VAERS Data Are Health Problems Linked to COVID-19 Vaccines?
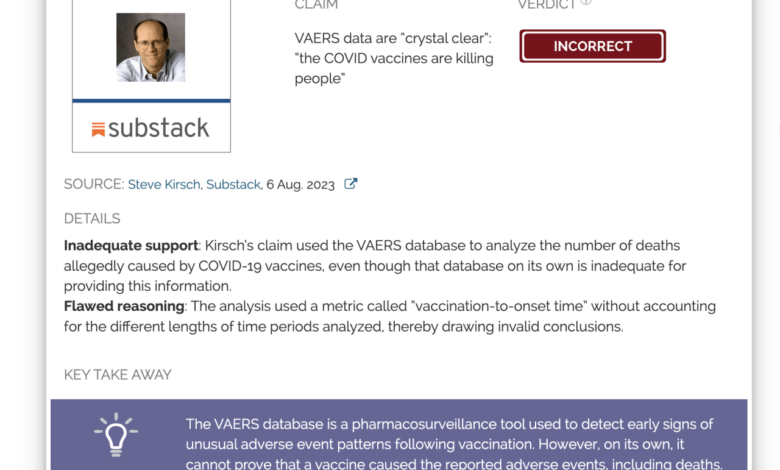
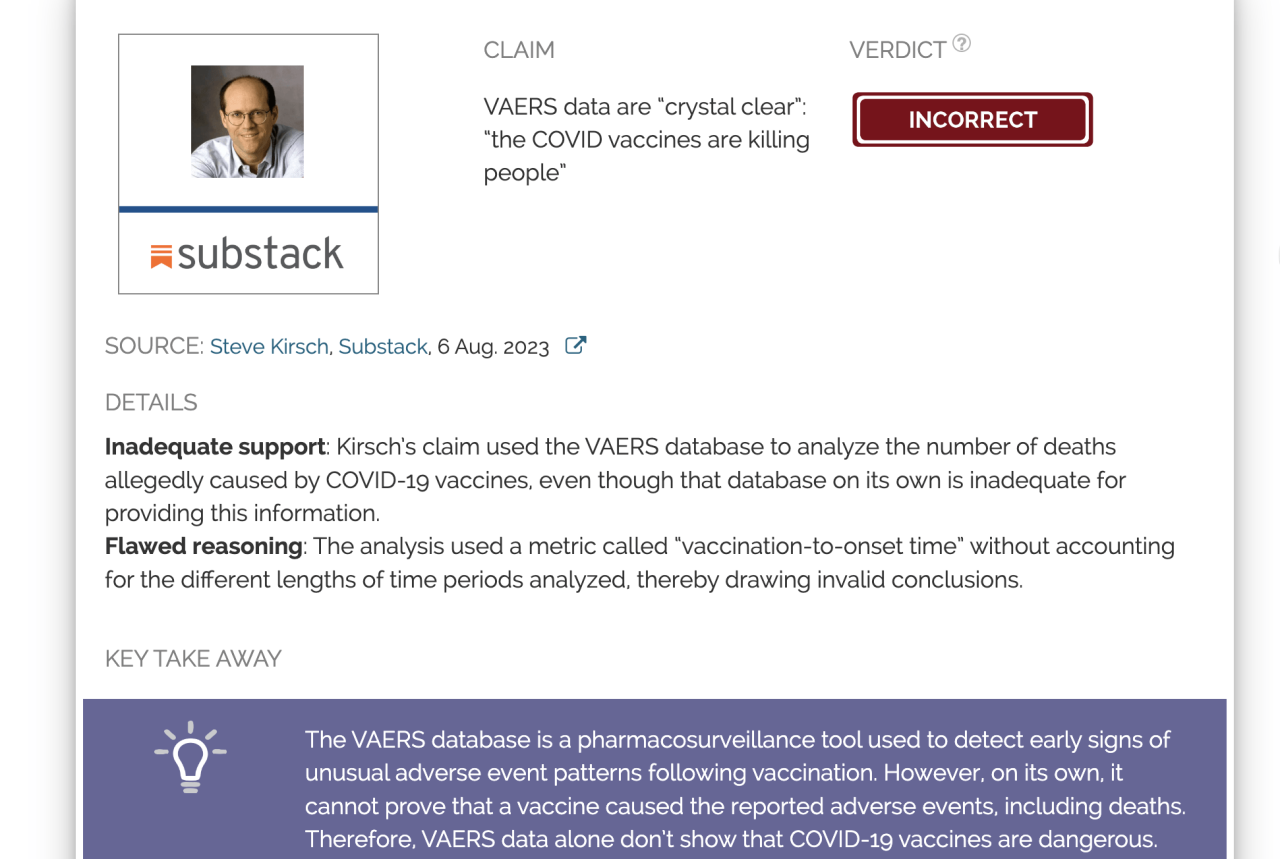
Numerous health problems more likely due to covid 19 vaccines than coincidence vaers data analysis – VAERS Data: Are Health Problems Linked to COVID-19 Vaccines? The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) has been a source of both concern and debate, with some individuals attributing numerous health problems to COVID-19 vaccines. While it’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of reporting potential adverse events, it’s equally vital to understand the limitations of VAERS data and the complexities of determining causality.
