Guillain-Barré Syndrome Linked to COVID-19 Vaccine: CDC Study
Guillain barre syndrome linked to covid 19 vaccine cdc study – Guillain-Barré syndrome linked to COVID-19 vaccine: CDC study – this headline has sparked widespread discussion and concern. While the COVID-19 vaccines have proven to be highly effective in protecting against severe illness and death, the possibility of rare side effects like Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a serious issue.
This autoimmune disorder attacks the peripheral nervous system, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis. The CDC study, which investigated the potential link between GBS and the COVID-19 vaccines, has shed light on this complex relationship.
The study, which involved a large dataset of vaccinated individuals, found a slightly increased risk of GBS after receiving certain COVID-19 vaccines, particularly the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. However, it’s important to remember that the overall risk of developing GBS after vaccination remains extremely low.
Furthermore, the benefits of vaccination against COVID-19 far outweigh the potential risks of GBS.
Potential Mechanisms: Guillain Barre Syndrome Linked To Covid 19 Vaccine Cdc Study
The precise mechanisms by which the COVID-19 vaccine might trigger GBS are still under investigation, but several potential pathways have been proposed. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for both risk assessment and the development of strategies to mitigate potential adverse events.
Molecular Mimicry
Molecular mimicry is a key theory explaining the link between the COVID-19 vaccine and GBS. This theory suggests that certain components of the vaccine, such as the spike protein, share similarities with proteins found in the peripheral nervous system. This resemblance can trigger an immune response against the vaccine components, which can cross-react with the nervous system’s own proteins, leading to nerve damage.
For example, the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to share some structural similarities with gangliosides, which are lipids found on the surface of nerve cells. This similarity could potentially lead to the immune system attacking both the spike protein and gangliosides, causing GBS.
The recent CDC study linking Guillain-Barré syndrome to the COVID-19 vaccine has sparked a lot of discussion, but it’s important to remember that the risk is still extremely low. Meanwhile, Florida is taking steps to protect its citrus industry, a vital part of the state’s economy, by implementing measures to safeguard valuable farmland from foreign buyers.
It’s interesting how these seemingly unrelated topics highlight the importance of public health and economic stability, both of which are crucial for a thriving society.
Autoimmune Activation
Another potential mechanism involves the activation of the immune system’s own cells, leading to an autoimmune attack on the nervous system. The COVID-19 vaccine, like any vaccine, can stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies and T cells. In some cases, these immune cells may mistakenly target components of the nervous system, leading to GBS.
Research has shown that the COVID-19 vaccine can induce a temporary increase in the production of antibodies that bind to gangliosides, which could contribute to GBS development.
Cytokine Storm, Guillain barre syndrome linked to covid 19 vaccine cdc study
A cytokine storm, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by excessive inflammation, is another possible contributor to GBS after vaccination. While rare, a cytokine storm can occur when the immune system overreacts to a stimulus, such as a vaccine. The excessive inflammation can damage various tissues, including the nervous system, potentially leading to GBS.
While the link between cytokine storms and GBS is not fully established, some studies have suggested that excessive inflammation could contribute to the development of GBS.
