
Millions Comply: Lockdowns, Cases, and Deaths
Millions comply with lockdowns stay at home policies as coronavirus cases deaths mount sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with personal blog style and brimming with originality from the outset.
The COVID-19 pandemic, a global health crisis, forced governments worldwide to implement stringent lockdown measures to curb the spread of the virus. This unprecedented event led to a dramatic shift in daily life, impacting everything from social interactions to economic activity.
The world witnessed a collective effort to slow the virus’s spread, with millions adhering to stay-at-home orders, social distancing guidelines, and mask mandates. These measures, while necessary, came at a cost. Lockdowns disrupted economies, strained healthcare systems, and profoundly impacted mental well-being.
As we navigate the aftermath of the pandemic, it’s crucial to examine the complex interplay between lockdowns, compliance, and the virus’s impact.
The Impact of Lockdowns on Daily Life: Millions Comply With Lockdowns Stay At Home Policies As Coronavirus Cases Deaths Mount
Lockdowns, implemented globally to curb the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, had a profound impact on daily life, disrupting routines, social interactions, and economic activities. From school closures to business shutdowns, the restrictions imposed by lockdowns reshaped the way people lived, worked, and interacted with each other.
Changes in Daily Routines
Lockdowns significantly altered daily routines, forcing people to adapt to new ways of living. The most noticeable change was the shift to remote work for many professionals, with offices closed and employees working from home. This led to a blurring of boundaries between work and personal life, with many individuals finding it challenging to maintain a healthy balance.
The closure of schools and universities resulted in the adoption of online learning, with students attending classes virtually. This presented challenges for both students and educators, as it required adjustments to teaching methods and learning styles. Social interactions among students were also significantly reduced, impacting their social development and well-being.
Impact on Businesses
Lockdowns had a devastating impact on businesses across various sectors. Many businesses were forced to temporarily close or operate at reduced capacity, leading to job losses, reduced revenue, and financial instability. The hospitality industry was particularly hard hit, with restaurants, bars, and hotels experiencing significant declines in customer traffic.
The tourism sector also suffered, with travel restrictions and lockdowns discouraging people from traveling.
Effects on Healthcare Services
Lockdowns impacted healthcare services in several ways. Hospitals and clinics faced challenges in managing patient flow and ensuring the safety of both patients and staff. Non-essential medical procedures were often postponed, leading to delays in treatment for some patients. The focus on COVID-19 care also strained resources and led to a redirection of medical personnel and supplies.
This, in turn, impacted the availability of care for other health conditions.
Psychological and Emotional Effects
Prolonged isolation and social distancing had a significant impact on people’s mental health. Many individuals experienced feelings of loneliness, anxiety, depression, and stress. The lack of social interaction and the uncertainty surrounding the pandemic contributed to these psychological challenges. The disruption of daily routines and the fear of contracting the virus also took a toll on mental well-being.
Some individuals struggled with sleep disturbances, changes in appetite, and difficulty concentrating.
Compliance and Public Sentiment
The success of lockdown measures in curbing the spread of a virus hinges on public compliance. This section delves into the factors influencing people’s decisions to adhere to these restrictions, exploring the diverse perspectives and motivations behind compliance. It also examines the role of government communication, trust, and public health messaging in shaping public sentiment and ultimately, compliance.
Factors Influencing Compliance
Public compliance with lockdown measures is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. These factors can be categorized into individual, social, and governmental influences.
- Individual Factors:Personal beliefs, risk perception, and trust in authorities play a significant role in shaping individual compliance. Individuals who perceive a higher risk of contracting the virus or who have a strong sense of civic duty are more likely to comply with lockdown measures.
Conversely, individuals who downplay the severity of the virus or distrust official information may be less likely to comply.
- Social Factors:Social norms and peer pressure can also influence compliance. If an individual’s social circle generally complies with lockdown measures, they are more likely to follow suit. Conversely, if an individual’s social circle disregards lockdown measures, they may be more likely to do the same.
- Governmental Factors:Government policies, communication strategies, and enforcement measures are crucial in influencing public compliance. Clear and consistent messaging from government officials, coupled with effective enforcement measures, can encourage compliance. However, inconsistent messaging, perceived government overreach, or lack of transparency can erode public trust and reduce compliance.
