Federal Deficit to Double to $2 Trillion Even as Biden Boasts Deficit Cutting
Federal deficit to double to 2 trillion even as biden boasts deficit cutting – Federal deficit to double to $2 trillion even as Biden boasts deficit cutting – a statement that seems paradoxical, but one that reflects the complex reality of the U.S. economy. Despite President Biden’s pledges to reduce the deficit, projections indicate a significant increase in the coming years, raising concerns about the long-term sustainability of government finances.
This rise is fueled by a confluence of factors, including ongoing spending commitments, a sluggish economy, and the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The projected doubling of the federal deficit to $2 trillion is a stark reminder of the financial challenges facing the nation. While the Biden administration has implemented policies aimed at deficit reduction, these efforts have been met with mixed results.
The economic implications of such a large deficit are far-reaching, potentially impacting inflation, interest rates, and economic growth. The political climate surrounding the deficit is also fraught with tension, as different parties grapple with the best way to address this pressing issue.
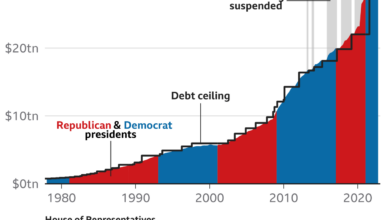
Federal Deficit Projections
The projected doubling of the federal deficit to $2 trillion raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of the U.S. economy. This significant increase in borrowing represents a substantial challenge for policymakers and the nation as a whole.
It’s mind-boggling how the federal deficit is set to double to $2 trillion even as President Biden touts his deficit-cutting efforts. Meanwhile, newly released surveillance footage challenges the official January 6th narrative , raising even more questions about the events of that day.
With such conflicting narratives swirling around us, it’s hard to know what to believe about our government’s fiscal policies and the events that have shaped our recent history.
Factors Contributing to the Projected Deficit Increase
The projected increase in the federal deficit is driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Increased government spending:The recent passage of major spending bills, such as the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and the American Rescue Plan Act, has significantly increased government spending. These programs aim to address various challenges, including infrastructure development, economic recovery, and climate change.
However, they also contribute to a larger deficit.
- Declining tax revenues:Despite a strong economy, tax revenues have not kept pace with spending increases. This is partly due to factors like tax cuts implemented in recent years and the changing composition of the economy, which has led to a decline in corporate tax revenues.
- Rising interest rates:The Federal Reserve has been raising interest rates to combat inflation, which increases the cost of borrowing for the government. This means that the government has to pay more interest on its existing debt, further contributing to the deficit.
Historical Context for the Current Deficit Projection
The current deficit projection is not unprecedented. The U.S. has experienced periods of large deficits in the past, particularly during times of war or economic crisis. For example, the deficit soared during World War II and the Great Recession. However, the current projection is notable for its magnitude and the fact that it is occurring during a period of relative economic stability.
Comparison to Previous Years
The projected $2 trillion deficit is significantly larger than the deficits seen in recent years. For example, the deficit in 2022 was around $1 trillion. The projected increase reflects the impact of the factors discussed above, including increased spending and declining tax revenues.
Potential Consequences of the Deficit
A large and growing federal deficit can have a number of potential consequences, including:
- Higher interest rates:As the government borrows more money, it can push up interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money.
- Inflation:A large deficit can contribute to inflation, as the government prints more money to finance its spending. This can erode the purchasing power of consumers.
- Reduced economic growth:A large deficit can crowd out private investment, leading to slower economic growth. This is because the government’s borrowing can make it more difficult for businesses to access capital.
- Slower economic growth:A large deficit can crowd out private investment, leading to slower economic growth. This is because the government’s borrowing can make it more difficult for businesses to access capital.
