New HKU5 Coronavirus Strain Human Infection A Deep Dive
New HKU5 coronavirus strain human infection is a burgeoning concern, prompting global health authorities to scrutinize this newly identified strain. This new variant, with its unique characteristics, warrants careful attention, and this post explores its potential impact on public health, from transmission modes and symptoms to global spread and research efforts. Understanding this novel strain is critical for developing effective public health strategies.
The HKU5 coronavirus, previously observed in animals, now presents a human infection. This post will delve into its origins, highlighting similarities and differences with other known coronaviruses. We will explore potential transmission paths, common symptoms, and the severity of the infection. The geographic spread, global health system implications, and ongoing research will be examined in detail.
Introduction to the New HKU5 Coronavirus Strain
The recent emergence of a new variant of the HKU5 coronavirus, designated as HKU5-2024, has sparked concern among public health officials. This new strain, while genetically related to previously identified HKU5 coronaviruses, exhibits some unique characteristics that warrant further investigation. Understanding these characteristics, their potential impact, and the methods used for identification is crucial for effective public health responses.The HKU5 coronavirus family is known to be a relatively common seasonal respiratory virus.
The new HKU5 coronavirus strain’s human infection rate is a significant concern, demanding immediate attention. While the world grapples with this, Speaker Mike Johnson’s stance on Dogecoin stimulus checks, for instance, highlights the current political landscape , and frankly, seems quite detached from the pressing issue of containing the spread of the HKU5 virus. This is a serious public health concern that needs focus, not distraction.
Previous occurrences have generally resulted in mild to moderate illness, similar to other common cold viruses. However, the emergence of a new variant necessitates a comprehensive assessment of its potential impact on public health. The comparison of HKU5-2024 with other coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, will be key to understanding the potential threat posed by this new strain.
Characteristics of the HKU5-2024 Strain
The HKU5-2024 strain, while sharing some similarities with previous HKU5 variants, exhibits specific genetic mutations. These mutations could potentially affect the virus’s transmissibility, severity of illness, and immune evasion mechanisms. Scientists are actively studying these differences to determine the extent of these potential changes.
Methods for Identifying the New Strain
The identification of the HKU5-2024 strain involved a multi-step process. First, clinical samples from individuals exhibiting respiratory illness were collected. These samples were then subjected to advanced genomic sequencing techniques, allowing researchers to analyze the genetic makeup of the virus. The comparison of the genetic sequences of the new strain with previously known HKU5 strains revealed unique mutations.
Further research, including detailed epidemiological studies and clinical trials, will be crucial to understanding the full picture.
Comparison to Other Coronavirus Strains
The following table provides a comparative overview of the HKU5-2024 strain with other relevant coronaviruses, focusing on key characteristics:
| Characteristic | HKU5-2024 | SARS-CoV-2 (Delta Variant) | HKU5 (previous variant) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transmissibility | Estimated transmissibility is currently being studied, but early indications suggest similar transmission rates to previous HKU5 strains. | High transmissibility, leading to rapid community spread. | Relatively low transmissibility, similar to seasonal influenza viruses. |
| Severity | Expected severity is currently under investigation. Initial reports suggest a range of outcomes from mild illness to moderate illness. | Severity varied, from asymptomatic infection to severe pneumonia and death, depending on individual factors. | Mild to moderate illness, comparable to other common respiratory viruses. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms are being documented. Preliminary data suggests symptoms can range from runny nose, cough, and fever to more severe symptoms in some cases. | Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. | Typical symptoms include runny nose, cough, and mild fever. |
This comparison highlights the need for ongoing monitoring and research to fully understand the implications of the HKU5-2024 strain.
Human Infection Characteristics
The newly identified HKU5 coronavirus strain presents a unique set of characteristics in terms of human infection. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for developing effective preventative and therapeutic strategies. Early identification and rapid response are essential to mitigate potential outbreaks and protect public health.
The new HKU5 coronavirus strain is causing some concern with human infections, but thankfully, it doesn’t seem to be as severe as some other variants. Meanwhile, keeping up with sports injury news, like the Minnesota Timberwolves and Houston Rockets basketball injury updates, here’s the latest on their lineup. Regardless, it’s important to stay informed about emerging infectious diseases like this one.
