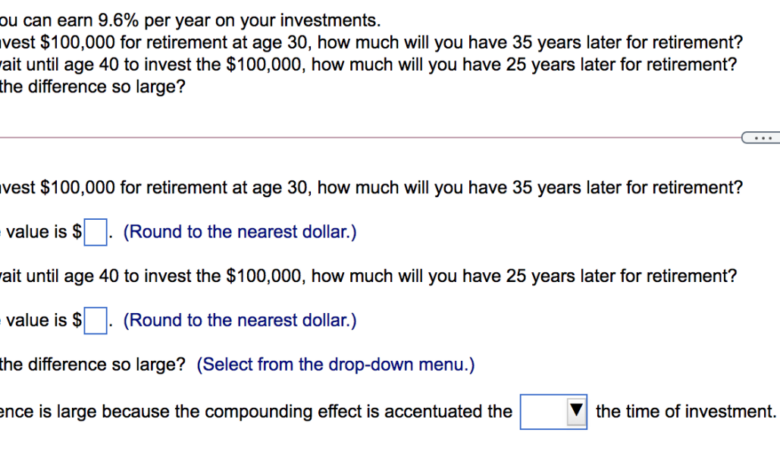
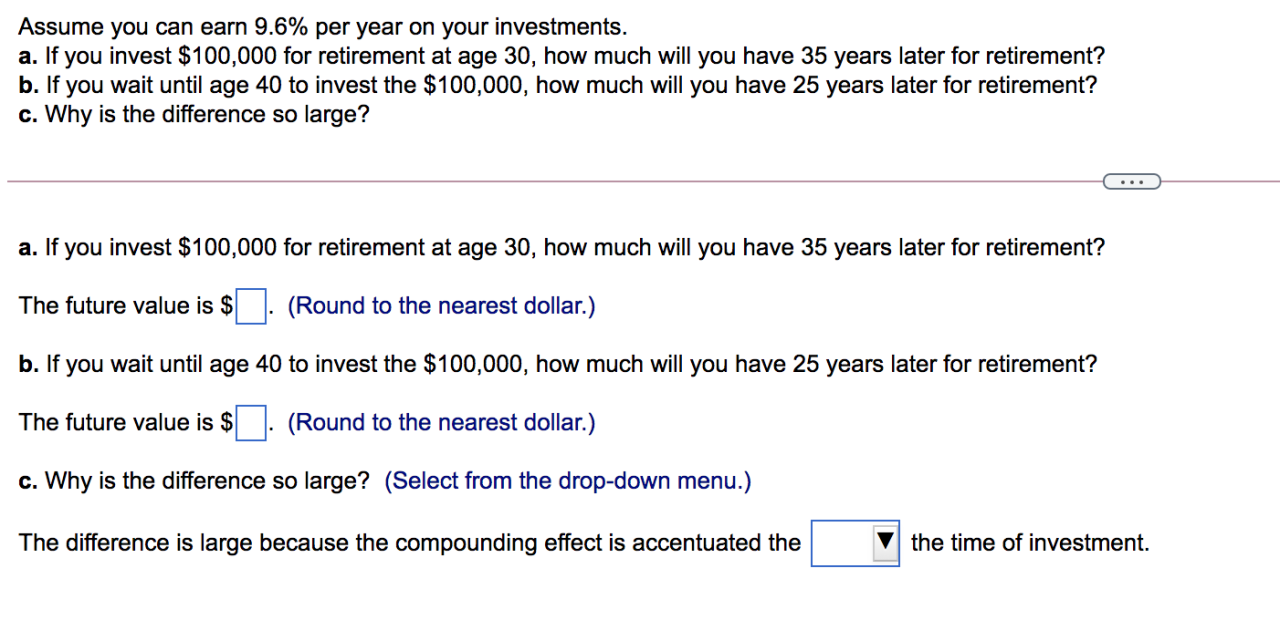
Over $100,000 Income Needed for Median US Home
Over 100000 income required to buy a median priced american home – Over $100,000 income required to buy a median priced American home? It’s a reality for many aspiring homeowners in today’s market. The dream of homeownership is becoming increasingly elusive as housing prices soar, driven by a complex interplay of factors including inflation, interest rates, and limited housing supply.
The average American household simply can’t keep up with the escalating costs, creating a widening affordability gap that impacts both first-time buyers and those seeking to upgrade their living situations.
