Heart Failure Mortality Rates Surge to Highest Levels in 20 Years
Heart failure mortality rates surge to highest levels in 20 years, a grim statistic that underscores a growing health crisis. This alarming trend raises critical questions about the factors driving this increase and the potential consequences for individuals and healthcare systems.
Over the past two decades, the number of deaths attributed to heart failure has steadily climbed, reaching a peak not seen in generations. This alarming trend demands immediate attention, prompting a closer examination of the underlying causes and potential solutions.
This surge in heart failure mortality rates isn’t simply a matter of numbers; it represents a human tragedy, affecting countless individuals and families. The rising death toll highlights the urgency of addressing this public health challenge. Understanding the factors contributing to this increase is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent future tragedies and improve patient outcomes.
Heart Failure Mortality Rates
The recent surge in heart failure mortality rates to their highest levels in 20 years is a cause for serious concern. This alarming trend underscores the need for a renewed focus on prevention, early detection, and improved management of this chronic condition.
The news about heart failure mortality rates surging to the highest levels in 20 years is truly alarming. It’s a stark reminder of the critical need for proactive healthcare measures. Meanwhile, the world watches with bated breath as tensions escalate between Russia and Ukraine.
Ukraine’s president is urging for preemptive sanctions against Russia before a possible invasion, not after, as outlined in this article ukraines president urges sanctions against russia before a possible invasion not after. It’s a delicate situation, and the consequences of inaction could be dire.
Just as we need to address the rising heart failure crisis, we must also work towards preventing a potential conflict that could have devastating global ramifications.
Heart Failure Mortality Trends: A Historical Perspective
Heart failure mortality rates have fluctuated over the past two decades, with periods of decline interspersed with periods of stagnation or even increase. The decline in mortality rates observed in the early 2000s can be attributed to advancements in medical treatments, such as the development of new medications and improved diagnostic tools.
It’s a grim reality: heart failure mortality rates have surged to their highest levels in 20 years. This trend, unfortunately, mirrors the alarming decline in our nation’s commitment to public health. While we grapple with this critical issue, a recent ruling by a Trump-appointed judge, which could undo more than 50 years of voting rights law , further undermines our democracy.
We must prioritize both our physical and civic well-being to create a healthier and more equitable future for all.
However, this progress has been overshadowed by the recent surge in mortality rates, which has reversed the positive trend.
Data and Statistics Illustrating the Increase
The magnitude of the increase in heart failure mortality rates is significant. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), heart failure is a leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for over 600,000 deaths annually.
The CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics reported that heart failure mortality rates increased by 10% between 2019 and 2020, reaching the highest level in 20 years. This surge in mortality rates is particularly concerning considering the significant advancements in heart failure treatment and management over the past two decades.
The increasing prevalence of heart failure, coupled with the aging population and the rising rates of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, are contributing factors to the surge in mortality rates.
Factors Contributing to the Surge in Mortality Rates
The recent surge in heart failure mortality rates is likely a complex interplay of several factors, including:
- Aging Population:As the population ages, the prevalence of heart failure increases, leading to a higher number of deaths from this condition.
- Rising Prevalence of Risk Factors:The increasing prevalence of risk factors for heart failure, such as obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, is contributing to the rising number of heart failure cases.
- Access to Healthcare:Disparities in access to healthcare and quality of care can impact the management of heart failure, leading to poorer outcomes and higher mortality rates.
- COVID-19 Pandemic:The COVID-19 pandemic has also contributed to the increase in heart failure mortality rates, as the virus can exacerbate existing heart conditions and increase the risk of developing heart failure.
Underlying Factors Contributing to the Surge
The recent surge in heart failure mortality rates, reaching their highest levels in 20 years, is a concerning trend that demands a thorough understanding of the contributing factors. This alarming rise cannot be attributed to a single cause, but rather a complex interplay of several factors, including the aging population, increasing prevalence of risk factors, and disparities in healthcare access and quality.
Risk Factors Associated with Heart Failure
Several risk factors are associated with heart failure, increasing an individual’s susceptibility to developing the condition. These risk factors can act independently or synergistically, making it crucial to address them proactively to prevent heart failure and improve outcomes.
