Federal Reserve Pauses Tightening as Emergency Lending Hits $300 Billion
Federal reserve pauses tightening as emergency lending hits 300 billion – Federal Reserve pauses tightening as emergency lending hits $300 billion sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, has made a significant decision: to pause its campaign of interest rate hikes.
This move comes as the economy navigates a complex landscape of inflation and economic growth, with the Fed’s emergency lending program reaching a staggering $300 billion. The decision to pause tightening signals a cautious approach by the Fed, acknowledging the potential impact of continued rate increases on an already delicate economic balance.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause tightening is a direct response to the current economic landscape. Inflation, while showing signs of moderation, remains a persistent concern, prompting the Fed to carefully consider its next steps. Meanwhile, economic growth has slowed, raising concerns about a potential recession.
The Fed’s emergency lending program, designed to provide liquidity to financial institutions during periods of stress, has been heavily utilized, highlighting the ongoing challenges facing the financial system.
Federal Reserve’s Decision to Pause Tightening: Federal Reserve Pauses Tightening As Emergency Lending Hits 300 Billion
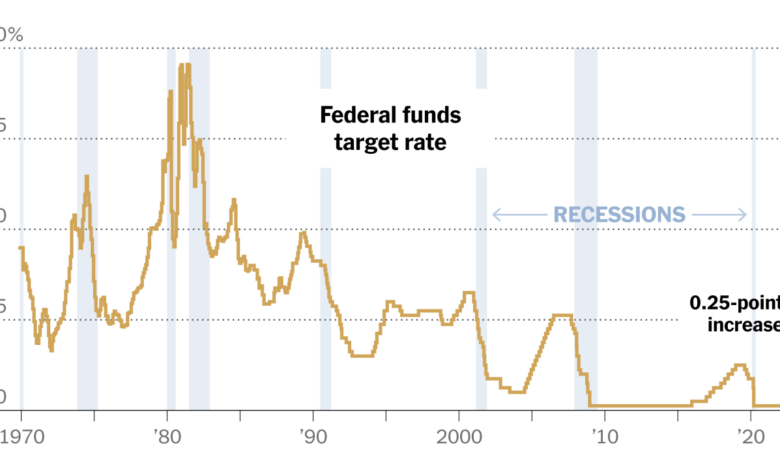
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause interest rate hikes marks a significant shift in monetary policy, signaling a potential change in the trajectory of the US economy. This decision comes after a period of aggressive rate increases aimed at combating high inflation.
Current Economic Conditions
The Federal Reserve’s decision reflects the current state of the US economy, characterized by a complex interplay of factors. Inflation, while showing signs of moderation, remains elevated, posing a challenge to policymakers. The latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) report revealed a 4.9% year-over-year increase in April 2023, demonstrating a slowdown from the previous month’s 5% rise.
However, core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, remained stubbornly high at 5.5%, indicating that underlying inflationary pressures persist. Economic growth has also slowed, with the US economy expanding at an annualized rate of 1.1% in the first quarter of 2023.
This slowdown is attributed to several factors, including rising interest rates, persistent supply chain disruptions, and a decline in consumer spending.
Factors Influencing the Federal Reserve’s Decision
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause rate hikes is influenced by a complex interplay of factors.
- Recent Economic Data: The recent economic data, particularly the slowdown in inflation and economic growth, has provided the Federal Reserve with a reason to pause its rate-hiking cycle. The moderation in inflation suggests that the Fed’s aggressive rate hikes are starting to have the desired effect of cooling the economy.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause tightening, despite emergency lending hitting $300 billion, seems to be a reflection of the current economic climate. The fact that homebuilder sentiment drops for 12 months in a row to lowest in decade is a clear indicator of a weakening housing market, and the Fed may be hesitant to push interest rates higher until they see more signs of stability.
It’s a balancing act, trying to manage inflation while also avoiding a potential recession.
- Inflation Expectations: The Federal Reserve closely monitors inflation expectations, which reflect market participants’ beliefs about future inflation. While inflation expectations have moderated somewhat, they remain elevated, suggesting that the Fed may need to remain vigilant in its fight against inflation.
- Market Conditions: The Federal Reserve also considers market conditions when making its monetary policy decisions. Financial markets have been volatile in recent months, reflecting uncertainty about the economic outlook. The Fed’s decision to pause rate hikes may provide some stability to financial markets and help to boost investor confidence.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause tightening comes amidst a backdrop of growing economic uncertainty. While the Fed’s emergency lending program has reached $300 billion, indicating a need for intervention, the recent slowdown in the US economy, with the fourth-quarter GDP growth rate dropping to 2.9%, as reported here , adds to the pressure on the Fed to navigate a delicate path.