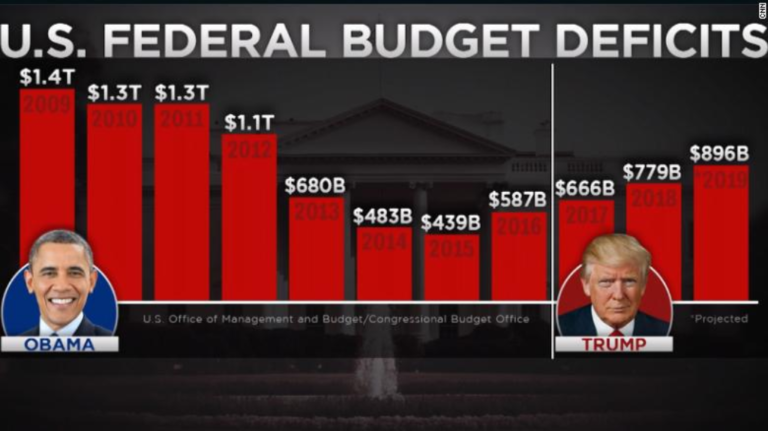
President Biden’s Deficit Cutting Claims
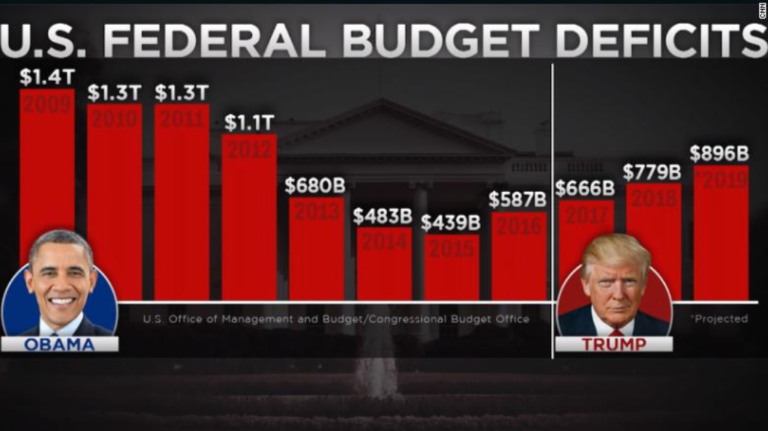
President Biden has repeatedly asserted his commitment to reducing the federal deficit, a key economic issue that has garnered significant attention in recent years. While the federal deficit has recently reached a record high, exceeding $2 trillion, Biden’s administration has implemented various policies aimed at addressing this issue.
Analysis of President Biden’s Statements
President Biden has consistently emphasized the importance of fiscal responsibility and the need to reduce the national debt. He has argued that deficit reduction is crucial for long-term economic stability and prosperity. In his State of the Union address in 2023, he stated, “We have to make smart choices to bring down the deficit and invest in our future.”
Specific Policies and Initiatives, Federal deficit to double to 2 trillion even as biden boasts deficit cutting
The Biden administration has implemented several policies intended to reduce the federal deficit. Some notable examples include:
- The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021: This legislation, enacted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, included provisions aimed at stimulating the economy and providing relief to individuals and businesses. While the act significantly increased the deficit in the short term, it also contributed to economic recovery, potentially leading to long-term deficit reduction through increased tax revenue.
- The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act: This bipartisan infrastructure bill allocated significant funding for infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and broadband internet. Proponents argue that these investments will boost economic growth and productivity, ultimately leading to increased tax revenue and a reduction in the deficit.
- Tax Policy: The Biden administration has proposed various tax policy changes, including raising taxes on corporations and high-income earners. These proposals aim to increase tax revenue and reduce the deficit. However, these proposals have faced significant opposition from Republicans, making their implementation uncertain.
The news that the federal deficit is set to double to $2 trillion, even as President Biden boasts about deficit cutting, feels like a punch to the gut. It’s a stark reminder that promises don’t always translate to reality. And it’s not the only piece of bad news.
Longtime Democrat Senator announces she won’t seek another term , leaving a void in the party’s ranks. This kind of news, coupled with the looming deficit, makes you wonder if the party can even hold onto its current power, let alone make any real progress on the issues that matter.
Effectiveness of Policies
The effectiveness of Biden’s deficit-cutting policies remains a subject of debate. While some argue that these policies have contributed to a reduction in the deficit, others contend that they have had a minimal impact or even exacerbated the problem. The impact of these policies on the deficit will likely depend on various factors, including economic growth, inflation, and the effectiveness of implementation.
Comparison to Previous Administrations
Comparing Biden’s deficit-cutting efforts to those of previous administrations is complex. The size and trajectory of the federal deficit have been influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, wars, and policy decisions. While some administrations have focused on deficit reduction, others have prioritized spending on social programs or tax cuts.
The effectiveness of deficit-cutting efforts can also be influenced by political factors, such as the level of cooperation between the executive and legislative branches.
Impact on the Economy
The impact of deficit-cutting policies on the economy can be significant. Reducing the deficit can lead to lower interest rates, stimulate investment, and improve economic growth. However, it can also lead to decreased government spending, potentially impacting economic growth and social programs.
The impact of deficit reduction on the economy will likely depend on the specific policies implemented and the overall economic context.
