Jobless Claims Jump as CCP Virus Bites US Labor Market
Jobless claims jump as CCP virus bites into US labor market, a stark reminder of the pandemic’s lingering impact on the economy. The surge in unemployment benefits applications signals a continued struggle for many Americans, with industries like hospitality, retail, and travel bearing the brunt of job losses.
The pandemic’s economic ripple effects have been far-reaching, impacting consumer spending, business operations, and government budgets.
The rise in jobless claims paints a sobering picture of the pandemic’s ongoing influence on the US labor market. While some sectors have begun to recover, others remain deeply affected, leaving many individuals facing financial hardship and uncertainty. This situation highlights the need for continued government support and strategies to promote economic recovery and job creation.
Impact of the CCP Virus on the US Labor Market
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the CCP virus pandemic, had a devastating impact on the US labor market, leading to widespread job losses and economic hardship. The pandemic’s effects were felt across all sectors, with some industries experiencing more significant disruptions than others.
Relationship between the CCP Virus Pandemic and Jobless Claims
The surge in jobless claims directly reflects the economic impact of the pandemic. As businesses shut down or scaled back operations due to lockdowns and social distancing measures, millions of workers were laid off or furloughed. This resulted in a sharp increase in the number of people filing for unemployment benefits.
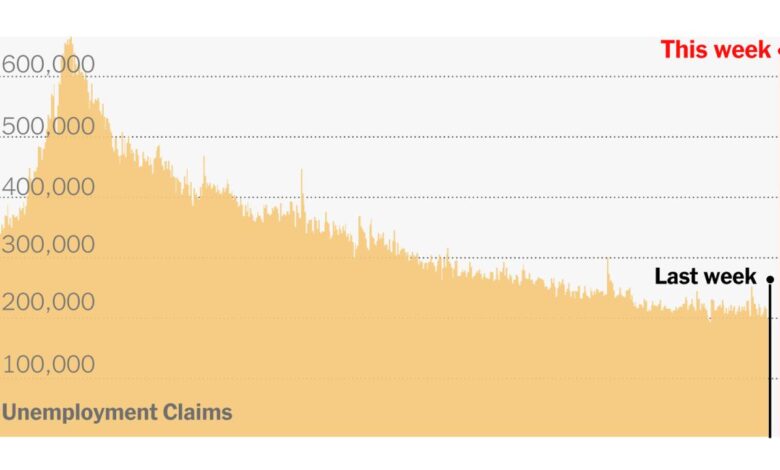
The initial surge in jobless claims occurred in March and April 2020, when the pandemic first hit the United States. The number of claims peaked at over 6.8 million in the week ending March 28, 2020.
Industries Most Affected by the Pandemic
The pandemic had a disproportionate impact on certain industries, particularly those that rely on face-to-face interactions or involve large gatherings. Some of the industries most affected by job losses include:
- Leisure and Hospitality:This sector, which includes restaurants, hotels, and entertainment venues, was among the hardest hit, as businesses were forced to close or operate at reduced capacity.
- Retail:Non-essential retail businesses faced significant challenges, with many forced to close temporarily or permanently.
- Transportation and Warehousing:Disruptions in supply chains and travel restrictions led to job losses in this sector.
- Education and Health Services:While healthcare workers were in high demand, some schools and other educational institutions faced closures and staff reductions.
Unemployment Rate Fluctuations during the Pandemic
The unemployment rate, which measures the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed, surged during the pandemic. The unemployment rate reached a peak of 14.7% in April 2020, the highest level since the Great Depression. The rate has since declined, but it remains elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels.
- April 2020:14.7%
- May 2020:13.3%
- June 2020:11.1%
- July 2020:10.2%
- August 2020:8.4%
Impact of Government Policies on the Labor Market
The government implemented a series of policies aimed at mitigating the economic impact of the pandemic on the labor market. These policies included:
- Unemployment Insurance:The government expanded unemployment benefits, increasing the duration and amount of benefits available to unemployed workers.
- Payroll Protection Program (PPP):This program provided forgivable loans to small businesses to help them retain their employees.
- Stimulus Checks:The government distributed direct payments to individuals and families to help them cover essential expenses.
These policies helped to stabilize the economy and prevent a deeper recession. However, the long-term impact of these policies on the labor market remains to be seen.
