COVID Vaccine, Gut Health, and Autoimmune Disease: A Deep Dive
How the covid vaccine harms your gut leading to dysbiosis brain fog and autoimmune disease – How the COVID vaccine harms your gut leading to dysbiosis, brain fog, and autoimmune disease is a topic that’s sparked a lot of debate and concern. While the benefits of vaccination are undeniable, understanding the potential impact on our gut health is crucial.
This blog delves into the complex relationship between the COVID vaccine, gut microbiome, and overall well-being, exploring the science behind these connections and offering insights into potential risks and protective measures.
Our gut microbiome, a vast ecosystem of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a critical role in our health, influencing everything from digestion and immunity to mental well-being. Research suggests that COVID-19 infection itself can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to gut dysbiosis, a state of imbalance in the microbiome.
The COVID-19 vaccine, designed to trigger an immune response against the virus, may also have unintended consequences for our gut health, potentially contributing to inflammation and dysbiosis. While more research is needed to fully understand the long-term implications, it’s important to be aware of these potential risks and explore strategies to protect our gut health.
Gut Microbiome and COVID-19

The gut microbiome, the vast community of bacteria, fungi, and viruses that reside in our digestive system, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. These microscopic inhabitants contribute to digestion, nutrient absorption, immune system development, and even mental well-being.
A healthy gut microbiome is characterized by a diverse population of microbes that work in harmony to perform these essential functions. However, disruptions to this delicate balance, known as dysbiosis, can have far-reaching consequences for our health.COVID-19 infection has emerged as a significant threat to gut microbiome health.
Research suggests that the virus can directly impact the gut, leading to alterations in the composition and function of the gut microbiota.
Impact of COVID-19 on Gut Microbiome
The impact of COVID-19 on the gut microbiome is multifaceted and complex. Research findings indicate that the virus can disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria in several ways:
- Direct Viral Infection:COVID-19 can directly infect cells in the gut lining, leading to inflammation and damage. This disruption can alter the composition and function of the gut microbiota.
- Immune System Response:The body’s immune response to COVID-19 can also impact the gut microbiome. The inflammatory response triggered by the virus can lead to changes in the gut environment, favoring the growth of certain bacteria while suppressing others.
- Antibiotic Use:Antibiotic use, often prescribed to treat COVID-19 complications, can further disrupt the gut microbiome. Antibiotics can kill off beneficial bacteria, creating opportunities for opportunistic pathogens to thrive.
- Changes in Diet and Lifestyle:The illness itself and associated hospitalizations can lead to changes in diet and lifestyle, further impacting the gut microbiome. Reduced food intake, changes in eating habits, and decreased physical activity can all contribute to alterations in gut bacteria composition.
COVID-19 Vaccines and Gut Health
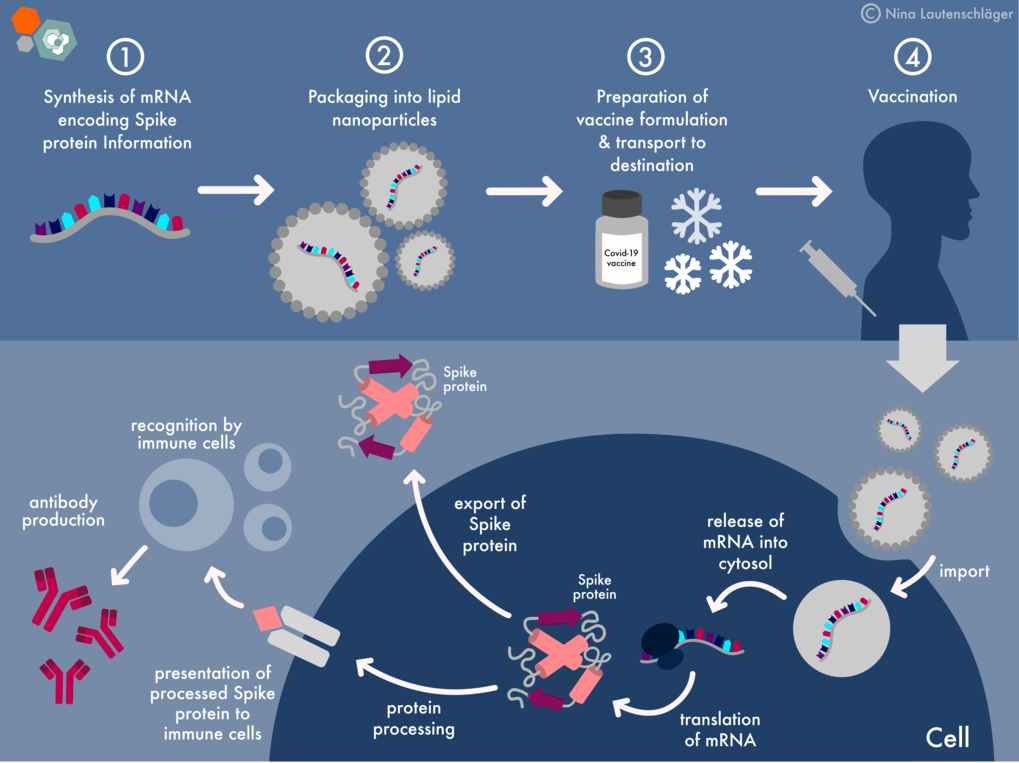
The gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and viruses residing in the gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in overall health and immunity. Emerging evidence suggests that COVID-19 vaccines, while offering protection against severe illness, may potentially influence gut health.
