Student Debt Cancellation $379 Billion Price Tag
Student debt cancellation to cost 379 billion education department estimates sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The Education Department’s recent estimate of $379 billion for the cost of canceling student debt has sparked a national conversation about the economic and social implications of such a move.
This staggering figure has ignited a debate among policymakers, economists, and the public at large, raising questions about the feasibility and potential consequences of widespread debt forgiveness.
The debate surrounding student debt cancellation is multifaceted, encompassing a wide range of perspectives. Some argue that canceling student debt would provide significant economic relief to millions of Americans, stimulate consumer spending, and boost the overall economy. Others contend that the cost of such a program would be prohibitive, potentially leading to increased deficits and inflation. The potential impact on higher education institutions, the future of student lending, and the overall fairness of the system are also hotly debated topics.
This article delves into the intricacies of this complex issue, examining the arguments for and against student debt cancellation, analyzing the potential economic and social impacts, and exploring alternative approaches to addressing the student debt crisis.
The Cost of Student Debt Cancellation
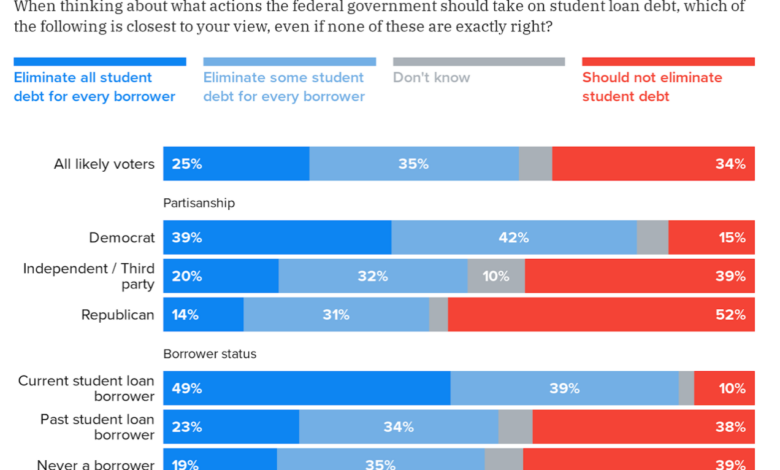
The Biden administration’s plan to cancel student loan debt has been a topic of much debate, with supporters praising it as a necessary step to alleviate financial burdens on borrowers and critics questioning its cost and feasibility. The Education Department has estimated that the cost of canceling up to $20,000 in student loan debt per borrower would be $379 billion.
This estimate has been the subject of much scrutiny, with some arguing that it is too high and others maintaining that it is a realistic assessment of the potential cost.
The Education Department’s Cost Estimate, Student debt cancellation to cost 379 billion education department estimates
The Education Department’s $379 billion estimate is based on a variety of factors, including the number of borrowers who would be eligible for cancellation, the average amount of debt they owe, and the expected impact on interest rates and loan repayments. The department has used a combination of data from the Federal Student Aid office, the U.S. Census Bureau, and other sources to arrive at this figure.
Methods Used to Estimate the Cost
The Education Department has used a variety of methods to arrive at its cost estimate, including:
- Modeling the impact of cancellation on the number of borrowers and loan balances. This involves projecting how many borrowers would be eligible for cancellation and how much debt they would have forgiven.
- Estimating the impact of cancellation on interest rates and loan repayments. This involves projecting how cancellation would affect the demand for student loans and the cost of borrowing.
- Analyzing the impact of cancellation on the federal budget. This involves projecting how cancellation would affect the amount of revenue the government collects from student loan repayments and the amount of money it spends on interest payments on student loans.
The Potential Impact of Student Debt Cancellation on the Federal Budget
The potential impact of student debt cancellation on the federal budget is a complex issue. Some argue that it would lead to a significant increase in the federal deficit, while others maintain that it would actually generate economic growth and lead to increased tax revenue. The impact of cancellation on the federal budget would depend on a number of factors, including the size of the program, the way it is financed, and the overall state of the economy.