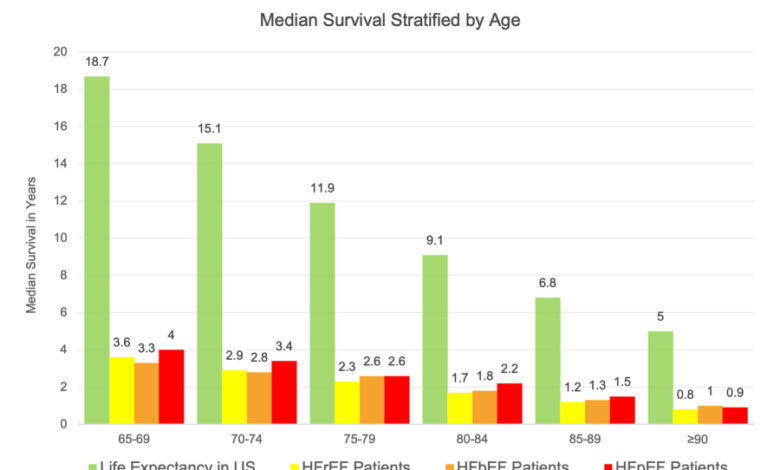
- Age:As people age, their heart muscle weakens and becomes less efficient, making them more vulnerable to heart failure. This is due to the cumulative effects of wear and tear on the heart over time, as well as the increasing prevalence of other risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes, with age.
- Obesity:Obesity places significant strain on the heart, leading to increased blood pressure and a higher workload for the heart. This can contribute to the development of heart failure, especially when combined with other risk factors.
- Diabetes:Diabetes damages blood vessels and increases the risk of high blood pressure, both of which contribute to heart failure. The long-term effects of diabetes on the heart can lead to a weakened heart muscle and reduced pumping capacity, increasing the risk of heart failure.
- Hypertension:High blood pressure puts extra strain on the heart, forcing it to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. Over time, this can weaken the heart muscle and lead to heart failure. Untreated hypertension is a significant risk factor for heart failure, making its management essential for preventing the condition.
Impact of Healthcare Access and Quality
Access to quality healthcare is critical for preventing and managing heart failure. However, disparities in healthcare access and quality can significantly impact heart failure mortality rates.
- Socioeconomic Disparities:Individuals with limited access to healthcare due to socioeconomic factors, such as low income or lack of health insurance, are more likely to experience delayed diagnosis and treatment of heart failure. This can lead to more severe disease progression and higher mortality rates.
- Limited Access to Specialists:Access to specialized cardiac care, including cardiologists and heart failure specialists, is essential for effective management of the condition. However, geographical limitations, financial constraints, and healthcare system barriers can hinder access to these specialists, particularly in underserved communities.
- Quality of Care:The quality of care received for heart failure is crucial for improving outcomes. Factors such as adherence to treatment guidelines, timely interventions, and comprehensive management plans can significantly impact mortality rates. However, disparities in the quality of care exist, often related to socioeconomic factors and geographical location.