This article delves into the intricacies of VAERS data analysis, exploring the difference between correlation and causation, and emphasizing the importance of scientific rigor in evaluating vaccine safety.
Understanding the limitations of VAERS data is crucial. It relies on voluntary reporting, which can lead to underreporting and inaccuracies. Additionally, VAERS reports don’t establish a causal link between vaccines and health problems; they simply document potential associations. This means that a correlation between a vaccine and a health issue doesn’t necessarily imply that the vaccine caused it. Other factors, such as pre-existing conditions, lifestyle choices, and environmental exposures, can also contribute to health outcomes.
VAERS Data and Its Limitations
The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) is a national passive surveillance system that collects reports of adverse events that occur after vaccination. The purpose of VAERS is to monitor the safety of vaccines and to identify any potential safety concerns. It is important to understand the limitations of VAERS data before drawing any conclusions about vaccine safety.
It’s mind-boggling how the government can simultaneously be so focused on pushing experimental vaccines, while also pushing for a minimum tax on billionaires. It seems they’re more interested in taxing the wealthy than addressing the white house announces new minimum tax on billionaires concerns about the potential long-term health consequences of these vaccines, as evidenced by the increasing number of reports on VAERS.
It’s almost like they’re trying to distract us from the real issues at hand.
Underreporting
VAERS is a passive reporting system, which means that it relies on individuals to voluntarily report adverse events. This can lead to underreporting, as not everyone who experiences an adverse event after vaccination will report it. Several factors can contribute to underreporting, including:
- Lack of awareness of VAERS
- Difficulty in reporting
- Reluctance to report
- Uncertain if the event was related to the vaccine
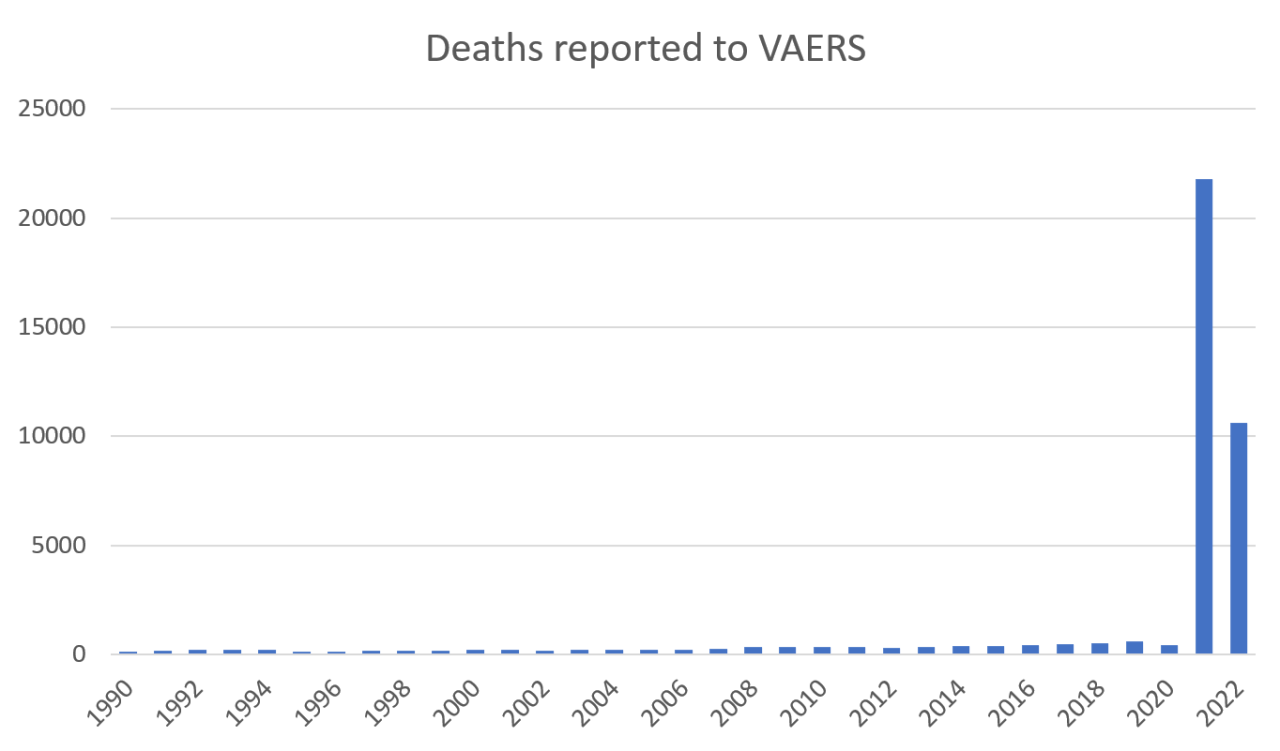
Studies have estimated that only a small percentage of adverse events are actually reported to VAERS. For example, a study published in the journal Vaccine estimated that only 1% of serious adverse events following vaccination are reported to VAERS. This means that the data in VAERS may not accurately reflect the true incidence of adverse events following vaccination.
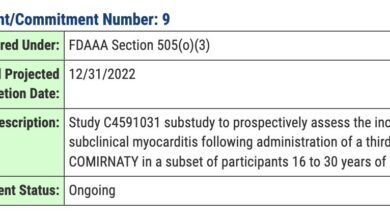
The VAERS data analysis suggests that numerous health problems are more likely due to the COVID-19 vaccines than mere coincidence. This raises serious concerns about the safety of these vaccines, and it’s encouraging to see a judge block the COVID-19 vaccine mandate for the entire Navy. This decision highlights the need for further investigation into the potential risks associated with these vaccines and underscores the importance of individual choice in healthcare decisions.
Lack of Causality Determination
