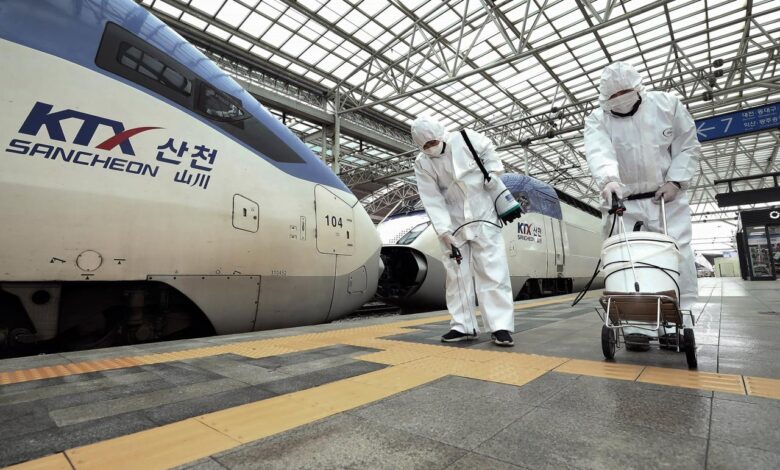
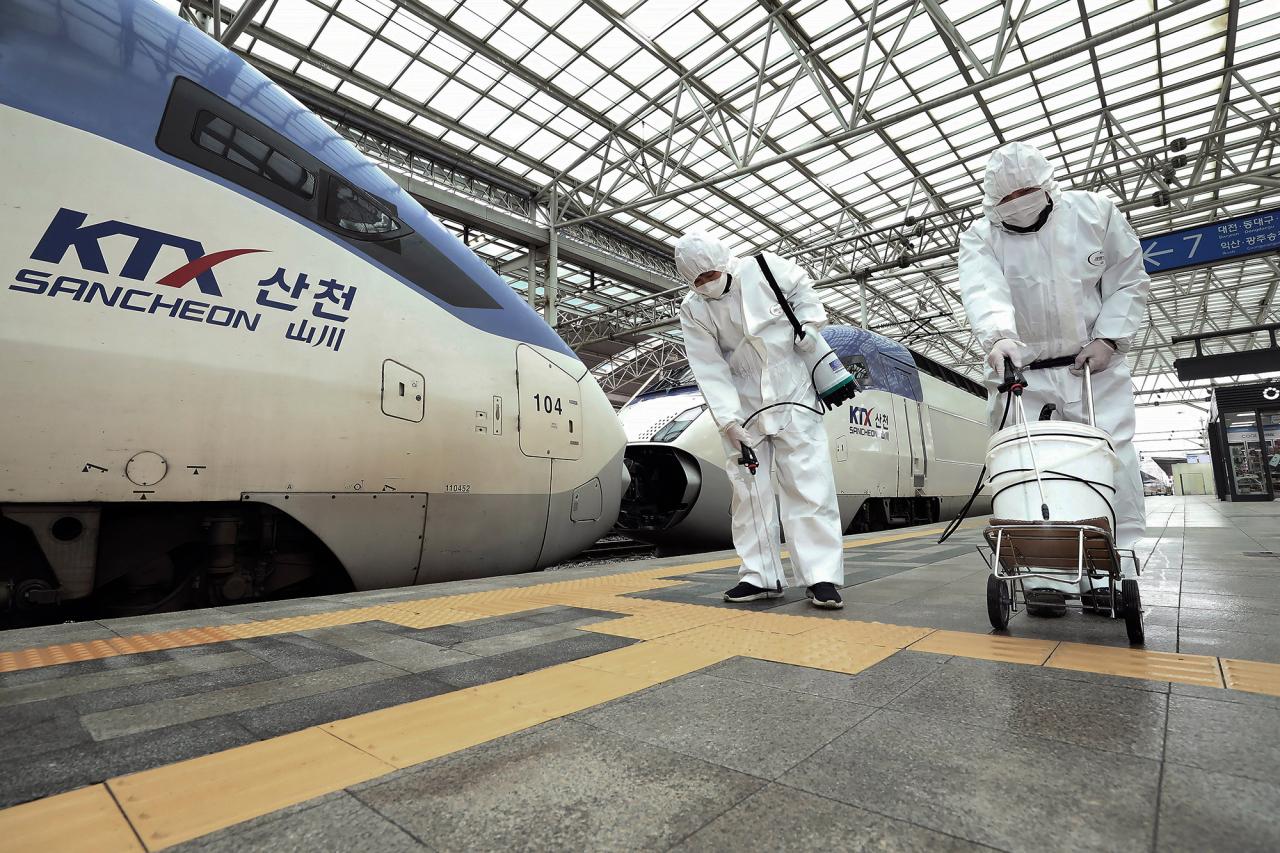
Fed Quarantines Cash from Asia to Curb Coronavirus
Fed quarantines cash from asia in precautionary bid to stem coronavirus spread – Fed Quarantines Cash from Asia to Curb Coronavirus: In a bold move aimed at containing the spread of the deadly virus, the Federal Reserve took the unprecedented step of quarantining cash shipments from Asia. This decision, driven by a desire to protect public health, sparked a global debate about the economic and political implications of such a drastic measure.
The quarantine, while intended to safeguard against the virus’s transmission, triggered concerns about potential economic disruptions. The move, which effectively restricted the flow of physical currency, raised questions about the impact on Asian economies, global supply chains, and consumer goods.
The potential for trade diversion and market shifts, as well as the role of international organizations in mitigating these disruptions, became key areas of discussion.
The Quarantine’s Impact on Global Trade
The quarantine imposed on cash from Asia, a precautionary measure to curb the spread of the coronavirus, has had a significant impact on global trade, disrupting supply chains and affecting economies worldwide. While the primary focus was on public health, the economic consequences of the quarantine have been far-reaching, particularly for Asian economies heavily reliant on global trade.
Economic Consequences for Asian Economies
The quarantine has significantly impacted Asian economies, particularly those heavily reliant on trade.
- Reduced Exports:The quarantine has led to a decline in exports from Asian countries, as businesses face challenges in transporting goods and securing financing. For example, the export of goods from China, a major manufacturing hub, has been significantly affected, impacting global supply chains.
- Disruption of Supply Chains:The quarantine has disrupted global supply chains, causing delays in production and delivery of goods. This has resulted in shortages of essential goods, particularly medical supplies, and has disrupted manufacturing processes across various industries.