Perspectives and Motivations for Compliance
People’s motivations for complying with lockdown measures vary widely, reflecting diverse perspectives and priorities.
- Protecting Others:Some individuals comply with lockdown measures primarily out of concern for the well-being of others, particularly vulnerable populations like the elderly or those with underlying health conditions. They view compliance as a civic duty and a way to contribute to the collective effort to slow the spread of the virus.
- Personal Safety:Others prioritize their own safety and health, adhering to lockdown measures to minimize their risk of contracting the virus. This motivation is particularly strong among individuals who perceive a higher risk of severe illness or death from the virus.
- Economic Concerns:Some individuals may comply with lockdown measures out of economic necessity, fearing job loss or financial hardship if they fail to comply. This is particularly relevant for individuals in industries heavily affected by the pandemic, such as tourism or hospitality.
It’s a strange time, watching millions comply with lockdowns and stay-at-home policies as coronavirus cases and deaths mount. It makes me wonder how much of this obedience stems from genuine concern and how much from a deep-seated sense of societal obligation.
It’s almost like a collective anxiety, a fear that if we don’t follow the rules, the whole system will collapse. It’s a phenomenon that begs for deeper analysis, perhaps even a look into the mind of the Sanders millennial, a demographic often perceived as the driving force behind progressive ideals and social change.
Ultimately, the current situation raises complex questions about our relationship with authority, our willingness to sacrifice individual freedom for the greater good, and the very nature of collective action in a time of crisis.
- Disagreement with Policies:Some individuals may comply with lockdown measures despite disagreeing with the government’s policies or approach. They may comply out of a sense of obligation, a fear of legal repercussions, or a desire to avoid conflict.
Government Communication and Public Trust
Effective government communication is essential for fostering public trust and encouraging compliance with lockdown measures. Clear, consistent, and transparent messaging from government officials can build public confidence and enhance compliance.
- Transparency and Honesty:Public trust is built on transparency and honesty. Governments must be open and transparent about the risks associated with the virus, the rationale behind lockdown measures, and the progress being made in combating the pandemic.
- Clear and Consistent Messaging:Consistent and clear communication from government officials is crucial. Conflicting or ambiguous messages can sow confusion and undermine public trust.
- Targeted Messaging:Government communication should be tailored to specific demographics and communities. This ensures that information is received and understood by everyone, regardless of their background or language.
- Engaging with the Public:Governments should actively engage with the public, seeking feedback and addressing concerns. This helps build trust and ensures that policies are informed by public perspectives.
The Spread and Severity of the Coronavirus

The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, has had a profound impact on global health and society. The virus’s rapid spread and the severity of its effects have led to widespread lockdowns, disruptions to daily life, and a significant loss of life.
The Spread of the Coronavirus
The coronavirus spreads primarily through respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets can travel up to six feet and can be inhaled by others or land on their eyes, nose, or mouth. The virus can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
It’s a strange time to be alive, isn’t it? Millions are complying with lockdowns and stay-at-home policies as coronavirus cases and deaths mount, and while we all worry about the health of our communities, we’re also left wondering about the future of our nation.
Even the political landscape is in flux, with Michigan officials saying complete primary results won’t be released until Wednesday afternoon. It seems like everything is on hold, waiting for the dust to settle and for us to figure out what comes next.
In the meantime, we’re all trying to adapt and find some sense of normalcy in this new reality.
The virus has spread rapidly around the world, with cases reported in almost every country. The initial outbreak was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, and the virus quickly spread to other parts of the world, leading to a global pandemic.
Factors Contributing to the Rise in Cases and Deaths
Several factors have contributed to the rapid spread and high death toll associated with COVID-19:
- High transmissibility:The virus is highly contagious, with an average person infected with COVID-19 potentially infecting 2-3 other people.
- Asymptomatic spread:A significant number of people infected with COVID-19 experience no symptoms or mild symptoms. This allows the virus to spread unknowingly, contributing to its rapid transmission.
- Lack of immunity:The virus is novel, and humans have no prior immunity to it. This lack of immunity makes the population susceptible to infection.
- Global travel:The interconnected nature of the global community facilitated the rapid spread of the virus across borders.
