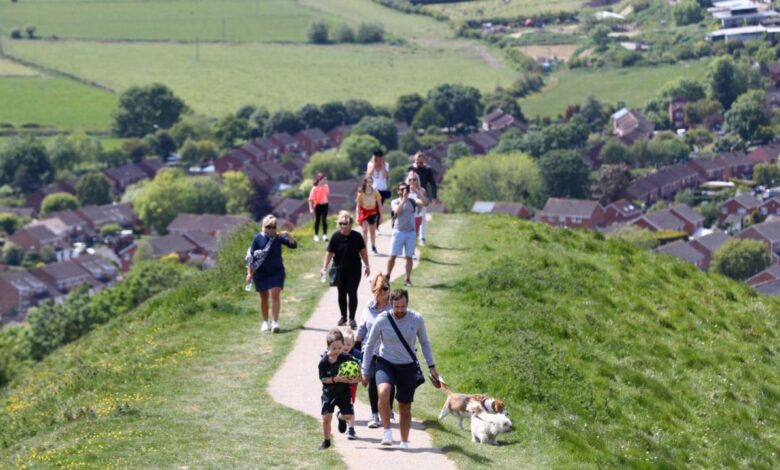
Public Resistance Might Stop the Next Lockdown
Public resistance might stop the next lockdown. This idea, once a fringe thought, is now being whispered in hushed tones across the internet and in living rooms around the world. The pandemic has shown us that the public isn’t always willing to accept the mandates of governments, even when those mandates are presented as necessary for public health.
We’ve seen protests, civil disobedience, and even outright defiance of lockdown measures, and this raises a crucial question: could public resistance become a powerful enough force to prevent future lockdowns?
This question is particularly relevant in a world where we are increasingly reliant on technology and globalized supply chains. Lockdowns, while intended to slow the spread of disease, have the potential to disrupt these systems and cause widespread economic and social upheaval.
It’s a complex issue, with no easy answers, but understanding the potential for public resistance is crucial to navigating this uncertain future.
Historical Context
Throughout history, public resistance has played a pivotal role in shaping societies and influencing government policies. From the American Revolution to the Civil Rights Movement, ordinary citizens have risen up to challenge the status quo and demand change. These acts of resistance, often driven by a desire for freedom, justice, or equality, have had a profound impact on the course of history.
Examples of Public Resistance Throughout History
Public resistance has taken many forms, from peaceful protests and civil disobedience to armed rebellion. Each form has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the effectiveness of any given resistance movement depends on a variety of factors, including the nature of the government, the level of public support, and the strategies employed by the resisters.
- The American Revolution (1775-1783): This iconic struggle for independence was sparked by British colonial policies that were seen as oppressive and unjust. The colonists, through a combination of protests, boycotts, and ultimately armed rebellion, successfully secured their independence from British rule.
- The Indian Independence Movement (1920-1947): This movement, led by Mahatma Gandhi, employed nonviolent resistance, including civil disobedience and boycotts, to achieve independence from British colonial rule. Gandhi’s strategy, which drew inspiration from the teachings of Henry David Thoreau and Leo Tolstoy, proved highly effective in mobilizing public opinion and putting pressure on the British government.
- The Civil Rights Movement (1954-1968): This movement, which sought to end racial segregation and discrimination in the United States, employed a variety of tactics, including protests, sit-ins, and boycotts. The movement, led by figures such as Martin Luther King Jr., was successful in achieving landmark legislation that outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
Instances Where Public Resistance Effectively Prevented or Altered Government Actions
- The Tiananmen Square Protests (1989): While the protests were ultimately crushed by the Chinese government, they served as a powerful symbol of public resistance against authoritarian rule. The protests, which were sparked by the death of a prominent reformer, brought international attention to the issue of human rights in China and led to increased pressure on the Chinese government to reform.
- The Arab Spring (2010-2012): This wave of protests and uprisings, which swept across the Middle East and North Africa, led to the overthrow of several authoritarian regimes. The protests, which were largely fueled by social media and the desire for democracy and economic opportunity, demonstrated the power of popular mobilization in challenging entrenched power structures.