Potential Mechanisms of Vaccine Impact on Gut Health
Understanding how COVID-19 vaccines might affect gut health requires examining the potential mechanisms involved. The immune system, particularly the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), is intricately connected to the gut microbiome. Vaccines, designed to stimulate the immune system, can trigger responses that may extend beyond the targeted pathogen.
- Immune System Activation and Gut Inflammation:Vaccines, by design, activate the immune system, potentially leading to systemic inflammation. This inflammation might extend to the gut, affecting the delicate balance of the microbiome.
- Gut Microbiota Composition Changes:The immune system’s activation in response to vaccination could alter the composition and function of the gut microbiota. This shift, known as dysbiosis, can disrupt the delicate balance of beneficial and potentially harmful microorganisms in the gut.
- Gut Barrier Integrity:The gut lining, a crucial barrier preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream, can be compromised by inflammation. Vaccines, through their immune activation, might contribute to gut barrier disruption, potentially allowing harmful substances to enter the bloodstream and trigger systemic inflammation.
Vaccine-Induced Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis
Studies have explored the potential link between COVID-19 vaccines and gut inflammation or dysbiosis. While the evidence is still emerging, some studies suggest that certain vaccines might induce changes in the gut microbiome.
- Studies on mRNA Vaccines:A study published in the journal “Gut Microbes” in 2021 investigated the impact of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines on the gut microbiome in healthy individuals. The study found that vaccination was associated with a decrease in the abundance of certain beneficial bacteria, including -Akkermansia muciniphila*, known for its role in gut barrier integrity.
However, it’s important to note that this study was small and further research is needed to confirm these findings.
- Studies on Viral Vector Vaccines:Research is ongoing to understand the potential impact of viral vector vaccines on gut health. Preliminary findings suggest that these vaccines may also induce changes in the gut microbiome, but more research is needed to determine the long-term effects.
Studies Investigating Gut Microbiota Changes
Researchers are actively investigating the link between COVID-19 vaccines and changes in gut microbiota composition. Studies utilizing various techniques, including metagenomic sequencing, are being conducted to analyze the impact of vaccination on the gut microbiome. These studies aim to:
- Identify Specific Microbiota Changes:Researchers are exploring whether certain types of bacteria are more susceptible to changes following vaccination.
- Understand Functional Consequences:The focus is on understanding how changes in the gut microbiome might affect gut health, immune function, and overall health outcomes.
- Develop Strategies for Mitigation:If significant changes in the gut microbiome are observed, researchers aim to develop strategies to mitigate potential negative effects, such as dietary interventions or probiotic supplementation.
Dysbiosis and Its Consequences
Dysbiosis, a disruption in the delicate balance of microorganisms in the gut, can have profound implications for overall health. It occurs when the composition and activity of the gut microbiota deviate from their normal state, leading to an imbalance of beneficial and harmful bacteria.
It’s a complex issue, and while I’m concerned about the potential gut-related complications of the COVID vaccine, I also find myself drawn to the global implications of events like the war in Ukraine. Understanding the unprecedented American sanctions on Russia explained is crucial for grasping the broader geopolitical landscape.
Ultimately, the impact of these sanctions on the global economy could have far-reaching consequences, potentially exacerbating existing health concerns and further complicating the narrative surrounding vaccine-related health issues.
