
Franchise Failures: McDonalds Struggles to Uphold Founders Vision
Franchise failures mcdonalds struggles to uphold founders vision – Franchise Failures: McDonald’s Struggles to Uphold Founder’s Vision sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
The golden arches of McDonald’s are a familiar sight around the world, synonymous with fast food and convenience. But behind the iconic brand lies a story of evolving business models, shifting consumer preferences, and the challenges of maintaining a founder’s vision.
This blog explores the journey of McDonald’s, examining how the company’s franchise model has evolved and the impact of these changes on its success. We’ll delve into the challenges faced by franchisees, the impact of franchise failures on the brand’s reputation, and explore strategies for McDonald’s to re-align with its founding principles.
McDonald’s Legacy and Founding Principles
Ray Kroc, the man who transformed McDonald’s into a global fast-food empire, had a clear vision for his company. Beyond simply selling burgers and fries, Kroc aimed to establish a system that emphasized efficiency, consistency, and customer satisfaction. His principles, meticulously implemented in the early days of the franchise, laid the foundation for McDonald’s remarkable success.
Implementation of Founding Principles
Kroc’s vision for McDonald’s was built on a set of core principles that were deeply ingrained in the company’s early franchise model. These principles guided every aspect of the business, from the design of the restaurants to the training of employees.
- Efficiency:Kroc believed in streamlining operations to maximize speed and minimize costs. This was evident in the adoption of assembly-line production methods, where each employee was assigned a specific task, ensuring a smooth and efficient workflow.
- Consistency:Kroc emphasized the importance of providing a consistent experience for customers across all locations. This was achieved through strict quality control measures, standardized recipes, and meticulous training programs for employees.
- Customer Satisfaction:Kroc recognized the paramount importance of customer satisfaction. The company implemented a “customer-first” philosophy, prioritizing speed, cleanliness, and friendly service to create a positive dining experience.
Examples of McDonald’s Early Success
The successful implementation of Kroc’s principles in the early years of McDonald’s is evident in several key areas.
It’s a strange thought, isn’t it? McDonald’s, the fast food giant, struggling to maintain the spirit of its founder, while the US government expedites the delivery of Abrams battle tanks to Ukraine. One represents the pursuit of profit and efficiency, the other, the defense of freedom and democracy.
Both, however, are grappling with the complexities of a changing world, and the challenge of staying true to their core values in the face of evolving circumstances. McDonald’s, perhaps, has a tougher fight ahead, as its success depends on maintaining a consistent brand image, while the US, in its defense of Ukraine, faces a much more immediate and existential threat.
- The “Speedee Service System”:This system, inspired by assembly lines in automobile factories, revolutionized the fast-food industry. By breaking down the burger-making process into individual tasks, McDonald’s could serve customers quickly and efficiently. This efficiency was a key factor in the company’s early success, as it attracted customers who valued speed and convenience.
- Standardized Recipes and Ingredients:Kroc insisted on using only the highest quality ingredients, but also on strict adherence to standardized recipes. This ensured that every Big Mac tasted the same, regardless of the location. This consistency was crucial in building brand loyalty and creating a recognizable taste experience for customers.
- The “Golden Arches”:The iconic golden arches, designed by architect Stanley Meston, became a symbol of McDonald’s brand. The arches were designed to be easily recognizable and visually appealing, creating a sense of familiarity and trust among customers.
Challenges to Maintaining the Founder’s Vision

McDonald’s, a fast-food giant, has faced numerous challenges in upholding the vision of its founder, Ray Kroc. While the company has enjoyed immense success, its journey has been marked by significant shifts in the fast-food landscape, consumer preferences, and market competition, which have tested its ability to adhere to its founding principles.
Impact of Changes in the Fast-Food Industry
The fast-food industry has undergone a dramatic transformation since McDonald’s inception. The rise of fast-casual dining, the emergence of food delivery platforms, and the increasing demand for healthier and more diverse menu options have all challenged the traditional fast-food model.
- Fast-Casual Dining:The emergence of fast-casual restaurants, which offer a more upscale dining experience with higher-quality ingredients and a wider variety of menu options, has eroded McDonald’s market share. These restaurants have successfully appealed to consumers seeking a more sophisticated dining experience while still offering convenient service.
