Follow the Money and Brace for Recession
Follow the money and brace for recession: these words are becoming increasingly familiar as economic headwinds intensify. The recent surge in inflation and interest rates, coupled with geopolitical tensions, has painted a picture of economic uncertainty. This situation has many investors and businesses looking for answers, wondering how to navigate the choppy waters ahead.
This blog post dives into the heart of the matter, exploring key economic indicators that signal potential recession, the impact of inflation and interest rates on our wallets and businesses, and strategies for navigating this challenging landscape. We’ll examine both investment and business approaches, delve into the psychology of consumer behavior during economic downturns, and explore the role of government policies in mitigating the effects of a recession.
Economic Indicators and Recessionary Signals
Recessions are a complex economic phenomenon, and identifying them in advance can be challenging. However, certain economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health of the economy and can signal potential recessionary pressures. These indicators help us “follow the money” by tracking key aspects of economic activity, consumer spending, and business confidence.
Key Economic Indicators
The following economic indicators are closely monitored by economists and investors to gauge the state of the economy and predict potential recessions:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country. A decline in GDP for two consecutive quarters is often considered a recessionary signal.
- Unemployment Rate: This indicator measures the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking work. A rising unemployment rate suggests a weakening economy and can be a leading indicator of a recession.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): CPI measures the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services. High inflation, as measured by a significant increase in CPI, can erode consumer purchasing power and contribute to economic slowdowns.
- Industrial Production: This indicator tracks the output of manufacturing, mining, and utilities sectors. A decline in industrial production suggests a slowdown in economic activity and can be a signal of a recession.
- Housing Starts: This indicator measures the number of new residential construction projects started in a given period. A decline in housing starts reflects weak consumer demand and can indicate a broader economic slowdown.
- Retail Sales: This indicator tracks the total value of goods sold by retailers. A decline in retail sales suggests a decrease in consumer spending, which is a key driver of economic growth.
- Leading Economic Indicators (LEI): This composite index is compiled by the Conference Board and includes 10 economic indicators that tend to lead the overall economy. A decline in the LEI can signal a potential recession in the months ahead.
Understanding “Follow the Money”
The phrase “follow the money” emphasizes the importance of tracking the flow of funds within the economy. By analyzing how money is being spent, saved, and invested, we can gain insights into the health of different sectors and identify potential areas of weakness.
For example, if businesses are cutting back on investment due to uncertainty about the future, it can signal a decline in economic activity. Similarly, if consumers are reducing their spending due to concerns about job security or rising prices, it can contribute to a slowdown in economic growth.
Comparing Current Economic Climate with Historical Recessions
The current economic climate is characterized by a number of factors, including:
- High Inflation: The current inflation rate is significantly higher than in recent years, putting pressure on consumers and businesses.
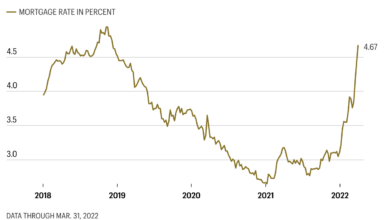
- Rising Interest Rates: Central banks around the world have been raising interest rates to combat inflation, which can slow down economic growth.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Ongoing supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic and geopolitical tensions have contributed to inflation and slowed economic activity.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: The war in Ukraine and other geopolitical tensions have created uncertainty and volatility in the global economy.
While these factors share some similarities with historical recessionary periods, there are also key differences. For instance, the current economic climate is characterized by a strong labor market, which is a positive factor that can help cushion the economy against a recession.
However, the high level of inflation and the potential for a prolonged period of high interest rates pose significant risks to economic growth.
Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and rising interest rates are powerful economic forces that can significantly impact economic growth and stability. Their combined effect can create a challenging environment for businesses and consumers, leading to uncertainty and volatility in the market.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Rising inflation erodes the purchasing power of consumers, making it more expensive to buy essential goods and services. This can lead to a decline in consumer spending, as people become more cautious with their money. As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, making it more expensive for consumers to finance large purchases like cars, homes, or appliances.
This can further dampen consumer spending, as individuals may choose to delay these purchases or reduce their overall spending.
Impact on Business Investment
High interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money to fund expansion, new projects, or investments. This can lead to a decrease in business investment, as companies become more hesitant to take on debt due to the increased cost of borrowing.
Additionally, rising inflation can create uncertainty for businesses, making it difficult to plan for the future. Businesses may postpone investment decisions until they have a clearer understanding of the economic landscape.