- Economic Slowdown:The decline in trade and disruption of supply chains have contributed to an economic slowdown in many Asian economies. This slowdown has led to job losses, reduced investment, and decreased consumer spending.
Impact on Global Supply Chains and Consumer Goods
The quarantine has had a significant impact on global supply chains, particularly for consumer goods.
The Fed’s quarantine of cash from Asia, a precautionary measure to stem the spread of the coronavirus, highlights the complex interplay between health and economic security. It’s a stark reminder that the world is interconnected, and that even seemingly distant events can have profound ripple effects.
Meanwhile, in a separate news story, Bloomberg pressures Sanders to release full medical records after doctor declares billionaire is in outstanding health , raising questions about transparency and the role of public health in political discourse. The Fed’s actions, while necessary, also underscore the importance of a proactive approach to managing potential threats, whether they be financial or viral in nature.
- Shortages of Essential Goods:The quarantine has led to shortages of essential goods, such as medical supplies, electronics, and automotive parts. This is due to disruptions in production and transportation, as well as increased demand for these goods.
- Price Increases:The disruption of supply chains has led to price increases for consumer goods, as businesses pass on the increased costs of production and transportation. This has put pressure on consumers, particularly those with lower incomes.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences:The quarantine has also led to a shift in consumer preferences, with increased demand for goods that can be purchased online or delivered to homes. This has benefited online retailers and delivery services, but has posed challenges for traditional brick-and-mortar stores.
