Electric Vehicles: Next Big Flop, Says FreedomWorks Economist?
Electric vehicles set to be auto markets next big flop says freedomworks economist – a bold claim, indeed. It’s a statement that’s sparked debate, dividing opinions on the future of the automotive industry. While electric vehicles have seen a surge in popularity in recent years, driven by environmental concerns and government incentives, some experts believe the current trajectory is unsustainable.
This article dives into the arguments both for and against the “flop” prediction, exploring the factors that will shape the future of the electric vehicle market.
The FreedomWorks economist, echoing concerns of some traditional automotive players, points to a number of potential pitfalls for widespread EV adoption. They highlight the high cost of electric vehicles, the limited range of many models, and the lack of robust charging infrastructure as key challenges.
They also argue that government subsidies, which have played a significant role in driving EV sales, are unsustainable in the long term.
The Claim: Electric Vehicles as the Next Big Flop
The statement that electric vehicles (EVs) are poised to be the next big flop in the auto market has been made by FreedomWorks, a conservative advocacy group, through its affiliated economist. This prediction is based on their belief that the EV market is overhyped and that various factors will hinder its widespread adoption.
Economic and Market Factors
FreedomWorks’ economist likely considers several economic and market factors as potential pitfalls for EV adoption. These factors include:
- High Costs:EVs are currently more expensive than gasoline-powered vehicles, especially when considering the cost of batteries and charging infrastructure. This price difference can be a significant barrier for many consumers, particularly in the face of economic uncertainties.
- Limited Range:The range of EVs on a single charge is still a concern for many consumers, especially those who travel long distances or live in areas with limited charging infrastructure. This range limitation can be a significant deterrent for those who rely on their vehicles for daily commutes and travel.
- Charging Infrastructure:The lack of widespread charging infrastructure is another major challenge for EV adoption. Many areas lack sufficient charging stations, making it difficult for consumers to reliably charge their vehicles. This issue is particularly acute in rural areas and for long-distance travel.
The idea that electric vehicles are the next big flop in the auto market, as FreedomWorks economists suggest, is a bold claim. However, it highlights the importance of engaging consumers in meaningful dialogue, rather than bombarding them with marketing messages.
Remember, a successful marketing strategy is about building relationships, not interruptions, and that’s why I find the insights in this article why your marketing strategy should be about conversations not interruptions so valuable. If automakers want to convince consumers to embrace electric vehicles, they need to listen and understand their concerns, rather than just pushing a product.
Only then will they truly connect with their audience and drive adoption.
- Government Incentives:FreedomWorks argues that government incentives for EV purchases, such as tax credits, are unsustainable and create an artificial demand for EVs. They believe that the market will not be able to sustain EV adoption without these subsidies, leading to a potential decline in demand once incentives are removed.
FreedomWorks’ Reasoning, Electric vehicles set to be auto markets next big flop says freedomworks economist
FreedomWorks argues that the EV market is driven by government policies and subsidies rather than genuine consumer demand. They believe that these incentives are distorting the market and creating a false sense of demand for EVs. The group further asserts that the technology is not yet mature enough to compete with gasoline-powered vehicles in terms of affordability, range, and charging infrastructure.
They predict that once government incentives are phased out, the EV market will collapse, leaving consumers with expensive, impractical vehicles and a significant investment in charging infrastructure.
Counterarguments to the “Flop” Prediction

While some economists predict electric vehicles (EVs) to be the next big market flop, a closer look at the current state of the EV market reveals a more optimistic picture. The reality is that EVs are experiencing significant growth, driven by various factors, and are poised to become a major force in the automotive industry.
Positive Indicators of EV Market Growth
The EV market is far from a flop. In fact, it’s experiencing substantial growth. Several factors contribute to this positive trend, including:
- Increasing Sales:Global EV sales have been consistently rising in recent years. In 2022, global EV sales reached a record high, with China leading the way, followed by Europe and the United States. This strong demand demonstrates consumer interest and confidence in EVs.
- Government Incentives:Many governments worldwide are offering financial incentives to encourage EV adoption. These incentives, such as tax credits, subsidies, and rebates, make EVs more affordable for consumers, boosting demand.
- Environmental Concerns:Growing awareness of climate change and the need for sustainable transportation solutions is driving consumer preference towards EVs. The zero-emission nature of EVs aligns with environmental concerns, making them an attractive alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Technological Advancements in Battery Technology and Charging Infrastructure
One of the major concerns surrounding EVs has been their limited range and long charging times. However, advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure are rapidly addressing these challenges.
While economists debate whether electric vehicles are the future or the next big flop, there’s a more immediate concern for some consumers: food safety. Produce Packaging Inc. has recalled its Red Curry Grain Bowl and Barcelona Vinaigrette Grain Bowl due to a potential health risk , reminding us that even as we look to the future of transportation, we still need to be mindful of what we put in our bodies today.
The debate about EVs will continue, but for now, it seems like a healthy meal is a much more pressing concern.
- Battery Range and Efficiency:Battery technology is constantly improving, leading to increased range and faster charging times. For example, Tesla’s Model S Plaid boasts a range of over 400 miles on a single charge, while newer EVs are achieving charging speeds of up to 200 miles per hour.
- Charging Infrastructure:The expansion of charging infrastructure is crucial for widespread EV adoption. Public and private charging networks are growing rapidly, making it easier for EV owners to charge their vehicles on the go. Many fast-charging stations are being installed along highways and in urban areas, providing convenient and efficient charging options.
