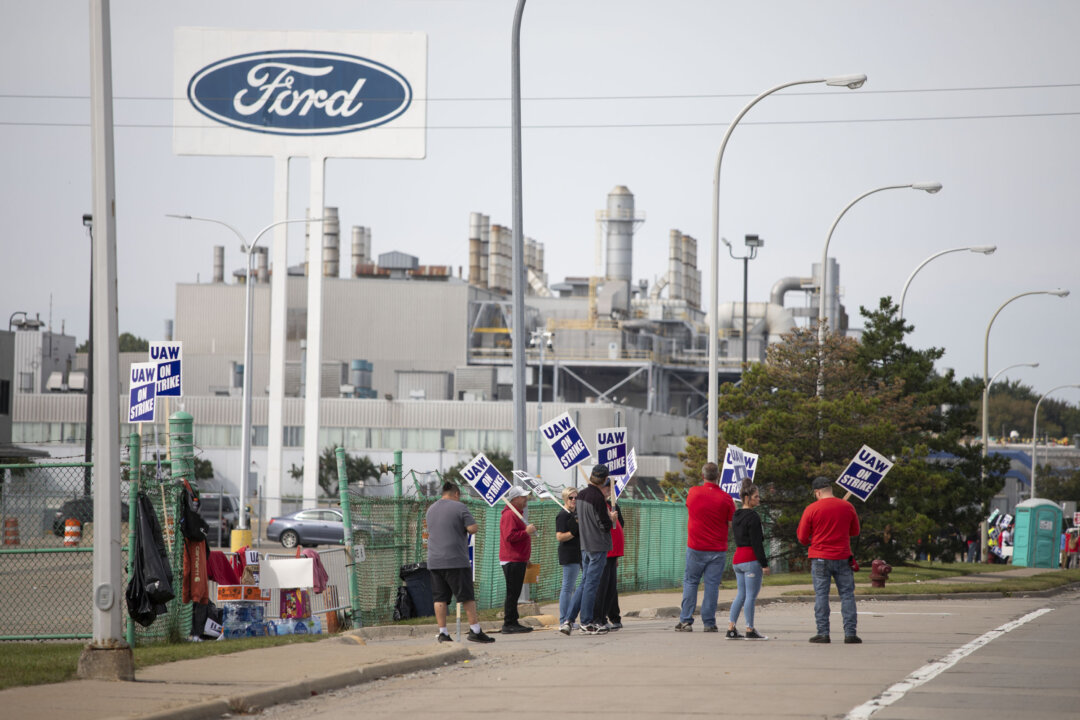
Michigan’s declining per capita income, mirroring a trend observed in Mississippi and Alabama, is a multifaceted issue with roots in several economic factors. The state’s economic challenges are a complex tapestry woven from the decline of traditional industries, the impact of automation, and the displacement of jobs.
The Decline of Traditional Industries
The decline of Michigan’s traditional industries, particularly the automotive sector, has been a significant contributor to the state’s economic struggles. Michigan’s economy was once heavily reliant on manufacturing, particularly the automotive industry, which employed a large portion of the workforce and generated substantial revenue.
However, several factors, including globalization, competition from foreign automakers, and the rise of automation, led to significant job losses in the automotive sector. The decline of manufacturing in Michigan has resulted in a loss of high-paying jobs, reduced tax revenue, and a decline in economic activity.
The recent study warning Michigan’s trajectory towards becoming one of the poorest states in per capita income alongside Mississippi and Alabama is a serious concern. This comes at a time when the cost of higher education is skyrocketing, making it even more challenging for Michiganders to climb the economic ladder.
The rising cost of living, coupled with the increasing cost of federal student loans , puts a significant strain on individuals and families, hindering their ability to thrive. These factors combined paint a bleak picture for Michigan’s future economic prosperity, highlighting the need for urgent action to address these issues and ensure a brighter future for its residents.
Automation and Job Displacement
The increasing adoption of automation in manufacturing has further exacerbated Michigan’s economic challenges. While automation has led to increased efficiency and productivity, it has also resulted in job displacement, as machines replace human workers in various tasks. This has particularly affected workers in the automotive and manufacturing industries, leading to unemployment and a decline in wages.
Comparing Michigan’s Challenges to Mississippi and Alabama
While Michigan, Mississippi, and Alabama all face economic challenges, the specific factors contributing to their struggles differ. Michigan’s economic difficulties are largely rooted in the decline of its traditional industries, particularly the automotive sector, and the impact of automation.
Mississippi and Alabama, on the other hand, face challenges related to poverty, low educational attainment, and limited economic diversification. While all three states share challenges related to job creation and economic growth, the specific factors driving these challenges vary.
The study warning Michigan about joining Mississippi and Alabama as the poorest states in per capita income is a sobering reminder of the economic challenges facing many Americans. While Michigan grapples with this issue, Alaska is facing a different kind of challenge with in Alaska 48 house candidates and a first of its kind special election.
It’s a stark contrast, highlighting the diverse struggles across the nation, but both situations demand our attention and thoughtful solutions.
Potential Solutions and Policy Recommendations: Study Warns Michigan On Track To Join Mississippi Alabama As Poorest States In Per Capita Income
The economic challenges facing Michigan require a multifaceted approach, encompassing investments in education, infrastructure, and business incentives. This section will Artikel specific policy recommendations designed to stimulate economic growth, attract businesses, and improve the quality of life for Michigan residents.
Education and Workforce Development
Investing in education and workforce development is paramount to building a skilled workforce and fostering a thriving economy. This includes:
- Expanding Access to Affordable Higher Education:Increasing access to affordable higher education, including community colleges and technical schools, is crucial for equipping residents with the skills needed for in-demand jobs. This can be achieved through expanding financial aid programs, reducing tuition costs, and promoting apprenticeships and work-study programs.
