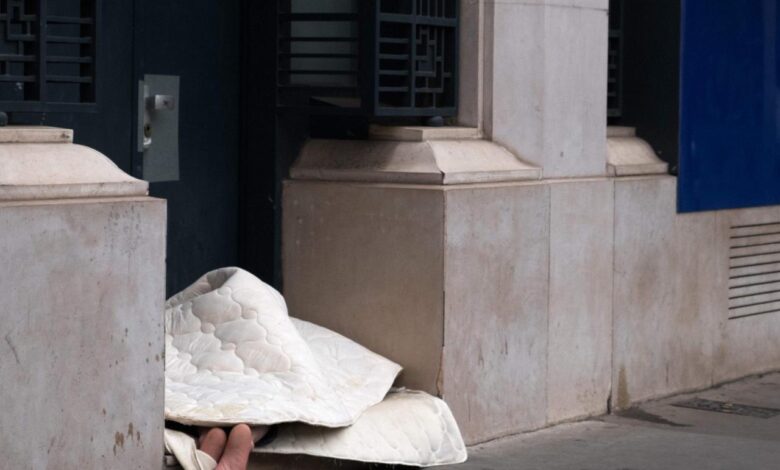
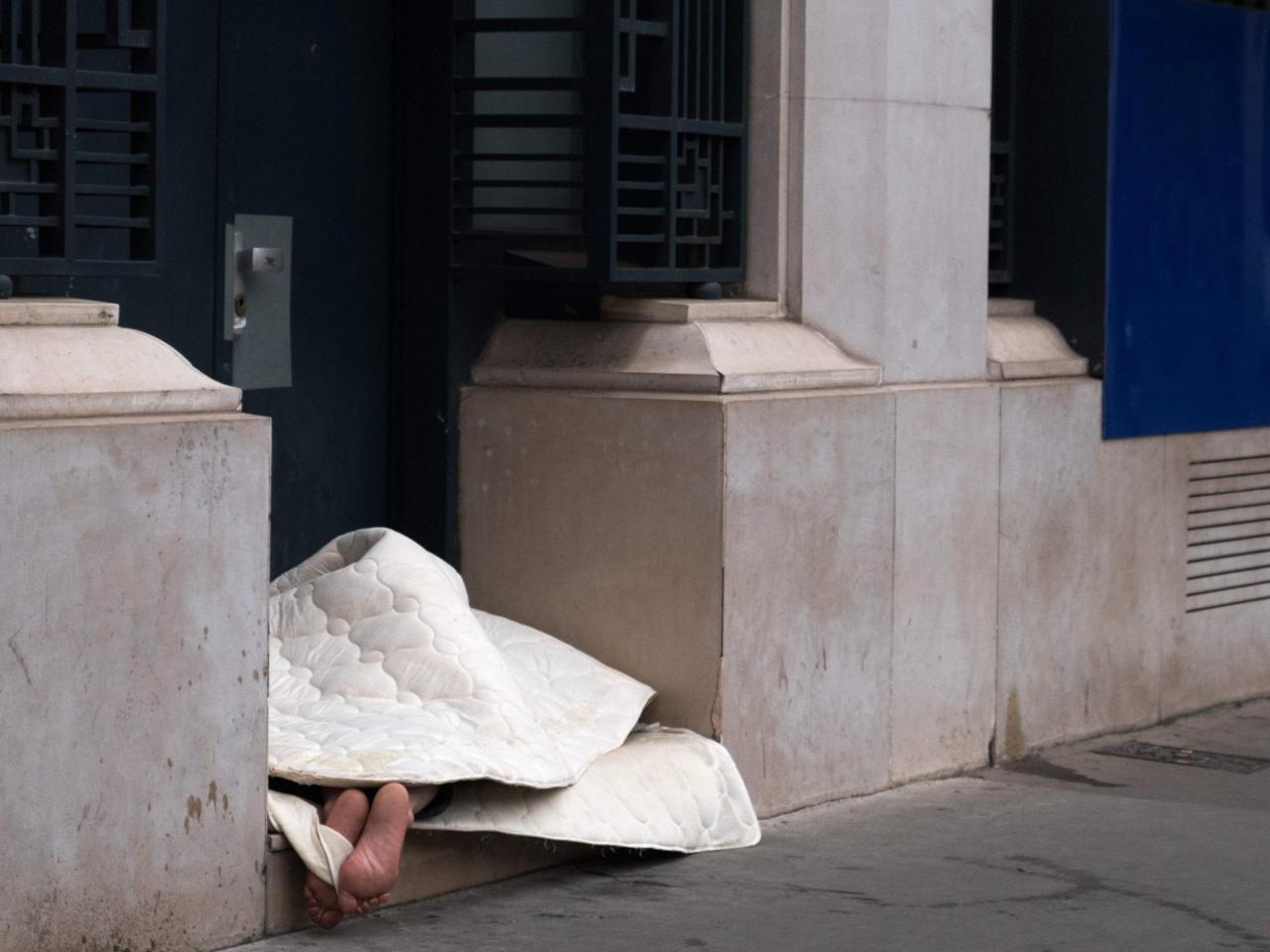
Misguided Policies Worsen US Homelessness Crisis Report
Misguided government policies worsen us homelessness crisis report – The report, “Misguided Government Policies Worsen US Homelessness Crisis,” throws a harsh spotlight on the failings of current policies and their devastating impact on the homeless population. It delves into the complexities of the issue, examining how inadequate government programs, a lack of affordable housing, and insufficient support for mental health and addiction issues contribute to the growing crisis.
