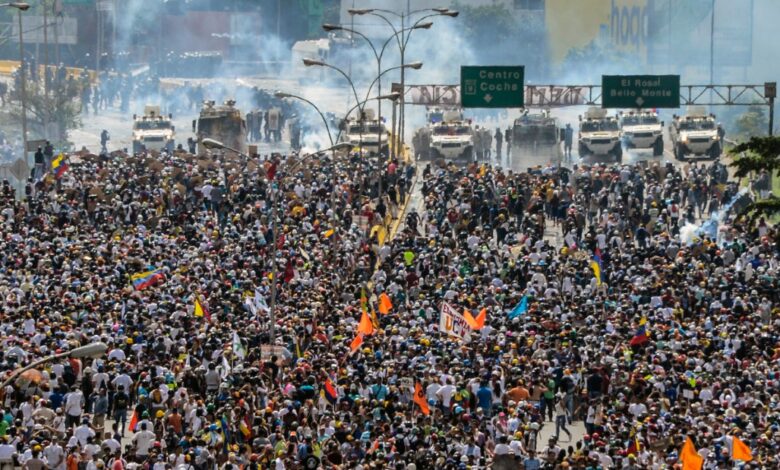
Venezuela Protests Erupt After Disputed Election
Protests erupt in Venezuela after disputed election results, igniting a volatile situation that has captured global attention. The recent election, marred by allegations of fraud and irregularities, has triggered widespread unrest, as citizens take to the streets to voice their dissent.
The country, already grappling with an economic crisis and political turmoil, finds itself at a crossroads, with the future hanging in the balance.
The protests, which began shortly after the election results were announced, have escalated rapidly, drawing in people from all walks of life. They are demanding transparency, accountability, and a democratic transition. The government, however, has responded with a heavy hand, deploying security forces to quell the demonstrations, leading to clashes and arrests.
The international community is watching closely, expressing concerns about the escalating violence and calling for dialogue and a peaceful resolution.
Background of the Venezuelan Election
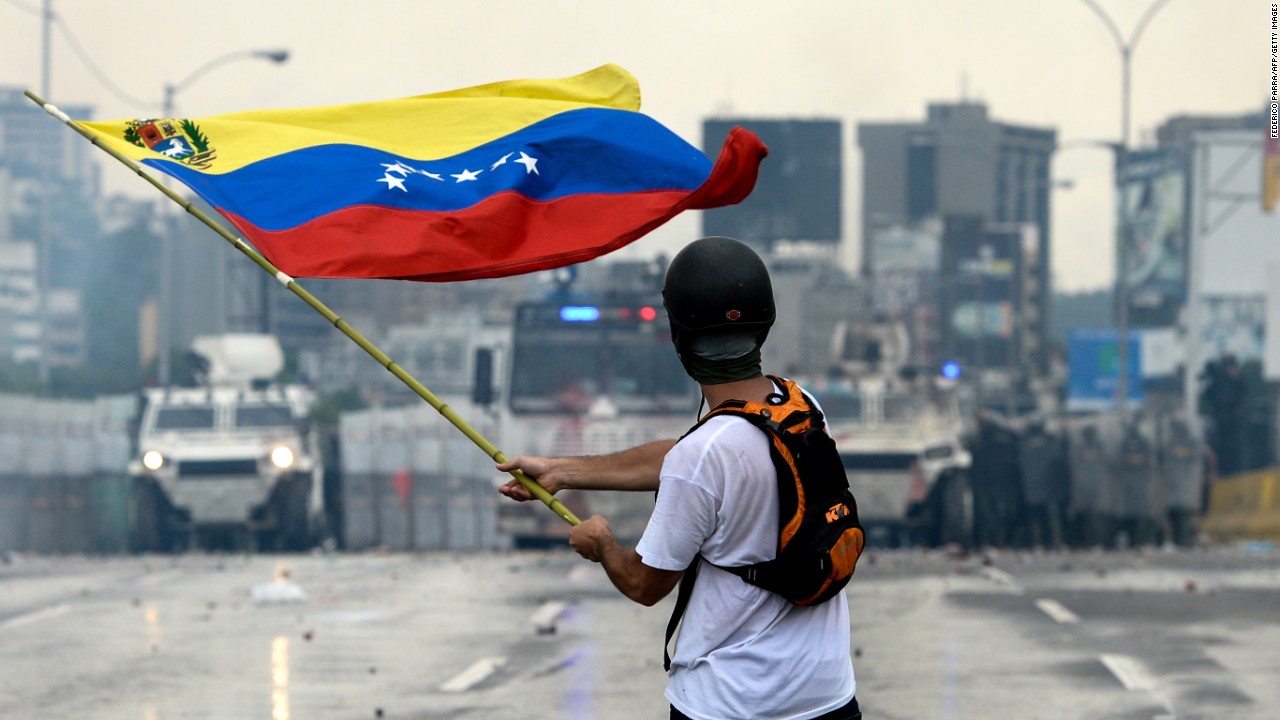

Venezuela’s 2020 presidential election, held amidst a prolonged political and economic crisis, was marred by controversy and accusations of irregularities. The election, widely considered to be a sham by the international community, saw Nicolás Maduro, the incumbent president, secure a second term in office.
Political Landscape and Candidates
Venezuela’s political landscape is characterized by deep divisions and a long history of political instability. The ruling United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV), led by Maduro, has been in power since 1999. The opposition, however, remains fragmented and has struggled to unite against the government.
The main opposition candidate in the 2020 election was Henri Falcón, a former governor of Lara state who had previously been a member of the PSUV.
Electoral Process and Allegations of Irregularities
The electoral process was widely criticized by international observers and opposition leaders, who alleged widespread fraud and manipulation.