- The Black Lives Matter Movement (2013-present): This movement, which seeks to address systemic racism and police brutality against Black people, has been a powerful force for social change in the United States. The movement, which has organized protests, boycotts, and other forms of resistance, has raised awareness of racial injustice and led to policy changes in some cities and states.
Comparison and Contrast of the Effectiveness of Different Forms of Resistance
The effectiveness of different forms of resistance depends on a variety of factors, including the context in which they are used, the goals of the resisters, and the response of the government.
The idea that public resistance might stop the next lockdown is gaining traction, and it’s easy to see why. People are tired of restrictions, and they’re starting to feel like their voices aren’t being heard. This sentiment is echoed in the political sphere, as evidenced by the recent call to action from the GOP panel chair demanding a solution to the dire border situation, which has become a major point of contention.
If people feel like their concerns are being ignored, it’s likely they’ll be even more resistant to future lockdowns, no matter how dire the circumstances may seem.
- Protests: Protests are a common form of public resistance that can be used to raise awareness of a particular issue, mobilize public opinion, and put pressure on government officials. Protests can be effective in achieving specific goals, such as the passage of legislation or the removal of a particular official.
However, protests can also be met with violence or repression by the government, which can limit their effectiveness.
- Civil disobedience: Civil disobedience is a form of resistance that involves breaking the law in a nonviolent manner. Civil disobedience can be an effective way to challenge unjust laws and policies, but it can also be risky, as resisters may face arrest and punishment.
- Boycotts: Boycotts are a form of economic resistance that involves refusing to buy or use goods or services from a particular company or country. Boycotts can be effective in putting pressure on businesses and governments to change their policies, but they can also be difficult to sustain over the long term.
The Nature of Lockdowns

Lockdowns, a controversial public health measure, have become a defining feature of the COVID-19 pandemic. While they have been implemented globally with the aim of slowing the spread of the virus, their effectiveness and consequences have been subject to intense debate.
It’s fascinating to see how public resistance can influence major decisions, like the possibility of stopping the next lockdown. It’s a reminder that we all have a voice, and that even seemingly small acts of defiance can have a ripple effect.
But while we’re focused on larger societal issues, it’s important to stay grounded in our own lives. News like Wells Fargo warning customers of incorrect balances or missing transactions reminds us that individual concerns still matter, and that even in the face of collective action, we need to be vigilant about our personal finances and well-being.
Perhaps the same spirit of resistance that could stop a lockdown could also inspire us to demand better from our institutions and hold them accountable for their actions.
Understanding the rationale behind lockdowns, their economic and social impacts, and their potential benefits and drawbacks is crucial for evaluating their role in pandemic response.
Rationale Behind Lockdowns
Lockdowns are implemented to reduce the transmission of infectious diseases by limiting social interactions and physical contact. The rationale behind this approach is based on the concept of “flattening the curve,” which aims to slow the rate of new infections to prevent overwhelming healthcare systems.
By reducing the number of people who can spread the virus, lockdowns can buy time for healthcare providers to prepare, develop treatments, and potentially create a vaccine.
Economic and Social Consequences of Lockdowns
Lockdowns have far-reaching economic and social consequences. The restrictions on businesses and movement can lead to widespread job losses, business closures, and economic recession. The disruption of education, social gatherings, and essential services can also have significant social and psychological impacts, leading to increased stress, isolation, and mental health issues.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Lockdowns in Different Contexts
The effectiveness of lockdowns in different contexts can vary depending on factors such as the severity of the outbreak, the population density, and the level of compliance with restrictions.
- In areas with high transmission rates, lockdowns can be effective in reducing the spread of the virus, particularly in the early stages of an outbreak.
- However, lockdowns can also have unintended consequences, such as increasing poverty and inequality, exacerbating mental health issues, and leading to a decline in public trust in government.
