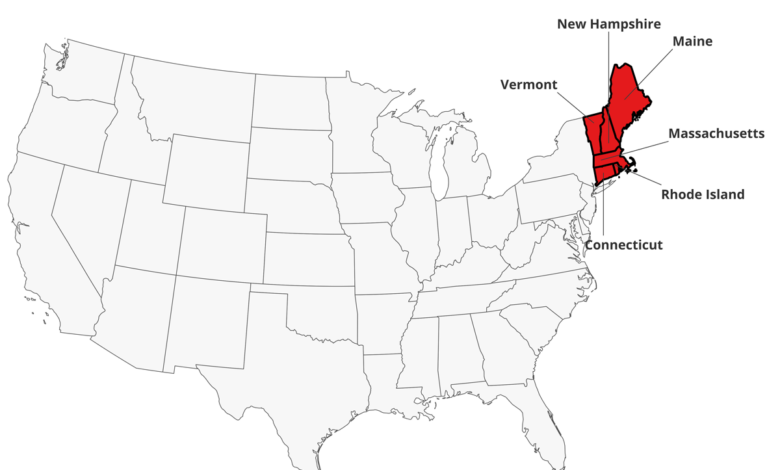
NH: The Mask-Free State of New England
Nh is the only new england state not mandating masks and it plans to stay that way – NH: The Mask-Free State of New England sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. While the rest of New England has embraced mask mandates as a public health measure, New Hampshire stands apart, choosing to leave the decision to individuals.
This bold stance has sparked debate and controversy, with some praising the state’s commitment to personal liberty while others express concern about the potential health risks.
This blog post delves into the complexities surrounding New Hampshire’s mask policy, exploring the rationale behind its decision, the public health considerations, and the economic and social implications. We’ll examine the arguments for and against mask mandates, analyze public opinion, and speculate on the future of New Hampshire’s mask policy.
New Hampshire’s Mask Policy
New Hampshire stands out as the only New England state that has not mandated masks during the COVID-19 pandemic. This decision has sparked debate, with some praising the state’s emphasis on personal responsibility and others expressing concern about the potential health risks.
New Hampshire’s Mask Policy
The state of New Hampshire has taken a hands-off approach to mask mandates. While the state’s Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) has issued guidance recommending mask use in certain settings, it has not imposed any statewide mandates. This means that individuals and businesses are free to make their own decisions regarding mask use.
Comparison with Other New England States
In contrast to New Hampshire, all other New England states have implemented mask mandates at some point during the pandemic. These mandates have varied in their scope and duration, but they have generally required mask use in public indoor settings.
For example, Massachusetts has had a statewide mask mandate in place for much of the pandemic, with exceptions for vaccinated individuals.
Rationale for New Hampshire’s Approach
New Hampshire’s decision to not mandate masks is rooted in a belief in individual liberty and personal responsibility. State officials have argued that mandates are an infringement on individual freedom and that individuals should be able to make their own decisions about their health and safety.
They also contend that mandates are ineffective and that people are more likely to comply with recommendations than with mandates.
Public Health Considerations
The decision by New Hampshire to not mandate masks, even as other New England states have, raises important questions about the potential health risks and the effectiveness of such measures. While individual choices are respected, the public health implications of this decision deserve careful consideration.
Potential Health Risks Associated with Not Mandating Masks
Not mandating masks can increase the risk of COVID-19 transmission, particularly in settings where physical distancing is difficult to maintain. Masks act as a barrier to respiratory droplets, which can carry the virus. When masks are not worn, these droplets can travel further, increasing the chance of infecting others.
This is especially concerning in indoor settings with poor ventilation, where the virus can linger in the air for extended periods.
Effectiveness of Mask Mandates in Reducing COVID-19 Transmission
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of mask mandates in reducing COVID-19 transmission. A 2021 study published in the journal “Nature” found that mask mandates were associated with a significant reduction in COVID-19 cases and deaths. The study analyzed data from 15 countries and found that mask mandates were associated with a 20% reduction in COVID-19 cases and a 15% reduction in deaths.
Public Health Arguments for and Against Mask Mandates
The debate surrounding mask mandates often centers on the balance between individual liberty and public health. Proponents of mask mandates argue that they are a necessary public health measure to protect vulnerable populations and prevent the spread of COVID-19.
They cite the evidence showing the effectiveness of masks in reducing transmission and the potential for widespread outbreaks in the absence of mandates. Opponents of mask mandates argue that they are an infringement on individual liberty and that the benefits of mask mandates are not well-established.
They also raise concerns about the potential negative impacts of mask-wearing, such as discomfort and difficulty breathing.