Economic Consequences of Rising Jobless Claims
The surge in jobless claims, a direct consequence of the CCP virus pandemic, has had a profound impact on the US economy. The economic implications are far-reaching, affecting consumer spending, business operations, government budgets, and the long-term outlook of the labor market.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Economic Growth
Rising jobless claims directly impact consumer spending, a key driver of economic growth. With millions of Americans losing their jobs, disposable income decreases, leading to reduced spending on goods and services. This decline in consumer spending can trigger a vicious cycle, as businesses respond by cutting production and laying off more workers, further exacerbating the economic downturn.
The latest jobless claims figures are a stark reminder of the devastating impact the CCP virus is having on the US labor market. With millions of Americans out of work, President Trump has declared himself a “wartime president” and invoked the Defense Production Act in a bid to ramp up production of critical medical supplies.
The president’s actions, outlined in this article , underscore the gravity of the situation and the need for a coordinated national response to this unprecedented crisis.
The decline in consumer spending can be illustrated by the drop in retail sales during the initial months of the pandemic. For example, in April 2020, retail sales plummeted by 16.4% compared to the previous month, reflecting the sharp decline in consumer spending due to widespread job losses.
Consequences for Businesses Struggling with Labor Shortages
The rise in jobless claims also presents challenges for businesses already struggling with labor shortages. While some industries, such as healthcare and technology, are experiencing a demand for skilled workers, others are facing difficulties filling open positions. Businesses may find it challenging to attract and retain qualified employees in a competitive job market, potentially hindering their growth and productivity.
For instance, the hospitality industry, which relies heavily on low-wage workers, has faced significant labor shortages since the pandemic. Many restaurants and hotels have been forced to reduce operating hours or close temporarily due to a lack of staff.
Impact of Unemployment on Government Budgets and Social Welfare Programs
Rising unemployment has significant implications for government budgets and social welfare programs. As unemployment benefits and other social safety nets are activated to support those who have lost their jobs, government spending increases. This can lead to budget deficits and potentially strain government resources.
The latest jobless claims report paints a grim picture, with the CCP virus continuing to wreak havoc on the US labor market. It’s not just affecting our wallets, though – it’s even impacting our love lives. A recent coronavirus alert on Tinder surprised dating apps users , highlighting how the pandemic is influencing our daily interactions.
With so much uncertainty, it’s hard to know what the future holds, but hopefully, the economy will bounce back soon, and we can all get back to swiping right without fear of a pandemic.
For example, the unemployment insurance system in the US has faced unprecedented strain during the pandemic, with the number of claims reaching record highs. The government’s response, including the expansion of unemployment benefits and other economic relief programs, has resulted in substantial increases in government spending.
Potential Long-Term Implications of the Pandemic on the US Labor Market
The pandemic has fundamentally altered the US labor market, with long-term implications for the economy. The rise in remote work and the adoption of new technologies may lead to a shift in job demand, potentially creating new opportunities in some sectors while displacing workers in others.
The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of job security and social safety nets, leading to calls for reforms in the labor market to provide greater protection for workers. For example, the rise of gig work and the decline of traditional employment have raised concerns about worker rights and benefits.