- The potential benefits and drawbacks of lockdowns need to be carefully weighed against each other, taking into account the specific context and the potential risks and consequences.
Public Resistance to Lockdowns: Public Resistance Might Stop The Next Lockdown
The imposition of lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic triggered widespread public resistance, a phenomenon with diverse motivations and complex implications. While the primary goal of lockdowns was to curb the spread of the virus, the restrictions imposed on individual liberties and economic activities sparked significant opposition.
This section explores the multifaceted nature of public resistance to lockdowns, examining the arguments used by those who opposed them and the ethical considerations surrounding the use of such measures.
Motivations for Public Resistance
The decision to implement lockdowns, despite their potential benefits in slowing the spread of disease, was met with considerable opposition. This resistance stemmed from a confluence of factors, including:
- Economic Concerns:Lockdowns imposed significant economic hardships, leading to widespread job losses, business closures, and financial instability. Many individuals and businesses argued that the economic consequences of lockdowns outweighed the potential benefits in terms of public health.
- Individual Liberty:Lockdowns imposed restrictions on individual freedoms, including the right to movement, assembly, and association.
Many individuals felt that these restrictions were excessive and violated their fundamental rights.
- Scientific Uncertainty:The scientific understanding of the virus and the effectiveness of lockdowns was evolving rapidly. Some individuals questioned the scientific basis for lockdowns, arguing that the evidence was inconclusive or that alternative strategies might be more effective.
- Government Overreach:The implementation of lockdowns raised concerns about government overreach and the potential for abuse of power. Some individuals argued that the government was using the pandemic as an opportunity to expand its control over citizens’ lives.
- Social and Psychological Impacts:Lockdowns had significant social and psychological impacts, leading to increased isolation, loneliness, and mental health problems.
Many individuals argued that the negative consequences of lockdowns on mental well-being outweighed the potential benefits.
Arguments Against Lockdowns
Individuals and groups opposing lockdowns employed a range of arguments, often challenging the effectiveness of lockdowns, highlighting their negative consequences, and emphasizing the importance of individual liberty.
- Lockdowns Ineffectiveness:Some argued that lockdowns were ineffective in controlling the spread of the virus, pointing to studies suggesting that lockdowns had minimal impact on mortality rates.
- Economic Damage:Opponents emphasized the severe economic consequences of lockdowns, arguing that the damage to businesses and livelihoods outweighed the potential benefits in terms of public health.
- Violation of Rights:Many argued that lockdowns violated fundamental rights, such as the right to movement, assembly, and association. They emphasized the importance of individual liberty and the right to make personal choices regarding health and safety.
- Unintended Consequences:Opponents highlighted the potential unintended consequences of lockdowns, such as increased domestic violence, mental health problems, and disruptions to education and healthcare services.
- Alternative Strategies:Some advocated for alternative strategies, such as targeted interventions, focusing on vulnerable populations and emphasizing personal responsibility and hygiene practices.
Ethical Considerations
The use of public health measures that restrict individual liberties, such as lockdowns, raises complex ethical considerations.
- Balancing Individual Rights and Public Health:The ethical dilemma lies in balancing the need to protect individual liberties with the responsibility to safeguard public health.
- Proportionality of Restrictions:The extent to which individual liberties can be restricted for public health purposes requires careful consideration. Restrictions should be proportionate to the threat posed by the disease and should be implemented only when necessary.
- Transparency and Accountability:Public health measures should be implemented with transparency and accountability. The public should be informed about the rationale behind the measures, the evidence supporting their effectiveness, and the potential consequences of their implementation.
- Respect for Autonomy:Individuals should be respected as autonomous agents capable of making informed decisions about their own health and well-being.
Potential Impacts of Resistance
Public resistance to lockdowns is a complex phenomenon with potential ramifications that extend beyond the immediate issue of preventing a lockdown. The effectiveness of resistance depends on various factors, including the level of public mobilization, the government’s response, and the broader political and social context.
Potential Scenarios for Successful Resistance
The success of public resistance in preventing a lockdown hinges on several key factors.