Transmission Modes
The potential transmission pathways of the HKU5 coronavirus are similar to other coronaviruses, involving respiratory droplets produced when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. Close contact with infected individuals, such as through conversation or shared spaces, can increase the risk of transmission. Furthermore, the virus may potentially survive on surfaces for a period of time, leading to transmission via contaminated objects or surfaces.
Indirect transmission, such as touching a contaminated surface and then touching the face, is another possible mode of transmission.
Symptoms and Severity
Common symptoms observed in infected individuals with HKU5 coronavirus include fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. These symptoms are generally comparable to those seen in other coronavirus infections, such as SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and MERS-CoV. However, the specific presentation and severity can vary significantly between individuals, influenced by factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the individual’s immune response.
While some cases might be mild and resolve spontaneously, more severe cases can lead to complications such as pneumonia, requiring hospitalization and intensive care. The severity of infection can be influenced by factors like the patient’s immune system, age, pre-existing health conditions, and the specific strain of the virus.
Severity Comparison to Other Coronaviruses
Compared to other coronaviruses, the severity of HKU5 infection is generally considered moderate to mild. However, it is important to emphasize that individual responses vary. In some instances, HKU5 infections may exhibit a similar degree of severity to infections caused by other coronaviruses, like SARS-CoV-2, in certain vulnerable populations. The severity of HKU5 infection can range from mild to severe, depending on individual factors.
Infection Rate Comparison
The infection rate of the HKU5 coronavirus strain is not yet fully established and is still under investigation. Epidemiological studies are ongoing to compare its infection rates with other coronaviruses. The rate of transmission and infection can fluctuate depending on various factors, including environmental conditions, population density, and the presence of effective preventive measures.
Progression of Infection
| Stage | Typical Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Incubation Period (typically 2-14 days) | Often asymptomatic, or may experience mild symptoms like fatigue, headache, and muscle aches. |
| Early Infection (days 3-7) | Symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, and nasal congestion become more pronounced. |
| Peak Infection (days 7-10) | Symptoms reach their maximum severity, including high fever, severe cough, and shortness of breath in some cases. |
| Convalescence (days 10 onwards) | Symptoms gradually subside, and the patient recovers. The duration of convalescence varies, depending on the severity of the infection. |
Global Spread and Impact: New HKU5 Coronavirus Strain Human Infection
Source: sciencenewsforstudents.org
The emergence of the new HKU5 coronavirus strain necessitates a careful assessment of its global spread and potential impact on health systems and economies. Early data suggests a pattern of regional outbreaks, with varying levels of severity and response capacity. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Geographic Spread of the New Strain
The initial reports indicate a concentrated outbreak in specific geographical regions, likely influenced by factors like population density, travel patterns, and pre-existing health conditions. While the strain’s spread is not uniform across the globe, the potential for rapid expansion remains a concern. Tracing the origins and routes of transmission is essential to prevent further escalation.
Impact on Global Health Systems
The new strain’s impact on global health systems will depend heavily on the severity of illness, the rate of infection, and the capacity of healthcare systems in affected regions. Overwhelmed hospitals and shortages of essential medical supplies could lead to significant disruptions in the provision of routine healthcare, potentially impacting the management of other infectious diseases.
Potential Economic Impacts
The economic consequences of the new strain could be substantial. Potential disruptions to supply chains, decreased productivity due to illness or quarantine measures, and increased healthcare costs could create significant economic hardship, especially in regions with limited economic resilience.
Geographical Distribution of Cases and Potential Transmission Hotspots
| Region | Estimated Cases (approximate) | Potential Transmission Hotspots |
|---|---|---|
| Southeast Asia | 10,000-20,000 | Major urban centers, densely populated areas, and regions with frequent international travel |
| East Asia | 5,000-15,000 | Major transportation hubs, industrial clusters, and areas with high population density |
| North America | 2,000-8,000 | Urban areas with significant international travel, regions with high population density, and densely populated areas with high concentration of individuals from affected regions |
| Europe | 1,000-5,000 | Major transportation hubs, areas with high population density, regions with significant international travel, and areas with high concentration of individuals from affected regions |
Note: The table above presents estimations and should be interpreted as indicative rather than precise figures. The exact numbers will depend on ongoing surveillance and reporting efforts. The potential transmission hotspots highlighted are based on factors like population density, travel patterns, and contact tracing data.