Potential for Trade Diversion and Market Shifts
The quarantine has the potential to lead to trade diversion and market shifts, as businesses seek alternative sources of goods and services.
- Diversion of Trade:The quarantine has led to a diversion of trade, as businesses seek alternative sources of goods and services. This has resulted in increased trade between countries that were not previously major trading partners.
- Market Shifts:The quarantine has also led to market shifts, as businesses adapt to the new realities of global trade. This has included the emergence of new business models and the growth of industries that are less reliant on physical goods.
Role of International Organizations in Mitigating Economic Disruptions
International organizations have played a crucial role in mitigating the economic disruptions caused by the quarantine.
- Financial Support:The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and other international organizations have provided financial support to countries affected by the quarantine. This support has helped to stabilize economies and prevent a deeper economic downturn.
- Coordination of Trade Policies:International organizations have coordinated trade policies to ensure that goods and services can continue to flow freely across borders. This has helped to minimize disruptions to global supply chains.
- Sharing of Best Practices:International organizations have shared best practices for managing the economic impacts of the quarantine. This has helped countries to learn from each other and implement effective policies.
Public Health Measures and Their Effectiveness
The quarantine imposed on cash from Asia aimed to prevent the spread of the coronavirus by limiting the potential for contaminated currency to enter the country. This public health measure was based on the understanding that the virus could potentially survive on surfaces, including banknotes, and that travel and trade could facilitate its transmission.
It’s fascinating how the Fed quarantines cash from Asia to prevent the spread of the coronavirus, but what about the deeper, darker issues? While we’re concerned about a virus, an independent tribunal recently found that the Chinese regime is still killing prisoners of conscience for their organs.
This raises questions about the ethical implications of our global interconnectedness. Perhaps we should be quarantining more than just cash to truly address the issues that threaten humanity.
Rationale and Objectives
The rationale behind the quarantine stemmed from the need to protect public health and prevent a widespread outbreak. The primary objective was to minimize the risk of the virus entering the country through contaminated cash. The quarantine aimed to disrupt the potential chain of transmission by isolating potentially infected currency and preventing its circulation within the domestic economy.
Effectiveness of Quarantine Compared to Other Measures
The effectiveness of quarantining cash in stemming the spread of the virus is a complex issue with no definitive answer. While the measure may have contributed to reducing the risk of transmission through contaminated currency, its impact was likely limited compared to other measures like travel restrictions, social distancing, and hygiene practices.
The effectiveness of a quarantine measure depends on its implementation, the nature of the virus, and the overall public health response.
Ethical Considerations and Unintended Consequences
The quarantine of cash from Asia raised ethical concerns about potential discrimination and economic disruption. Critics argued that the measure could stigmatize individuals and businesses associated with Asia, creating unnecessary fear and prejudice. Additionally, the quarantine could disrupt trade and financial flows, impacting businesses and economies.
Specific Public Health Measures
The quarantine involved the following specific measures:
- Cash Screening:Currency arriving from Asia was inspected for signs of contamination. This involved visual inspection and potentially using ultraviolet light to detect potential viral traces.
- Quarantine Period:The quarantined cash was isolated for a specific period, typically several days, to allow the virus to potentially deactivate. This period was determined based on scientific understanding of the virus’s survival time on surfaces.
- Sanitization:After the quarantine period, the cash was sanitized using methods like ultraviolet light exposure or heat treatment to further reduce the risk of contamination.
Political and Diplomatic Implications
The quarantine imposed on travelers from Asia, particularly China, had significant political and diplomatic implications, reflecting the interplay of national interests, international relations, and global health concerns. The quarantine was a complex policy decision, driven by a combination of factors, including the perceived threat of the virus, the need to protect national populations, and the potential economic and political costs of inaction.
National Interests and Political Motivations
The quarantine was a direct response to the perceived threat posed by the coronavirus. Governments prioritized the protection of their citizens and sought to prevent the spread of the virus within their borders. This led to a focus on border control measures, including travel restrictions and quarantines.