This trend has far-reaching consequences for housing market dynamics, impacting accessibility, affordability, and even the overall health of communities. It’s a complex issue that demands a multifaceted approach, exploring potential solutions like increased housing supply, government incentives, and innovative housing models.
The Rising Cost of Homeownership
The dream of owning a home in America is becoming increasingly elusive for many. The median home price has been steadily climbing, making it challenging for individuals and families to afford a place to call their own. This trend is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including limited inventory, strong demand, and rising inflation.
It’s crazy to think that you need to make over $100,000 a year just to afford a median-priced home in America. It’s a reminder that sometimes we need to take shortcuts to make life a little easier, like when it comes to baking.
For those flaky, oozy stuffed biscuits, why stress over making the dough from scratch when you can just grab a package of store-bought dough at the grocery store? for flaky oozy stuffed biscuits just use store bought dough That way, you can focus on what really matters – maybe saving up for a down payment on a home that won’t break the bank.
Factors Contributing to Rising Home Prices
Several key factors contribute to the escalating cost of homeownership in the United States. Understanding these factors is crucial to grasping the challenges faced by potential homebuyers.
- Limited Housing Inventory:The supply of available homes for sale has not kept pace with the growing demand. This shortage, exacerbated by factors like slow construction rates and restrictive zoning regulations, has pushed prices upward.
- Strong Demand:A robust economy, low interest rates, and a growing population have fueled strong demand for housing. As more people seek to buy homes, competition intensifies, driving up prices.
- Rising Construction Costs:The cost of building materials, labor, and land has been on the rise, contributing to higher home prices. Increased regulations and environmental concerns have also played a role in escalating construction costs.
- Low Interest Rates:While historically low interest rates have made mortgages more affordable, they have also contributed to rising home prices. The accessibility of cheap financing has encouraged more buyers to enter the market, leading to increased demand and price inflation.
Median Home Price Growth Over the Past Decade
The past decade has witnessed a significant surge in median home prices across the United States.
- National Median Home Price:According to the National Association of Realtors, the median home price in the United States has risen from $169,900 in 2012 to $375,300 in 2022, representing a substantial increase of over 120%.
- Regional Variations:While the national median home price has seen a dramatic rise, regional variations exist. Some areas, particularly in coastal cities and high-demand suburbs, have experienced even more significant price increases.
Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates play a significant role in determining home affordability.
It’s crazy to think that you need to make over $100,000 a year just to afford the median-priced home in America. It seems like the American Dream is getting further and further out of reach. And it’s not just the housing market that’s making things tough.
Amidst all the global chaos, even the tech industry, which has been a beacon of stability for so long, is taking a rare tumble. Read more about this surprising turn of events here. With so much uncertainty in the air, it’s hard to imagine how things will play out for the housing market in the long run, but one thing is for sure: it’s a tough time to be a homebuyer.
- Inflation:Rising inflation erodes the purchasing power of individuals and families, making it more challenging to save for a down payment and manage monthly mortgage payments.
- Interest Rates:Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing money, leading to higher monthly mortgage payments. This can significantly impact affordability, particularly for first-time homebuyers.
“The rising cost of homeownership is a significant challenge for many Americans. Understanding the factors driving this trend is crucial for developing effective solutions to address the affordability crisis.”
Income Requirements for Homeownership: Over 100000 Income Required To Buy A Median Priced American Home
The dream of owning a home is a cornerstone of the American experience, but the financial reality can be daunting. The cost of housing has risen dramatically in recent years, making homeownership a significant financial hurdle for many. To understand the financial implications of homeownership, it’s crucial to analyze the income requirements needed to purchase a median-priced home in various parts of the country.
Income Requirements Across Major Cities
The income required to purchase a median-priced home varies significantly across the United States. Here is a breakdown of the estimated annual income needed for a 20% down payment and a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage in several major cities:
- New York City: $165,000
- San Francisco: $150,000
- Los Angeles: $120,000
- Chicago: $80,000
- Houston: $65,000
- Phoenix: $70,000
- Atlanta: $75,000
- Denver: $90,000
- Seattle: $105,000
These figures highlight the stark reality of the housing market in major metropolitan areas. In many cities, the required income significantly surpasses the average household income, creating a substantial affordability gap.