Consequences of High Inflation and Interest Rates, Follow the money and brace for recession
The combined effect of high inflation and interest rates can lead to several consequences for the economy:
- Economic Slowdown:Reduced consumer spending and business investment can lead to a slowdown in economic growth.
- Increased Unemployment:Businesses may be forced to lay off workers or reduce hiring due to decreased demand and higher borrowing costs.
- Financial Distress:High interest rates can put pressure on businesses and individuals with existing debt, potentially leading to financial distress and defaults.
- Reduced Asset Values:Inflation can erode the value of assets, such as real estate and stocks, leading to losses for investors.
Investment Strategies During Economic Downturns
Recessions are inevitable parts of the economic cycle. They present challenges for investors, but also opportunities to navigate the market strategically and potentially profit from the downturn. This section explores various investment strategies commonly employed during recessions, highlighting their rationale and potential benefits.
Value Investing
Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued assets with strong fundamentals, aiming to buy low and sell high. During recessions, many companies experience temporary dips in stock prices due to market sentiment or short-term challenges. This creates opportunities for value investors to acquire stocks at discounted prices, potentially generating significant returns as the economy recovers.
Defensive Stocks
Defensive stocks are those that tend to perform well, even during economic downturns. These companies operate in sectors less affected by recessions, such as consumer staples, healthcare, and utilities. Examples include companies like Walmart, Johnson & Johnson, and NextEra Energy.
Investors seeking to preserve capital and generate stable income during recessions often turn to defensive stocks.
It’s always a good idea to “follow the money” when trying to understand economic trends, especially during times of uncertainty. The recent spike in interest rates and the looming recession have many people worried, and it’s natural to look for clues.
Perhaps a little holiday cheer could provide some perspective, as we learn about the fascinating origins of Christmas in the history of christmas. After all, the tradition of gift-giving during this season has deep roots, and understanding those roots might offer a glimpse into how we navigate the economic challenges ahead.
Short Selling
Short selling is a strategy that involves borrowing and selling shares of a company, hoping to buy them back at a lower price later and pocket the difference. This strategy can be profitable during recessions when companies face significant challenges and their stock prices decline.
Following the money often reveals the truth, and right now, the economic indicators are flashing red. It’s no surprise then that CNN, a network known for its focus on financial news, just recorded its lowest ratings week in 9 years.
People are tuning out, not because they’re not interested in the economy, but because they’re scared. The fear is real, and it’s a clear signal that we need to brace ourselves for a potential recession.
However, short selling is a high-risk strategy that requires careful analysis and risk management.
Real Estate
Real estate can be a good investment during recessions, particularly in the long term. Recessions often lead to lower interest rates and reduced property prices, creating opportunities for investors to acquire assets at discounted prices. While the short-term outlook may be uncertain, long-term investors can benefit from potential price appreciation and rental income.
Gold and Precious Metals
Gold and other precious metals are often considered safe-haven assets during economic downturns. They tend to hold their value or even increase in price during periods of uncertainty and inflation. Investors seeking to preserve capital and hedge against inflation often allocate a portion of their portfolio to gold and other precious metals.
Hypothetical Investment Portfolio
A hypothetical investment portfolio reflecting a “follow the money” approach during a recession could include the following:* Defensive Stocks:40% (Walmart, Johnson & Johnson, NextEra Energy)
Value Stocks
30% (Companies with strong fundamentals but currently undervalued)
Gold and Precious Metals
15% (Gold, Silver, Platinum)
Short-Term Bonds
10% (For liquidity and income)
Cash
5% (For emergency reserves and potential opportunistic buys)This portfolio aims to balance risk and reward, providing exposure to both growth and stability. The defensive stocks and gold provide a buffer against market volatility, while value stocks and short-term bonds offer potential for capital appreciation and income generation.
Cash reserves provide flexibility to capitalize on opportunities that may arise during the recession.
Business Strategies for Recessionary Periods: Follow The Money And Brace For Recession

Recessions present significant challenges for businesses, but they also offer opportunities for those who adapt and innovate. By implementing strategic initiatives, companies can navigate these turbulent economic times and emerge stronger. This section delves into various business strategies that can help mitigate the impact of a recession.
Cost Reduction Strategies
Cost reduction is a crucial element of recessionary survival. By carefully analyzing expenses and streamlining operations, companies can preserve cash flow and maintain profitability.
- Expense Optimization:Identifying and eliminating unnecessary expenses is essential. This can involve reviewing contracts, renegotiating terms, and exploring alternative suppliers to secure better pricing. For instance, a manufacturing company might negotiate lower material costs by consolidating orders or exploring alternative materials.