- Opposition candidates were barred from running, including the popular leader Leopoldo López, who was under house arrest at the time.
- The National Electoral Council (CNE), which is controlled by the government, was accused of bias and irregularities.
- There were reports of voter intimidation and manipulation of the electoral system.
The international community, including the United States, the European Union, and the Organization of American States (OAS), condemned the election as undemocratic and illegitimate.
Historical Context of Political Unrest
Venezuela has a long history of political unrest and instability. The country has experienced numerous coups, uprisings, and periods of political violence. The current crisis began in 2014, with protests against Maduro’s government. The protests were met with a brutal crackdown by security forces, resulting in hundreds of deaths and thousands of arrests.
The Disputed Election Results
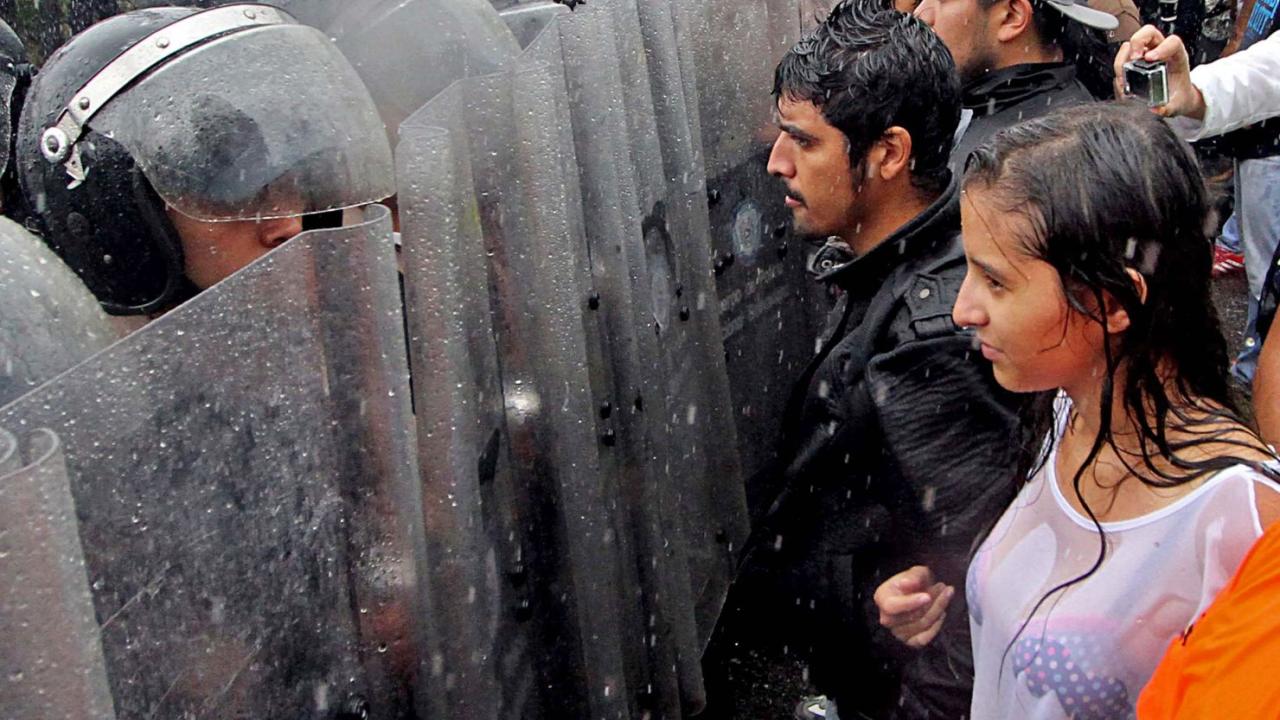

The Venezuelan presidential election of 2018 was marred by controversy, with widespread allegations of fraud and irregularities. The opposition boycotted the election, claiming it was rigged in favor of the incumbent, Nicolás Maduro.The official results declared by the Venezuelan National Electoral Council (CNE) showed Maduro winning with 67.8% of the vote, while his closest challenger, Henri Falcón, received 21.2%.
The CNE claimed a voter turnout of 66.2%, a figure that was disputed by many observers.
International Reactions to the Election Results
The international community reacted swiftly and decisively to the election results, with many countries condemning the process as undemocratic and illegitimate. The United States, Canada, and several European countries refused to recognize Maduro as the legitimate president, while the Organization of American States (OAS) and the European Union (EU) called for new elections.
- The United States imposed sanctions on Venezuela, targeting Maduro and his inner circle. The US also recognized Juan Guaidó, the leader of the opposition-controlled National Assembly, as the interim president of Venezuela.