Economic Implications of the Deficit
A $2 trillion federal deficit represents a significant burden on the U.S. economy. While the government can borrow money to cover the deficit, this borrowing has real consequences for inflation, interest rates, economic growth, and future generations.
Impact on Inflation
A large deficit can contribute to inflation by increasing the money supply. When the government borrows money, it essentially prints more money, which can lead to a decrease in the value of the dollar and an increase in prices for goods and services.
This is particularly relevant in the current economic climate, where inflation is already a major concern.
Impact on Interest Rates
As the government borrows more money, it competes with businesses and individuals for available funds. This increased demand for borrowing can drive up interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses to invest and individuals to borrow for things like homes or education.
Higher interest rates can also slow economic growth.
Impact on Economic Growth
While some government spending can stimulate economic growth, a large deficit can also have negative consequences. If the government spends money on unproductive projects or uses borrowed funds to cover current expenses, it can crowd out private investment and reduce economic growth.
Impact on Government Spending and Tax Revenue
A large deficit can lead to a cycle of increased government spending and higher taxes. As the government borrows more money, it incurs interest payments on that debt, which further increases government spending. To pay for this increased spending, the government may have to raise taxes, which can stifle economic growth and discourage investment.
Comparison to Other Economic Challenges
The economic implications of the deficit are compounded by other challenges facing the nation, such as rising healthcare costs, an aging population, and climate change. These challenges require significant government investment, which can further increase the deficit and its negative consequences.
Consequences for Future Generations
The largest share of the federal debt will be borne by future generations. As the government continues to borrow money, it is accumulating a debt that will eventually have to be repaid. This will likely lead to higher taxes, reduced government services, or both, for future generations.
Political Context and Perspectives
The projected doubling of the federal deficit to $2 trillion has ignited a heated political debate, with different parties and stakeholders offering contrasting viewpoints on its implications and potential solutions.
Key Political Actors and Their Stances
The political climate surrounding the deficit is marked by stark differences in perspective.
- Democrats, generally, advocate for increased government spending on social programs, infrastructure, and education, arguing that these investments stimulate economic growth and benefit the overall well-being of citizens. They often view deficit spending as necessary to address pressing social and economic issues, particularly during times of crisis, such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
While acknowledging the importance of fiscal responsibility, they prioritize social and economic goals, often proposing tax increases on corporations and high-income earners to offset spending.
- Republicans, on the other hand, tend to prioritize fiscal conservatism and reducing the national debt. They often argue that excessive deficit spending undermines economic stability, leads to inflation, and burdens future generations with unsustainable debt. They frequently advocate for tax cuts, particularly for businesses and corporations, claiming that these measures stimulate economic growth and create jobs.
Republicans often propose reducing government spending, particularly on social programs, as a means of addressing the deficit.
Potential Political Implications of the Deficit
The growing deficit has significant political implications.
- It fuels partisan debates about the role of government in society and the appropriate balance between spending and revenue.
- It can influence the outcome of elections, as voters may hold elected officials accountable for their handling of the deficit.
- It can impact the political landscape, potentially leading to increased polarization and gridlock in government as different parties struggle to agree on solutions.
Perspectives of Different Political Parties on the Deficit
The two major political parties in the United States, Democrats and Republicans, have contrasting perspectives on the deficit.
It’s a head-scratcher, isn’t it? The federal deficit is projected to double to $2 trillion, even as President Biden touts his deficit-cutting measures. Meanwhile, concerns are mounting about the CDC’s risk-benefit assessment for new COVID-19 vaccines, as highlighted in this article cdcs risk benefit assessment for new covid 19 vaccines flawed experts.
It seems like we’re facing a perfect storm of economic uncertainty and public health anxieties, making it harder than ever to navigate these challenging times.
- Democratsgenerally argue that the deficit is a consequence of necessary government spending on social programs, infrastructure, and education, which they believe are crucial for economic growth and societal well-being. They often support raising taxes on corporations and high-income earners to offset spending, believing that this approach is fairer and more sustainable.
- Republicans, on the other hand, typically prioritize fiscal conservatism and reducing the national debt. They often argue that excessive deficit spending undermines economic stability, leads to inflation, and burdens future generations with unsustainable debt. They frequently advocate for tax cuts, particularly for businesses and corporations, claiming that these measures stimulate economic growth and create jobs.
Republicans often propose reducing government spending, particularly on social programs, as a means of addressing the deficit.
Potential Impact of the Deficit on Future Elections
The growing deficit is likely to be a significant issue in future elections.