The Education Department estimates that cancelling student debt would cost a whopping $379 billion, a hefty price tag that’s sure to spark debate. Meanwhile, former President Trump has slammed the Department of Justice for appealing a special master ruling in the FBI raid document case, a move he views as an attempt to hinder his legal team’s access to the documents.
While these two issues seem unrelated, they both highlight the ongoing battle between the current administration and its predecessors, with significant financial and legal implications at stake. The student debt cancellation proposal, if implemented, could have a major impact on the economy, while the FBI raid documents case continues to raise questions about the handling of classified information.
The potential impact of student debt cancellation on the federal budget is a complex issue that has been the subject of much debate.
The Education Department estimates that canceling student debt would cost a whopping $379 billion. It’s a hefty price tag, but it’s not the only one we’re facing. The recent decision to rescind religious vaccine mandate exemptions has sparked a firestorm of legal challenges, as outlined in this article: health care system ripe for lawsuits after rescinding religious vaccine mandate exemptions lawyer.
It’s a stark reminder that navigating complex issues like student debt and healthcare mandates requires careful consideration of both the financial and legal ramifications.
Political and Social Implications: Student Debt Cancellation To Cost 379 Billion Education Department Estimates
Student debt cancellation is a highly contentious issue in the United States, sparking fierce debates across the political spectrum. The potential ramifications of this policy extend far beyond the realm of economics, touching upon deeply ingrained societal values and the very fabric of American politics.
The estimated $379 billion cost of student debt cancellation is a hefty price tag, and it’s a reminder that even with good intentions, financial decisions have ripple effects. For instance, California’s recent extension of its Flex Alert, warning drivers not to charge their electric vehicles during peak hours, highlights the need to manage energy resources responsibly. Ultimately, finding solutions to complex issues like student debt and energy consumption requires careful consideration of the financial and environmental consequences.
Political Landscape
The political landscape surrounding student debt cancellation is deeply polarized. Democrats, generally, are more supportive of debt cancellation, viewing it as a necessary step towards promoting economic mobility and addressing systemic inequalities. Republicans, on the other hand, tend to oppose debt cancellation, arguing that it would be unfair to those who have already paid off their loans and could exacerbate inflation.
Arguments for and Against Student Debt Cancellation
Arguments for Student Debt Cancellation
- Economic Stimulus: Proponents argue that cancelling student debt would inject billions of dollars into the economy, boosting consumer spending and fostering economic growth. This is especially true for younger generations who are burdened by debt and may be hesitant to make large purchases or invest in their future.
- Promoting Equity: Student debt cancellation is often framed as a crucial step towards addressing racial and socioeconomic disparities. Studies have shown that Black and Hispanic borrowers are disproportionately affected by student debt, and cancelling this debt could help to level the playing field.
- Reducing Financial Strain: Many borrowers struggle to make their monthly payments, leading to financial stress, delayed homeownership, and difficulty starting families. Cancelling debt would alleviate this burden, allowing borrowers to focus on other financial goals and contribute more fully to the economy.
Arguments Against Student Debt Cancellation
- Moral Hazard: Critics argue that cancelling student debt would create a moral hazard, encouraging future generations to take on more debt with the expectation of forgiveness. This could lead to a cycle of irresponsible borrowing and unsustainable government spending.
- Unfairness to Non-Borrowers: Opponents argue that cancelling student debt would be unfair to those who have already paid off their loans or never took out student loans in the first place. They argue that these individuals should not be forced to bear the financial burden of others’ decisions.
- Inflationary Concerns: Some critics worry that cancelling student debt could lead to inflation, as borrowers spend their newfound disposable income, driving up demand for goods and services.