Government Response and Measures: Jobless Claims Jump As Ccp Virus Bites Into Us Labor Market
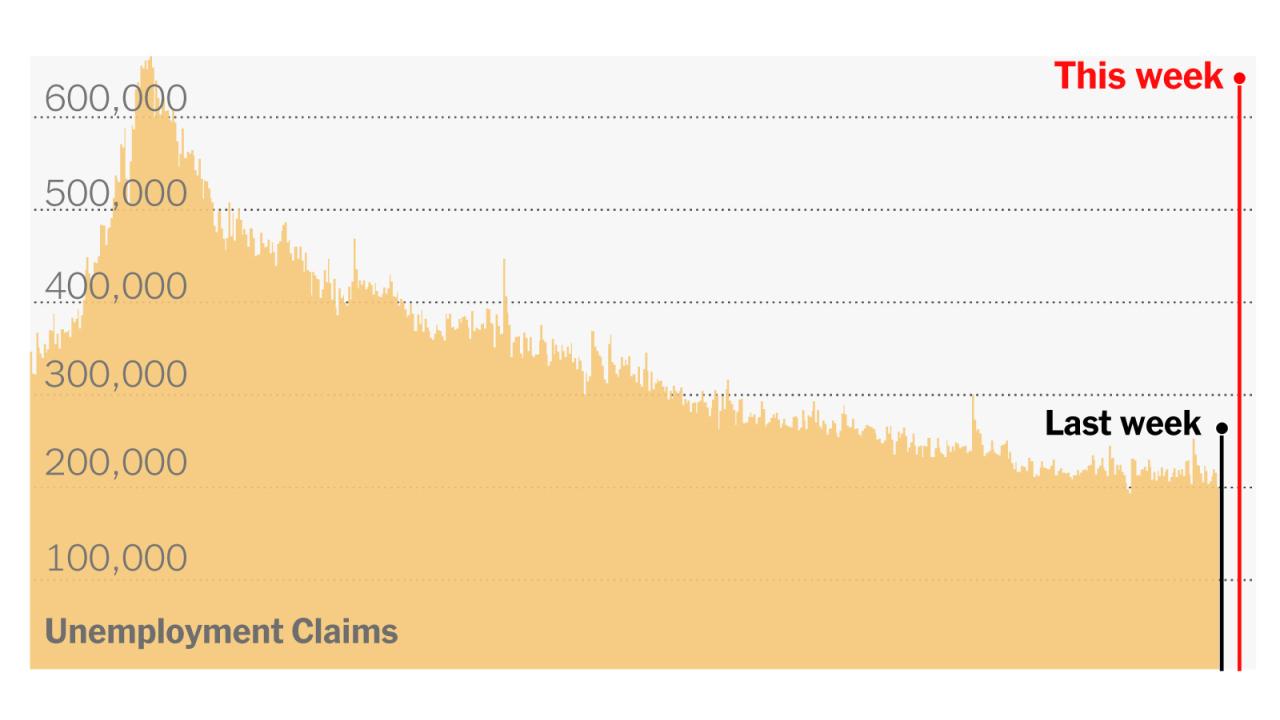
The unprecedented surge in jobless claims triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic forced the US government to implement a series of measures to support the labor market and mitigate the economic fallout. These measures included expanded unemployment benefits, stimulus packages, and other initiatives aimed at providing financial relief to individuals and businesses.
Unemployment Benefits and Stimulus Packages
The government’s response to the rising jobless claims was swift and comprehensive. The CARES Act, passed in March 2020, expanded unemployment benefits by providing an additional $600 per week to eligible recipients, extending the duration of benefits, and making it easier for self-employed individuals and gig workers to qualify.
This measure aimed to provide immediate financial assistance to unemployed individuals and help stabilize household incomes.The CARES Act also included significant stimulus packages, such as direct payments to individuals, loans for small businesses, and increased funding for healthcare providers. These measures were designed to stimulate the economy by boosting consumer spending and supporting businesses struggling to survive the pandemic.
Effectiveness of Government Measures
The government’s response to the pandemic-induced economic crisis was widely lauded for its speed and scale. The expanded unemployment benefits and stimulus packages played a crucial role in preventing a deeper economic recession and providing a safety net for millions of Americans who lost their jobs.
Studies have shown that these measures significantly reduced poverty and helped to stabilize household incomes during the pandemic.
Challenges and Limitations of Government Interventions, Jobless claims jump as ccp virus bites into us labor market
Despite the positive impact of government interventions, several challenges and limitations were associated with these measures. One key concern was the potential for disincentivizing work, as the expanded unemployment benefits provided a significant financial safety net. This concern led to debates about the potential for prolonging unemployment and hindering economic recovery.Another challenge was the logistical complexity of administering these programs, which involved a significant increase in the workload for state unemployment agencies.
The recent surge in jobless claims paints a grim picture of the US labor market, as the CCP virus continues to wreak havoc. While we grapple with our own challenges, it’s important to remember the global impact of this pandemic.
The situation in Iran, with reports suggesting a death toll far higher than officially reported, has prompted the US to extend an olive branch, as reported here. This underscores the need for international cooperation to combat this virus, and hopefully, the US labor market will eventually recover from the blow it’s currently facing.
The surge in applications and the need to adapt to new eligibility criteria created backlogs and delays in processing claims, leading to frustration among unemployed individuals.
Impact of Government Policies on Jobless Claims
| Policy | Impact on Jobless Claims ||————————————-|————————–|| CARES Act (Expanded Unemployment) | Reduced initial claims || Stimulus Packages | Mixed impact, potentially || | delayed recovery || Loan Programs for Small Businesses | Stabilized employment, || | but potential for long-term || | debt burdens || Payroll Protection Program (PPP) | Supported job retention, || | but potential for misuse | Note:The impact of government policies on jobless claims was complex and multifaceted.
While some measures, such as expanded unemployment benefits, provided immediate relief, others, such as stimulus packages, had a more nuanced impact. It is important to consider both the short-term and long-term effects of these policies when assessing their overall effectiveness.