This report is not simply a litany of problems; it offers a roadmap for change. It meticulously analyzes the unintended consequences of policies designed to help, highlighting how well-intentioned efforts often fall short. By revealing the underlying causes of homelessness, the report empowers us to advocate for solutions that address the root of the problem, not just its symptoms.
The Scope of the Homelessness Crisis

The homelessness crisis in the United States is a complex and multifaceted issue with far-reaching consequences for individuals, families, and communities. It’s not just about lacking a roof over one’s head; it’s about the ripple effects on health, education, and economic opportunities.
Statistics on Homelessness in the United States
The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) conducts an annual Point-in-Time (PIT) count of homeless individuals and families on a single night in January. This count provides a snapshot of homelessness across the country.
- According to the 2022 PIT count, an estimated 582,462 individuals experienced homelessness on a single night in January 2022. This represents a 0.3% increase from the previous year.
- Among those experiencing homelessness, 39% were unsheltered, meaning they were sleeping in places not meant for human habitation, such as streets, parks, or abandoned buildings.
- The remaining 61% were sheltered in emergency shelters, transitional housing programs, or safe havens.
Impact of Homelessness on Individuals, Families, and Communities
Homelessness can have a devastating impact on individuals, families, and communities.
The recent report highlighting how misguided government policies are worsening the US homelessness crisis is a stark reminder of the complex challenges facing our nation. Adding fuel to the fire is the news that grocery store inflation has soared at the fastest pace in 43 years , making it even harder for vulnerable populations to afford basic necessities.
This economic pressure, coupled with inadequate housing support, is pushing more and more people into a desperate cycle of poverty and homelessness.
- Individuals: Homelessness can lead to physical and mental health problems, including chronic illnesses, substance abuse, and mental health disorders. It can also increase the risk of violence and victimization.
- Families: Homelessness can disrupt children’s education, social development, and overall well-being. It can also strain family relationships and increase the risk of family separation.
- Communities: Homelessness can strain local resources, such as emergency shelters, healthcare services, and law enforcement. It can also contribute to social stigma and a sense of insecurity in communities.
Key Demographics Affected by Homelessness
Certain demographics are disproportionately affected by homelessness, including:
- Veterans: Veterans are at a higher risk of homelessness due to factors such as mental health issues, substance abuse, and difficulty transitioning back to civilian life.
- People with Disabilities: Individuals with disabilities are more likely to experience homelessness due to barriers to employment, affordable housing, and accessible transportation.
- Families with Children: Families with children are increasingly experiencing homelessness due to factors such as poverty, job loss, and domestic violence.
Misguided Government Policies
The homelessness crisis in the United States is a complex issue with multifaceted causes. While the lack of affordable housing is a major contributing factor, certain government policies have exacerbated the situation, hindering efforts to address homelessness effectively. This section will delve into specific policies that have been deemed detrimental to the fight against homelessness and analyze their unintended consequences.
Policies Restricting Access to Affordable Housing
The scarcity of affordable housing options is a significant challenge for individuals experiencing homelessness. However, government policies that restrict the development and availability of affordable housing have exacerbated this problem. One such policy is the zoning regulations that often limit the construction of multi-family housing units, especially in desirable areas. These regulations, often driven by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) sentiments, can lead to a shortage of affordable housing options, forcing individuals to seek shelter in overcrowded or unsafe conditions.
“Zoning regulations that restrict the development of multi-family housing have a significant impact on the availability of affordable housing options, ultimately contributing to the homelessness crisis.”