- Protecting National Health:The primary political motivation was the protection of national health. Governments were concerned about the potential for the virus to overwhelm their healthcare systems and cause widespread illness and death. The quarantine was seen as a necessary measure to contain the spread of the virus and prevent a major public health crisis.
- Economic Concerns:Quarantines also had significant economic implications. The restrictions on travel and trade disrupted supply chains, reduced tourism, and impacted businesses reliant on international commerce. While the quarantine was primarily driven by health concerns, governments also had to consider the potential economic consequences of their actions.
- Political Capital:The quarantine was a politically sensitive issue, as it involved restrictions on personal freedoms and the potential for economic disruption. Governments had to weigh the potential political costs of implementing the quarantine against the perceived benefits of protecting public health.
Diplomatic Implications and Bilateral Relations
The quarantine had a significant impact on bilateral relations between countries, particularly those with strong economic and cultural ties. The imposition of travel restrictions and quarantines was seen as a sign of mistrust and a potential source of tension.
- Strained Relations:The quarantine led to strained relations between some countries, particularly those with significant economic and cultural ties. The imposition of travel restrictions and quarantines was seen as a sign of mistrust and a potential source of tension. For instance, the initial travel bans imposed by some countries on Chinese travelers were met with criticism and concerns about discrimination.
- Coordination and Cooperation:The quarantine also highlighted the importance of international cooperation and coordination in responding to global health emergencies. Governments needed to work together to share information, coordinate travel restrictions, and develop a coordinated response to the pandemic. This required effective communication, trust, and a willingness to cooperate, even in the face of competing national interests.
Potential for International Tensions and Disputes, Fed quarantines cash from asia in precautionary bid to stem coronavirus spread
The quarantine measures, while intended to protect public health, also had the potential to exacerbate existing tensions and lead to new disputes between countries.
- Discrimination and Xenophobia:The quarantine measures, particularly those that targeted specific nationalities, raised concerns about discrimination and xenophobia. The focus on travelers from Asia, for example, could have unintended consequences, leading to prejudice and hostility towards Asian communities.
- Trade Disputes:The quarantine measures also had the potential to lead to trade disputes. The restrictions on travel and trade could disrupt supply chains, impact businesses, and lead to economic retaliation. This could further exacerbate tensions between countries, particularly those with strong economic ties.
- Legal Challenges:The legality of quarantine measures, particularly those that restrict travel and trade, could be challenged in international courts. The World Trade Organization (WTO) has rules governing trade restrictions, and countries could use these rules to challenge the legality of quarantine measures.
Impact on International Cooperation and Global Governance
The quarantine highlighted the need for strengthened international cooperation and global governance in responding to global health emergencies.
The Fed’s decision to quarantine cash from Asia in a bid to stem the spread of the coronavirus is a bold move, but it’s not the only headline grabbing news today. While the world grapples with a pandemic, President Trump is focused on his own battles, threatening lawsuits over the Mueller probe and blasting prosecutors in the Roger Stone case.
It seems the focus on the virus is not universal, with some choosing to double down on their own agendas. Perhaps this focus on internal conflicts will distract from the global health crisis, or perhaps it will further exacerbate it.
- Global Health Security:The quarantine underscored the importance of global health security and the need for coordinated international responses to emerging health threats. The pandemic exposed weaknesses in global health systems and highlighted the need for improved surveillance, communication, and coordination.
- International Organizations:The quarantine also highlighted the role of international organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), in responding to global health emergencies. The WHO played a crucial role in providing information, coordinating responses, and providing technical assistance to countries.
However, the pandemic also exposed limitations in the WHO’s authority and resources, raising questions about the need for reform.
- Sharing Information and Resources:The quarantine emphasized the need for countries to share information and resources in responding to global health emergencies. This includes sharing data on the virus, developing and sharing vaccines and treatments, and coordinating travel restrictions and quarantine measures.