This imbalance can contribute to a range of health issues, impacting digestion, immunity, and even brain function.
The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem that plays a vital role in our overall health. Research suggests that the COVID-19 vaccine can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to dysbiosis, a condition marked by an imbalance in gut bacteria. This imbalance can contribute to brain fog, fatigue, and even autoimmune disorders.
It’s fascinating how advancements in science are constantly revealing new possibilities, like the potential to detect earthquakes using gravity signals at the speed of light, as reported in this article. Understanding these complex interactions between our bodies and the environment is crucial for maintaining optimal health, especially in the face of emerging challenges like vaccine-related side effects.
The Link Between Gut Dysbiosis and Autoimmune Diseases
Gut dysbiosis can play a significant role in the development of autoimmune diseases. The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in immune system development and regulation. When dysbiosis occurs, the immune system can become dysregulated, leading to an inappropriate immune response that targets the body’s own tissues.
This can trigger autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and type 1 diabetes.
The gut microbiota can influence the immune system through various mechanisms, including the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have anti-inflammatory effects, and the regulation of immune cell populations.
Gut Dysbiosis and Brain Fog
Gut dysbiosis can contribute to brain fog and cognitive impairment through various mechanisms. The gut-brain axis, a complex communication network between the gut and the brain, is heavily influenced by the gut microbiota. When dysbiosis occurs, the communication along this axis can be disrupted, leading to changes in brain function.
- Increased inflammation:Dysbiosis can trigger inflammation in the gut, which can spread to the brain, contributing to brain fog and cognitive decline.
- Altered neurotransmitter production:The gut microbiota produces neurotransmitters that influence mood, cognition, and sleep. Dysbiosis can disrupt this production, leading to imbalances in neurotransmitter levels and cognitive impairment.
- Reduced production of essential nutrients:The gut microbiota plays a role in the production of essential nutrients, such as vitamin B12 and short-chain fatty acids. Dysbiosis can reduce the production of these nutrients, which are vital for brain health and cognitive function.
Dietary and Lifestyle Interventions: How The Covid Vaccine Harms Your Gut Leading To Dysbiosis Brain Fog And Autoimmune Disease
Supporting gut health is crucial for overall well-being, especially in the context of potential gut dysbiosis linked to COVID-19 vaccines. By adopting a holistic approach that includes dietary and lifestyle changes, you can promote a balanced gut microbiome and mitigate the potential adverse effects.
Dietary Interventions
A balanced diet rich in prebiotics, probiotics, and diverse nutrients is essential for fostering a healthy gut microbiome.
- Consume Prebiotic-Rich Foods:Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that act as food for beneficial gut bacteria. Include foods like asparagus, bananas, garlic, onions, and leeks in your diet.
- Incorporate Probiotic Foods:Probiotics are live microorganisms that can help restore balance to the gut microbiome. Consume fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso.
- Limit Processed Foods:Processed foods often contain high amounts of sugar, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives that can disrupt gut health.
- Increase Fiber Intake:Fiber is essential for promoting regular bowel movements and feeding beneficial gut bacteria. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet.
- Stay Hydrated:Adequate hydration is crucial for digestive health. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Lifestyle Interventions, How the covid vaccine harms your gut leading to dysbiosis brain fog and autoimmune disease
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact gut health.
- Manage Stress:Chronic stress can negatively affect the gut microbiome. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature.
- Get Enough Sleep:Adequate sleep is essential for gut health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Regular Exercise:Physical activity promotes gut health by improving blood flow and reducing inflammation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption:Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt gut health. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation.
- Avoid Smoking:Smoking damages the gut lining and can contribute to dysbiosis. If you smoke, quitting is the best way to improve your gut health.
Sample Meal Plan
A sample meal plan focusing on gut-friendly foods might look like this:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts, or yogurt with chia seeds and fruit.
- Lunch:Salad with grilled chicken or fish, or a lentil soup with whole-grain bread.
- Dinner:Salmon with roasted vegetables, or chicken stir-fry with brown rice.
- Snacks:Fruits, vegetables, nuts, or yogurt.
Final Thoughts
The link between the COVID vaccine, gut health, and autoimmune diseases is a complex and evolving area of research. While the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks for most individuals, it’s essential to acknowledge the potential impact on gut health and take steps to mitigate any negative effects.
By understanding the science behind these connections, adopting a gut-friendly lifestyle, and staying informed about ongoing research, we can make informed decisions about our health and well-being.

