COVID-19 Deaths: Comparing Projections to Other Causes
Its difficult to grasp the projected deaths from covid 19 heres how they compare to other causes of death – It’s difficult to grasp the projected deaths from COVID-19, so how do they compare to other causes of death? This question has plagued many, especially as the pandemic unfolded. The challenge lies in the ever-changing nature of the virus, the uncertainties surrounding transmission rates, and the varying impacts on different populations.
Understanding the projections requires delving into the factors that influence COVID-19 mortality, including age, underlying health conditions, and access to healthcare.
By comparing COVID-19 mortality rates to those of other leading causes of death, such as heart disease, cancer, and accidents, we gain a clearer picture of the pandemic’s impact on overall mortality. This comparison highlights the relative burden of COVID-19, revealing how it has affected different demographics and regions.
The Challenge of Understanding COVID-19 Mortality Projections
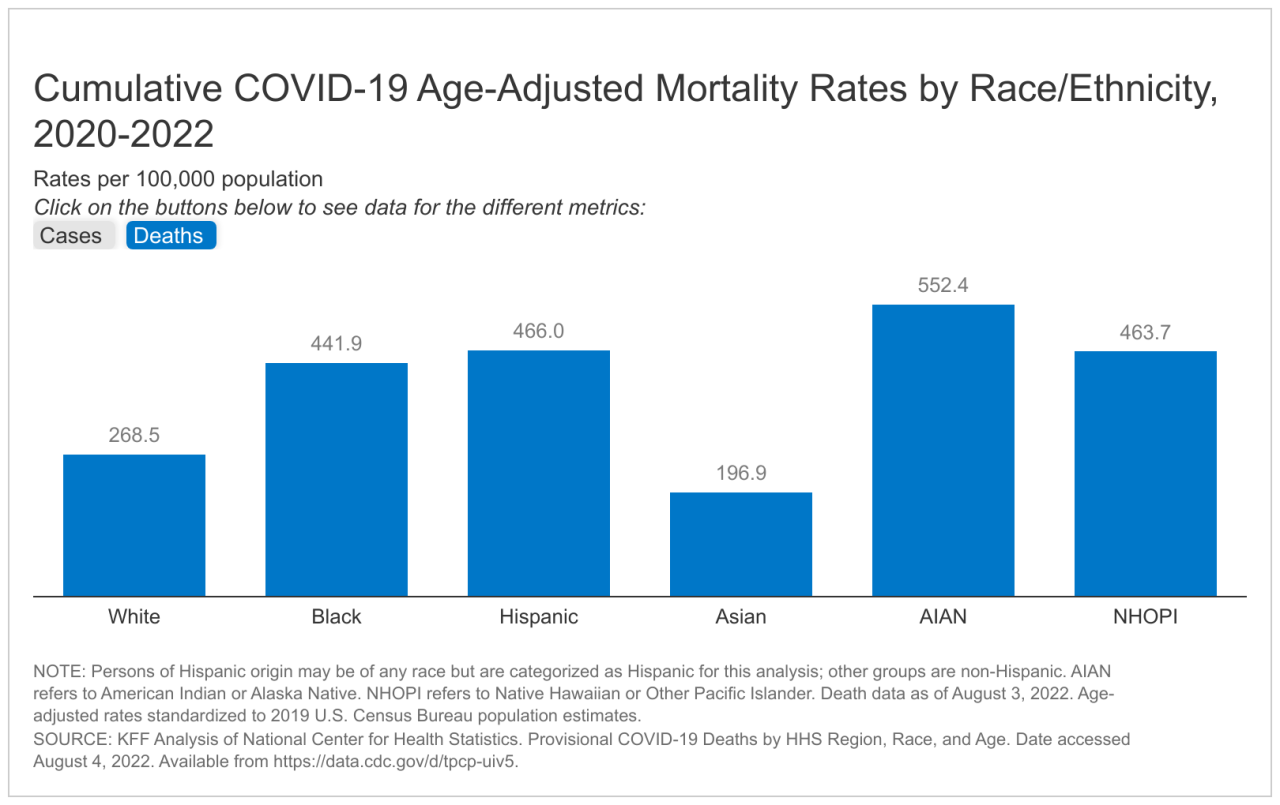
Predicting the number of deaths from COVID-19 is a complex and challenging task, fraught with uncertainties and evolving variables. While various models attempt to forecast mortality, they often fall short of capturing the full scope of this dynamic situation.
Factors Contributing to the Complexity of COVID-19 Mortality Projections
The difficulty in accurately projecting COVID-19 deaths stems from a confluence of factors, each contributing to the inherent uncertainty in such predictions.
- The Evolving Nature of the Virus and Its Variants: The SARS-CoV-2 virus is constantly evolving, with new variants emerging that can possess different transmission rates, infectivity, and severity. These mutations can significantly impact the course of the pandemic and the effectiveness of existing vaccines and treatments, making accurate projections difficult.