- Food Delivery Platforms:The proliferation of food delivery platforms such as Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub has fundamentally changed the way people consume food. These platforms have made it easier for consumers to order food from a wider range of restaurants, including those that previously lacked a physical presence in their area.
This has increased competition for McDonald’s, as it now has to compete with a vast array of restaurants, not just those in its immediate vicinity.
- Healthier and More Diverse Menu Options:Consumers are increasingly demanding healthier and more diverse menu options. This trend has been driven by growing awareness of the health risks associated with fast food and the increasing popularity of dietary restrictions such as veganism and gluten-free diets. McDonald’s has responded to this trend by introducing healthier menu items, but these efforts have been met with mixed results.
Impact of Changing Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences have evolved significantly since the early days of McDonald’s. Consumers are now more demanding and have higher expectations for quality, value, and convenience.
- Quality and Value:Consumers are more discerning about the quality of food they consume and are increasingly demanding value for their money. They are more likely to choose restaurants that offer high-quality ingredients, fresh produce, and unique flavor profiles.
- Convenience:Consumers value convenience and are increasingly looking for fast and easy ways to get their food. This has led to the growth of food delivery platforms and the rise of restaurants that offer mobile ordering and curbside pickup.
- Transparency:Consumers are also demanding more transparency from food companies. They want to know where their food comes from, how it is produced, and what ingredients it contains.
Impact of Market Competition
McDonald’s faces intense competition from a wide range of fast-food chains, independent restaurants, and emerging food delivery platforms. This competition has forced McDonald’s to adapt its business model and menu offerings to remain competitive.
- Price Wars:McDonald’s has often been engaged in price wars with its competitors, which has put pressure on its margins. These price wars can be difficult to win, as they often lead to a race to the bottom in terms of pricing.
- Innovation:McDonald’s has had to innovate to keep up with its competitors. This has included introducing new menu items, experimenting with new marketing strategies, and investing in technology to improve its operations.
- Brand Differentiation:McDonald’s has had to differentiate itself from its competitors to stand out in a crowded marketplace. This has included focusing on its brand identity, its core values, and its commitment to customer satisfaction.
Comparison to Early Days, Franchise failures mcdonalds struggles to uphold founders vision
McDonald’s early success was driven by its simple, efficient business model, its focus on quality and consistency, and its commitment to customer service. However, the company has faced challenges in maintaining these core principles in the face of changing market dynamics.
- Menu Complexity:McDonald’s menu has become increasingly complex over the years, as the company has added new items to cater to changing consumer preferences. This has made it more difficult for McDonald’s to maintain the consistency and efficiency that were hallmarks of its early days.
- Operational Complexity:McDonald’s operations have also become more complex, as the company has expanded its global footprint and introduced new technologies. This has made it more difficult for McDonald’s to ensure that its restaurants are operating efficiently and consistently.
- Focus on Profitability:McDonald’s has also faced criticism for its focus on profitability at the expense of its core values. Some critics argue that the company has become too focused on maximizing profits and has lost sight of its commitment to quality, customer service, and community involvement.