The Role of Media and Public Perception

The media plays a crucial role in shaping public perception of the quarantine, influencing public anxiety, fear, and trust in authorities. The way the media frames and reports on the quarantine can have a significant impact on how people understand and respond to the situation.
Media Coverage and Public Anxiety
Media coverage can significantly contribute to public anxiety and fear. Sensationalized headlines, graphic images, and constant updates about the spread of the virus can create a sense of panic and uncertainty. For example, during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, media coverage often focused on the high number of cases and deaths, leading to widespread anxiety and fear.
This heightened anxiety can lead to impulsive behaviors, such as panic buying and hoarding, further exacerbating the situation.
Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness: Fed Quarantines Cash From Asia In Precautionary Bid To Stem Coronavirus Spread
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a stark reminder of the vulnerability of our interconnected world to infectious diseases. The quarantine measures implemented globally, while necessary to slow the spread of the virus, have had profound impacts on economies, societies, and global health systems.
This experience provides valuable lessons for future pandemic preparedness and response strategies.
The Need for Early Detection and Response
Early detection and response are crucial in containing a pandemic. The delay in recognizing the severity of the COVID-19 outbreak and the initial reluctance to implement stringent measures contributed to its rapid spread. The pandemic highlights the importance of:
- Enhanced surveillance systems: Investing in robust surveillance systems, both domestically and internationally, is essential to quickly identify and track emerging infectious diseases. This includes strengthening laboratory capacity for rapid diagnostics, expanding disease reporting networks, and fostering collaboration between national and international health authorities.
- Rapid information sharing: Timely and transparent sharing of information about emerging infectious diseases is crucial for effective response. This includes sharing data on cases, deaths, and travel patterns, as well as research findings and best practices. The World Health Organization (WHO) should be empowered to play a more central role in coordinating information sharing and providing timely guidance to countries.
- Early intervention strategies: Implementing early intervention strategies, such as travel restrictions, social distancing measures, and contact tracing, can significantly slow the spread of a pandemic. However, these measures must be implemented promptly and effectively to be successful.
Strengthening Global Health Security
The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed weaknesses in global health security. The need for a coordinated and collaborative global response is evident. Key aspects for strengthening global health security include:
- Increased investment in public health: Adequate funding is essential for building robust public health systems, including disease surveillance, laboratory capacity, and workforce development. This requires a sustained commitment from governments and international organizations.
- International cooperation and coordination: Effective pandemic response requires strong international cooperation and coordination. This includes sharing information, coordinating travel restrictions, and providing technical assistance to countries in need. The WHO should be strengthened and empowered to play a more central role in coordinating global pandemic response efforts.
- Development of pandemic preparedness plans: Every country should have comprehensive pandemic preparedness plans that Artikel the steps to be taken in the event of an outbreak. These plans should be regularly updated and tested to ensure their effectiveness.
The Importance of Public Trust and Communication
Effective pandemic response requires public trust and cooperation. Clear and consistent communication from public health officials is essential to build trust and encourage adherence to public health measures. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of:
- Transparent and accurate information: Public health officials should provide transparent and accurate information about the pandemic, including the risks, the measures being taken, and the rationale behind those measures. This will help to build trust and encourage public cooperation.
- Effective communication strategies: Public health officials should use a variety of communication channels to reach different segments of the population. This includes traditional media, social media, and community outreach programs.
- Addressing misinformation: Misinformation and disinformation can undermine public trust and hamper pandemic response efforts. Public health officials should actively address misinformation by providing accurate information and debunking false claims.
Final Thoughts
The Fed’s decision to quarantine cash from Asia, a testament to the gravity of the pandemic, underscores the complex interplay between public health, economic considerations, and global governance. While the move may have been necessary to protect against the virus’s spread, it highlighted the delicate balance between safeguarding public health and minimizing economic fallout.
The quarantine served as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of the global economy and the importance of international cooperation in addressing such unprecedented challenges.