Another policy that has been criticized for its impact on affordable housing is the federal government’s reliance on housing vouchers as the primary means of assisting individuals experiencing homelessness. While housing vouchers can be an effective tool for providing rental assistance, they often face challenges in finding landlords willing to accept them. This is due to various factors, including concerns about tenant screening, potential damage to property, and the perception that voucher holders are less desirable tenants.
“The reliance on housing vouchers as the primary means of assisting individuals experiencing homelessness can be problematic due to the difficulty in finding landlords willing to accept them.”
The lack of affordable housing options can lead to individuals experiencing homelessness being forced to live in overcrowded or unsafe conditions, further perpetuating the cycle of homelessness. This can also have negative consequences for their health and well-being, as they may be exposed to violence, disease, and other hazards.
The Role of Affordable Housing
The shortage of affordable housing is a significant contributor to the homelessness crisis in the United States. This shortage is a complex issue with various contributing factors, including limited housing construction, rising housing costs, and a lack of government support for affordable housing programs. The relationship between affordable housing and homelessness is undeniable, as individuals and families struggling to find affordable housing are at a higher risk of becoming homeless.
The recent report on the worsening homelessness crisis in the US highlights the devastating consequences of misguided government policies. It’s a stark reminder that while political battles rage on, like the one surrounding the DOJ’s investigation into former President Trump, as outlined in this article ex fbi intelligence chief says doj has no case against trump , the fundamental needs of our most vulnerable citizens are being neglected.
We must prioritize solutions to address this crisis and ensure everyone has access to safe and affordable housing.
The Shortage of Affordable Housing
The United States faces a severe shortage of affordable housing, particularly for low-income households. The National Low Income Housing Coalition reports that there is a shortage of 7.2 million affordable and available rental homes for extremely low-income renters. This shortage translates to a national vacancy rate of just 1%, highlighting the intense competition for limited affordable housing options.
Government Policies and Affordable Housing
Government policies have a significant impact on the availability and affordability of housing. Federal housing programs, such as the Housing Choice Voucher Program (Section 8), provide rental assistance to low-income families. However, funding for these programs has been consistently reduced, leading to a decline in the number of available vouchers and a waiting list of millions of families seeking assistance.
Furthermore, policies related to zoning, land use, and development can influence the construction of affordable housing. Some municipalities have restrictive zoning laws that limit the development of multi-family housing, contributing to the shortage of affordable housing units.
Potential Solutions for Increasing Affordable Housing
Addressing the affordable housing shortage requires a multi-pronged approach, involving government initiatives, private sector investment, and community-based solutions.
It’s disheartening to see the report detailing how misguided government policies are exacerbating the homelessness crisis in the US. Meanwhile, political battles continue to rage, as seen in the recent request by the House GOP leader for documents from Attorney General Merrick Garland regarding the Mar-a-Lago raid. house gop leader seeks documents from merrick garland over mar a lago raid While these political clashes dominate headlines, the real-world consequences of policy failures are felt by those struggling to find shelter and support.
- Increased Funding for Affordable Housing Programs: Expanding funding for existing federal housing programs like Section 8 and creating new programs that incentivize the development of affordable housing are crucial steps. Increased funding would enable more families to access affordable housing and reduce the waitlist for assistance.
- Relaxing Zoning Regulations: Encouraging the construction of more multi-family housing by relaxing restrictive zoning laws can increase the supply of affordable housing units.
- Tax Incentives for Affordable Housing Developers: Providing tax breaks and other financial incentives to developers who build affordable housing can encourage private sector investment in affordable housing projects.
- Community Land Trusts: Community Land Trusts (CLTs) are non-profit organizations that own land and lease it to affordable housing developers. CLTs can help to preserve affordability by ensuring that housing remains affordable for future generations.
The Impact of Mental Health and Addiction: Misguided Government Policies Worsen Us Homelessness Crisis Report
The homelessness crisis is inextricably linked to the prevalence of mental health and addiction issues among those experiencing homelessness. Individuals experiencing homelessness are disproportionately affected by mental health and addiction challenges, often exacerbating their vulnerability and making it difficult to escape the cycle of homelessness.
Prevalence of Mental Health and Addiction Issues
Mental health and addiction issues are prevalent among the homeless population, significantly impacting their ability to find stable housing and support. Studies have shown that a large percentage of individuals experiencing homelessness have a mental health condition, such as depression, anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or struggle with substance abuse.
- A study by the National Alliance to End Homelessness found that approximately 20% of individuals experiencing homelessness have a serious mental illness, and 45% have a substance use disorder.