Comparison to Average Household Income, Over 100000 income required to buy a median priced american home
Comparing the income requirements for homeownership to the average household income in different regions reveals a concerning trend. For example, in the San Francisco Bay Area, the median home price is over $1 million, while the average household income is around $120,000.
It’s hard to believe that you need to earn over $100,000 a year just to afford a median-priced home in America. It’s a stark reminder of how out of reach the American Dream has become for many. It’s even more disheartening when you see news like texts showing Ginni Thomas embracing conspiracy theories , because it feels like the people who should be fighting for us are instead promoting the very things that are making our lives harder.
It makes you wonder if anyone is really working to make the American Dream attainable for everyone, not just the privileged few.
This gap underscores the affordability challenges faced by many aspiring homeowners.
- San Francisco Bay Area: Median home price – $1 million, Average household income – $120,000
- New York City: Median home price – $750,000, Average household income – $85,000
- Los Angeles: Median home price – $700,000, Average household income – $75,000
- Chicago: Median home price – $350,000, Average household income – $65,000
- Houston: Median home price – $300,000, Average household income – $60,000
Financial Implications of the Income Gap
The significant income gap between homeownership requirements and average income has far-reaching financial implications. It can lead to:
- Increased Housing Costs:Many individuals are forced to rent, leading to higher housing costs in the long run. Renters may face rising rents and limited control over their living space.
- Limited Access to Homeownership:The gap can prevent individuals from achieving the dream of homeownership, limiting their wealth-building potential.
- Financial Strain:Individuals struggling to meet the income requirements may experience financial strain, impacting their ability to save, invest, and plan for the future.
- Geographic Inequality:The affordability gap can contribute to geographic inequality, concentrating homeownership opportunities in certain regions while excluding others.
Alternative Housing Solutions
The American dream of homeownership is becoming increasingly elusive for many individuals and families. The rising cost of housing, coupled with stagnant wages, has made it challenging for many to afford a traditional home purchase. Fortunately, alternative housing solutions offer viable options for those seeking affordable and comfortable living arrangements.
Renting
Renting offers flexibility and lower upfront costs compared to homeownership. It allows individuals to live in various locations without the responsibility of property maintenance or mortgage payments.
- Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs: Renters do not need to pay a down payment or closing costs.
- Flexibility: Renters can move more easily when their circumstances change.
- No property maintenance responsibilities: Landlords are typically responsible for repairs and maintenance.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited control over the living space: Renters must adhere to the landlord’s rules and regulations.
- Rent increases: Rent prices can fluctuate, leading to higher living expenses.
- Lack of equity building: Rent payments do not contribute to building equity.
Co-ownership
Co-ownership models, such as shared ownership or co-housing, allow individuals to share the costs and responsibilities of homeownership.
- Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs: Individuals can share the down payment and mortgage payments.
- Shared responsibilities: Maintenance and repairs are divided among the co-owners.
- Sense of community: Co-ownership often fosters a sense of community and shared living experiences.
- Disadvantages:
- Potential for conflict: Sharing a living space can lead to disagreements among co-owners.
- Limited control over the property: Decisions regarding the property require consensus among all co-owners.
- Challenges in selling the property: Selling a co-owned property can be complex and require agreement from all co-owners.
Other Innovative Housing Models
Beyond traditional renting and co-ownership, several innovative housing models are emerging to address affordability concerns.
- Tiny Homes:These compact, energy-efficient homes offer a sustainable and affordable housing option. For example, the Tiny House Movement has gained popularity in recent years, with individuals opting for smaller living spaces to reduce their housing costs and environmental impact.
- Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs):ADUs are secondary dwelling units located on the same property as a primary residence. They can be a source of rental income or provide affordable housing for family members. For instance, in California, the passage of legislation promoting ADUs has led to a surge in their construction, helping to address the state’s housing shortage.
- Community Land Trusts (CLTs):CLTs are non-profit organizations that own land and lease it to individuals or families at affordable rates. This model helps to keep housing costs down and prevent displacement. For example, the Dudley Street Neighborhood Initiative in Boston has successfully utilized a CLT model to provide affordable housing options in a historically underserved neighborhood.
Conclusion
The high income requirement to buy a median-priced American home presents a significant challenge for many, highlighting the need for innovative solutions and policy changes to address the growing affordability gap. While the dream of homeownership may seem out of reach for some, exploring alternative housing options and advocating for policy reforms that prioritize affordability can help pave the way for a more accessible and equitable housing market.

