Producer Prices Surge, Sparking Fears of Inflationary Rebound
Producer prices surge sparking fears of inflationary rebound takes center stage, a concerning trend that could ripple through the economy. This recent surge in the Producer Price Index (PPI), a key gauge of inflation at the wholesale level, is raising alarms about a potential resurgence of inflation.
The PPI increase reflects a complex interplay of factors, including supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and rising energy and commodity prices.
The implications of this surge are far-reaching, potentially impacting businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. While the Federal Reserve and other central banks have taken steps to curb inflation, the recent PPI spike suggests that the battle against inflation may not be over.
Producer Price Index (PPI) Surge: Producer Prices Surge Sparking Fears Of Inflationary Rebound
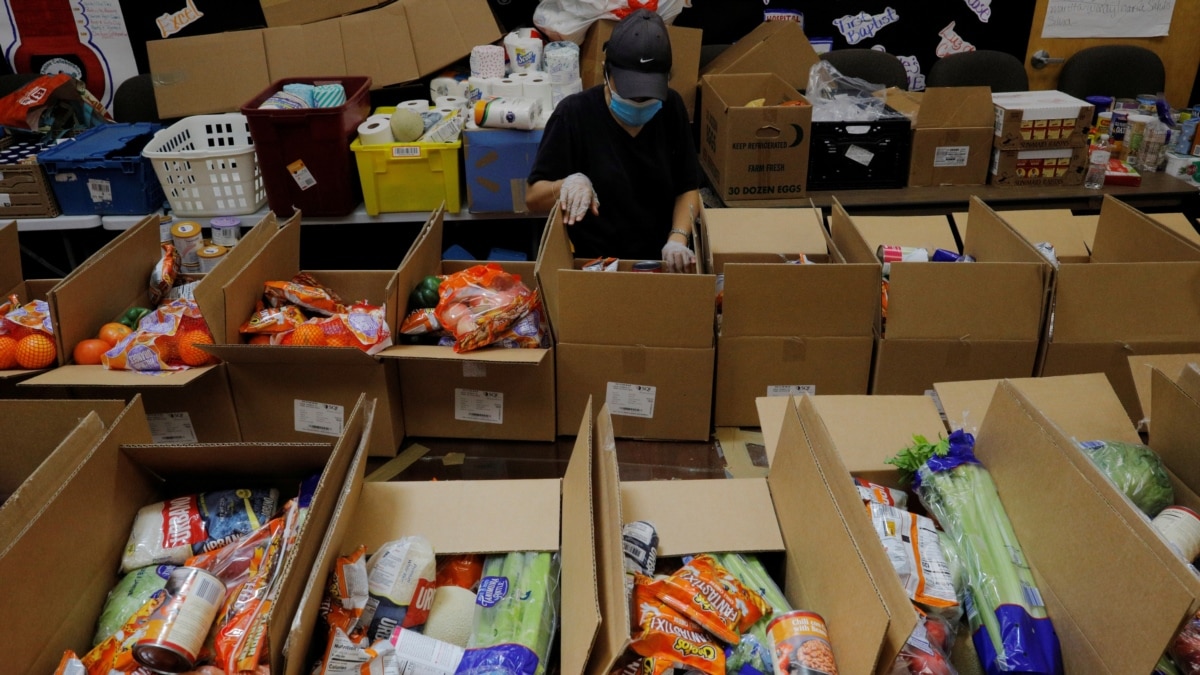