VAERS reports only provide information about events that occurred after vaccination. They do not establish a causal relationship between the vaccine and the reported event. Many factors can contribute to an adverse event, and it is often difficult to determine whether the event was caused by the vaccine or by another factor.
Misinterpretation of Data
VAERS data can be misinterpreted if it is not analyzed carefully. For example, some people may mistakenly conclude that a vaccine is unsafe if they see a large number of reports of a particular adverse event in VAERS. However, it is important to remember that the number of reports in VAERS does not necessarily reflect the true incidence of the event.
Other factors, such as the number of people vaccinated, the reporting rate, and the time period over which the reports were collected, can also influence the number of reports.
Examples of Misinterpretation
- Reporting bias: People who experience an adverse event after vaccination may be more likely to report it to VAERS than people who do not experience an adverse event. This can lead to an overestimation of the frequency of adverse events.
- Temporal association: Just because an event occurs after vaccination does not mean that it was caused by the vaccine. Many events occur after vaccination that are unrelated to the vaccine.
- Confounding factors: Other factors, such as underlying medical conditions or other medications, can contribute to adverse events. It is important to consider these factors when interpreting VAERS data.
Causality vs. Correlation
It’s crucial to understand the difference between correlation and causation when analyzing data, particularly when evaluating potential links between vaccines and health problems. Correlation simply means two things happen together, but it doesn’t necessarily mean one causes the other. Causation, on the other hand, means that one event directly causes another.
Factors Influencing Health Outcomes
Numerous factors can influence health outcomes, independent of vaccination status. These factors include:
- Genetics: Individual genetic predispositions can play a significant role in susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Lifestyle: Factors like diet, exercise, smoking, and alcohol consumption can significantly impact health.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to pollutants, toxins, or infectious agents can also influence health outcomes.
- Underlying health conditions: Pre-existing health conditions can increase the risk of developing other health problems.
- Access to healthcare: Limited access to quality healthcare can affect health outcomes.
The Importance of Controlled Studies
Establishing causality requires rigorous scientific methodology, particularly controlled studies. Controlled studies involve comparing a group of individuals who received the vaccine (treatment group) with a group who did not (control group). Researchers carefully control for other factors that could influence health outcomes, such as age, sex, and underlying health conditions. This allows them to isolate the effect of the vaccine.