Social and Cultural Implications
Student debt cancellation has the potential to reshape the social and cultural landscape of the United States. It could:
- Increase Social Mobility: By reducing the burden of debt, student debt cancellation could allow borrowers to pursue higher-paying jobs, start businesses, and invest in their futures, ultimately leading to greater social mobility.
- Shift Cultural Norms: The cancellation of student debt could signal a shift in cultural norms, moving away from a system that prioritizes individual responsibility for debt repayment and towards a more collective approach to addressing systemic issues like educational inequality.
- Promote a More Equitable Society: By addressing the disproportionate impact of student debt on marginalized communities, student debt cancellation could contribute to a more equitable society, where opportunities are more readily available to all individuals, regardless of their background.
Alternatives to Student Debt Cancellation
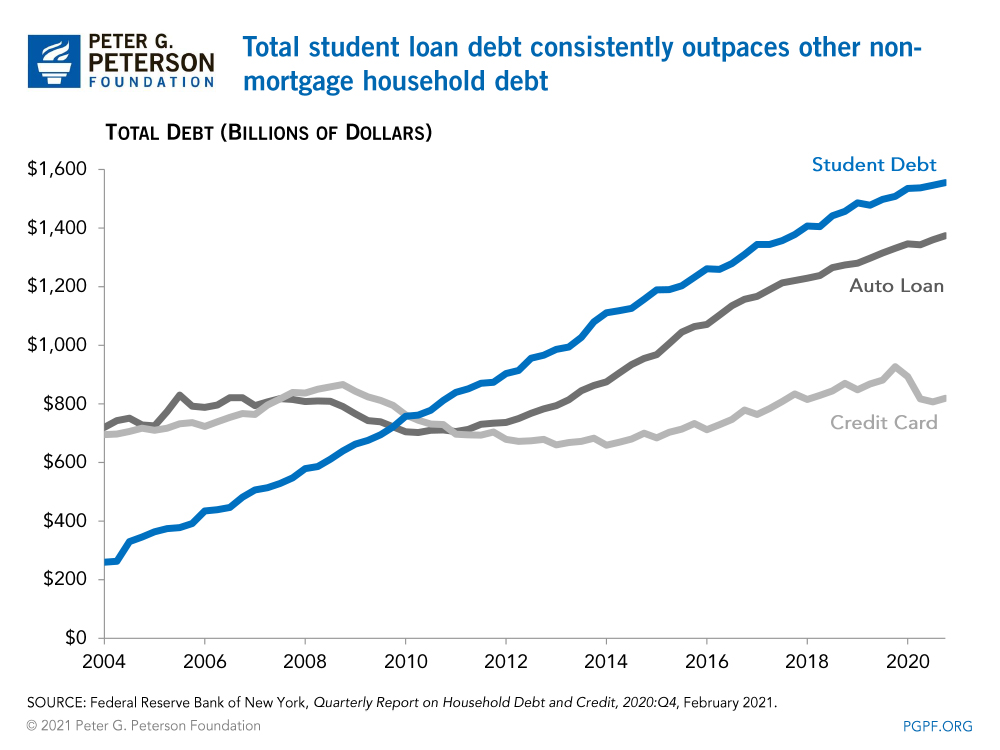
While student debt cancellation has gained significant attention as a potential solution to the student debt crisis, it’s important to consider alternative approaches that could address the issue more effectively and sustainably. Many argue that student debt cancellation is a blunt instrument that would disproportionately benefit high-income earners and exacerbate existing inequalities. Moreover, the cost of cancellation could strain government budgets and lead to unintended consequences.
Alternative Approaches to Student Debt
This section explores alternative approaches to addressing student debt, focusing on their pros and cons, feasibility, and effectiveness.
Income-Based Repayment Plans
Income-based repayment plans (IBRs) are designed to make student loan payments more affordable by tying monthly payments to a borrower’s income. There are various IBR plans, including the Pay As You Earn (PAYE) plan, the Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) plan, and the Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR) plan.