Economic and Social Impacts
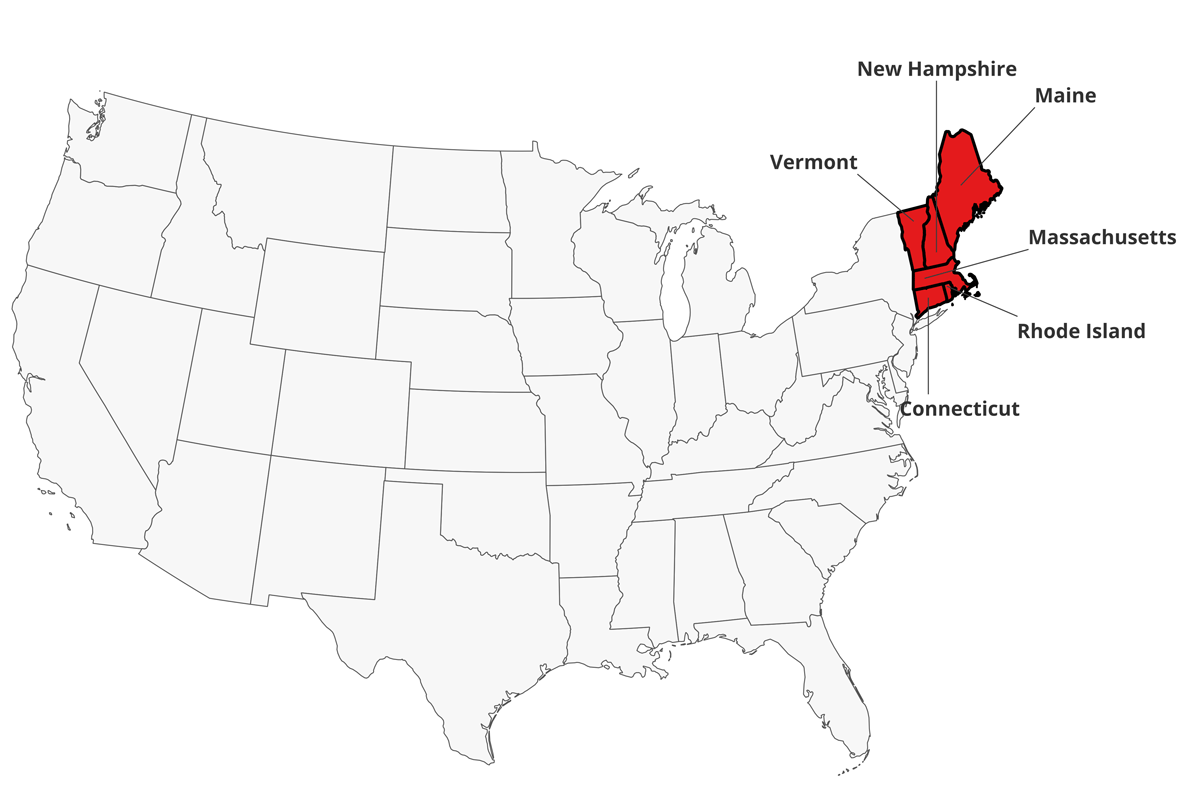
The decision by New Hampshire to not mandate masks has sparked debate about the potential economic and social implications of such a policy. While some argue that the lack of a mandate fosters economic growth and individual liberty, others contend that it could lead to increased health risks and social divisions.
Economic Impacts on Businesses and Individuals
The potential economic impacts of mask mandates on businesses and individuals in New Hampshire are a complex issue. While some businesses might experience a decrease in revenue due to customer reluctance to visit mask-mandated establishments, others could benefit from increased patronage from those seeking a mask-free environment.
Similarly, individuals might face challenges in finding employment or accessing services in mask-mandated areas, while others might feel more comfortable in such environments. The economic impact of mask mandates is likely to vary depending on the specific industry, the level of compliance with the mandate, and the public’s perception of the risks associated with mask-wearing.
For example, restaurants and bars in New Hampshire could experience a decline in business from customers who are uncomfortable dining in mask-free environments. Conversely, businesses that cater to a clientele that prioritizes mask-free environments, such as certain retail stores or recreational facilities, could potentially see an increase in business.
- Increased Costs for Businesses:Implementing and enforcing mask mandates can impose additional costs on businesses, such as purchasing masks, signage, and cleaning supplies. This could be a significant burden for small businesses with limited resources.
- Potential Loss of Revenue:Some businesses might experience a decrease in revenue if customers are reluctant to visit mask-mandated establishments. This could be particularly true for businesses that rely on high foot traffic, such as restaurants, bars, and retail stores.
- Potential Increase in Revenue:Other businesses might benefit from increased patronage from those seeking a mask-free environment. This could be particularly true for businesses that cater to a clientele that prioritizes mask-free environments, such as certain retail stores or recreational facilities.