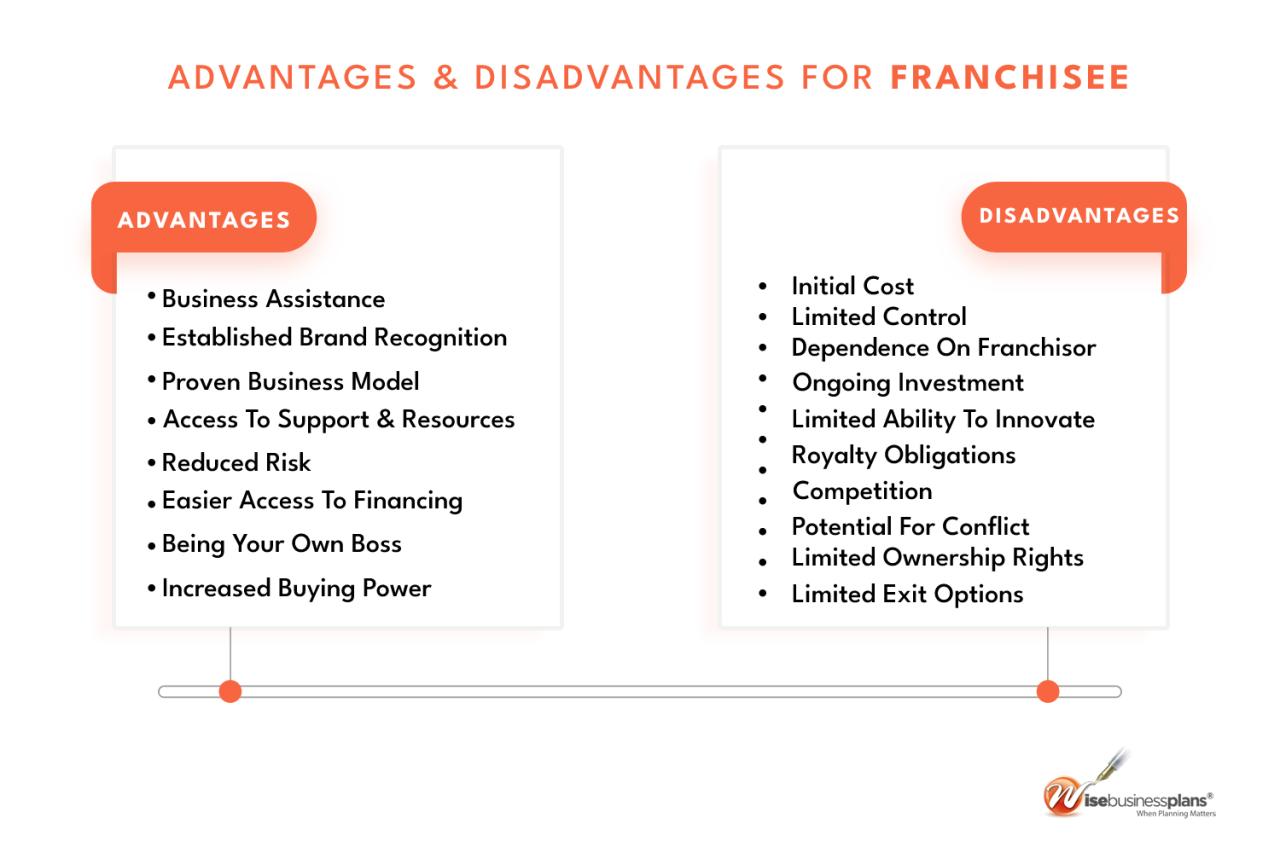
Franchisee Perspectives and Experiences
McDonald’s franchisees are the backbone of the company’s success, and their experiences provide valuable insights into the challenges of upholding Ray Kroc’s vision. From navigating operational changes to adapting to evolving consumer preferences, franchisees face a unique set of pressures that directly impact their profitability and the overall brand image.
Challenges Faced by McDonald’s Franchisees
Franchisees often face a delicate balancing act between maintaining the core values of the McDonald’s brand and adapting to evolving consumer demands. The following are some of the challenges they encounter:
- Maintaining Consistency and Quality: Ensuring consistent quality across all McDonald’s restaurants is paramount to the brand’s success. Franchisees face pressure to adhere to strict operational guidelines and quality standards, which can sometimes be challenging to maintain, especially in a rapidly changing environment.
It’s interesting to see how companies struggle to maintain their founder’s vision as they grow. McDonald’s, for example, has faced criticism for deviating from Ray Kroc’s original concept. This reminds me of Elon Musk’s recent decision to restrict the military use of Starlink in Ukraine, a move he justified by citing the potential for escalating the conflict.
Elon Musk defends restricting military use of starlink in ukraine cites possible escalation of conflict. Both situations highlight the challenges of balancing ethical considerations with the realities of business growth and global power dynamics.
- Balancing Innovation and Tradition: McDonald’s has introduced new menu items and marketing strategies over the years, but some franchisees believe these changes have diluted the core brand identity. The challenge lies in striking a balance between innovation and maintaining the classic McDonald’s experience that customers have come to expect.