- Healthcare system strain:The influx of COVID-19 patients overwhelmed healthcare systems in many countries, leading to delays in care and increased mortality rates.
- Inequalities in access to healthcare:Disparities in access to healthcare and social determinants of health have contributed to higher infection and death rates in marginalized communities.
The Effectiveness of Lockdown Measures
Lockdown measures, such as stay-at-home orders and social distancing guidelines, have been implemented in many countries to slow the spread of the virus. These measures aim to reduce the number of contacts between people, thereby limiting the transmission of the virus.
- Evidence of effectiveness:Studies have shown that lockdown measures have been effective in slowing the spread of the virus. For example, a study published in the journal Nature found that lockdown measures in China were associated with a significant reduction in the number of new COVID-19 cases.
- Challenges in implementation:The effectiveness of lockdown measures depends on factors such as compliance rates, the stringency of the measures, and the characteristics of the virus.
- Economic and social impacts:Lockdown measures have significant economic and social impacts, including job losses, business closures, and disruptions to education and healthcare services.
The Impact of the Coronavirus on Different Populations
The impact of the coronavirus has varied across different populations, with some groups experiencing disproportionate effects.
- Older adults:Older adults are at a higher risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19 due to their weakened immune systems and underlying health conditions.
- Individuals with underlying health conditions:People with conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and lung disease are also at increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
- Minorities and marginalized communities:These groups often face higher rates of chronic diseases, limited access to healthcare, and socioeconomic disadvantages, making them more vulnerable to the virus.
The Severity of the Coronavirus
COVID-19 can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild illness to severe disease and death. The severity of the illness can vary depending on factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the variant of the virus.
- Mild illness:Most people infected with COVID-19 experience mild illness, such as fever, cough, and fatigue.
- Severe illness:A smaller proportion of people develop severe illness, requiring hospitalization. This can include pneumonia, respiratory failure, and multi-organ failure.
- Death:COVID-19 can be fatal, particularly in older adults and those with underlying health conditions.
Economic and Social Consequences
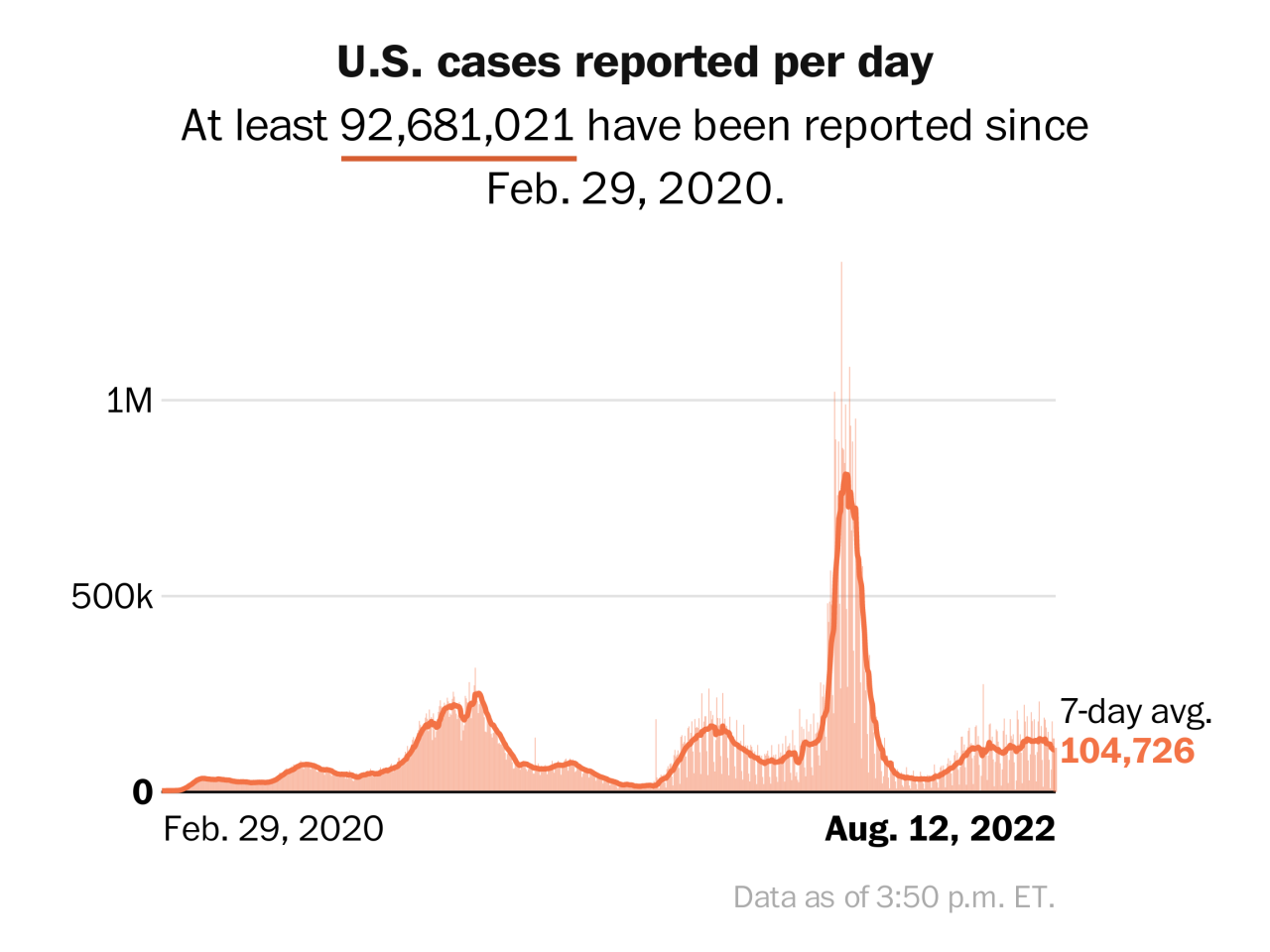
The COVID-19 pandemic and the accompanying lockdowns had profound economic and social consequences, impacting various aspects of daily life. The economic impact was felt across businesses, industries, and employment, while the social consequences extended to education, healthcare, and social services.