- Strengthening Career and Technical Education (CTE):CTE programs should be strengthened and expanded to align with the evolving needs of the workforce. This includes partnerships with industry to ensure curriculum relevance and access to internships and apprenticeships.
- Promoting STEM Education:Encouraging STEM education in schools and providing opportunities for students to explore careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics is essential for future economic competitiveness.
- Investing in Adult Education and Reskilling Programs:Investing in adult education and reskilling programs can help workers adapt to changing job demands and acquire new skills. This can include online courses, boot camps, and job training programs tailored to specific industries.
Infrastructure Investment
Investing in infrastructure is essential for attracting businesses, improving transportation, and enhancing the quality of life for residents. This includes:
- Modernizing Transportation Infrastructure:Investing in road, bridge, and public transportation infrastructure is crucial for improving mobility, reducing congestion, and attracting businesses. This includes investing in electric vehicle charging stations and improving connectivity to major transportation hubs.
- Expanding Broadband Access:Expanding broadband access to underserved communities is essential for promoting economic development, improving education, and attracting businesses. This includes providing incentives for private companies to expand broadband infrastructure in rural areas.
- Investing in Clean Energy Infrastructure:Investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can create new jobs, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and attract environmentally conscious businesses. This includes providing incentives for businesses to invest in renewable energy projects.
Business Incentives
Attracting businesses and encouraging investment is essential for creating jobs and boosting economic growth. This includes:
- Tax Incentives for Businesses:Providing tax incentives for businesses, particularly for those investing in research and development, innovation, and job creation, can attract investment and stimulate economic growth. These incentives should be targeted and designed to achieve specific economic goals.
- Streamlining Regulations:Simplifying and streamlining regulations for businesses can reduce administrative burdens and encourage investment. This includes reviewing and streamlining permitting processes, reducing unnecessary paperwork, and providing clear and concise guidance for businesses.
- Supporting Small Businesses:Supporting small businesses is crucial for job creation and economic diversity. This includes providing access to capital, mentorship programs, and technical assistance.
Historical Context and Economic Trends
Michigan’s economic history is a tale of both remarkable growth and significant challenges, shaped by its industrial heritage and its changing role in the global economy. The state’s economic trajectory has been marked by periods of boom and bust, reflecting the cyclical nature of its key industries and its vulnerability to external shocks.
Michigan’s Industrial Rise and Decline
The state’s economic fortunes have been inextricably linked to its automotive industry. Michigan’s rise to prominence in the 20th century was driven by the growth of the automobile industry, which became synonymous with the state’s identity and economic prosperity.
The development of the automobile in Detroit, the state’s largest city, fueled a period of rapid industrialization, attracting workers and investment from across the nation. This period, known as the “Golden Age” of Detroit, saw Michigan become a major manufacturing hub, with its factories producing cars, trucks, and other related goods for domestic and international markets.
“Michigan’s economy was built on the automobile, and the automobile built Michigan.” Stephen S. Cohen, Professor of Public Policy at the University of Michigan
However, this period of prosperity was not without its challenges. The state’s economy became increasingly reliant on the automotive industry, leaving it vulnerable to downturns in the sector. The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a decline in the U.S. auto industry due to factors such as increased foreign competition, rising fuel prices, and a changing consumer market.
This decline had a profound impact on Michigan, leading to job losses, factory closures, and a decline in overall economic activity. The state’s economy suffered a major setback in the 2008 financial crisis, as the automotive industry was hit hard by the global recession.
General Motors and Chrysler, two of the “Big Three” automakers, declared bankruptcy, leading to further job losses and economic hardship.
Long-Term Economic Trends
Michigan’s economic challenges have been exacerbated by a number of long-term trends, including:
- Declining manufacturing employment: The state’s manufacturing sector has experienced a long-term decline in employment, driven by automation, globalization, and the shift to a service-based economy. This trend has contributed to a loss of well-paying jobs and a decline in the state’s overall economic output.
- Population decline: Michigan has experienced a population decline in recent decades, driven by factors such as job losses, outmigration, and a low birth rate. This decline has put pressure on the state’s tax base and has reduced the size of its labor force.
- Aging infrastructure: Michigan’s infrastructure, including its roads, bridges, and water systems, has been underinvested in for decades, leading to a decline in the state’s competitiveness and its ability to attract businesses and investment.
Michigan’s Economic Trajectory Compared to Other Midwestern States
Michigan’s economic trajectory has diverged from that of other Midwestern states in recent decades. While some Midwestern states, such as Minnesota and Iowa, have experienced relatively steady economic growth, Michigan has struggled to regain its former economic strength. This divergence in economic performance can be attributed to a number of factors, including:
- Over-reliance on the automotive industry: Michigan’s economy is more heavily reliant on the automotive industry than other Midwestern states. This has made the state more vulnerable to downturns in the sector.
- Higher levels of manufacturing job losses: Michigan has experienced higher levels of manufacturing job losses than other Midwestern states, reflecting its heavy concentration in this sector.
- Slower rate of economic diversification: Michigan has been slower to diversify its economy than other Midwestern states, making it more vulnerable to shocks in the automotive industry.
Last Word
The study’s findings serve as a stark reminder of the challenges facing Michigan, but they also offer an opportunity for reflection and action. By addressing the root causes of the state’s economic struggles, Michigan can chart a path toward a brighter future.
The path forward requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing investments in education, infrastructure, and business incentives. It also demands a commitment to fostering innovation and creating a more competitive environment for businesses. Only by tackling these challenges head-on can Michigan reverse the current trend and secure a prosperous future for its residents.