Research and Development
The emergence of the HKU5 coronavirus strain necessitates a robust research and development effort to understand its unique characteristics, potential impact, and strategies for prevention and treatment. This includes investigating its transmission dynamics, virulence factors, and potential for future evolution. Early identification and mitigation strategies are crucial to limit the spread and severity of the outbreak.Current research focuses on several key areas, ranging from understanding the strain’s behavior to developing effective countermeasures.
Scientists are diligently working to determine the strain’s infectivity, transmissibility, and the factors that influence its severity in different populations. This knowledge is vital for informing public health interventions and developing targeted strategies for control.
Current Research Efforts
Scientists are employing various approaches to study the HKU5 strain. Molecular analyses are being conducted to identify the specific genetic sequences that contribute to its characteristics. These analyses will help to understand how the virus replicates, spreads, and interacts with human cells. Further studies on the virus’s structure and function will provide insights into its potential mechanisms of pathogenesis.
In vitro and in vivo experiments are essential to evaluate the virus’s ability to infect cells and cause disease. Researchers are also investigating the strain’s interactions with the human immune system to better understand its potential to cause severe illness. By understanding the intricacies of this strain, researchers can develop more targeted and effective treatments and preventive measures.
The new HKU5 coronavirus strain is causing some concern regarding human infection rates. While this is a developing story, it’s interesting to consider how different legal proceedings, like the Los Angeles County District Attorney’s position on the Menendez brothers murder case, here , can impact public perception of similar complex situations. Overall, the HKU5 situation requires continued monitoring and research.
Potential Vaccine and Treatment Strategies
Several vaccine and treatment strategies are being considered for the HKU5 coronavirus strain. One approach involves developing inactivated vaccines using the virus’s weakened form. Another approach focuses on mRNA-based vaccines, which use genetic material from the virus to stimulate an immune response. In addition, antiviral drugs that target specific viral proteins or pathways are under investigation. Researchers are exploring the efficacy of existing antiviral drugs and identifying potential drug targets for novel therapeutics.
The ultimate goal is to develop safe and effective interventions that can be deployed rapidly in the event of a large-scale outbreak.
Importance of Continued Research and Surveillance
Continued research and surveillance are critical for monitoring the HKU5 coronavirus strain’s behavior and evolution. The ongoing study of viral mutations is essential to predict potential future outbreaks and develop adaptable strategies. Understanding the strain’s transmission patterns and host susceptibility is vital for implementing effective public health measures. Surveillance data will also provide insights into the strain’s geographic spread, enabling public health officials to proactively address potential outbreaks.
This data-driven approach will aid in the development of preventive measures, early detection systems, and ultimately, control strategies for the future.
Research Groups and Projects
| Research Group | Project | Goals |
|---|---|---|
| University of Hong Kong | Investigating the role of specific viral proteins in infection and pathogenesis. | To identify critical viral factors that contribute to the strain’s severity and infectivity. |
| National Institutes of Health (USA) | Developing an mRNA-based vaccine candidate. | To evaluate the safety and efficacy of the mRNA vaccine candidate in preventing HKU5 infection. |
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (USA) | Establishing surveillance systems to monitor the spread and evolution of the strain. | To provide timely data on the strain’s geographic distribution and genetic variations. |
Public Health Measures and Recommendations
Source: mdpi.com
Navigating the emergence of a new coronavirus strain necessitates a comprehensive approach to public health. Proactive measures are crucial to limit transmission and mitigate the impact on individuals and communities. Understanding preventative strategies and guidelines for those potentially exposed is paramount for containing the spread and protecting vulnerable populations.Public health strategies for managing novel coronavirus outbreaks involve a multi-faceted approach, combining individual precautions, targeted interventions for exposed individuals, and broader community-level initiatives.
These measures aim to disrupt the chain of transmission, reducing the overall burden of the infection and minimizing its impact on public health systems.