The Fed’s actions will be closely watched as it balances the need to curb inflation with the risk of exacerbating an economic slowdown.
Emergency Lending Program
The Federal Reserve’s emergency lending program is a critical tool used to provide liquidity to the financial system during times of stress. This program plays a vital role in maintaining financial stability by ensuring that banks and other financial institutions have access to the funds they need to operate effectively.
The Federal Reserve’s pause on tightening, coupled with the surge in emergency lending to $300 billion, reflects a cautious approach to navigating the current economic landscape. This comes as Goldman Sachs missed profit estimates, highlighting the impact of a slowdown in dealmaking and asset management, as reported in this article.
While the Fed’s actions signal a willingness to support the economy, the challenges faced by institutions like Goldman Sachs underscore the need for continued vigilance and adaptability in the face of evolving economic conditions.
Eligibility and Conditions
The Federal Reserve’s emergency lending programs are designed to provide short-term liquidity to a wide range of institutions, including banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. The specific types of institutions eligible for emergency lending and the conditions for accessing these funds vary depending on the program.
However, the Federal Reserve generally requires that institutions seeking emergency loans meet certain criteria, such as having a sound financial position and demonstrating a need for liquidity.
The Federal Reserve’s emergency lending programs are designed to provide short-term liquidity to a wide range of institutions, including banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions.
Types of Emergency Lending Programs
The Federal Reserve has a range of emergency lending programs available, each designed to address specific types of financial stress. These programs include:
- Discount Window Loans:These loans are available to banks and other depository institutions that are experiencing temporary liquidity shortages.
- Term Auction Facility (TAF):This program provides longer-term funding to banks and other financial institutions through competitive auctions.
- Commercial Paper Funding Facility (CPFF):This program provides funding for commercial paper, a type of short-term debt issued by corporations.
- Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility (MMMLF):This program provides liquidity to money market mutual funds, which invest in short-term debt securities.
- Primary Dealer Credit Facility (PDCF):This program provides liquidity to primary dealers, which are large financial institutions that trade government securities with the Federal Reserve.
- Secondary Market Corporate Credit Facility (SMCCF):This program provides liquidity to the market for corporate bonds, which are long-term debt securities issued by corporations.
Current Usage
The Federal Reserve’s emergency lending programs have been used extensively during the COVID-19 pandemic. As of June 2023, the Federal Reserve has extended over $300 billion in emergency loans to various financial institutions. This lending has helped to stabilize the financial system and support the economy during a period of unprecedented uncertainty.
Impact on Financial Markets
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause tightening and provide emergency lending has significant implications for financial markets, potentially impacting stock prices, bond yields, and the dollar. The move signals a shift in the Fed’s approach to managing the economy, potentially influencing investor sentiment and market volatility.
Impact on Stock Prices
The Fed’s pause on rate hikes could be interpreted as a sign of confidence in the economy, potentially boosting investor confidence and driving stock prices higher. However, the continued economic uncertainty and potential for future rate hikes might limit the upside potential for stocks.
The emergency lending program could also have a mixed impact on stock prices. While it could provide a lifeline to struggling businesses, it could also signal concerns about the health of the financial system, potentially dampening investor enthusiasm.