The CDC study on Guillain-Barré syndrome linked to the COVID-19 vaccine is a reminder of the importance of ongoing research and monitoring, even as operations resume gradually after all flights were grounded across the US federal agency, as reported by Molnewsnet.
While the risk of developing Guillain-Barré syndrome after vaccination is still considered rare, it’s essential to stay informed about potential side effects and seek medical attention if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Public Health Implications
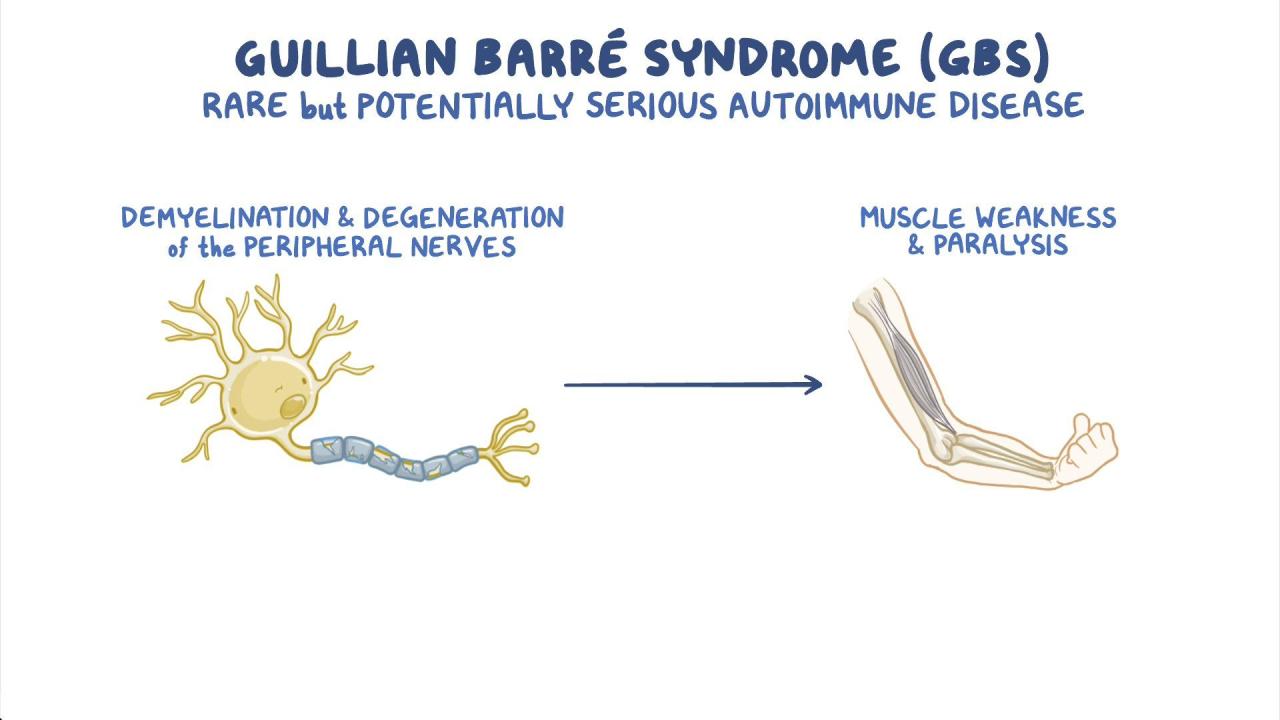
The CDC study’s findings regarding the association between COVID-19 vaccination and Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) have significant implications for public health policy and decision-making. It highlights the need for a balanced approach that considers both the benefits and risks of vaccination while ensuring informed decision-making by individuals and healthcare providers.
Implications for Public Health Policy
The CDC study’s findings raise important questions about the potential risks associated with COVID-19 vaccination, particularly in the context of GBS. Public health officials need to carefully consider these findings and their implications for vaccination policies. This includes:
- Transparency and Communication:Public health agencies should transparently communicate the findings of the study to the public, healthcare providers, and policymakers. This communication should be clear, concise, and accessible, addressing concerns and providing accurate information about the risks and benefits of vaccination.
The recent CDC study linking Guillain-Barré syndrome to the COVID-19 vaccine has raised concerns, but it’s important to remember that the benefits of vaccination still outweigh the risks. Meanwhile, the world of search is experiencing its own seismic shift, as the creator of Gmail warns that ChatGPT is posing a serious challenge to Google’s dominance.
This article explores the potential implications of this new AI technology, which could revolutionize how we access and process information. Back to the Guillain-Barré study, it’s crucial to consult with your doctor to weigh the individual risks and benefits of vaccination.
- Surveillance and Monitoring:Enhanced surveillance systems are crucial to monitor the incidence of GBS following COVID-19 vaccination. This includes collecting data on GBS cases, their temporal association with vaccination, and other potential risk factors.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation:Public health officials should conduct thorough risk assessments to determine the balance between the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination and the potential risks associated with GBS. This assessment should consider factors such as the severity of COVID-19 infection, the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing severe disease, and the incidence of GBS after vaccination.
- Informed Decision-Making:Public health policy should promote informed decision-making by individuals. This involves providing clear and accurate information about the risks and benefits of vaccination, as well as the potential for GBS, allowing individuals to make informed choices based on their own health circumstances and risk tolerance.
Benefits and Risks of COVID-19 Vaccination in the Context of GBS
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination far outweigh the risks, including the potential for GBS. Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death.
- Benefits:
- Reduced risk of severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death.
- Protection against long-term complications of COVID-19.
- Reduced transmission of the virus, contributing to community immunity.
- Risks:
- Potential for rare adverse events, such as GBS.
- Mild side effects, such as pain at the injection site, fatigue, or headache, which are usually temporary.