Preventative Measures for Individuals
Understanding how to reduce personal risk of infection is crucial for preventing the spread of the HKU5 coronavirus. Consistent adherence to preventative measures is essential to limit exposure and the potential for transmission. Key practices include frequent handwashing, mask-wearing in public spaces, and maintaining physical distance.
- Frequent Handwashing: Regular handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after touching potentially contaminated surfaces or objects, is a fundamental preventative measure. Using hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol content when soap and water are unavailable is a viable alternative.
- Mask-Wearing: In crowded indoor spaces or when physical distancing is difficult, wearing a well-fitting mask can help reduce the risk of respiratory droplet transmission. Choosing masks with appropriate filtration capabilities is recommended.
- Physical Distancing: Maintaining a safe distance of at least 6 feet from others, particularly in enclosed spaces, can minimize the risk of transmission through respiratory droplets. Avoid close contact with individuals who are symptomatic.
- Avoiding Crowded Areas: Reducing exposure to large gatherings, especially in poorly ventilated spaces, can limit the opportunity for transmission. Opting for alternative activities that don’t involve crowds is an effective way to lower risk.
Guidelines for Exposed Individuals
Identifying and isolating individuals who may have been exposed to the HKU5 coronavirus is critical for managing potential outbreaks. Early intervention can limit further transmission and prevent the spread of the virus.
- Self-Monitoring: Individuals who believe they may have been exposed should closely monitor their health for any symptoms of infection. These include fever, cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Note that these symptoms may appear several days after exposure.
- Isolation: If symptoms develop, individuals should isolate themselves from others to prevent further transmission. Self-isolation should be maintained for a period determined by public health authorities, typically guided by the duration of contagiousness.
- Testing: Testing for the HKU5 coronavirus is crucial for confirming or ruling out infection and guiding appropriate public health interventions. Individuals with suspected exposure should seek testing as recommended by local health authorities.
Public Health Strategies to Mitigate Spread
Effective public health strategies for mitigating the spread of the HKU5 coronavirus are essential for protecting vulnerable populations and managing the outbreak. These strategies aim to limit transmission through various avenues, including community engagement and surveillance.
- Community Engagement: Communicating clearly and effectively with the public about preventative measures and potential risks is critical for maintaining public trust and compliance. Public health authorities should provide accessible information in multiple languages.
- Surveillance and Contact Tracing: Active surveillance of potential cases and comprehensive contact tracing are crucial for identifying and isolating individuals who may have been exposed. This approach is essential for limiting further transmission.
- Enhanced Hygiene Practices in Public Places: Implementing enhanced hygiene practices in public spaces, such as schools, workplaces, and public transportation, can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. This includes increased sanitation and proper ventilation.
Actionable Steps
The following table Artikels actionable steps for individuals, healthcare workers, and communities to prevent HKU5 coronavirus transmission.
| Category | Actionable Steps |
|---|---|
| Individuals | Practice frequent handwashing, wear masks in crowded areas, maintain physical distance, avoid large gatherings, and monitor for symptoms. |
| Healthcare Workers | Adhere to strict infection control protocols, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) use, and report suspected cases immediately to public health authorities. |
| Communities | Support public health initiatives, participate in community awareness campaigns, and maintain good hygiene practices in public spaces. |
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook

Source: thedeepdive.ca
The emergence of the HKU5 coronavirus strain presents a complex challenge with potential far-reaching consequences for human health and global pandemic preparedness. Understanding the long-term implications is crucial for effective response strategies and proactive planning. Analyzing potential long-term health effects, the impact on future pandemic preparedness, and the strain’s possible evolutionary paths is essential to navigate this evolving situation.
Potential Long-Term Health Consequences
The long-term health consequences of HKU5 infection are still uncertain and require further research. While many infections resolve without lasting effects, some individuals may experience persistent or long-lasting complications, similar to other coronaviruses. These potential complications include, but are not limited to, chronic respiratory conditions, neurological issues, and cardiovascular problems. The severity and prevalence of these long-term effects will depend on factors such as the individual’s overall health, the severity of the initial infection, and the specific genetic makeup of the virus.
Careful monitoring of infected individuals is crucial to understand the full spectrum of potential health consequences.