Future Outlook
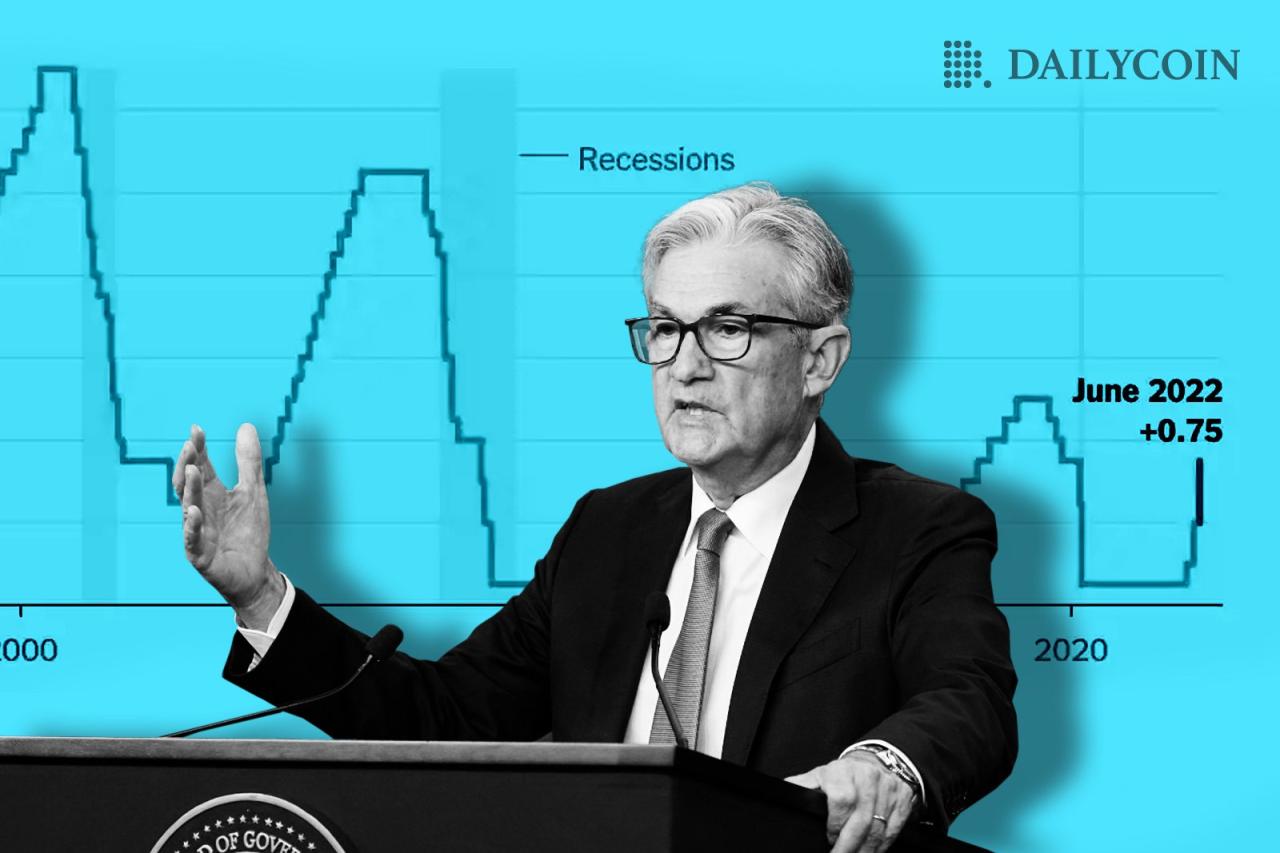
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause tightening and deploy emergency lending facilities creates a complex landscape for future policy decisions. The Fed will carefully monitor economic indicators and financial market conditions to determine the appropriate course of action.
Factors Influencing Future Policy Decisions, Federal reserve pauses tightening as emergency lending hits 300 billion
The Fed’s future decisions will be influenced by a confluence of economic factors, including inflation trends, economic growth, and financial market stability.
- Inflation Trends:The Fed’s primary objective is to bring inflation down to its 2% target. The path of inflation will be a key determinant of future policy decisions. If inflation remains stubbornly high, the Fed may resume rate hikes to curb demand and cool the economy.
However, if inflation starts to moderate, the Fed may maintain its pause or even consider rate cuts to support economic growth.
- Economic Growth:The Fed will also consider the pace of economic growth. If the economy shows signs of weakening, the Fed may be more inclined to ease monetary policy to stimulate growth. Conversely, if the economy remains resilient, the Fed may be more comfortable with a tighter stance.
- Financial Market Stability:The Fed will also be mindful of financial market stability. The recent banking sector turmoil has highlighted the interconnectedness of the financial system. If the financial system shows signs of stress, the Fed may take steps to provide liquidity and support market stability.
Potential Scenarios for Future Policy Decisions
Based on the interplay of these factors, several potential scenarios for future policy decisions can be envisioned.
- Continued Pause:The Fed may maintain its pause on rate hikes for an extended period, especially if inflation shows signs of moderating and economic growth remains steady. This scenario assumes that the financial system stabilizes and does not pose a systemic risk.
- Resumption of Rate Hikes:If inflation remains stubbornly high and economic growth remains robust, the Fed may resume rate hikes to curb demand and cool the economy. This scenario assumes that the financial system remains stable and the Fed is comfortable with the risks associated with further tightening.
