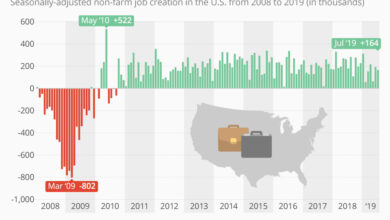
American Workers Quitting: Labor Market Squeeze
Record number of american workers quit their jobs signaling labor market squeeze – American Workers Quitting: Labor Market Squeeze – this isn’t just a headline, it’s a reflection of a massive shift in the workforce. Millions of Americans have walked away from their jobs, creating a labor market squeeze that’s unlike anything we’ve seen before.
The pandemic, burnout, and a desire for better opportunities are just some of the factors fueling this trend. This “Great Resignation,” as it’s been dubbed, has left employers scrambling to fill open positions and has reshaped the power dynamic between workers and companies.
The implications of this mass exodus are far-reaching. Businesses are struggling to keep up with demand, wages are rising, and the very nature of work is being redefined. We’re witnessing a historic moment, one that will likely have lasting effects on the economy and society as a whole.
The Great Resignation

The year 2021 witnessed a historic shift in the American labor market, with a record number of workers voluntarily leaving their jobs. This phenomenon, dubbed “The Great Resignation,” signaled a fundamental change in employee attitudes and expectations, forcing businesses to re-evaluate their strategies for attracting and retaining talent.
Factors Driving the Great Resignation
The Great Resignation was driven by a confluence of factors, reflecting a growing sense of dissatisfaction and a desire for greater control over one’s work life.
With a record number of American workers quitting their jobs, it’s clear the labor market is in a squeeze. Employers are scrambling to fill positions, leading to higher wages and more benefits. But with all this economic upheaval, you might be wondering, should you be worried about your money in the bank – experts sound off.
The good news is, this tight labor market can actually be good for your finances, as workers gain more leverage to negotiate better pay and benefits.
- Burnout:The pandemic’s relentless stress and demands led to widespread burnout, with many employees feeling overwhelmed and exhausted.
- Dissatisfaction with Work-Life Balance:The blurring of lines between work and personal life during the pandemic heightened awareness of work-life balance issues, leading many to prioritize their well-being.
- Desire for Better Opportunities:The pandemic forced many to re-evaluate their career paths, leading them to seek out jobs with higher pay, greater flexibility, and better benefits.
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic played a pivotal role in shaping the Great Resignation. It forced many employees to re-evaluate their priorities and consider alternative career paths.
- Remote Work:The widespread adoption of remote work during the pandemic provided employees with a taste of flexibility and autonomy, making them less willing to return to traditional office settings.
- Economic Uncertainty:The pandemic’s economic impact led many to seek out more secure and financially rewarding opportunities, particularly in industries that thrived during the pandemic, such as technology and healthcare.
- Shifting Priorities:The pandemic forced many to confront their mortality and re-evaluate their priorities, leading some to pursue more fulfilling and meaningful careers.
The Labor Market Squeeze: Record Number Of American Workers Quit Their Jobs Signaling Labor Market Squeeze

The American labor market is experiencing a dramatic shift, characterized by a persistent shortage of skilled workers and an unprecedented demand for employees. This phenomenon, often referred to as the “labor market squeeze,” has far-reaching implications for businesses, workers, and the overall economy.
Historical Context of Labor Market Dynamics
The current labor market squeeze is a stark departure from historical trends. Traditionally, periods of economic expansion have been accompanied by a rise in unemployment, as businesses expand and hire new workers. However, the current situation is unique, with unemployment rates at historically low levels despite strong economic growth.
It’s a crazy time in the job market right now, with record numbers of Americans quitting their jobs. It’s a clear sign of a labor market squeeze, with workers feeling empowered to demand better conditions. This trend is especially interesting considering the recent news of an Iowa woman arrested for voter fraud scheme , which highlights the importance of maintaining trust in our institutions.
Ultimately, both situations speak to a larger societal shift, with individuals seeking more agency and control over their lives, whether in the workplace or the voting booth.
This divergence from historical patterns suggests a fundamental shift in the dynamics of the labor market.
Industries and Occupations Most Affected by the Labor Shortage
The labor shortage is not affecting all industries and occupations equally. Some sectors, particularly those requiring specialized skills and expertise, are facing the most acute challenges. The following industries and occupations are among those most impacted by the labor shortage:
- Healthcare:The aging population and increasing demand for healthcare services have created a significant shortage of nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals. This shortage is particularly pronounced in rural areas and underserved communities.
- Technology:The rapid growth of the tech industry has fueled a high demand for software engineers, data scientists, and other tech professionals. This demand has outpaced the supply of qualified candidates, leading to intense competition for talent and high salaries.