The Producer Price Index (PPI) has recently surged, raising concerns about a potential resurgence of inflation. This surge in PPI reflects a broad-based increase in prices across various sectors of the economy, indicating that businesses are facing higher costs for raw materials, labor, and transportation.
The recent surge in producer prices has sent shivers down the spines of economists, sparking fears of an inflationary rebound. It’s a tough time to be navigating the economic landscape, but it’s important to remember that we have the power to influence our own well-being.
A Harvard researcher suggests that adopting two simple mindset changes, which you can read about here , can help us weather these storms. By focusing on what we can control and fostering a sense of gratitude, we can navigate the uncertainties of the economy with greater resilience and optimism.
Ultimately, while the producer price index may be a cause for concern, it’s our individual choices and mindset that will shape our experience.
This trend has implications for consumer prices, as businesses may pass on these higher costs to consumers, leading to a rise in inflation.
The recent surge in producer prices has everyone on edge, sparking fears of an inflationary rebound. It’s a wild time for everyone, especially tech startups trying to navigate the economic uncertainty. For insights on navigating these turbulent waters, check out this great article about Madrona’s Tim Porter and his take on the current state of tech startups: wild times for tech startups making sense of the uncertainty with madronas tim porter.
With so much up in the air, understanding the challenges and opportunities facing the tech sector is crucial, and this article offers valuable perspectives on how to weather the storm.
Key Components Contributing to PPI Increase
The PPI increase is driven by a combination of factors, including rising energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and labor shortages.
- Energy Prices:Energy prices have been a significant driver of PPI inflation. The war in Ukraine has disrupted global energy markets, leading to a sharp increase in oil and natural gas prices. These higher energy prices have rippled through the economy, increasing the cost of transportation, manufacturing, and other industries.
The recent surge in producer prices is raising serious concerns about a potential inflationary rebound. This comes at a time when businesses are grappling with rising input costs and supply chain disruptions. Meanwhile, Fanatics, the sports merchandise giant, is bolstering its leadership team by adding a Softbank executive and former Airbnb marketing chief to its board of directors.
This move suggests that Fanatics is looking to expand its reach and capitalize on the growing demand for sports-related merchandise, even as the economic landscape remains uncertain.
- Food Prices:Food prices have also risen significantly, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions, rising fertilizer costs, and extreme weather events. The war in Ukraine has further exacerbated these pressures, as Russia and Ukraine are major exporters of wheat, corn, and other agricultural commodities.
- Materials Prices:Prices of key materials, such as lumber, steel, and semiconductors, have also increased. These increases are driven by supply chain bottlenecks, increased demand, and rising transportation costs.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions and Labor Shortages
Supply chain disruptions and labor shortages have also contributed to the PPI surge. The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted global supply chains, leading to delays in production and transportation. Labor shortages have also put upward pressure on wages, increasing costs for businesses.
Historical Trends in PPI and its Correlation with Consumer Price Inflation
Historically, the PPI has been a leading indicator of consumer price inflation. Increases in PPI often precede increases in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), as businesses pass on their higher costs to consumers. The correlation between PPI and CPI is not always perfect, but it is generally strong.
The PPI can be a valuable tool for policymakers and businesses to track inflation trends.
Inflationary Rebound Concerns

The recent surge in producer prices, as reflected in the Producer Price Index (PPI), has sparked fears of an inflationary rebound. While inflation has shown signs of cooling in recent months, this unexpected spike in input costs raises concerns that the fight against inflation may not be over yet.
Potential Factors Contributing to Inflationary Rebound
The PPI surge raises concerns about a potential inflationary rebound due to several factors. These include:
- Rising Wages:A tight labor market and ongoing wage pressures could fuel inflationary pressures as businesses pass on higher labor costs to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Demand Pressures:Continued strong consumer demand, fueled by pent-up spending and a resilient economy, could further push prices higher as businesses struggle to meet demand with limited supply.
- Geopolitical Tensions:Ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly the war in Ukraine, have disrupted global supply chains and driven up energy and commodity prices, adding to inflationary pressures.
Implications of an Inflationary Rebound, Producer prices surge sparking fears of inflationary rebound
An inflationary rebound could have significant implications for businesses, consumers, and the overall economy:
- Businesses:Businesses may face challenges in managing rising input costs, potentially impacting profit margins and investment decisions. They may also have to navigate price increases, potentially leading to a decline in consumer demand.
- Consumers:Consumers may experience a decline in purchasing power as prices rise, potentially leading to reduced spending and economic slowdown. This could also put pressure on household budgets, especially for lower-income households.
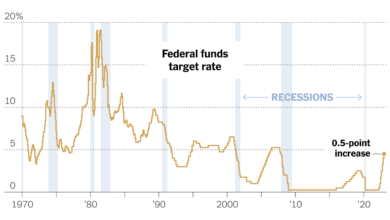
- Overall Economy:An inflationary rebound could lead to higher interest rates as central banks attempt to control inflation. This could stifle economic growth, potentially leading to a recession.
Comparison with Previous Inflationary Periods
The current situation shares similarities with previous inflationary periods, such as the 1970s oil crisis. However, there are also key differences:
- Globalized Economy:The current globalized economy, with complex interconnected supply chains, makes it more challenging to control inflation compared to previous periods. The impact of disruptions in one region can quickly ripple across the globe.
- Technological Advancements:Technological advancements have enabled businesses to improve efficiency and reduce costs, potentially mitigating inflationary pressures. However, these advancements may also contribute to increased automation and job displacement, creating social and economic challenges.
Conclusive Thoughts

The recent surge in producer prices has sparked concerns about an inflationary rebound, highlighting the fragility of the economic recovery. The PPI increase underscores the ongoing challenges facing businesses and consumers as they navigate a complex economic landscape. While the full impact of the PPI surge remains to be seen, it serves as a reminder of the importance of monitoring inflation and implementing appropriate policy responses to ensure a sustainable economic future.