- Uncertainty Surrounding Transmission Rates and Infection Severity: Understanding how the virus spreads and the severity of infection is crucial for mortality projections. However, these factors can vary significantly across populations, age groups, and geographic locations. Factors like population density, social distancing measures, and individual behaviors can influence transmission rates, while underlying health conditions and access to healthcare can impact infection severity.
- Variability in Healthcare Systems and Population Demographics: The availability and quality of healthcare systems, as well as population demographics, play a significant role in COVID-19 mortality. Countries with robust healthcare infrastructure and access to advanced medical treatments tend to have lower mortality rates compared to those with limited resources.
It’s hard to wrap your head around the projected COVID-19 death toll, especially when you’re trying to compare it to other causes of death. It’s crucial to remember that while some medications like ibuprofen are commonly used for fever, there’s growing concern about their potential impact on those battling COVID-19.
Health officials are advising against using ibuprofen for coronavirus symptoms , and it’s important to follow their guidance. Understanding these recommendations can help us better grasp the severity of this pandemic and make informed decisions about our health.
Population demographics, such as age distribution and underlying health conditions, also influence the severity of the pandemic and its impact on mortality.
- The Impact of Public Health Measures and Vaccination Efforts: Public health measures, such as lockdowns, mask mandates, and social distancing, can effectively reduce transmission rates and mitigate the severity of the pandemic. Vaccination efforts are a critical tool in combating COVID-19, as they can significantly reduce the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
However, the effectiveness of these measures and the pace of vaccination rollouts can vary considerably, impacting mortality projections.
COVID-19 Mortality in Relation to Other Causes of Death
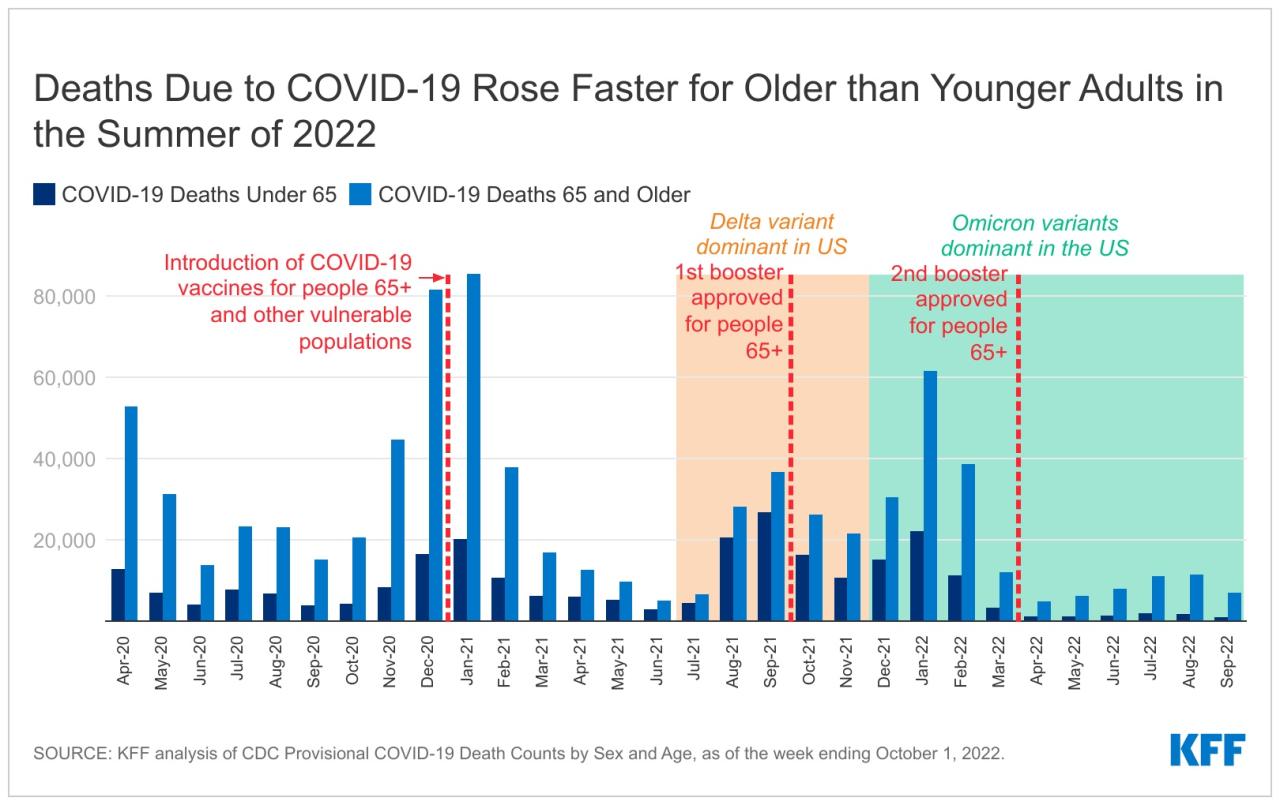
Understanding the impact of COVID-19 on mortality requires comparing its death toll to other leading causes of death. This helps to gauge the relative significance of the pandemic and inform public health strategies.