- Widespread Public Mobilization:A large-scale and sustained mobilization of the public, encompassing diverse groups and perspectives, is crucial. This can create a powerful social pressure that makes it difficult for governments to impose restrictions.
- Effective Communication and Organization:A coordinated effort involving clear communication, effective organization, and the use of various platforms to disseminate information and mobilize support is essential.
- Political Pressure:Public resistance can exert significant political pressure on governments, forcing them to reconsider lockdown measures or risk losing public support. This pressure can be amplified through protests, petitions, and engagement with elected officials.
- Legal Challenges:Legal challenges to lockdown measures, based on constitutional rights or scientific evidence, can create legal hurdles for governments and potentially delay or prevent their implementation.
Factors Contributing to Success or Failure
The success or failure of resistance efforts is influenced by several factors:
- Level of Public Support:The level of public support for resistance is a crucial determinant of its effectiveness. If a large majority of the population opposes lockdowns, governments are more likely to reconsider their policies.
- Government Response:The government’s response to resistance can significantly influence its trajectory. A government that is willing to engage with public concerns and consider alternative approaches is more likely to be persuaded to avoid lockdowns.
- Media Coverage:Media coverage plays a critical role in shaping public opinion and influencing government decision-making. Positive media coverage of resistance efforts can help to build public support and pressure governments to reconsider their policies.
- Economic and Social Impacts:The potential economic and social impacts of lockdowns can influence public sentiment and motivate resistance. If people perceive the economic and social costs of lockdowns to be too high, they are more likely to oppose them.
Hypothetical Scenario of Successful Resistance, Public resistance might stop the next lockdown
Imagine a scenario where a government announces plans to impose a lockdown in response to a surge in COVID-19 cases. However, a large-scale public resistance movement emerges, mobilizing people across various sectors and demographics.
- Protests and Demonstrations:Large-scale protests and demonstrations take place across the country, highlighting the economic and social consequences of lockdowns and demanding alternative measures.
- Legal Challenges:Legal challenges are filed, arguing that the lockdown measures violate constitutional rights or lack scientific justification.
- Political Pressure:The resistance movement exerts significant political pressure on the government, with elected officials facing growing public opposition to the proposed lockdown.
- Media Coverage:Media coverage of the resistance movement is extensive, highlighting the public’s concerns and the government’s response. This media attention helps to mobilize public support and amplify the pressure on the government.
- Government Response:Faced with widespread public opposition, legal challenges, and political pressure, the government reconsiders its plans to impose a lockdown. Instead, it adopts a more nuanced approach, focusing on targeted interventions and encouraging individual responsibility.
The Role of Government and Public Health Officials
In times of public health crises, governments and public health officials bear the weighty responsibility of safeguarding the well-being of their citizens. This involves balancing the need for public health measures with the protection of individual liberties, a complex task that often sparks public debate and resistance.
It’s becoming increasingly clear that public resistance might be the only thing standing between us and another lockdown. We’ve seen the backlash against mandates and restrictions, and the growing distrust of government overreach. This same spirit of defiance is evident in the reaction to the potential ATF expansion, as seen in the article gun owners of america aghast at potential atf expansion.
This shows that people are ready to fight for their freedoms, and that’s a powerful force that could very well stop the next lockdown in its tracks.
Strategies for Mitigating Public Resistance
Governments and public health officials can adopt several strategies to mitigate public resistance to lockdowns. Transparency and open communication are paramount. Providing clear and consistent information about the nature of the crisis, the rationale behind public health measures, and the potential consequences of non-compliance can foster public trust and understanding.
- Engaging with the Public:Public health officials should actively engage with the public, seeking input and addressing concerns. This can involve town hall meetings, online forums, and community outreach programs.
- Tailoring Measures:Lockdown measures should be tailored to local circumstances, taking into account factors such as population density, healthcare infrastructure, and the prevalence of the virus. This approach can demonstrate responsiveness and sensitivity to community needs.