- Streamlining Operations:Businesses should analyze their processes and identify areas for efficiency improvements. Automation, process simplification, and workforce optimization can significantly reduce operational costs. A retail company could implement self-checkout kiosks to reduce staffing requirements, while a software company could automate repetitive tasks.
- Inventory Management:Maintaining a lean inventory can help reduce storage costs and minimize potential losses due to obsolescence or price fluctuations. Implementing just-in-time inventory management or optimizing supply chain processes can significantly impact cost reduction.
- Downsizing:In extreme circumstances, downsizing may be necessary to align staffing levels with reduced demand. However, this should be a last resort, as it can impact morale and potentially hinder future growth. Companies should carefully consider alternative options, such as reduced work hours or temporary layoffs, before resorting to permanent staff reductions.
Revenue Generation Strategies
While cost reduction is important, businesses must also focus on generating revenue to sustain operations.
- Product/Service Innovation:Developing new products or services that meet emerging customer needs can drive revenue growth during a recession. For example, a restaurant might introduce new, budget-friendly menu items or a technology company could develop software solutions addressing remote work needs.
- Market Expansion:Exploring new markets or expanding into existing ones can open up new revenue streams. This could involve targeting new customer segments, entering new geographic regions, or developing partnerships with complementary businesses. A clothing retailer might open stores in new cities or expand its online presence to reach a wider audience.
- Pricing Strategies:Adjusting pricing strategies can be a crucial factor in maintaining revenue. While price increases may be necessary to offset rising costs, companies should consider offering discounts or promotions to attract price-sensitive customers. A car manufacturer might offer incentives to boost sales during a recession.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling:Encouraging customers to purchase additional products or services can increase revenue. This can involve offering bundled packages or promoting complementary items to existing customers. A telecommunications company might offer a bundle of internet, phone, and cable services at a discounted rate.
Market Adaptation Strategies
Recessions often lead to shifts in consumer behavior and market dynamics. Businesses must adapt to these changes to remain competitive.
- Customer Focus:Understanding customer needs and adapting products or services accordingly is essential. This involves conducting market research, monitoring customer feedback, and adjusting strategies based on evolving preferences. A furniture retailer might offer more affordable options or introduce modular furniture that can be easily customized.
- Digital Transformation:Embracing digital technologies can enhance efficiency, improve customer engagement, and expand market reach. This could involve implementing online ordering systems, developing mobile apps, or leveraging social media marketing. A restaurant might introduce online ordering and delivery services to cater to customers seeking convenience.
- Strategic Partnerships:Collaborating with other businesses can provide access to new markets, resources, or expertise. This could involve joint ventures, distribution agreements, or co-marketing initiatives. A small business might partner with a larger company to leverage its marketing reach or distribution network.
The economic landscape is looking increasingly shaky, and the “follow the money” adage is more relevant than ever. As we brace for a potential recession, it’s crucial to pay attention to the ripple effects of major decisions. A recent call by a doctor for withdrawal of Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines following new research highlights the importance of scrutinizing claims and their potential financial implications.
This event could trigger a cascade of legal and financial repercussions, further complicating the economic outlook.
- Flexibility and Agility:Recessions often require businesses to be flexible and adaptable. This involves being able to quickly respond to changing market conditions, adjust production plans, and re-allocate resources. A manufacturing company might shift production to focus on higher-demand products or adjust its supply chain to minimize disruptions.
Government Policies and Economic Stimulus
Governments play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of recessions by implementing policies aimed at stimulating economic activity and providing support to individuals and businesses. These policies are designed to address the underlying causes of economic downturns, such as decreased consumer spending, reduced investment, and job losses.The effectiveness of economic stimulus measures varies depending on the specific policies implemented and the economic conditions prevailing at the time.
While some measures, such as tax cuts and increased government spending, can provide a short-term boost to the economy, their long-term impact may be less significant. Moreover, these measures can also lead to unintended consequences, such as increased government debt or inflation.
Effectiveness of Economic Stimulus Measures
The effectiveness of economic stimulus measures can be assessed based on their ability to achieve the desired outcomes, such as increasing employment, boosting consumer spending, and stimulating investment. However, the effectiveness of these measures can vary depending on the specific context and the timeliness of their implementation.
- Tax Cuts: Tax cuts can stimulate economic activity by increasing disposable income, which can lead to increased consumer spending. However, the effectiveness of tax cuts depends on factors such as the size of the tax cut, the target group, and the overall economic environment.