- Rate Cuts:If inflation falls significantly below the Fed’s target and economic growth weakens, the Fed may consider rate cuts to stimulate the economy. This scenario assumes that the financial system is stable and the Fed is confident that rate cuts will not lead to uncontrolled inflation.
Key Economic Indicators and Their Impact on Future Policy Decisions
| Economic Indicator | Potential Impact on Future Policy Decisions |
|---|---|
| Inflation (CPI, PCE) | High inflation may lead to further rate hikes, while moderating inflation could lead to a pause or even rate cuts. |
| Economic Growth (GDP, Unemployment Rate) | Strong economic growth may justify continued tightening, while weak growth could lead to a pause or even rate cuts. |
| Financial Market Volatility (VIX, Credit Spreads) | Increased financial market volatility may prompt the Fed to provide liquidity and support market stability. |
| Consumer Confidence | Declining consumer confidence could indicate weakening demand and potentially lead to a pause or rate cuts. |
| Business Investment | Strong business investment may support continued tightening, while weak investment could lead to a pause or rate cuts. |
Closure
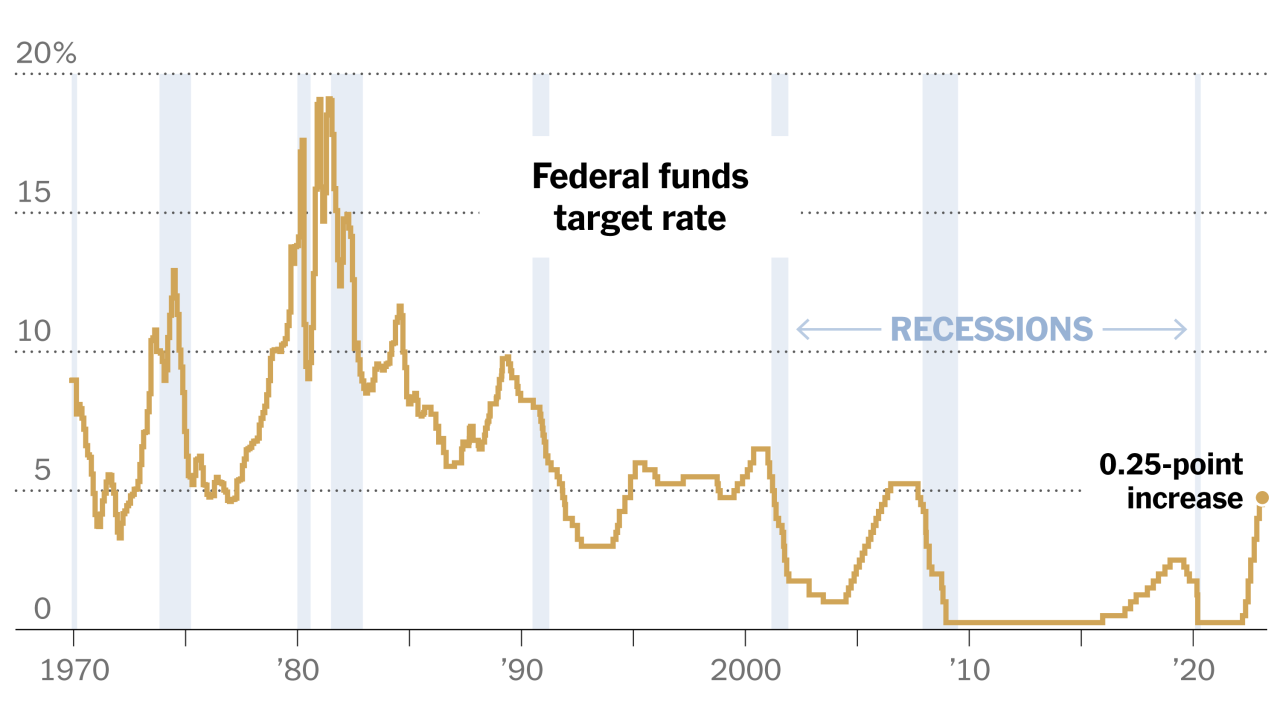
The Federal Reserve’s decision to pause tightening is a pivotal moment in the ongoing battle against inflation and the quest for economic stability. While the pause provides a temporary reprieve from rate hikes, the future remains uncertain. The Fed’s next move will be closely watched by investors, businesses, and consumers alike, as it will shape the trajectory of the economy for months to come.
The emergency lending program, a testament to the challenges facing the financial system, will continue to play a crucial role in providing stability during this period of uncertainty.