Impact on Healthcare Systems and Patient Outcomes
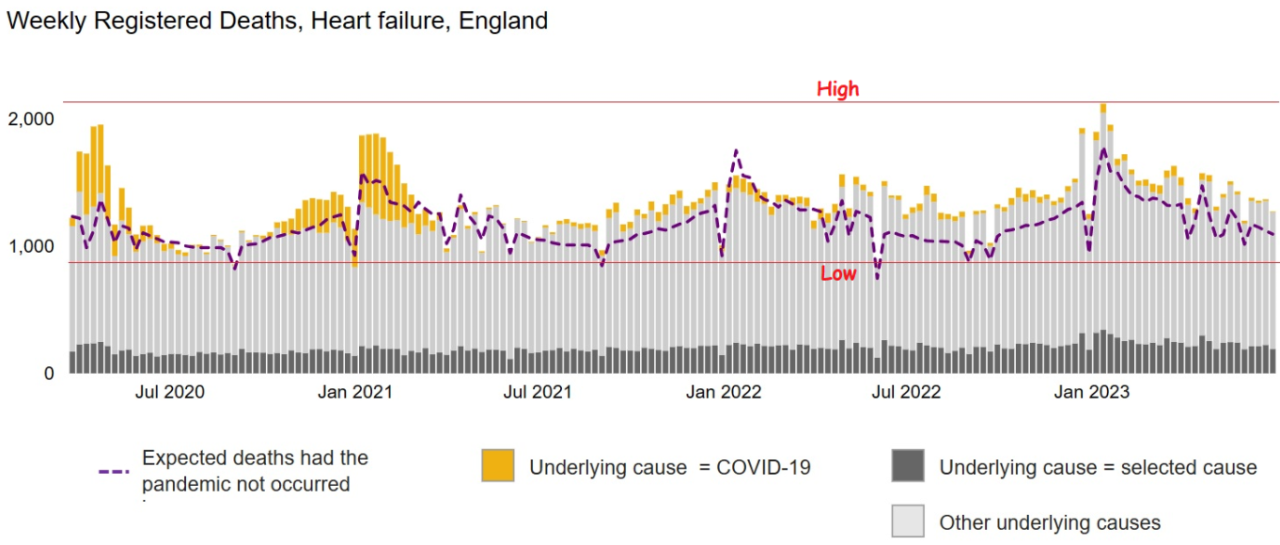
The surge in heart failure mortality rates has placed a significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide. Hospitals are facing increased demands for resources, including beds, medical staff, and specialized care, as the number of patients requiring treatment for heart failure rises.
This strain on resources can lead to longer wait times for patients, reduced access to essential services, and potential delays in receiving critical care.
The Impact of Rising Mortality Rates on Patient Outcomes and Quality of Life
The rise in heart failure mortality rates has a profound impact on patient outcomes and quality of life. Patients with heart failure often experience a decline in their physical and cognitive abilities, leading to limitations in daily activities and reduced independence.
It’s a grim reminder of the fragility of life, seeing heart failure mortality rates surge to their highest levels in 20 years. It’s a stark contrast to the recent fear and loathing return to tech start ups , where the focus is on innovation and the future.
Perhaps we need to refocus our priorities, remembering that health and well-being are paramount, even in the face of technological advancements.
The fear of sudden death or hospitalization can significantly impact mental well-being, leading to anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Challenges Faced by Healthcare Providers in Managing Heart Failure, Heart failure mortality rates surge to highest levels in 20 years
Healthcare providers face numerous challenges in managing heart failure effectively. These challenges include:
- Early Detection and Diagnosis:Heart failure can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages, as symptoms can be subtle and often mistaken for other conditions. Early diagnosis is crucial for timely treatment and improving patient outcomes.
- Adherence to Treatment Plans:Many patients with heart failure struggle to adhere to their prescribed medication regimens and lifestyle modifications. This can lead to complications and a higher risk of hospital readmission.
- Limited Access to Specialized Care:Access to specialized heart failure care, such as cardiac rehabilitation programs and advanced diagnostic testing, is often limited, particularly in rural areas.
- Lack of Awareness and Education:Public awareness of heart failure and its risk factors remains low. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, contributing to poorer outcomes.