A controlled study is considered the gold standard for establishing causality because it minimizes the influence of confounding factors.
COVID-19 Vaccine Safety and Efficacy
The COVID-19 vaccines have proven to be remarkably effective in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19. They have played a crucial role in mitigating the pandemic’s impact worldwide. This section delves into the safety and efficacy of these vaccines, providing a comprehensive overview of their benefits and potential risks.
Rigorous Testing and Safety Protocols
The development and approval of COVID-19 vaccines involved stringent safety protocols and rigorous testing phases. This ensured that the vaccines met the highest standards of safety and efficacy before being made available to the public.
It’s hard to ignore the growing number of reports linking serious health problems to the COVID-19 vaccines. While some dismiss it as coincidence, a closer look at VAERS data suggests a more troubling reality. Meanwhile, in a surprising turn of events, Russia has announced a reduction in military activity near Ukraine’s capital , raising questions about the future of the conflict.
Whether this shift in strategy is a genuine de-escalation or a tactical maneuver remains to be seen, but it highlights the complex and evolving nature of the global landscape. Regardless, the growing concerns surrounding vaccine safety are a pressing issue that demands open and transparent discussion.
- Pre-clinical Testing: Before human trials, extensive laboratory testing was conducted on animal models to assess the vaccine’s safety and ability to generate an immune response.
- Clinical Trials: Multiple phases of clinical trials were conducted involving thousands of participants. These trials evaluated the vaccine’s effectiveness, safety, and optimal dosage.
- Independent Review: Data from clinical trials was reviewed by independent regulatory agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), before authorization for emergency use or full approval.
Benefits of COVID-19 Vaccination
The proven benefits of COVID-19 vaccination are substantial, outweighing the potential risks.
- Reduced Risk of Severe Illness: Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of developing severe COVID-19, including hospitalization and death. Studies have consistently shown that vaccinated individuals are far less likely to experience severe illness compared to unvaccinated individuals.
- Reduced Risk of Transmission: Vaccines also help reduce the spread of COVID-19 by decreasing the likelihood of transmission to others.
- Protection against Variants: While vaccine efficacy may decline over time, particularly against emerging variants, booster doses can help restore protection against new strains.
- Reduced Hospitalizations and Deaths: The widespread vaccination efforts have resulted in a significant decrease in COVID-19-related hospitalizations and deaths.
- Protection for Vulnerable Populations: Vaccination is particularly important for individuals with underlying health conditions and older adults, who are at higher risk of severe COVID-19 complications.
Potential Risks of COVID-19 Vaccination
While the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination far outweigh the potential risks, it is important to acknowledge that, like any medical intervention, there is a possibility of side effects.
- Common Side Effects: Most side effects are mild and short-lived, such as pain at the injection site, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, and chills. These are generally considered normal immune responses to the vaccine.
- Rare Side Effects: Rare side effects, such as allergic reactions or myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), have been reported. However, the risk of these rare events is extremely low compared to the risk of severe COVID-19 illness.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Systems for monitoring and reporting adverse events following vaccination are in place to ensure early detection and investigation of any potential safety concerns.
Comparing Risks: COVID-19 Infection vs. Vaccination
It is essential to compare the risks of COVID-19 infection and its complications with the potential risks associated with vaccination.
- COVID-19 Infection: COVID-19 infection can lead to a range of complications, including pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, and death. The severity of illness can vary significantly depending on individual factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the variant of the virus.
- Vaccination: While there are potential side effects associated with vaccination, they are generally mild and temporary. The risk of serious adverse events is extremely low, particularly when compared to the risks of severe COVID-19 illness.
| Risk | COVID-19 Infection | Vaccination |
|---|---|---|
| Severe Illness | High | Low |
| Hospitalization | High | Low |
| Death | High | Extremely Low |
| Long COVID | Significant risk | Lower risk |
Conclusion
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination far outweigh the potential risks. The vaccines have proven to be highly effective in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19. The rigorous testing and safety protocols employed during vaccine development ensure that they meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy. While there is a possibility of side effects, most are mild and short-lived.
It is crucial to weigh the risks and benefits of vaccination and to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Public Health Considerations
Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health, playing a crucial role in protecting individuals and communities from infectious diseases. Vaccines work by stimulating the body’s immune system to develop immunity against specific pathogens, preventing serious illness, hospitalization, and even death. This protection extends beyond the individual, contributing to the collective well-being of society.