Outlook for the Labor Market
The recent surge in jobless claims, a direct consequence of the CCP virus’s impact on the US economy, raises concerns about the future trajectory of the labor market. While the immediate outlook remains uncertain, several factors will influence the recovery process and shape the long-term landscape of employment.
Factors Influencing Future Jobless Claims
The future trajectory of jobless claims will depend on a complex interplay of factors, including:
- The course of the pandemic:The pace and effectiveness of vaccine rollout, the emergence of new variants, and public health measures will significantly impact the rate of economic recovery and job creation. As long as the pandemic persists, businesses will face continued uncertainty and may be hesitant to hire.
- Government policies:Fiscal and monetary policies, including stimulus packages, extended unemployment benefits, and loan programs, can provide much-needed support to workers and businesses. The continuation of these policies will be crucial for maintaining consumer spending and supporting economic growth.
- Consumer confidence:Consumer spending is a key driver of economic activity. If consumers remain wary about the future due to health concerns or economic uncertainty, they may be less likely to spend, which could further slow down the recovery process.
- The pace of business reopenings:The reopening of businesses across various sectors, particularly those in the hospitality, tourism, and entertainment industries, will be essential for job creation. The speed and extent of reopening will depend on factors like public health guidelines, consumer demand, and business confidence.
Potential for Economic Recovery and Job Creation
Despite the challenges, there are reasons for optimism about the potential for economic recovery and job creation in the post-pandemic period.
- Pent-up demand:As the pandemic recedes, consumers are expected to unleash pent-up demand for goods and services, boosting economic activity and driving job growth in sectors like retail, travel, and entertainment.
- Technological advancements:The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies across various industries. This trend is expected to continue, creating new opportunities for job creation in fields like software development, data analysis, and e-commerce.
- Government support:Continued government support through infrastructure investments, education and training programs, and tax incentives can create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
- Resilience of the US economy:The US economy has historically shown resilience in the face of crises. The strong fundamentals of the economy, including a skilled workforce, a robust financial system, and a dynamic entrepreneurial culture, provide a foundation for recovery.
Challenges and Opportunities Facing the US Labor Market
The US labor market faces several challenges and opportunities in the coming months and years.
- Skill gaps:The pandemic has exacerbated existing skill gaps in the workforce, as some jobs have become obsolete while others have emerged. Addressing these skill gaps through education and training programs will be crucial for ensuring a smooth transition to a post-pandemic economy.
- Automation and job displacement:Automation is expected to continue to displace workers in certain sectors, leading to concerns about job losses and income inequality. Policymakers will need to address these concerns by promoting reskilling and upskilling programs and creating a safety net for workers affected by automation.
- Remote work and the future of the workplace:The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work, leading to a shift in the way people work. This shift has implications for office space, commuting patterns, and the overall structure of the workforce. Policymakers will need to adapt labor laws and regulations to address these changes.
- Labor force participation:The pandemic has led to a decline in labor force participation, as some workers have left the workforce due to childcare responsibilities, health concerns, or early retirement. Encouraging workers to return to the workforce will be crucial for economic recovery.
Long-Term Impact of the CCP Virus on the US Labor Market
The long-term impact of the CCP virus on the US labor market will depend on several factors, including the speed and effectiveness of the recovery, the adoption of new technologies, and government policies.
- Increased automation:The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of automation in various sectors, which could lead to long-term job displacement in certain industries. However, it could also create new opportunities in fields related to automation and robotics.
- Shift towards remote work:The pandemic has normalized remote work, which could lead to a long-term shift in the way people work. This shift could have implications for office space, commuting patterns, and the overall structure of the workforce.
- Increased demand for skilled workers:The pandemic has highlighted the importance of skilled workers in fields like healthcare, technology, and logistics. This trend is likely to continue in the long term, creating opportunities for workers with specialized skills.
- Increased focus on worker well-being:The pandemic has raised awareness about the importance of worker well-being, leading to a focus on mental health, work-life balance, and flexible work arrangements. These changes could lead to a more humane and sustainable workplace in the long term.
Final Wrap-Up
The surge in jobless claims serves as a stark reminder of the pandemic’s enduring impact on the US economy. While the outlook for the labor market remains uncertain, proactive measures and strategic interventions are crucial for fostering economic recovery and supporting those affected by job losses.
The government’s role in providing unemployment benefits and stimulus packages remains critical in mitigating the pandemic’s negative effects and ensuring a more equitable recovery.