- Pros: IBRs can significantly reduce monthly payments, making it easier for borrowers to manage their debt. They also offer the potential for loan forgiveness after a certain number of years of payments.
- Cons: IBRs can lead to higher overall interest costs due to extended repayment periods. They also may not be accessible to all borrowers, particularly those with low or fluctuating incomes.
- Feasibility and Effectiveness: IBRs are already widely available and have helped millions of borrowers manage their student debt. However, their effectiveness can be limited by factors such as income fluctuations, high interest rates, and complex eligibility requirements.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
Several loan forgiveness programs exist, such as the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program and the Teacher Loan Forgiveness program. These programs offer loan forgiveness to borrowers who work in certain professions or meet specific eligibility criteria.
- Pros: Loan forgiveness programs can provide significant financial relief to borrowers who meet the eligibility requirements.
- Cons: These programs are often complex and difficult to navigate. Eligibility requirements can be restrictive, and the programs may not be accessible to all borrowers.
- Feasibility and Effectiveness: Loan forgiveness programs are already available, but their effectiveness is limited by their complexity and eligibility requirements. The PSLF program, for instance, has been plagued by administrative issues and low approval rates.
Lowering College Costs
Addressing the root cause of student debt by lowering college costs is a crucial long-term strategy. This could involve increasing financial aid, reducing tuition fees, and making college more affordable for all.
- Pros: Lowering college costs can reduce the need for student loans and make higher education more accessible to a wider range of students.
- Cons: Reducing college costs requires significant government funding and can be politically challenging. It may also require changes to the higher education system, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Feasibility and Effectiveness: Lowering college costs is a long-term strategy that can have a significant impact on student debt levels. However, it requires sustained political will and investment.
Other Approaches
Other approaches to addressing student debt include:
- Debt refinancing: Allowing borrowers to refinance their student loans at lower interest rates can reduce monthly payments and overall interest costs.
- Debt consolidation: Combining multiple student loans into a single loan with a lower interest rate can simplify repayment and reduce interest costs.