- Targeted Messaging:Public health campaigns should employ targeted messaging that resonates with different demographics and addresses specific concerns. This might involve leveraging social media, community leaders, and trusted messengers.
- Emphasizing Benefits:Public health officials should emphasize the benefits of lockdown measures, such as reducing transmission rates, protecting vulnerable populations, and preventing healthcare systems from being overwhelmed.
- Transparency and Accountability:Governments and public health officials should be transparent about their decision-making processes and accountable for their actions. This includes providing regular updates on the situation, acknowledging uncertainties, and being receptive to criticism.
Potential Compromises and Alternative Solutions
Recognizing the impact of lockdowns on individual liberties and the economy, governments and public health officials should explore compromises and alternative solutions.
- Targeted Restrictions:Instead of broad lockdowns, governments could implement targeted restrictions on high-risk activities or locations, such as bars, nightclubs, or large gatherings. This approach could minimize disruption to daily life while addressing specific transmission hotspots.
- Voluntary Measures:Encouraging voluntary compliance with public health guidelines, such as mask-wearing and social distancing, can be more effective than mandatory measures in the long term. This requires promoting personal responsibility and community cooperation.
- Financial Support:Governments should provide financial support to individuals and businesses affected by lockdowns, helping to mitigate economic hardship and fostering public cooperation. This could include unemployment benefits, business loans, and rent assistance.
- Focus on Vaccination and Treatment:Public health efforts should prioritize vaccination and the development of effective treatments, ultimately reducing the need for lockdowns. This involves investing in research, promoting vaccine uptake, and ensuring equitable access to healthcare.
The Role of Media and Information
The media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion about lockdowns, influencing public resistance to them, and facilitating informed decision-making during public health emergencies. The flow of information, its accuracy, and the way it is presented can significantly impact public understanding and response to lockdowns.
The Influence of Media on Public Opinion
The media, through various platforms such as television, newspapers, social media, and online news outlets, has the power to influence public opinion about lockdowns.
- Framing of Information:The way information about lockdowns is framed can influence public perception. For example, emphasizing the economic consequences of lockdowns might lead to greater resistance, while highlighting the potential health benefits might encourage compliance.
- Selective Coverage:Media outlets may choose to focus on specific aspects of lockdowns, potentially neglecting others. This can lead to a biased view of the situation, shaping public opinion accordingly.
- Public Figures and Experts:Media coverage of public figures and experts, such as politicians, scientists, and healthcare professionals, can influence public trust and acceptance of lockdowns.
The Impact of Misinformation and Disinformation
Misinformation and disinformation, often spread through social media and other online platforms, can significantly influence public resistance to lockdowns.
- False Claims and Conspiracy Theories:Spreading false claims about the effectiveness of lockdowns or their underlying motives can erode public trust and encourage resistance.
- Exaggerated Risks and Benefits:Misinformation can exaggerate the risks associated with lockdowns or the benefits of alternative measures, leading to misinformed decisions.
- Social Media Algorithms:Social media algorithms can amplify misinformation by promoting content that aligns with users’ existing beliefs, creating echo chambers and reinforcing biases.
The Importance of Accurate and Reliable Information
Accurate and reliable information is crucial for facilitating informed decision-making during public health emergencies, such as pandemics.
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making:Accurate information allows individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being based on scientific evidence and expert guidance.
- Trust in Public Health Officials:Access to reliable information can foster trust in public health officials and their recommendations, increasing compliance with lockdown measures.
- Reduced Fear and Anxiety:Accurate information can help alleviate fear and anxiety by providing a clear understanding of the situation and the risks involved.
Final Summary
In a world where the line between individual liberty and public health is increasingly blurred, the potential for public resistance to shape the future of pandemic response is undeniable. Whether it’s through protests, online activism, or simply a collective refusal to comply, the public has a powerful voice in shaping the future.
The question is, will that voice be heard, and will it be strong enough to prevent future lockdowns? Only time will tell, but the potential for change is undeniable.