Strategies for Addressing the Surge
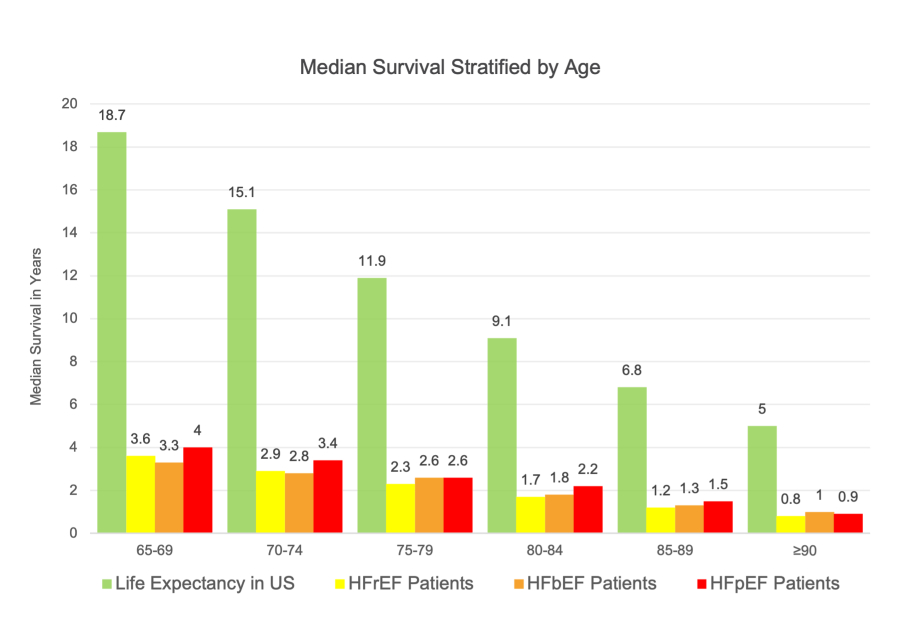
The recent surge in heart failure mortality rates demands a multifaceted approach involving public health initiatives, innovative treatment strategies, and a focus on improving healthcare delivery systems.
Public Health Initiatives for Prevention and Risk Factor Management
Effective public health initiatives are crucial in preventing heart failure and managing risk factors. These initiatives should aim to increase awareness about heart failure, promote healthy lifestyle choices, and improve access to preventative care.
- Public Awareness Campaigns:Public awareness campaigns should emphasize the importance of early detection and risk factor management. These campaigns can utilize various media platforms, including television, radio, social media, and community events, to disseminate information about heart failure, its symptoms, and preventive measures.
- Community-Based Programs:Community-based programs can play a significant role in promoting healthy lifestyle choices and addressing health disparities. These programs can provide educational workshops on nutrition, physical activity, smoking cessation, and blood pressure control. They can also offer support groups and counseling services to individuals at risk for heart failure.
- Improved Access to Healthcare:Expanding access to primary care and preventive services is essential for early detection and management of heart failure risk factors. This includes increasing the availability of healthcare providers in underserved communities, expanding insurance coverage, and reducing barriers to accessing care.
Innovative Approaches to Heart Failure Treatment and Care Delivery
The field of heart failure treatment is constantly evolving, with advancements in medical therapies, device-based interventions, and care delivery models.
- Personalized Medicine:Personalized medicine approaches tailor treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics, including genetics, lifestyle, and disease severity. This approach aims to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring:Telehealth technologies enable remote monitoring of heart failure patients, allowing for early detection of worsening symptoms and timely intervention. This approach improves patient engagement and reduces hospital readmissions.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs:Cardiac rehabilitation programs are essential for improving functional capacity and quality of life in heart failure patients. These programs provide supervised exercise, education, and counseling to support patients in managing their condition.
Future Implications and Research Directions: Heart Failure Mortality Rates Surge To Highest Levels In 20 Years
The alarming surge in heart failure mortality rates has far-reaching implications for individuals, healthcare systems, and society as a whole. Understanding the underlying factors contributing to this trend is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate the impact and improve patient outcomes.
This necessitates ongoing research and a focus on key areas that hold the potential to transform heart failure prevention and treatment.
The Long-Term Impact of Rising Heart Failure Mortality
The continued increase in heart failure mortality rates poses a significant challenge to healthcare systems worldwide. This trend is expected to place further strain on resources, leading to increased healthcare costs, longer hospital stays, and a greater burden on caregivers.
Additionally, the growing prevalence of heart failure will likely result in a larger population requiring specialized care, potentially leading to longer wait times for appointments, procedures, and access to essential medications. The economic impact of this trend will be substantial, affecting not only healthcare budgets but also productivity and workforce participation.
Conclusion
The surge in heart failure mortality rates serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing battle against this devastating condition. Addressing this crisis requires a multi-pronged approach that encompasses public health initiatives, improved risk factor management, and advancements in treatment and care delivery.
While the future remains uncertain, ongoing research and data collection are crucial for understanding the evolving landscape of heart failure and informing future interventions. It’s time to prioritize heart health, empowering individuals to take control of their well-being and ensuring access to quality healthcare for all.