For instance, tax cuts targeted at low-income households may have a larger impact on consumer spending than tax cuts for high-income households.
- Government Spending: Increased government spending on infrastructure projects, education, or healthcare can create jobs, stimulate demand, and boost economic activity. However, the effectiveness of government spending depends on the quality of the projects and the efficiency of their implementation. For example, infrastructure projects that are poorly planned or executed may not have the desired economic impact.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks can use monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing, to influence the availability and cost of credit. Lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and investment, while quantitative easing can increase the money supply and stimulate economic activity.
However, monetary policy can have unintended consequences, such as asset bubbles or inflation.
Potential Drawbacks of Economic Stimulus Measures
While economic stimulus measures can be effective in mitigating the impact of recessions, they also have potential drawbacks. These drawbacks include:
- Increased Government Debt: Government spending programs, particularly those financed by borrowing, can lead to increased government debt. This can create long-term fiscal challenges, particularly if the debt is not managed effectively.
- Inflation: Excessive government spending or loose monetary policy can lead to inflation, which can erode purchasing power and make it more difficult for businesses to plan for the future. This can lead to uncertainty and discourage investment.
- Moral Hazard: Economic stimulus measures can create a moral hazard, where individuals and businesses become less likely to take precautions against economic downturns, knowing that the government will provide support. This can lead to excessive risk-taking and potentially exacerbate future economic problems.
Comparative Approaches of Different Governments
Governments around the world have adopted different approaches to addressing economic downturns. Some governments have favored fiscal stimulus measures, such as tax cuts and increased government spending, while others have focused on monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing.
- United States: The US government has historically relied on a combination of fiscal and monetary policies to address recessions. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the US government implemented the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, which included tax cuts and increased government spending.
The Federal Reserve also lowered interest rates and implemented quantitative easing to stimulate economic activity.
- European Union: The European Union has adopted a more coordinated approach to addressing economic downturns, with member states sharing responsibility for fiscal and monetary policy. The European Central Bank has played a key role in providing liquidity to the banking system and stabilizing the euro.
The EU has also implemented a range of structural reforms aimed at improving the competitiveness of its economies.
- Japan: Japan has experienced a period of prolonged economic stagnation, known as the “Lost Decade.” The Japanese government has implemented a range of economic stimulus measures, including fiscal spending and monetary easing, but these measures have had limited success in reviving economic growth.
Consumer Behavior and Recessionary Psychology
Recessions significantly impact consumer behavior, forcing individuals to adjust their spending habits and adopt a more cautious approach. This shift is driven by a complex interplay of economic factors and psychological influences that shape spending decisions in times of economic uncertainty.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses and policymakers to navigate the challenges of a recession effectively.
Psychological Factors Influencing Spending Decisions
Recessions often trigger a wave of anxiety and uncertainty among consumers, leading to a shift in their spending priorities. The fear of job losses, declining incomes, and a potential decrease in purchasing power can significantly influence spending decisions.
- Fear of the Unknown:Recessions bring a sense of uncertainty about the future, making consumers hesitant to make significant purchases or invest in long-term projects. This uncertainty can lead to a “wait-and-see” approach, delaying major purchases and opting for more conservative spending patterns.
- Loss Aversion:Consumers tend to be more sensitive to losses than gains, and a recession can amplify this effect. The fear of losing accumulated savings or experiencing a decline in wealth can make consumers more reluctant to spend.
- Reduced Confidence:Economic downturns can erode consumer confidence, leading to a decrease in overall spending. This decline in confidence can be a self-fulfilling prophecy, as reduced spending can further weaken the economy, creating a vicious cycle.
Impact of Recession on Consumer Spending Categories
| Spending Category | Impact of Recession | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Discretionary Spending | Significant decline | Dining out, entertainment, vacations, luxury goods |
| Durable Goods | Moderate decline | Cars, appliances, furniture |
| Non-Durable Goods | Slight decline | Food, clothing, personal care products |
| Services | Mixed impact | Healthcare, education, utilities (may see an increase in demand for essential services) |
Final Conclusion
Navigating a recession requires a combination of understanding, planning, and adaptability. By following the money, understanding the signals, and implementing appropriate strategies, individuals, businesses, and governments can weather the storm and emerge stronger on the other side. This isn’t about panic, it’s about preparedness.
It’s about making informed decisions, taking calculated risks, and ultimately, finding opportunities amidst the challenges.