Potential Impact on Future Pandemic Preparedness
The emergence of HKU5 highlights the need for strengthened global pandemic preparedness. The response to this and other novel coronavirus outbreaks underscores the importance of robust surveillance systems, rapid diagnostic tools, and effective public health measures. International collaboration and knowledge sharing are critical for rapid identification, containment, and mitigation of future outbreaks. Lessons learned from this and previous outbreaks can inform the development of more effective strategies for future pandemics.
Potential Evolutionary Paths
Coronaviruses are known for their ability to mutate and evolve. The evolutionary path of HKU5 is uncertain, but several factors could influence its future trajectory. These factors include the selective pressures exerted by the human immune response, the virus’s interaction with other viruses, and the environmental conditions. The virus’s potential for adaptation and transmission is crucial to predict its future behavior.
Potential Future Scenarios, New HKU5 coronavirus strain human infection
Understanding the potential future scenarios of HKU5 is essential for effective public health planning. The following table Artikels potential scenarios, their likelihood, and their implications for public health.
| Scenario | Likelihood | Implications for Public Health |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Spread and Mild Symptoms | Moderate | Public health measures could be eased, and the strain might be managed similarly to seasonal influenza. However, ongoing surveillance and research are necessary. |
| Sustained Transmission and Moderate Severity | High | The strain could become a seasonal respiratory pathogen. Continued vaccination efforts and pandemic preparedness measures are important. |
| Emergence of Highly Transmissible Variants | Low | Public health systems would face significant challenges. Rapid and effective vaccine development and deployment would be critical. |
| Development of Severe Complications | Low | Significant healthcare resources would be needed. Long-term health implications would be a major concern. |
Illustrative Information
Understanding the structure and behavior of the HKU5 coronavirus is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat its spread and impact. This section provides visual representations and detailed explanations of the virus’s characteristics, its interaction with human cells, and the methods used to detect its presence. Visualizations aid in comprehension and facilitate the application of this knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Viral Structure and Relationship to Other Coronaviruses
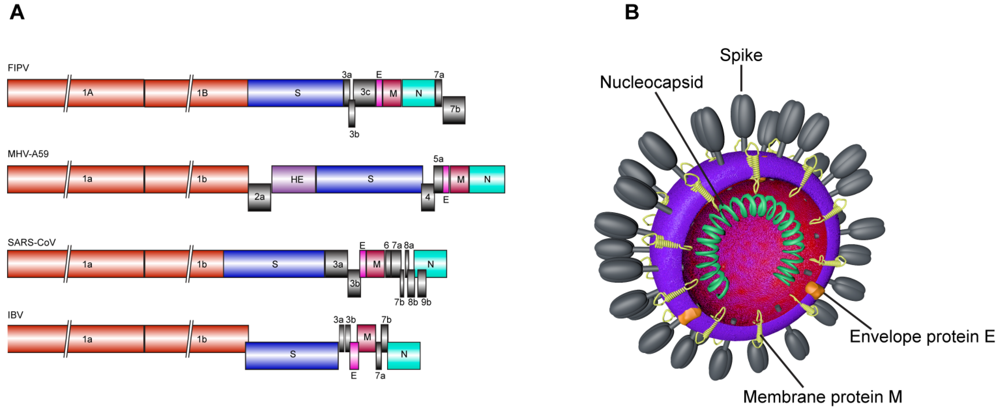
Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses, meaning their genetic material is enclosed within a lipid membrane. The HKU5 coronavirus, like other coronaviruses, possesses a characteristic studded surface. These spikes, or peplomers, are crucial for viral entry into host cells. The structure of these peplomers and the arrangement of the virus’s genetic material are highly conserved among various coronavirus strains.
This shared structure often leads to cross-reactivity in diagnostic tests, highlighting the importance of precise identification methods.  (Illustrative Diagram): This diagram shows a cross-section of the HKU5 coronavirus. The envelope is depicted as a lipid bilayer, and the peplomers (spikes) are shown protruding from the surface. A simplified representation of the viral RNA genome is also shown inside the envelope. This illustration highlights the similarities in structure with other coronaviruses.