- The European Union also imposed sanctions on Venezuelan officials, while several European countries, including Spain and France, recalled their ambassadors from Caracas.
- The OAS condemned the election as “illegitimate” and called for new elections under international observation.
Perspectives of the Ruling Party and the Opposition
The ruling socialist party, the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV), celebrated Maduro’s victory as a resounding endorsement of his policies. The PSUV maintained that the election was fair and transparent, and that the opposition’s boycott was an attempt to destabilize the country.The opposition, on the other hand, denounced the election as a sham and a blatant attempt by Maduro to consolidate his power.
They argued that the election was rigged, with the CNE manipulating the results in favor of Maduro. They also claimed that the election was marred by widespread intimidation and violence against opposition supporters.
Outbreak of Protests
The disputed election results sparked widespread protests across Venezuela, with citizens taking to the streets to voice their dissent. These protests, fueled by allegations of electoral fraud and a deep sense of injustice, quickly escalated, becoming a defining moment in the country’s political landscape.
Locations and Scale of Protests
Protests erupted in major cities and towns across Venezuela, with Caracas, the capital, witnessing some of the largest gatherings. The protests were characterized by their widespread nature, with demonstrations occurring in both urban and rural areas, highlighting the deep-seated discontent among the Venezuelan population.
Key Demands of the Protests
Protesters had a range of demands, unified by their desire for a democratic and just Venezuela. Some of the key demands included:
- Free and Fair Elections:Protesters demanded new elections, conducted with transparency and international observation, to ensure a fair and democratic outcome.