- Labor Shortages and Rising Costs: The fast-food industry is facing a labor shortage, leading to increased labor costs for franchisees. Additionally, rising food and energy costs put pressure on profit margins, making it difficult to maintain affordability for customers.
- Competition from Other Fast-Food Chains: The fast-food industry is highly competitive, with new players and established chains vying for customers. Franchisees must constantly adapt to stay ahead of the competition, offering competitive pricing, menu innovation, and customer service.
Impact of Operational Changes, Menu Modifications, and Marketing Strategies
Franchisees are often at the forefront of implementing changes dictated by the franchisor, and these changes can have a significant impact on their success.
- Operational Changes: Operational changes, such as new ordering systems, technology upgrades, or staffing adjustments, can impact efficiency and customer service. Franchisees must adapt to these changes while ensuring smooth operations and customer satisfaction.
- Menu Modifications: Introducing new menu items can be a double-edged sword. While it can attract new customers and boost sales, it also requires additional training, inventory management, and marketing efforts. Franchisees need to assess the feasibility and profitability of new menu items before implementing them.
- Marketing Strategies: McDonald’s marketing strategies, including advertising campaigns, promotions, and digital initiatives, play a crucial role in attracting customers. Franchisees must be aligned with these strategies and effectively implement them in their local markets to maximize impact.
Benefits and Challenges of Being a McDonald’s Franchisee
The following table highlights the benefits and challenges of being a McDonald’s franchisee today compared to the past:
| Benefits | Challenges | |
|---|---|---|
| Today |
|
|
| Past |
|
|
Impact of Franchise Failures on the Brand: Franchise Failures Mcdonalds Struggles To Uphold Founders Vision
Franchise failures, while a natural part of any business model, can have a significant impact on a brand’s reputation and image. In the case of McDonald’s, a global fast-food giant, franchise failures can ripple through the entire system, affecting customer perception and trust.
It’s interesting how McDonald’s struggles to maintain the vision of its founder, Ray Kroc, in the face of franchise failures. Just like the government struggles to balance its budget, and how the Senate just passed a one-week spending bill to avert a government shutdown , it seems the fast-food giant is facing a similar struggle to keep its core values alive in a rapidly changing world.
Maybe there’s a lesson to be learned here about how even the most iconic brands need to adapt and evolve to survive, just like our political system.
The Impact of Franchise Failures on McDonald’s Brand Image and Reputation
Franchise failures can damage McDonald’s brand image and reputation in several ways. When a franchise fails to meet the standards of quality, service, and cleanliness that customers expect from McDonald’s, it can lead to negative publicity and a decline in customer satisfaction.
This can, in turn, impact the brand’s overall image and reputation.
Customer Perception and Trust
Negative franchise experiences can significantly impact customer perception and trust. When customers have a bad experience at a particular McDonald’s franchise, they may generalize that experience to the entire brand. This can lead to a decline in customer loyalty and a decrease in repeat business.
For example, if a customer experiences slow service, dirty facilities, or incorrect orders at a specific franchise, they may perceive McDonald’s as a whole as being unreliable and inconsistent.
Strategies to Address Franchise Failures and Regain Consumer Confidence
McDonald’s has implemented several strategies to address franchise failures and regain consumer confidence. These include:
- Enhanced Training and Support for Franchisees:McDonald’s has invested in training programs to ensure franchisees understand and adhere to the brand’s standards. This includes training on food safety, customer service, and operational efficiency.
- Stricter Quality Control Measures:McDonald’s has implemented stricter quality control measures to ensure consistency across all franchises. This includes regular inspections and audits to ensure compliance with brand standards.
- Customer Feedback Mechanisms:McDonald’s has established mechanisms for customers to provide feedback on their experiences. This includes online surveys, comment cards, and social media monitoring. This feedback is used to identify and address issues promptly.
- Public Relations and Marketing Campaigns:McDonald’s has launched public relations and marketing campaigns to highlight its commitment to quality, service, and customer satisfaction. These campaigns aim to rebuild trust and reassure customers that the brand is taking steps to address franchise failures.