- Construction:The construction industry is facing a shortage of skilled tradespeople, such as electricians, plumbers, and carpenters. This shortage is attributed to a decline in apprenticeship programs and a growing preference for white-collar jobs among young people.
- Transportation and Logistics:The growth of e-commerce and the increasing reliance on supply chains have created a shortage of truck drivers, warehouse workers, and other logistics professionals. This shortage is exacerbated by long hours, low pay, and the difficulty of finding affordable housing in many areas.
Employer Responses to the Labor Squeeze
The Great Resignation has forced employers to rethink their strategies for attracting and retaining talent. The tight labor market has made it more challenging to find qualified candidates, and employees have more leverage than ever before. As a result, many employers are implementing new strategies to address the labor shortage.
Higher Wages
Increased wages are a direct response to the rising cost of living and the increased competition for talent. Many employers are offering higher starting salaries and bonuses to attract new hires. They are also increasing wages for existing employees to retain them.
According to a study by the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB), 44% of small businesses reported raising wages in the first quarter of 2023.
Improved Benefits
Employers are also offering more comprehensive benefits packages to attract and retain workers. These benefits may include health insurance, paid time off, retirement plans, and tuition reimbursement. Some companies are also offering unique benefits, such as pet insurance, childcare assistance, and employee discounts.
For example, Amazon recently announced that it would offer a $4,000 college tuition benefit to its employees.
Flexible Work Arrangements
The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work and flexible work arrangements. Many employers are now offering hybrid work models, where employees can work from home part-time. Others are offering fully remote work options. Flexible work arrangements can be a major draw for employees, especially those with families or other commitments.
Increased Training and Development
Employers are also investing more in training and development programs to upskill their workforce. This can help to improve employee retention and prepare workers for future roles. Training and development programs can include online courses, mentoring programs, and on-the-job training.
For example, Walmart has invested heavily in training programs for its employees, including a new program that teaches employees how to use technology to improve customer service.
Improved Work-Life Balance, Record number of american workers quit their jobs signaling labor market squeeze
Employers are also focusing on improving work-life balance for their employees. This can include offering more paid time off, flexible work hours, and on-site childcare. Improved work-life balance can help to reduce employee stress and burnout, which can lead to higher retention rates.
For example, Google has a number of initiatives to support employee well-being, including on-site childcare, fitness centers, and subsidized meals.
Enhanced Company Culture
Employers are also working to create a more positive and inclusive company culture. This can include initiatives such as diversity and inclusion programs, employee recognition programs, and social events. A positive company culture can help to attract and retain employees, as it creates a sense of belonging and purpose.
The record number of American workers quitting their jobs signals a labor market squeeze, but it also reveals something deeper. The frustration and dissatisfaction driving these decisions are often fueled by misinformation and a sense of powerlessness, echoing the themes explored in the disinformation industrial complex vs domestic terror.
This disconnect between the individual and the system they feel trapped within can be a breeding ground for discontent, further exacerbating the challenges of a tight labor market.
For example, Patagonia is known for its strong company culture, which is focused on sustainability and environmentalism.
Employee Perspectives on the Labor Market
The Great Resignation has brought a seismic shift in the power dynamics of the labor market. Employees, empowered by a tight labor market and a newfound sense of agency, are re-evaluating their priorities and demanding more from their employers. This section delves into the perspectives of employees, exploring their motivations for quitting, their expectations for new employment, and the impact of the labor market squeeze on their bargaining power and job satisfaction.
Motivations for Quitting
The reasons behind employees leaving their jobs are diverse and complex. While some may seek higher salaries or better benefits, others prioritize work-life balance, career growth opportunities, or a more fulfilling work environment.
- Higher Salaries and Benefits:The tight labor market has given employees leverage to negotiate higher salaries and better benefits. Many workers are leaving jobs that do not offer competitive compensation packages to pursue opportunities that meet their financial needs.
- Improved Work-Life Balance:The pandemic has forced many to re-evaluate their priorities, leading many to seek jobs that offer more flexibility and a better work-life balance. This includes remote work options, flexible schedules, and generous paid time off.
- Career Growth Opportunities:Employees are increasingly looking for jobs that offer clear career paths and opportunities for advancement. This may include mentorship programs, training opportunities, and the potential for promotions.
- More Meaningful Work:The desire for a more fulfilling work experience has become increasingly important for many employees. They seek jobs that align with their values and provide a sense of purpose.
Expectations and Priorities in Job Search
Employees are now more discerning in their job search, prioritizing factors that align with their personal and professional goals.