- Release of Political Prisoners:The release of political prisoners, who were detained for opposing the government, was a central demand, emphasizing the protesters’ call for respect for human rights and political freedom.
- End to Repression:Protesters demanded an end to the government’s crackdown on dissent, which included arbitrary arrests, intimidation, and violence against peaceful demonstrators.
- Humanitarian Aid:Protesters demanded the government allow humanitarian aid to enter the country, addressing the severe economic crisis and the growing humanitarian needs of the population.
Participating Groups and Motivations, Protests erupt in venezuela after disputed election results
The protests brought together a diverse range of groups, united by their shared dissatisfaction with the government and their desire for change. These included:
- Opposition Leaders and Parties:Opposition leaders, including Henrique Capriles Radonski and Leopoldo López, played a significant role in mobilizing and leading the protests. They used their platforms to denounce the election results and call for action.
- Student Groups:Students, particularly those from universities in Caracas and other major cities, were highly active in the protests, often leading marches and demonstrations. Their youthful energy and idealism fueled the movement, demanding a better future for their country.
- Civil Society Organizations:Non-governmental organizations, human rights groups, and labor unions joined the protests, advocating for democratic principles and a peaceful transition of power. They provided logistical support, documentation of human rights violations, and legal assistance to protesters.
- Ordinary Citizens:Ordinary Venezuelans, frustrated by the economic crisis, lack of basic necessities, and perceived corruption, joined the protests in large numbers. They sought a change in leadership and a return to democratic values.
Methods and Tactics of Protests
The protests were largely peaceful, with demonstrators using various methods to express their dissent:
- Marches and Demonstrations:Large-scale marches and demonstrations were held in major cities, with protesters carrying banners, chanting slogans, and expressing their grievances.
- Roadblocks and Protests:Protesters blocked roads and highways, creating a symbolic disruption of the government’s authority and drawing attention to their demands.
- Social Media Campaigns:Protests were amplified through social media, with hashtags and online campaigns spreading awareness and mobilizing support for the movement.
Government Response to Protests
The Venezuelan government, led by President Nicolás Maduro, responded to the protests with a mix of repression and attempts at appeasement. The government’s response was characterized by a heavy-handed approach, aimed at suppressing dissent and maintaining control.
Security Measures
The government deployed security forces, including the National Guard and the Bolivarian National Police, to quell the protests. These forces used tear gas, water cannons, and live ammunition to disperse protesters, resulting in numerous injuries and deaths. The government also implemented curfews and restrictions on movement, limiting the ability of protesters to gather and organize.
- Crackdowns and Arrests:Security forces conducted widespread crackdowns on protesters, arresting thousands of individuals. Many were detained without due process, and allegations of torture and mistreatment in detention centers were widespread. The government’s actions were widely condemned by human rights organizations as a violation of fundamental freedoms.
- Internet Shutdowns:The government resorted to internet shutdowns and restrictions on social media platforms, attempting to hinder the flow of information and communication among protesters. This strategy aimed to control the narrative and prevent the dissemination of images and videos documenting the government’s actions.
Communication Strategies
The government launched a counter-narrative campaign, accusing the protesters of being instigated by foreign powers and aiming to destabilize the country. They portrayed the protests as an attempt to overthrow the democratically elected government. The government also used state-controlled media outlets to broadcast pro-government messages and downplay the severity of the situation.
- State-Controlled Media:Government-controlled media outlets like VTV and Telesur played a significant role in shaping public opinion. These outlets presented a biased narrative, emphasizing the government’s efforts to maintain stability and portraying protesters as violent extremists.
- Social Media Propaganda:The government also employed social media platforms to spread propaganda and counter the narrative of the opposition. They used bots and fake accounts to amplify pro-government messages and discredit opposition figures.