It’s a strange time, isn’t it? Millions are complying with lockdowns and stay-at-home policies, even as coronavirus cases and deaths mount. We’re all grappling with the reality of a pandemic, and it’s hard not to think about the future. Reading an article like marc thiessen the actual cost of bernie sanders spending plans is terrifying makes me wonder if we’ll ever be able to get back to normal, or if the economic fallout from this pandemic will be permanent.
It’s certainly a lot to think about, especially when we’re all trying to stay safe and healthy.
Communities worldwide had to adapt and respond to these challenges, showcasing resilience and ingenuity.
Economic Impact of Lockdowns
The economic impact of lockdowns was significant, leading to widespread business closures, job losses, and economic recession. Many businesses, particularly in the service sector, were forced to shut down due to restrictions on movement and social gatherings. The travel and tourism industry suffered immense losses, as travel bans and quarantine measures drastically reduced demand.
Supply chains were disrupted, leading to shortages of essential goods and raw materials. The overall economic activity contracted, resulting in a global recession.
- Business Closures and Job Losses:Lockdowns resulted in widespread business closures, particularly in sectors like hospitality, retail, and entertainment. Many businesses faced financial difficulties due to reduced revenue and increased costs. This led to significant job losses, increasing unemployment rates globally. For example, in the United States, unemployment rates soared to record highs during the early stages of the pandemic.
- Economic Recession:The economic impact of lockdowns led to a global recession, with a significant decline in economic activity. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimated that the global economy contracted by 3.5% in 2020. This was the deepest recession since the Great Depression.
- Government Support Measures:Governments around the world implemented various support measures to mitigate the economic impact of lockdowns. These measures included financial assistance to businesses, unemployment benefits, and stimulus packages. However, these measures were not always sufficient to fully offset the economic losses.
Social Consequences of Lockdowns
Lockdowns had significant social consequences, impacting education, healthcare, and social services. School closures disrupted the education of millions of children, while healthcare systems were overwhelmed by the surge in COVID-19 cases. Social isolation and mental health issues also became prevalent.
- Education Disruption:School closures during lockdowns disrupted the education of millions of children worldwide. Many countries shifted to online learning, but this posed challenges for students without access to technology or adequate internet connectivity. The disruption to education could have long-term consequences for students’ academic progress and future opportunities.