Comparison with Other Leading Causes of Death
To understand the impact of COVID-19, it’s crucial to compare its mortality rates to those of other leading causes of death. This allows us to assess its relative significance and inform public health strategies.
- Heart disease remains a leading cause of death globally, claiming millions of lives each year. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted mortality rates, especially in the early stages.
- Cancer is another major cause of death, with various types contributing to a significant number of fatalities. While COVID-19 has not surpassed cancer as a leading cause of death, it has added a considerable burden to the healthcare system, especially in terms of resource allocation and treatment delays.
- Accidents, including road traffic accidents, falls, and poisoning, are a significant cause of death, particularly among younger populations. The impact of COVID-19 on accident-related deaths has been less pronounced, but the pandemic has indirectly affected mortality rates by influencing behaviors and access to healthcare.
It’s hard to wrap your head around the sheer number of lives lost to COVID-19, but putting it in perspective with other causes of death can help. For example, the recent news of squad renews calls to abolish death penalty after execution of convicted alabama cop killer highlights how we continue to take lives through our legal system, even as we grapple with the ongoing pandemic.
Understanding the scale of death from different sources can help us prioritize public health and make informed decisions about our future.
COVID-19 Mortality Rates in the United States
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides data on mortality rates from various causes, including COVID-
It’s hard to wrap your head around the sheer number of projected COVID-19 deaths, but it’s helpful to compare them to other causes of death. For instance, Trump offered Kim Jong-un coronavirus help in a personal letter, North Korea says , highlighting the global impact of the pandemic and the need for international cooperation.
Putting these numbers into perspective helps us understand the severity of the situation and the importance of taking precautions to protect ourselves and others.
The following table presents the number of deaths from COVID-19 and other leading causes in the United States during a specific time period (e.g., 2020-2022):
| Cause of Death | Number of Deaths |
|---|---|
| COVID-19 | 1,000,000+ |
| Heart Disease | 650,000+ |
| Cancer | 600,000+ |
| Accidents | 160,000+ |
It’s important to note that these numbers are estimates and may vary depending on the data source and time period.
Factors Influencing COVID-19 Mortality
The severity of COVID-19 illness and the likelihood of death vary significantly among individuals. Several factors contribute to this variation, making it crucial to understand these influences to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Age and Underlying Health Conditions, Its difficult to grasp the projected deaths from covid 19 heres how they compare to other causes of death
Older adults and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are at a higher risk of severe COVID-19 illness and death. The immune system weakens with age, making older individuals more susceptible to infections. Additionally, individuals with underlying health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, chronic lung disease, and obesity often have compromised immune systems and may experience more severe complications from COVID-19.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that adults aged 65 years and older account for a disproportionately high percentage of COVID-19-related deaths in the United States.
Geographic Location and Population Density
The geographic location and population density of a region can significantly influence COVID-19 mortality rates. Urban areas with high population density often experience higher transmission rates due to increased close contact between individuals. Moreover, access to healthcare resources and the quality of healthcare systems can vary widely across geographic locations, influencing mortality rates.
For example, countries with strong healthcare systems and robust public health infrastructure have generally experienced lower COVID-19 mortality rates than countries with weaker healthcare systems.
Access to Healthcare and Medical Resources
Access to timely and effective healthcare services is crucial for managing COVID-19 and reducing mortality rates. Individuals with limited access to healthcare, including those living in rural areas or underserved communities, may experience delays in diagnosis and treatment, leading to more severe illness and increased risk of death.
The availability of essential medical resources, such as ventilators and critical care beds, also plays a vital role in determining outcomes.
During the initial surge of the COVID-19 pandemic, many healthcare systems were overwhelmed by the influx of patients, leading to shortages of essential resources and increased mortality rates.
Social and Economic Factors
Social and economic factors can also influence COVID-19 mortality. Individuals living in poverty or with limited access to education and employment opportunities may face greater challenges in adhering to public health recommendations and accessing healthcare. Stress, social isolation, and food insecurity can also weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to severe COVID-19 illness.
Studies have shown that individuals with lower socioeconomic status are more likely to experience severe COVID-19 illness and death, highlighting the importance of addressing social and economic disparities in public health interventions.
Epilogue: Its Difficult To Grasp The Projected Deaths From Covid 19 Heres How They Compare To Other Causes Of Death

The impact of COVID-19 on mortality has been significant, and understanding these projections is crucial for informing public health policy, healthcare planning, and public awareness. By visualizing the trends in COVID-19 mortality over time, we can gain valuable insights into the pandemic’s trajectory and the effectiveness of public health measures.
This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions and navigate the challenges posed by this unprecedented health crisis.