Strategies for Realignment and Future Direction
McDonald’s, a fast-food giant, faces challenges in upholding its founder’s vision, leading to franchise failures. To address these issues and ensure a sustainable future, a strategic realignment is crucial. This involves re-evaluating the franchise model, strengthening the network, and addressing challenges while remaining committed to its core values.
Re-evaluating the Franchise Model
McDonald’s franchise model has been instrumental in its growth, but it needs reevaluation to ensure alignment with its founding principles. The model should prioritize the following:
- Quality and Consistency:McDonald’s success was built on its commitment to quality and consistency. The franchise model should emphasize stringent quality control measures and provide robust training programs to ensure uniform standards across all franchises.
- Operational Efficiency:The franchise model should encourage operational efficiency by providing support and resources to franchisees to optimize their operations. This includes streamlined processes, technology advancements, and best practices sharing.
- Customer Experience:The focus should shift towards enhancing the customer experience. This involves investing in technology, creating a welcoming atmosphere, and offering personalized services. Franchisees should be empowered to adapt to local preferences and market trends while maintaining brand consistency.
- Employee Engagement:A strong franchise model fosters employee engagement. McDonald’s should prioritize employee well-being, offer competitive compensation, and create a positive work environment. This will contribute to improved customer service and overall business performance.
Strengthening the Franchise Network
A robust franchise network is essential for McDonald’s success. To strengthen the network, the following recommendations are crucial:
- Franchisee Selection:McDonald’s should implement a rigorous franchisee selection process, ensuring that potential franchisees align with the brand’s values and have the necessary experience and resources to operate successfully.
- Support and Mentorship:The company should provide comprehensive support and mentorship to franchisees throughout their journey. This includes ongoing training, access to resources, and guidance on best practices.
- Communication and Collaboration:Open communication and collaboration between McDonald’s and its franchisees are vital. Regular meetings, feedback mechanisms, and shared decision-making processes will foster trust and a sense of partnership.
- Financial Assistance:McDonald’s should consider offering financial assistance to franchisees, particularly during challenging economic periods. This could involve loan programs, grants, or other forms of support to help them navigate difficult times.
Addressing Challenges
McDonald’s faces various challenges, including:
- Competition:The fast-food industry is highly competitive. McDonald’s needs to differentiate itself by offering innovative menu items, personalized services, and a compelling brand story.
- Changing Consumer Preferences:Consumer preferences are constantly evolving. McDonald’s must adapt to changing tastes and trends, incorporating healthier options, personalized experiences, and innovative technologies.
- Labor Shortages:The fast-food industry is experiencing labor shortages. McDonald’s should focus on attracting and retaining employees by offering competitive wages, benefits, and opportunities for growth.
- Sustainability:Consumers are increasingly concerned about sustainability. McDonald’s should adopt sustainable practices, reduce its environmental footprint, and promote ethical sourcing.
Sustainable Growth and Core Values
McDonald’s can achieve sustainable growth while maintaining its commitment to its core values by:
- Focusing on Quality:Maintaining high-quality food and service is essential for long-term success. This involves investing in quality ingredients, implementing rigorous quality control measures, and ensuring consistent service standards.
- Embracing Innovation:Continuously innovating and adapting to changing consumer preferences is crucial. This includes introducing new menu items, leveraging technology, and creating personalized experiences.
- Prioritizing Employee Well-being:A happy and engaged workforce is vital for customer satisfaction and business success. McDonald’s should offer competitive wages, benefits, and opportunities for growth to attract and retain employees.
- Building Strong Relationships:Cultivating strong relationships with franchisees, suppliers, and customers is essential for long-term success. This involves open communication, mutual respect, and a commitment to shared values.
Closing Notes
McDonald’s faces a critical juncture as it navigates the complexities of maintaining its legacy while adapting to a rapidly changing world. The success of its franchise model is intertwined with the ability to empower its franchisees, adapt to evolving consumer preferences, and uphold the core values that built its brand.
The future of McDonald’s hinges on finding a balance between innovation and tradition, ensuring that its iconic golden arches continue to represent quality, consistency, and a commitment to its founding principles.