- Increased financial literacy: Educating students about responsible borrowing and financial management can help them avoid excessive debt in the first place.
Impact on Higher Education
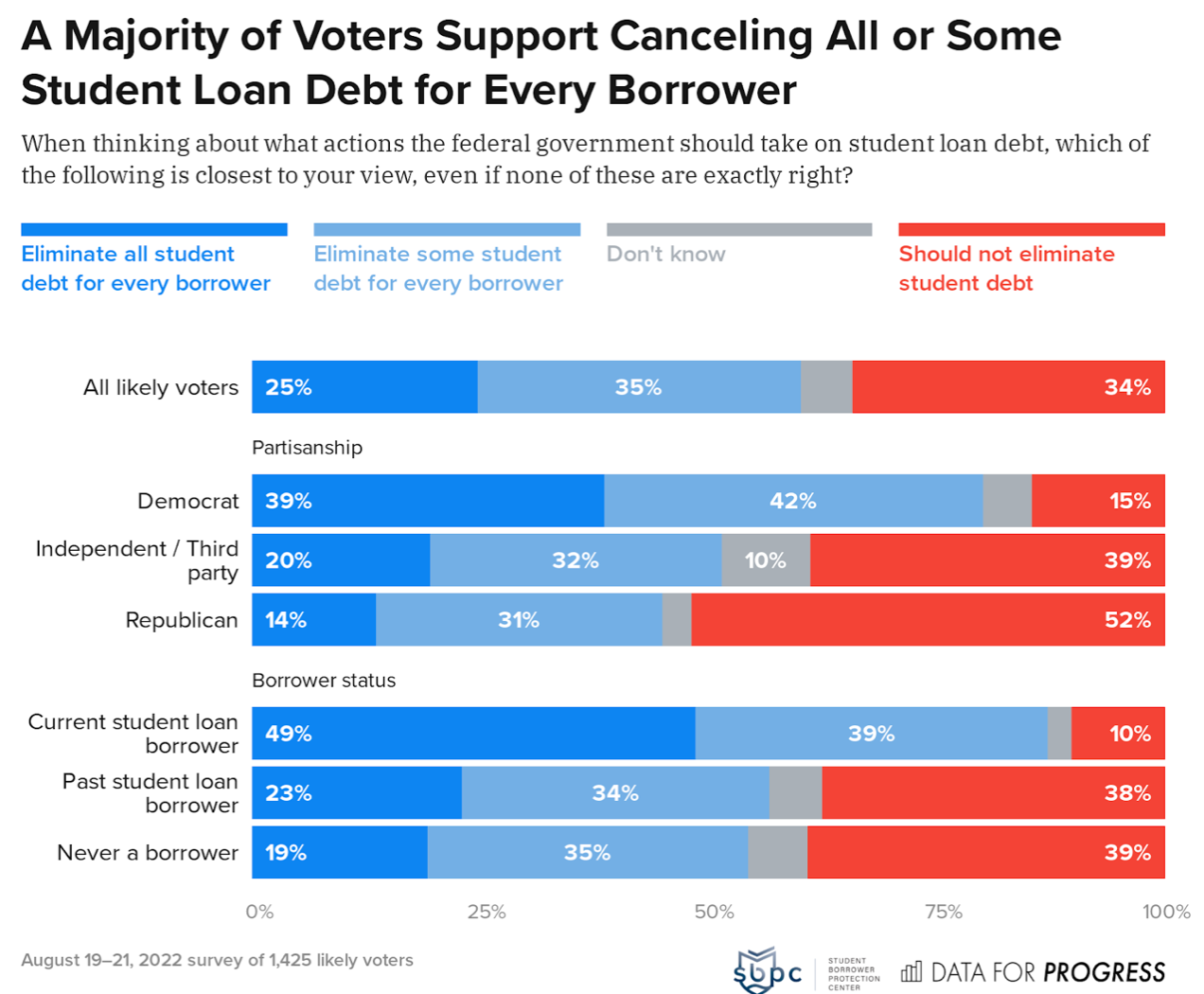
Student debt cancellation would have a significant impact on the future of higher education. It could potentially reshape the landscape of college affordability, access, and the overall financial health of institutions.
Impact on College Affordability and Access
Student debt cancellation could make college more affordable and accessible for many individuals. By eliminating the burden of student loans, graduates would have more disposable income, potentially leading to increased enrollment and a larger pool of potential students.
- Increased Enrollment: With reduced debt obligations, individuals may be more likely to pursue higher education, leading to an increase in enrollment rates. This could particularly benefit community colleges and other institutions that serve a large proportion of low-income and first-generation students.
- Greater Access for Underrepresented Groups: Debt cancellation could make college more accessible for underrepresented groups who are disproportionately burdened by student loan debt. This could lead to a more diverse student body and a more equitable higher education system.
Impact on Different Types of Colleges and Universities
| Type of Institution | Potential Impact ||—|—|| Public Universities | May experience increased enrollment and demand, leading to potential budget increases. However, they may also face pressure to reduce tuition costs to remain competitive. || Private Universities | Could see an increase in applications from students seeking more affordable options. However, they may also face challenges in maintaining their financial stability without tuition revenue.
|| For-Profit Colleges | Could experience a decline in enrollment as students opt for more affordable public or private institutions. || Community Colleges | May see a surge in enrollment as students seek affordable pathways to higher education. |
The debate over student debt cancellation is likely to continue for some time. The issue is complex, with far-reaching implications for individuals, the economy, and higher education. While there is no easy solution, understanding the potential costs and benefits of various approaches is crucial for making informed decisions about the future of student debt in the United States.
As we move forward, it is essential to engage in open and thoughtful dialogue, considering all perspectives and exploring innovative solutions to address this pressing challenge.