- The National Coalition for the Homeless estimates that 25% of people experiencing homelessness have a mental illness and 38% have a substance use disorder.
These conditions can lead to challenges with employment, relationships, and self-care, making it difficult to maintain stable housing.
The Role of Education and Employment
Breaking the cycle of homelessness requires addressing the barriers that prevent individuals from accessing education and employment opportunities. Without stable housing, it’s incredibly challenging for individuals to pursue education, gain work experience, and ultimately achieve economic independence.
The Challenges Faced by Homeless Individuals
The lack of a stable address poses significant challenges for homeless individuals seeking education and employment.
- Limited Access to Education: Many homeless individuals lack access to basic necessities like reliable transportation, childcare, and a quiet place to study. This makes it difficult to attend school regularly and succeed in their studies. Additionally, educational institutions often require proof of residency, which homeless individuals may not have.
- Employment Barriers: Homelessness can create significant obstacles in finding and maintaining employment. Employers may be hesitant to hire individuals without a stable address or a reliable way to get to work. Additionally, homeless individuals may face challenges with job interviews, background checks, and even accessing essential documents like identification.
The Impact of Government Policies
Government policies can either help or hinder homeless individuals’ access to education and employment.
- Positive Policies: Programs that provide financial assistance, job training, and educational support can empower homeless individuals to achieve economic independence. For example, the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA) offers job training and placement services to individuals experiencing homelessness.
- Negative Policies: Policies that restrict access to public assistance or create barriers to employment can worsen the situation for homeless individuals. For instance, some states have implemented policies that limit access to public benefits for individuals who have recently been homeless.
Potential Solutions for Improving Access to Education and Employment
Several strategies can be implemented to improve access to education and employment for homeless individuals.
- Increase Funding for Supportive Services: Investing in programs that provide financial assistance, childcare, transportation, and other support services can help homeless individuals overcome barriers to education and employment.
- Expand Access to Educational Opportunities: Schools and universities should implement policies that make it easier for homeless individuals to enroll and succeed in their studies. This could include offering flexible scheduling, providing on-site childcare, and waiving application fees.
- Promote Employer Partnerships: Government agencies and non-profit organizations can work with employers to create job training programs and employment opportunities specifically for homeless individuals.
- Address Criminal Justice Barriers: Policies that restrict employment opportunities for individuals with criminal records can disproportionately affect homeless individuals. States should consider policies that expunge criminal records for certain offenses and promote fair hiring practices.
Alternative Approaches

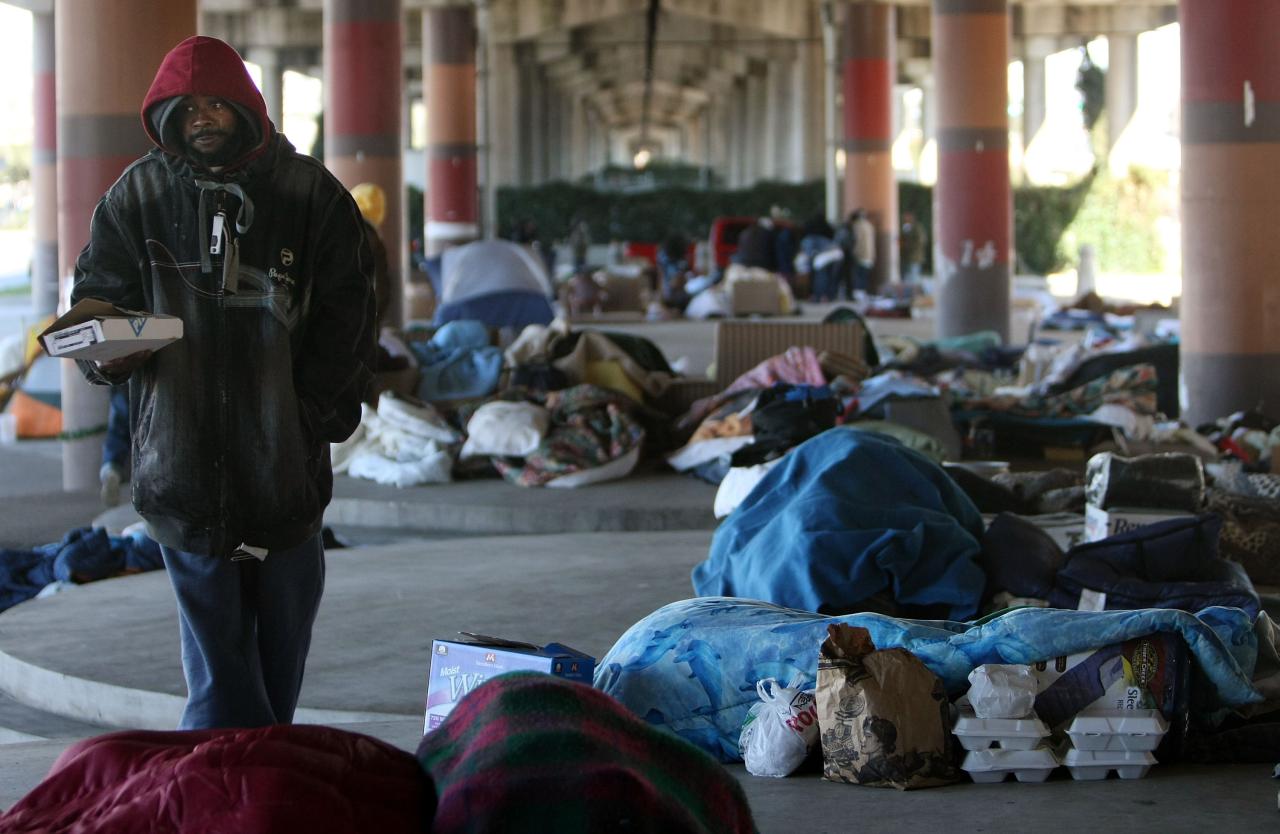
The current approach to addressing homelessness in the United States has proven ineffective. Many individuals and families remain trapped in a cycle of poverty and homelessness despite government programs and initiatives. Looking at alternative approaches implemented in other countries and communities can offer valuable insights into more effective strategies.
Housing First, Misguided government policies worsen us homelessness crisis report