- Increased Costs for Individuals:Individuals might face increased costs associated with mask-wearing, such as purchasing masks, laundry, and cleaning supplies. This could be a significant burden for low-income individuals.
- Potential Loss of Employment:Individuals might face challenges in finding employment or accessing services in mask-mandated areas, particularly if they are unwilling or unable to wear masks.
Social and Political Implications
The decision by New Hampshire to not mandate masks has also sparked debate about the social and political implications of such a policy. Some argue that the lack of a mandate promotes individual liberty and fosters a sense of community, while others contend that it could lead to increased health risks and social divisions.The social and political implications of mask mandates are likely to vary depending on the level of compliance with the mandate, the public’s perception of the risks associated with mask-wearing, and the political climate in the state.
For example, in a state with a high level of compliance with mask mandates, the social and political implications might be less pronounced. Conversely, in a state with a low level of compliance, the social and political implications could be more significant.
- Increased Social Divisions:Mask mandates can be a source of tension and conflict, particularly in communities with strong political or ideological divisions. This can lead to increased social polarization and make it more difficult to address public health issues.
- Potential for Discrimination:Mask mandates could potentially lead to discrimination against individuals who are unable or unwilling to wear masks, such as those with certain medical conditions or disabilities.
- Potential for Civil Liberties Concerns:Some individuals might view mask mandates as an infringement on their personal liberties, particularly in the absence of a clear public health justification.
- Increased Public Trust in Government:Conversely, mask mandates could potentially increase public trust in government if they are perceived as being effective in protecting public health.
Arguments for and Against Mask Mandates, Nh is the only new england state not mandating masks and it plans to stay that way
The debate over mask mandates is often framed in terms of their potential economic and social consequences. Those who support mask mandates argue that they are necessary to protect public health and prevent the spread of infectious diseases. They contend that the economic benefits of reduced disease transmission outweigh the costs of implementing and enforcing mandates.
Additionally, they argue that mask mandates promote social cohesion and reduce the risk of social divisions.
“Mask mandates are a necessary public health measure that can help to reduce the spread of infectious diseases. The economic benefits of reduced disease transmission outweigh the costs of implementing and enforcing mandates.”
Those who oppose mask mandates argue that they are ineffective, unnecessary, and infringe on individual liberties. They contend that the economic costs of mandates outweigh the potential benefits, particularly for small businesses. Additionally, they argue that mask mandates can lead to social divisions and create a sense of distrust in government.
“Mask mandates are ineffective, unnecessary, and infringe on individual liberties. The economic costs of mandates outweigh the potential benefits, particularly for small businesses.”
The debate over mask mandates is complex and multifaceted, with no easy answers. It is important to consider the potential economic and social consequences of such policies and to weigh the benefits against the costs.
Public Opinion and Perspectives
Public opinion on mask mandates in New Hampshire is diverse, reflecting a spectrum of viewpoints shaped by various factors, including personal beliefs, health concerns, economic considerations, and political affiliations.
Factors Influencing Perspectives on Mask Mandates
The public’s stance on mask mandates is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, ranging from personal beliefs about individual liberty and government intervention to concerns about public health and economic implications.
- Personal Beliefs and Values:Some individuals prioritize personal freedom and autonomy, viewing mask mandates as an infringement on their rights. Others place a high value on individual responsibility and believe that personal choices should guide behavior, even in matters of public health.
- Health Concerns and Risk Perception:Individuals with heightened health concerns or those who perceive a higher risk of contracting or transmitting COVID-19 are more likely to support mask mandates as a means of mitigating the spread of the virus. Conversely, those who feel less vulnerable to the virus or perceive the risk as low may be less inclined to support mandates.
- Economic Impacts:Concerns about the economic consequences of mask mandates, such as potential business closures or disruptions to the workforce, can influence opinions. Individuals who rely on businesses that might be affected by mandates may be more hesitant to support them.
- Political Affiliations and Trust in Government:Political affiliations and trust in government institutions play a role in shaping opinions on mask mandates. Individuals who align with political ideologies that emphasize individual liberty and limited government intervention may be less likely to support mandates, while those who trust government authority and prioritize public health may be more supportive.
Examples of Different Viewpoints on Mask Mandates
The debate over mask mandates in New Hampshire has showcased a range of perspectives, with each side presenting compelling arguments and concerns.
- Supporters of Mask Mandates:Proponents of mask mandates argue that they are an effective public health measure to curb the spread of COVID-19. They cite scientific evidence demonstrating the efficacy of masks in reducing transmission, emphasizing the importance of protecting vulnerable populations and preventing overwhelming healthcare systems.