- Healthcare System Strain:Lockdowns placed immense strain on healthcare systems worldwide. Hospitals were overwhelmed with COVID-19 patients, leading to delays in non-emergency care and shortages of medical supplies. The pandemic also highlighted the need for increased investment in public health infrastructure.
- Social Isolation and Mental Health:Lockdowns contributed to social isolation and mental health issues. Restrictions on social gatherings and travel limited people’s ability to interact with others. This isolation led to increased feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression.
Community Adaptation and Response, Millions comply with lockdowns stay at home policies as coronavirus cases deaths mount
Despite the challenges posed by lockdowns, communities worldwide demonstrated remarkable resilience and ingenuity. They adapted to the new realities of life under lockdown, finding innovative ways to stay connected, support each other, and maintain essential services.
- Community Support Networks:Communities established support networks to help vulnerable individuals and families. These networks provided food assistance, medical supplies, and emotional support.
- Online Platforms for Connection:Online platforms played a crucial role in keeping people connected during lockdowns. Video conferencing tools allowed people to stay in touch with family and friends, while social media platforms provided a sense of community and shared experiences.
- Innovation in Service Delivery:Businesses and organizations adapted their operations to continue providing essential services during lockdowns. This included shifting to online delivery models, implementing contactless services, and utilizing technology to facilitate remote work.
Long-Term Effects and Lessons Learned

The COVID-19 pandemic and the widespread implementation of lockdowns have left an indelible mark on societies around the world. While the immediate health crisis has receded in many regions, the long-term effects of these measures on various aspects of life continue to be studied and debated.
Understanding these impacts is crucial for shaping policies and preparing for future public health emergencies.
The Impact of Lockdowns on Mental Health
The prolonged social isolation, economic uncertainty, and disruption of daily routines associated with lockdowns have had a significant impact on mental health. Studies have shown an increase in anxiety, depression, and stress levels during the pandemic.
- The isolation and disruption of social connections have contributed to feelings of loneliness and isolation, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing mental health conditions.
- Economic hardship and job losses have led to increased financial stress, which can exacerbate mental health problems.
- The constant fear of infection and the uncertainty surrounding the pandemic have created a sense of anxiety and fear that has impacted mental well-being.
The Impact of Lockdowns on Education
School closures and the transition to online learning during lockdowns have had mixed effects on education. While some students have adapted well to remote learning, others have struggled with access to technology, motivation, and social interaction.
- Students from disadvantaged backgrounds have been disproportionately affected by school closures, as they may lack access to reliable internet or a suitable learning environment at home.
- The disruption to traditional classroom learning has raised concerns about learning loss and the potential for long-term academic consequences, particularly for younger children.
- The social and emotional development of children and adolescents has been impacted by the lack of in-person interaction with peers and teachers.
Lessons Learned from the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has provided valuable lessons about public health preparedness, communication, and the importance of a multi-sectoral approach to crisis management.
- The importance of early detection and rapid response: The pandemic highlighted the need for robust surveillance systems and the ability to quickly implement public health measures to contain the spread of infectious diseases.
- The role of clear and consistent communication: Effective communication from public health officials is crucial for building trust, promoting compliance with public health measures, and mitigating misinformation.
- The need for a multi-sectoral approach: Addressing public health emergencies requires collaboration between governments, healthcare systems, businesses, and communities.
Strategies for Managing Future Public Health Emergencies
Drawing on the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic, it is essential to develop strategies for managing future public health emergencies more effectively.
- Investing in public health infrastructure: Strengthening surveillance systems, expanding testing capacity, and improving access to healthcare are crucial for early detection and response.
- Developing robust communication strategies: Establishing clear channels of communication, promoting accurate information, and addressing public concerns are essential for building trust and ensuring public cooperation.
- Building resilience in communities: Investing in social safety nets, providing mental health support, and promoting community engagement can help mitigate the social and economic impacts of future emergencies.
Epilogue
The pandemic and its associated lockdowns have left an indelible mark on our world. The experience has taught us valuable lessons about public health, social resilience, and the importance of preparedness. As we move forward, it’s essential to learn from the past, adapt to new challenges, and build a more robust and resilient future.
The impact of lockdowns on daily life, the dynamics of compliance, and the enduring consequences of the pandemic remain topics of ongoing discussion and reflection.