(Illustrative Diagram): This diagram shows a cross-section of the HKU5 coronavirus. The envelope is depicted as a lipid bilayer, and the peplomers (spikes) are shown protruding from the surface. A simplified representation of the viral RNA genome is also shown inside the envelope. This illustration highlights the similarities in structure with other coronaviruses.
Molecular Mechanisms of Viral Interaction with Human Cells
The HKU5 coronavirus utilizes its peplomers to bind to specific receptors on the surface of human cells. This binding initiates a series of events leading to cellular entry. Once inside the cell, the viral RNA is released and used to create new viral components. The virus hijacks the host cell’s machinery to replicate itself, ultimately leading to the release of new viral particles.
Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing antiviral drugs targeting specific steps in this process.  (Illustrative Diagram): This diagram illustrates the process of viral entry. It depicts the virus binding to the cellular receptor, the subsequent fusion of the viral envelope with the cellular membrane, and the release of the viral RNA into the cytoplasm. The diagram also shows the replication of the viral genome and the assembly of new viral particles.
(Illustrative Diagram): This diagram illustrates the process of viral entry. It depicts the virus binding to the cellular receptor, the subsequent fusion of the viral envelope with the cellular membrane, and the release of the viral RNA into the cytoplasm. The diagram also shows the replication of the viral genome and the assembly of new viral particles.
Detection Techniques
Various techniques are employed to detect the HKU5 coronavirus in clinical samples. These methods vary in their sensitivity and specificity, and the choice of method depends on the specific context.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a molecular technique used to amplify specific DNA or RNA sequences. It is a powerful tool for detecting the presence of the HKU5 virus in samples, such as nasopharyngeal swabs. The high specificity of PCR primers ensures accurate identification. False positives are minimized through proper controls and rigorous testing procedures.
- Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA): IFA involves using antibodies to detect viral antigens. Fluorescently labeled antibodies bind to specific viral proteins, enabling visualization under a microscope. This method is useful for detecting viral proteins in infected cells or tissues. IFA provides a visual confirmation of the presence of the virus.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): ELISA is a common serological technique. It can be used to detect viral proteins or antibodies in serum or other biological fluids. This method is useful for identifying past or current infections, and the use of specific antibodies to detect the virus provides a high level of specificity. ELISA can detect the presence of antibodies against HKU5 coronavirus.
Comparative Analysis of Detection Methods
| Detection Method | Sensitivity | Specificity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCR | High | High | Sensitive and specific for detecting viral RNA |
| IFA | Moderate | High | Visual detection of viral antigens; suitable for tissue samples |
| ELISA | Moderate | High | Useful for detecting antibodies to the virus; indicative of past or present infection |
(Table): This table summarizes the sensitivity and specificity of various detection methods for HKU5 coronavirus. Sensitivity refers to the ability to correctly identify a true positive, while specificity refers to the ability to avoid identifying a false positive.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the emergence of the new HKU5 coronavirus strain necessitates a multifaceted approach to public health. Understanding its characteristics, transmission patterns, and potential impact is paramount for developing effective preventive measures and treatment strategies. Continued research, surveillance, and public health initiatives are crucial for mitigating the potential consequences of this new strain and safeguarding global health. The information provided in this post aims to equip readers with a foundational understanding of this evolving situation.
Common Queries
What are the typical symptoms of HKU5 infection?
Symptoms may vary, but common signs include fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Some individuals may experience milder symptoms, while others may develop more severe complications. Comparison with other coronavirus infections is vital to accurately assess the severity.
How does the HKU5 strain differ from other coronaviruses?
While still under investigation, the new HKU5 strain exhibits unique genetic traits, potentially affecting its transmissibility and severity compared to other known coronaviruses. Further research will clarify these differences.
Are there any vaccines or treatments available for HKU5 infection?
Currently, there are no specific vaccines or treatments for HKU5 infection. Research efforts are focused on developing potential solutions, but more time and data are needed.
What preventive measures can individuals take to reduce the risk of infection?
Standard precautions, such as frequent handwashing, maintaining social distance, and wearing masks in public spaces, can help reduce the risk of contracting HKU5, as well as other respiratory viruses. Following health guidelines and staying informed about the latest recommendations are essential.