International Reactions and Implications: Protests Erupt In Venezuela After Disputed Election Results
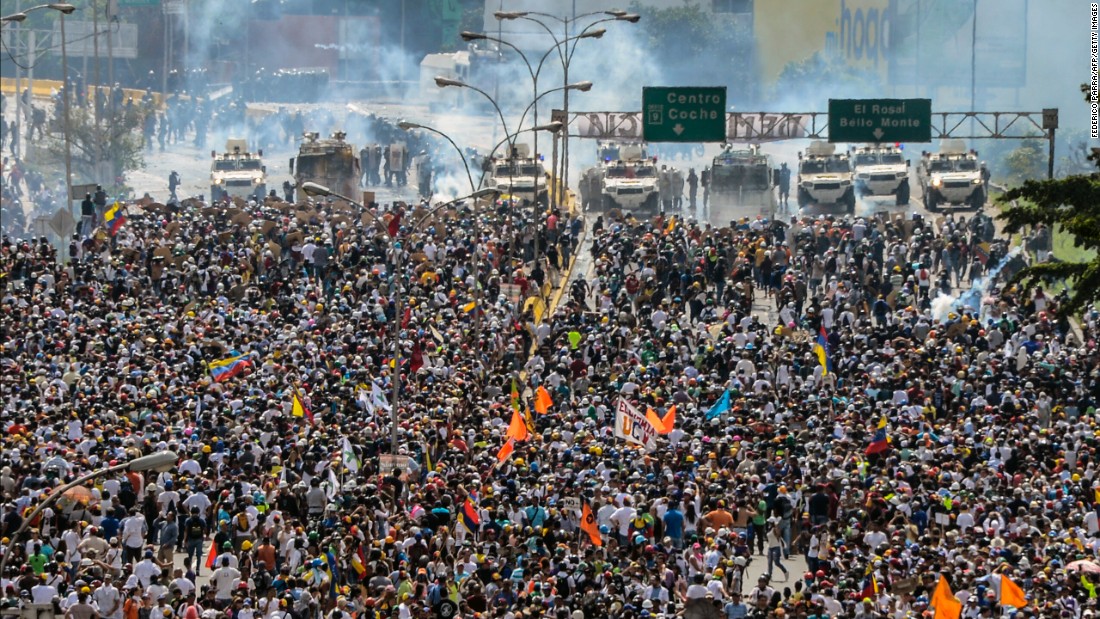

The disputed Venezuelan election results sparked widespread international condemnation and concerns about the future of democracy in the country. Numerous international actors, including governments, organizations, and individuals, voiced their disapproval and called for a peaceful resolution to the crisis. The situation has significant implications for regional and global stability, raising questions about the role of international organizations in mediating such crises.
International Reactions
The international community reacted swiftly and decisively to the disputed election results. Several countries, including the United States, Canada, and the European Union, condemned the election as illegitimate and called for a new, free, and fair election. These countries also imposed sanctions on Venezuelan officials, targeting their assets and travel.
- The United States, under President Donald Trump, imposed economic sanctions on Venezuela, including a ban on oil imports. The US government also recognized Juan Guaidó, the president of the National Assembly, as the interim president of Venezuela.
- The European Union also imposed sanctions on Venezuelan officials and called for a new election. The EU also offered humanitarian aid to Venezuela and urged the government to allow access to the country for international observers.
- Canada, a close ally of the United States, also condemned the election and imposed sanctions on Venezuelan officials. Canada also provided humanitarian aid to Venezuela and supported the efforts of the Organization of American States (OAS) to resolve the crisis.
Beyond these key actors, many other countries and organizations expressed their concerns about the situation in Venezuela. The United Nations Secretary-General, António Guterres, called for dialogue and a peaceful resolution to the crisis. The OAS also condemned the election and called for a new election.
Implications for Regional and Global Stability
The political and economic crisis in Venezuela has significant implications for regional and global stability. The crisis has led to a surge in migration from Venezuela to neighboring countries, straining their resources and social systems. The crisis has also fueled political instability in the region, with some countries aligning with the Venezuelan government and others supporting the opposition.
The streets of Venezuela are ablaze with protests after the recent election, a stark reminder of the growing dissatisfaction with the current political landscape. These protests are fueled by a deep sense of injustice, a feeling that the democratic process has been compromised, echoing the broader anxieties surrounding the the discrediting of free trade and its impact on developing nations.