- Voters may hold elected officials accountable for their handling of the deficit, potentially leading to shifts in political power.
- The issue of the deficit could become a central point of contention between political parties, influencing campaign strategies and voter turnout.
- The potential for economic instability due to the deficit could impact voter sentiment and influence their choices at the ballot box.
Potential Solutions and Strategies
Addressing the projected doubling of the federal deficit to $2 trillion requires a multifaceted approach that tackles both spending and revenue. This section explores potential solutions, analyzing their feasibility and effectiveness, and outlining a strategy for achieving sustainable deficit reduction.
Spending Reduction Strategies
Reducing government spending is a crucial aspect of deficit reduction.
- Enacting Spending Caps and Budgetary Restraint:Imposing limits on discretionary spending across various government departments and agencies can help control expenditures. However, this approach may require difficult choices regarding program cuts and priorities. For example, a recent proposal to cap spending growth at 1% per year would require significant cuts to programs like defense, education, and infrastructure.
- Reforming Entitlement Programs:Social Security and Medicare, the largest entitlement programs, contribute significantly to the deficit. Reforms such as raising the retirement age, adjusting benefits based on income, or increasing cost-sharing could help slow their growth. However, such changes can be politically challenging due to their impact on large segments of the population.
- Prioritizing Spending on High-Return Investments:Allocating resources to programs with demonstrably high returns on investment, such as infrastructure projects, research and development, and education, can stimulate economic growth and potentially reduce the deficit in the long run. This strategy requires careful evaluation and prioritization to ensure investments deliver the intended benefits.
Revenue Enhancement Strategies
Increasing government revenue is another critical element of deficit reduction.
- Tax Reform and Simplification:Broadening the tax base, closing loopholes, and simplifying the tax code can generate more revenue. This could involve raising tax rates for high-income earners, closing corporate tax loopholes, or eliminating tax deductions for certain expenses. However, tax reform proposals must be carefully designed to avoid unintended consequences and ensure fairness.
- Addressing Tax Avoidance and Evasion:Strengthening enforcement measures and addressing tax avoidance and evasion can increase tax revenue. This could involve improving audits, enhancing data sharing between government agencies, and cracking down on offshore tax havens.
- Exploring New Revenue Sources:Consideration of new revenue sources, such as a carbon tax, a financial transaction tax, or a wealth tax, can be explored. These proposals often face political challenges and require careful analysis of their potential economic and social impacts.
Feasibility and Effectiveness
The feasibility and effectiveness of these solutions depend on several factors, including political will, economic conditions, and public opinion.
- Political Will:Implementing significant changes to spending and revenue requires strong political leadership and a willingness to make difficult choices.
- Economic Conditions:The effectiveness of deficit reduction strategies can be influenced by economic conditions. Recessions or periods of slow growth can make it more difficult to reduce spending or increase revenue.
- Public Opinion:Public support is essential for successful deficit reduction efforts. Any proposed changes must be carefully communicated and explained to the public to ensure understanding and acceptance.
Strategy for Sustainable Deficit Reduction
A comprehensive strategy for sustainable deficit reduction should incorporate a balanced approach that combines spending reduction and revenue enhancement measures.
- Long-Term Perspective:Focusing on long-term sustainability rather than short-term fixes is crucial.
- Phased Implementation:Implementing changes gradually, rather than abruptly, can help minimize economic disruption and ensure public acceptance.
- Transparency and Accountability:Ensuring transparency and accountability in government spending and revenue collection is essential for building public trust and confidence.
Merits of Different Solutions
Comparing the merits of different solutions requires careful consideration of their potential economic, social, and political impacts.
- Spending Cuts:While spending cuts can help reduce the deficit, they can also lead to reduced government services and economic hardship, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Revenue Increases:Raising taxes can generate more revenue, but it can also discourage economic activity and create inequities if not implemented carefully.
- Combination of Approaches:A combination of spending cuts and revenue increases is often the most effective and sustainable approach to deficit reduction.
Conclusive Thoughts: Federal Deficit To Double To 2 Trillion Even As Biden Boasts Deficit Cutting
The looming $2 trillion federal deficit presents a complex challenge that requires careful consideration and decisive action. While President Biden has made efforts to reduce the deficit, the projected increase raises serious concerns about the long-term health of the U.S.
economy. Finding sustainable solutions to address this issue will require a bipartisan approach that prioritizes fiscal responsibility and long-term economic stability. The potential consequences of inaction are significant, and the nation must find a way to navigate this challenging terrain with foresight and resolve.