- Opponents of Mask Mandates:Critics of mask mandates contend that they are an infringement on individual liberties and that the government should not dictate personal choices. They argue that masks are ineffective or even harmful, citing anecdotal evidence and questioning the scientific consensus. They also express concerns about the economic and social consequences of mandates.
Future Implications: Nh Is The Only New England State Not Mandating Masks And It Plans To Stay That Way
The decision by New Hampshire to forgo a statewide mask mandate, while seemingly a matter of individual liberty, carries with it a range of potential long-term implications for public health, social dynamics, and even the state’s economy. Understanding these implications requires a nuanced examination of the potential impacts on both the state itself and its interactions with other states and regions.
Potential Long-Term Implications for Public Health and Society
The absence of a statewide mask mandate in New Hampshire could lead to a number of potential long-term consequences for public health and social dynamics. While some individuals may see this as a positive step toward individual liberty, others may express concern about the potential for increased transmission of respiratory illnesses, including COVID-19.
- Increased Transmission of Respiratory Illnesses:The lack of a mask mandate could potentially lead to a higher rate of transmission of respiratory illnesses, including COVID-19, influenza, and other viruses. This could result in more hospitalizations, strain on healthcare systems, and potentially higher mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable populations.
The impact could be especially pronounced in densely populated areas or during periods of peak transmission.
- Increased Health Disparities:The lack of a mask mandate could exacerbate existing health disparities, particularly in communities with limited access to healthcare or those with a higher prevalence of chronic conditions. These communities may be more vulnerable to the consequences of increased transmission, potentially leading to a wider gap in health outcomes.
- Social Division and Polarization:The mask mandate debate has already become a point of contention in many communities, with strong opinions on both sides. The lack of a mandate could further fuel these divisions, leading to social polarization and strained relationships within communities.
This could manifest in various ways, such as increased tensions in public spaces, reluctance to participate in community activities, and difficulty in reaching consensus on public health measures.
- Impact on Education and Business:The lack of a mask mandate could create challenges for schools and businesses. Schools might face increased absenteeism and difficulty maintaining in-person learning environments. Businesses, particularly those with close contact interactions, could experience higher rates of employee illness, leading to disruptions in operations and potentially reduced productivity.
Potential for Changes in New Hampshire’s Mask Policy
While New Hampshire has chosen to maintain its current mask policy, the potential for future changes remains. Several factors could influence a shift in the state’s approach, including:
- Evolving Scientific Evidence:As new scientific evidence emerges about the effectiveness of masks in preventing transmission of respiratory illnesses, particularly new variants of COVID-19, public health officials may recommend changes to the state’s mask policy.
- Changes in Public Opinion:If public opinion shifts significantly in favor of a mask mandate, due to concerns about rising transmission rates or the emergence of new variants, there could be pressure on state officials to reconsider their stance.
- Economic and Social Impacts:If the lack of a mask mandate leads to significant negative impacts on the state’s economy or social fabric, such as a surge in hospitalizations or a decline in tourism, officials might be prompted to reevaluate their policy.
- Action by Other States or Federal Government:If neighboring states or the federal government implement mask mandates, it could influence New Hampshire’s decision-making process. The state may feel compelled to align its policies with those of other jurisdictions to maintain consistency and avoid potential negative economic or social consequences.
Potential Impact of New Hampshire’s Mask Policy on Other States and Regions
New Hampshire’s decision to forgo a mask mandate could have implications for other states and regions, particularly those that share borders or have close economic ties.
- Increased Transmission Across State Lines:The lack of a mask mandate in New Hampshire could contribute to increased transmission of respiratory illnesses across state lines, potentially impacting neighboring states that have stricter mask policies. This could lead to a more challenging public health situation in those states, as they attempt to control transmission while facing potential spillover from neighboring areas.
- Economic and Social Implications for Neighboring States:New Hampshire’s mask policy could have economic and social implications for neighboring states, particularly in terms of tourism and interstate travel. States with stricter mask policies may see a decline in visitors from New Hampshire, leading to potential economic losses.
Additionally, the different approaches to mask policies could create social tensions and friction between states.
- Potential for Policy Convergence or Divergence:New Hampshire’s mask policy could serve as a model for other states, potentially leading to a wider adoption of a “no mandate” approach. Conversely, it could also lead to a strengthening of mask policies in other states, as they seek to differentiate themselves from New Hampshire and implement stricter measures to protect public health.
Conclusive Thoughts
New Hampshire’s decision to forgo mask mandates has ignited a passionate debate, highlighting the complex interplay between individual liberties, public health, and economic concerns. As the pandemic evolves, it remains to be seen whether New Hampshire will maintain its unique stance or eventually adopt a more widespread approach to mask usage.
Regardless of the outcome, the state’s experience offers valuable insights into the evolving landscape of public health policy in a time of unprecedented uncertainty.