The Venezuelan situation is a stark reminder of the fragility of democracy and the urgent need for fair and transparent elections, especially in a world where economic and political systems are under increasing pressure.
- The crisis has also contributed to the rise of organized crime and drug trafficking in the region. Venezuela’s porous borders and weak law enforcement have allowed criminal groups to flourish, posing a threat to regional security.
- The crisis has also implications for the global oil market. Venezuela is a major oil producer, and the country’s economic crisis has disrupted its oil production, leading to higher oil prices.
The crisis in Venezuela is a reminder of the importance of democratic institutions and the rule of law. It also highlights the challenges of managing political and economic crises in a globalized world.
The streets of Venezuela are boiling with anger after the disputed election results, a stark reminder of the fragility of democracy. While the world watches, it’s important to remember that fostering understanding and appreciation for diverse cultures can help build a more peaceful and inclusive future.
Check out these 18 Asian Pacific American Heritage Month activities for students to learn about the rich tapestry of Asian Pacific American history and culture. In a world grappling with conflict and division, it’s crucial to remember the power of education and understanding in fostering a more just and equitable society, both at home and abroad.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations have played a significant role in mediating the crisis in Venezuela. The OAS has been particularly active, condemning the election and calling for a new election. The UN has also played a role, providing humanitarian aid and urging dialogue between the government and the opposition.
- The OAS has been critical of the Venezuelan government, accusing it of human rights abuses and undermining democracy. The OAS has also called for the release of political prisoners and the restoration of democratic institutions.
- The UN has provided humanitarian aid to Venezuela, including food, medicine, and other essential supplies. The UN has also urged the government to allow access to the country for international observers and humanitarian organizations.
The role of international organizations in mediating the crisis in Venezuela is crucial. They can provide a platform for dialogue, promote human rights, and support the efforts of the Venezuelan people to achieve a peaceful and democratic transition.
Impact on the Venezuelan People
The disputed election results and subsequent protests have had a profound and multifaceted impact on the Venezuelan people, exacerbating existing social and economic hardships and undermining fundamental rights. The protests, while expressing dissent, have also become a flashpoint for violence and repression, further straining the fabric of Venezuelan society.
Social and Economic Consequences
The protests and the political uncertainty surrounding the election have had a devastating impact on the Venezuelan economy, already grappling with hyperinflation and shortages of basic goods. The economic crisis has led to widespread poverty, malnutrition, and a decline in access to essential services such as healthcare and education.
The protests have disrupted businesses and transportation, further hindering economic activity.
- Hyperinflation and Shortages:The Venezuelan economy has been in a state of hyperinflation for several years, with the value of the bolivar plummeting drastically. This has made it extremely difficult for people to afford basic necessities such as food, medicine, and transportation.
The streets of Caracas are ablaze with anger as Venezuelans protest the disputed election results, a stark reminder of the power of public dissent. It’s a stark contrast to the quiet turmoil Andy Dunn, co-founder of Bonobos, faced when his own mental health struggles nearly crippled his company, as detailed in this article.
Dunn’s story highlights the importance of acknowledging and addressing mental health challenges, not just in our personal lives, but also within the high-pressure world of business. While Venezuela’s political landscape remains volatile, the protests offer a powerful testament to the human spirit’s resilience in the face of injustice.
- Poverty and Malnutrition:The economic crisis has led to a sharp increase in poverty rates, with many Venezuelans struggling to make ends meet. This has also resulted in widespread malnutrition, particularly among children and vulnerable populations.
- Decline in Essential Services:The government’s inability to provide adequate funding has led to a decline in the quality and availability of essential services such as healthcare and education. Hospitals are often short of supplies, and schools are struggling to operate due to lack of resources.
Impact on Human Rights and Civil Liberties
The protests have been met with a heavy-handed response from the Venezuelan government, leading to widespread human rights violations. Security forces have used excessive force against protesters, resulting in injuries, deaths, and arbitrary detentions. The government has also cracked down on freedom of speech and assembly, silencing dissenting voices and limiting the ability of citizens to express their views.