Herd Immunity and its Importance, Numerous health problems more likely due to covid 19 vaccines than coincidence vaers data analysis
Herd immunity, also known as community immunity, is a phenomenon where a large portion of a population is immune to a disease, making it difficult for the disease to spread. When a significant number of people are immune, the chain of transmission is broken, protecting those who are not vaccinated, such as infants, the elderly, or those with weakened immune systems.
This concept is particularly important for diseases that are highly contagious, such as measles, mumps, and rubella.
Herd immunity is achieved when a sufficiently high percentage of the population is immune to a disease, typically around 80-95%, depending on the disease.
This level of immunity makes it challenging for the disease to spread, effectively protecting those who are susceptible.
Ethical Considerations surrounding Vaccine Hesitancy
Vaccine hesitancy, the reluctance or refusal to receive vaccines, poses a significant challenge to public health efforts. It can arise from various factors, including misinformation, mistrust in healthcare systems, concerns about vaccine safety, or religious beliefs. While individuals have the right to make informed decisions about their health, vaccine hesitancy can have detrimental consequences for both individuals and communities.
- Increased Risk of Outbreaks: When vaccination rates decline, the risk of outbreaks increases, potentially leading to a resurgence of diseases that were previously controlled.
- Impact on Vulnerable Populations: Individuals who cannot be vaccinated due to medical conditions or age rely on herd immunity to protect them. Vaccine hesitancy undermines this protection, putting vulnerable populations at higher risk.
- Economic and Social Costs: Outbreaks can strain healthcare systems, disrupt economic activity, and lead to social unrest.
Addressing vaccine hesitancy requires a multifaceted approach, including:
- Promoting Accurate Information: Providing clear and reliable information about vaccines, their benefits, and safety profiles can help dispel myths and misinformation.
- Building Trust: Establishing open and transparent communication channels with the public can foster trust in healthcare systems and vaccine programs.
- Addressing Concerns: Openly addressing concerns and providing evidence-based answers can help alleviate anxieties and promote informed decision-making.
Alternative Explanations for Health Problems: Numerous Health Problems More Likely Due To Covid 19 Vaccines Than Coincidence Vaers Data Analysis
It’s important to remember that while the COVID-19 vaccines have been proven safe and effective, some individuals may experience health problems that coincide with their vaccination. However, it’s crucial to consider that these problems may not necessarily be caused by the vaccine. Many factors can contribute to health issues, and it’s essential to explore these alternative explanations to avoid misattributing them to the vaccine.
Pre-existing Conditions
Pre-existing conditions can play a significant role in the development of health problems. Individuals with underlying medical conditions may be more susceptible to certain health issues, even if they are unrelated to the vaccine. For example, a person with a history of autoimmune disorders may experience a flare-up following vaccination, but this flare-up may be due to the underlying condition rather than the vaccine itself.
Similarly, individuals with heart disease may experience chest pain after vaccination, but this could be related to their pre-existing condition.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices can also influence health outcomes. Factors like diet, exercise, and stress levels can impact overall health and potentially contribute to health problems. For instance, individuals with poor dietary habits or a sedentary lifestyle may be more prone to developing certain health issues, regardless of vaccination status.
It’s essential to consider the role of lifestyle choices in health outcomes and not automatically attribute health problems to the vaccine.
Environmental Exposures
Environmental exposures can also play a role in health problems. Exposure to pollutants, toxins, or allergens can trigger various health issues, such as respiratory problems, skin rashes, or headaches. For example, a person living in an area with high levels of air pollution may experience respiratory problems after vaccination, but these problems may be due to the environmental exposure rather than the vaccine.
Mimicking Vaccine Side Effects
It’s important to note that some health problems may mimic common vaccine side effects, leading to misdiagnosis. For example, a person experiencing fatigue and muscle aches after vaccination may assume these symptoms are due to the vaccine. However, these symptoms could be caused by other factors, such as the flu, a viral infection, or even stress.
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and to rule out other potential causes of health problems.
In conclusion, while VAERS data plays a vital role in monitoring vaccine safety, it’s crucial to interpret it with caution. Attributing health problems to COVID-19 vaccines solely based on VAERS reports without considering other contributing factors can lead to misinterpretations. Rigorous scientific studies, including controlled trials, are essential for establishing causality and determining the true safety profile of vaccines. It’s essential to rely on evidence-based information from reputable sources and engage in informed discussions about vaccine safety and public health.