- Competitive Salaries and Benefits:Employees expect competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages that include health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
- Flexible Work Arrangements:Remote work options, flexible schedules, and the ability to work from anywhere are becoming increasingly important for many employees.
- Career Growth Opportunities:Employees seek employers who offer clear career paths, mentorship programs, and opportunities for professional development.
- Strong Company Culture:Employees value companies with a positive and inclusive work environment that fosters collaboration, communication, and respect.
- Work-Life Balance:Employees are looking for jobs that allow them to maintain a healthy work-life balance, with generous paid time off, flexible schedules, and supportive policies.
Impact on Employee Bargaining Power and Job Satisfaction
The labor market squeeze has significantly impacted employee bargaining power and job satisfaction.
- Increased Bargaining Power:Employees have more leverage to negotiate better salaries, benefits, and working conditions. This is due to the high demand for workers and the low unemployment rate.
- Higher Job Satisfaction:Employees are more likely to be satisfied with their jobs when they feel valued, respected, and compensated fairly. The current labor market empowers employees to seek out employers who meet their needs and priorities.
- Greater Job Security:Employees have more job security in a tight labor market. Employers are less likely to lay off workers due to the difficulty of finding replacements.
Economic and Social Implications
The Great Resignation, characterized by a record number of workers quitting their jobs, has far-reaching economic and social implications. This mass exodus has created a labor shortage, impacting businesses across various industries and potentially altering the future of work.
Economic Consequences
The labor shortage has significant economic consequences, impacting productivity, inflation, and economic growth.
- Reduced Productivity:With fewer workers available, businesses may struggle to maintain their output levels, leading to reduced productivity. This can impact economic growth and competitiveness. For example, a shortage of skilled workers in the construction industry can lead to delays in projects, increasing costs and hindering overall economic development.
- Inflationary Pressures:The tight labor market can drive up wages, as employers compete for a limited pool of talent. This increased labor cost can contribute to inflation, as businesses pass on higher expenses to consumers through increased prices. This can create a vicious cycle, as higher prices lead to demands for higher wages, further fueling inflation.
- Slower Economic Growth:The combination of reduced productivity and inflationary pressures can hinder economic growth. With businesses operating at lower capacity and consumers facing higher prices, overall economic activity may slow down. For instance, a shortage of qualified engineers in the technology sector can limit innovation and slow down the development of new products and services, impacting economic growth.
Social Implications
The Great Resignation has also brought about significant social changes, impacting work-life balance, social mobility, and income inequality.
- Shifting Work-Life Balance:Many workers have used the Great Resignation as an opportunity to prioritize their well-being and seek jobs that offer better work-life balance. This has led to increased demand for flexible work arrangements, remote work options, and shorter workweeks. This shift in priorities can have a positive impact on employee well-being, but it may also require businesses to adapt their operations to accommodate these new demands.
- Social Mobility:The labor shortage has created opportunities for workers to move into higher-paying jobs and advance their careers. This can promote social mobility, allowing individuals to improve their economic standing and access better opportunities. However, it’s crucial to ensure that these opportunities are accessible to all, regardless of their background or prior experience.
- Income Inequality:The tight labor market can exacerbate income inequality, as workers in high-demand fields see their wages increase while those in lower-demand fields may struggle to keep up. This can create a widening gap between the wealthy and the poor, requiring policies aimed at addressing this issue, such as increasing the minimum wage or providing job training programs.
Long-Term Effects on the Workforce
The Great Resignation has the potential to reshape the future of work, leading to long-term changes in the workforce.
- Increased Demand for Skills:The labor shortage has highlighted the importance of specialized skills and knowledge. Businesses are increasingly seeking workers with specific technical abilities, digital literacy, and problem-solving skills. This will likely lead to a greater focus on education and training programs that equip individuals with the skills needed to thrive in the evolving job market.
- Rise of the Gig Economy:The flexibility and autonomy offered by the gig economy have become more appealing to workers, particularly in the wake of the pandemic. This trend is likely to continue, with more individuals opting for freelance work or contract-based employment. This shift will require businesses to adapt their hiring practices and embrace new models of work.
- Greater Focus on Employee Well-being:The Great Resignation has shown that employees prioritize their well-being and seek employers who offer supportive work environments. This has led to a growing emphasis on employee mental health, work-life balance, and workplace culture. Businesses that fail to adapt to these changing expectations may struggle to attract and retain talent.
Outcome Summary
The “Great Resignation” is a complex phenomenon with no easy answers. It’s a reflection of changing priorities, a desire for more control, and a growing awareness of our own value. Whether this trend continues or eventually subsides, one thing is certain: the workplace is changing, and workers are demanding more.
This is a story that will continue to unfold, and it’s one that we should all be paying attention to.