Housing First is a philosophy and approach to ending homelessness that prioritizes providing permanent housing to individuals experiencing homelessness without preconditions such as sobriety, employment, or mental health treatment. The Housing First model emphasizes that stable housing is the foundation for addressing other challenges, such as mental health, addiction, and employment.
- Focus on Housing Stability: The core principle of Housing First is to provide permanent housing as the first step in addressing homelessness. This means offering individuals experiencing homelessness a place to live without requiring them to meet certain criteria or undergo specific programs.
- Supportive Services: While housing is the priority, individuals are offered access to supportive services such as mental health care, addiction treatment, and employment assistance. These services are offered voluntarily and tailored to the individual’s needs.
- Long-Term Stability: Housing First aims to provide long-term housing stability. The model emphasizes providing permanent housing solutions, not temporary shelters or transitional housing.
Finland’s Housing First Model
Finland has successfully implemented a Housing First model that has significantly reduced chronic homelessness. The Finnish model emphasizes providing individuals experiencing homelessness with permanent, affordable housing, along with comprehensive support services. The success of the Finnish model is attributed to a combination of factors:
- Strong Government Commitment: The Finnish government has made a significant financial commitment to Housing First, ensuring adequate funding for housing, support services, and staff.
- Collaboration Between Agencies: The Finnish model involves strong collaboration between housing providers, social services, and healthcare agencies. This coordination ensures that individuals receive the support they need.
- Focus on Individual Needs: The Finnish approach emphasizes individualized support, with case managers working closely with each person to understand their needs and develop a personalized plan.
The Role of Community
Community-based approaches can play a vital role in addressing homelessness. These approaches often involve collaborations between local organizations, government agencies, and community members.
- Community-Based Housing: Community-based housing initiatives focus on developing affordable housing options within existing neighborhoods. These initiatives can include creating affordable housing units, converting existing buildings into housing for individuals experiencing homelessness, or partnering with landlords to offer affordable rental units.
- Community Outreach: Outreach programs connect with individuals experiencing homelessness on the streets and provide them with information about available resources, support services, and housing options. Community outreach teams can also build relationships with individuals and help them navigate the complex systems of support.
- Community-Based Support Services: Community organizations can provide a range of support services to individuals experiencing homelessness, such as job training, life skills development, and mental health and addiction treatment. These services are often tailored to the specific needs of the community.
As we grapple with the disheartening reality of rising homelessness, this report serves as a critical wake-up call. It compels us to re-evaluate our approach, demanding that we move beyond short-term fixes and embrace long-term solutions. The report’s recommendations offer a blueprint for meaningful change, emphasizing the need for increased affordable housing, comprehensive mental health and addiction services, and targeted programs to empower individuals to achieve economic independence.
By taking action, we can create a future where homelessness is not a defining feature of our society, but a relic of the past.