Key Points for Public Health Officials and Healthcare Providers
| Point | Description |
|---|---|
| GBS is a rare but serious neurological disorder. | The CDC study suggests a possible association between COVID-19 vaccination and GBS, but the risk remains very low. |
| Benefits of COVID-19 vaccination outweigh the risks. | Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of severe COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. |
| Surveillance and monitoring of GBS cases are essential. | Collecting data on GBS cases following vaccination is crucial for understanding the risk and informing public health policy. |
| Transparent communication is vital. | Public health officials and healthcare providers should clearly communicate the findings of the study, addressing concerns and providing accurate information. |
| Informed decision-making is paramount. | Individuals should be provided with accurate information about the risks and benefits of vaccination, allowing them to make informed choices. |
Further Research
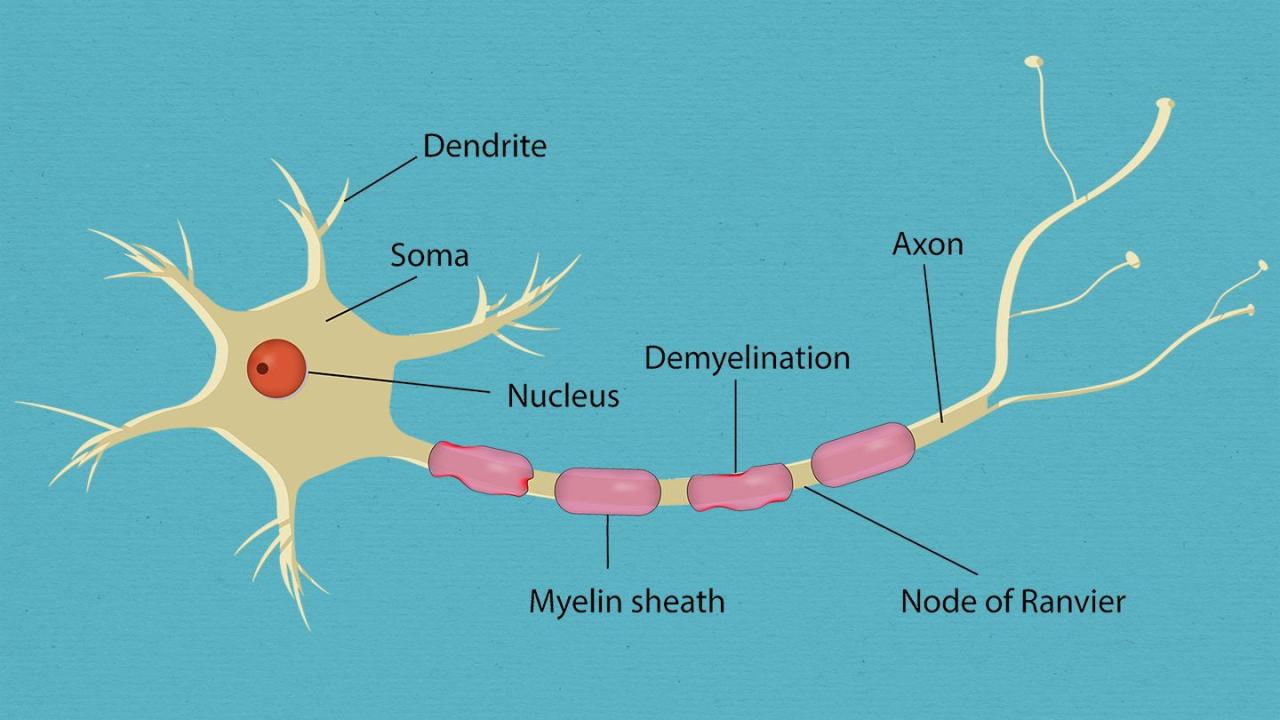
While the CDC study has provided valuable insights into the potential link between the COVID-19 vaccine and GBS, more research is needed to fully understand this association. This research is crucial to inform public health strategies and ensure vaccine safety.
Areas for Further Research
Further research should explore the following areas to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the link between the COVID-19 vaccine and GBS:
- Investigate the temporal association between vaccination and GBS onset.This involves determining the precise time frame between vaccination and GBS development to identify any potential temporal patterns.
- Explore the role of different vaccine types.The CDC study focused on mRNA vaccines. Research should be conducted to assess the risk of GBS associated with other COVID-19 vaccine types, such as adenovirus-vectored vaccines.
- Examine the potential influence of underlying medical conditions.Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders, may increase the risk of GBS. Research should assess whether these conditions interact with the COVID-19 vaccine to elevate GBS risk.
- Determine the long-term impact of GBS following vaccination.Understanding the long-term neurological outcomes and recovery patterns of GBS cases linked to vaccination is crucial for patient management and rehabilitation.
Research Questions
To address the knowledge gaps identified above, the following research questions should be investigated:
- What is the specific time window between COVID-19 vaccination and GBS onset, and are there any distinct patterns in the temporal association?
- Does the risk of GBS vary significantly across different COVID-19 vaccine types, and if so, what are the underlying mechanisms responsible for these differences?
- How do underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders, influence the risk of GBS in individuals who have received the COVID-19 vaccine?
- What are the long-term neurological outcomes and recovery rates of individuals who develop GBS after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine?
Methods for Future Studies
Future studies should employ a variety of research methods to address the identified research questions. These methods may include:
- Large-scale observational studies:These studies can track a large population over time to identify any association between vaccination and GBS.
- Case-control studies:These studies compare individuals with GBS to individuals without GBS to identify risk factors, including vaccination status.
- Cohort studies:These studies follow a group of individuals over time, allowing researchers to assess the long-term effects of vaccination on GBS risk.
- Molecular and immunological studies:These studies can investigate the mechanisms by which the COVID-19 vaccine may trigger GBS.
Final Conclusion

The CDC study serves as a reminder that even with groundbreaking medical advancements like COVID-19 vaccines, ongoing research and monitoring are crucial. It’s essential to stay informed about the latest scientific findings and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
While the potential link between GBS and COVID-19 vaccines is a concern, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced perspective and understand that the benefits of vaccination significantly outweigh the risks.