- Excessive Force and Violence:Security forces have been accused of using excessive force and violence against protesters, including the use of tear gas, rubber bullets, and live ammunition. This has resulted in injuries, deaths, and arbitrary detentions.
- Restrictions on Freedom of Speech and Assembly:The government has cracked down on freedom of speech and assembly, silencing dissenting voices and limiting the ability of citizens to express their views. Journalists and human rights defenders have been harassed, intimidated, and detained.
- Arbitrary Detentions and Impunity:Many protesters have been arbitrarily detained and subjected to torture and ill-treatment. The government has also failed to hold security forces accountable for human rights violations, creating a culture of impunity.
Potential Long-Term Effects
The disputed election results and the subsequent protests have had a profound impact on Venezuelan society, with the potential to further exacerbate existing divisions and undermine the rule of law. The lack of political stability and the erosion of human rights have created a climate of fear and uncertainty, making it difficult to address the country’s many challenges.
- Erosion of Trust in Institutions:The disputed election results and the government’s response to protests have eroded trust in institutions, including the judiciary and electoral bodies. This has created a climate of distrust and suspicion, making it difficult to build consensus and address the country’s challenges.
- Increased Polarization and Division:The protests have further polarized Venezuelan society, deepening divisions between supporters and opponents of the government. This polarization has made it difficult to find common ground and build a shared future.
- Long-Term Economic and Social Instability:The continued political instability and economic crisis have the potential to lead to long-term economic and social instability, further exacerbating poverty, inequality, and human suffering.
Possible Resolutions and Future Outlook
The Venezuelan crisis, fueled by political and economic turmoil, demands multifaceted solutions. Finding a peaceful resolution is crucial to alleviate suffering and restore stability. This section explores potential paths forward, focusing on political dialogue, international mediation, and humanitarian assistance.
Potential Solutions to the Crisis
A comprehensive approach is needed to address the multifaceted crisis in Venezuela. Potential solutions include:
- Political Dialogue:Facilitating open and inclusive dialogue between the government and opposition is essential. This dialogue should address core issues such as electoral reforms, human rights, and economic policies. A neutral and trusted mediator could help facilitate this process.
- International Mediation:International actors, such as the United Nations or regional organizations, can play a crucial role in mediating a peaceful resolution. They can provide a platform for dialogue, monitor agreements, and offer technical assistance.
- Humanitarian Assistance:Addressing the humanitarian crisis is paramount. This includes providing food, medicine, and other essential supplies to those in need. International organizations and donor countries should work together to ensure timely and efficient delivery of aid.
The Potential for a Peaceful Resolution
While the path to peace is challenging, there is potential for a peaceful resolution. Examples from other countries, such as Colombia’s peace process, demonstrate that even in deeply divided societies, dialogue and compromise can lead to lasting peace. However, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Lack of Trust:Deep distrust between the government and opposition makes it difficult to establish meaningful dialogue. Building trust requires concrete steps, such as releasing political prisoners and ensuring the independence of institutions.
- Foreign Interference:External actors can exacerbate tensions and hinder progress towards a solution. A commitment from all parties to avoid foreign interference is crucial.
- Economic Challenges:The economic crisis in Venezuela creates a complex backdrop for any political solution. Addressing the economic crisis is essential for restoring stability and building a sustainable future.
The Future of Venezuela
The future of Venezuela depends on the ability of its leaders and citizens to overcome the current crisis. A peaceful resolution, based on dialogue and compromise, is essential for rebuilding the country and creating a better future for all Venezuelans.
End of Discussion
The protests in Venezuela, fueled by deep-seated grievances and a sense of disillusionment, highlight the fragility of democracy and the importance of free and fair elections. The situation is complex, with no easy solutions. The path forward will require a commitment to dialogue, respect for human rights, and a willingness to compromise.
Only through a peaceful and inclusive process can Venezuela hope to emerge from this crisis and rebuild its future.