Successful EV Manufacturers and Their Strategies
Several EV manufacturers have achieved significant success in the market, demonstrating the viability of EVs.
- Tesla:Tesla, a pioneer in the EV industry, has established itself as a leading brand with its innovative technology, high-performance vehicles, and strong brand image. Tesla’s focus on vertical integration, from battery production to charging infrastructure, has given it a competitive advantage.
- Volkswagen:Volkswagen has made a major push into the EV market with its ID. series of electric vehicles. The company’s global reach and established manufacturing capabilities have allowed it to rapidly scale up EV production and offer a wide range of models.
- General Motors:General Motors is another major automaker that has invested heavily in EVs. Its Chevrolet Bolt and Cadillac Lyriq are popular models, and the company has announced plans to launch several new EV models in the coming years.
Factors Affecting EV Adoption: Electric Vehicles Set To Be Auto Markets Next Big Flop Says Freedomworks Economist
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex process influenced by a variety of factors, including consumer preferences, technological advancements, and government policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for assessing the future of the EV market and its potential impact on the automotive industry.
Price and Affordability
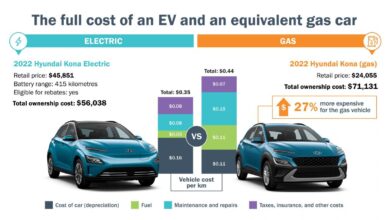
The price of EVs remains a significant barrier to adoption for many consumers. While EV prices have been decreasing in recent years, they still tend to be higher than comparable gasoline-powered vehicles. This price difference is partly due to the cost of battery technology, which is a major component of EV production.
However, as battery technology improves and production scales up, EV prices are expected to continue to fall.
The average price of a new EV in the United States was around $60,000 in 2023, compared to an average price of around $40,000 for a new gasoline-powered vehicle.
Range and Charging Infrastructure
Range anxiety, or the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station, is a common concern among potential EV buyers. The range of an EV depends on factors such as battery size, driving conditions, and vehicle weight.
While EV ranges have been increasing steadily, they still lag behind the typical range of gasoline-powered vehicles.
The news that electric vehicles are set to be the next big flop in the auto market, according to a FreedomWorks economist, is a bit of a surprise. But maybe not so surprising when you consider that President Biden is making a strong case for his administration’s policies by highlighting how Republicans are trying to raise taxes on everyday Americans.
Mitch McConnell’s worst nightmare comes true as Biden annihilates GOP for wanting to raise your taxes – this kind of political rhetoric could certainly influence consumer spending decisions, especially when it comes to big-ticket items like cars.
- The average range of a new EV in the United States is around 250 miles, while the average range of a new gasoline-powered vehicle is around 350 miles.
- The availability of charging infrastructure is another critical factor affecting EV adoption. While the number of public charging stations is growing, it is still not as widespread as gasoline stations. This can be a major inconvenience for EV owners, especially those who live in rural areas or travel long distances.
Cost of Ownership
While the initial purchase price of an EV may be higher, the long-term cost of ownership can be lower than that of a gasoline-powered vehicle.
- Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, especially when charging at home during off-peak hours.
- EVs require less maintenance than gasoline-powered vehicles, as they have fewer moving parts and do not require oil changes or emissions checks.
A recent study by the Union of Concerned Scientists found that the total cost of ownership for an EV over 10 years can be significantly lower than that of a gasoline-powered vehicle, even after factoring in the higher initial purchase price.
Government Policies
Government policies play a significant role in shaping EV adoption rates.
- Subsidies and tax credits can make EVs more affordable for consumers, increasing demand.
- Investment in charging infrastructure can help to alleviate range anxiety and encourage more people to switch to EVs.
- Regulations that promote cleaner vehicles, such as emissions standards and fuel economy requirements, can also incentivize EV adoption.
The United States government offers a federal tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of a new EV, while many states also offer additional incentives.
Future of the Electric Vehicle Market

The electric vehicle (EV) market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by a confluence of factors including technological advancements, government policies, and changing consumer preferences. While the market is still in its nascent stages, the long-term prospects for EVs appear promising, with the potential to disrupt the automotive industry and impact related sectors.
Technological Advancements and Impact on EV Adoption
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in driving the adoption of EVs. Battery technology is constantly improving, leading to increased range, faster charging times, and lower costs. This progress is crucial for addressing consumer concerns about range anxiety and charging infrastructure.
Additionally, advancements in electric motors, power electronics, and software are enhancing the performance and efficiency of EVs. These advancements are making EVs increasingly competitive with traditional gasoline-powered vehicles in terms of performance, cost, and convenience.
Potential Disruption of the Automotive Industry
The rise of EVs has the potential to disrupt the automotive industry in several ways. Traditional automakers are facing increasing competition from new entrants, such as Tesla, who are specializing in EVs. Furthermore, the emergence of shared mobility services, such as ride-hailing and car-sharing, is challenging the traditional model of car ownership.
The automotive industry is also experiencing a shift towards software-defined vehicles, with EVs becoming increasingly connected and equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving capabilities.
Key Challenges and Opportunities Facing the EV Market
The EV market faces a number of challenges, including:
- High upfront cost:EVs are generally more expensive than comparable gasoline-powered vehicles, although the cost gap is narrowing.
- Limited charging infrastructure:The availability of public charging stations remains a significant barrier to EV adoption, especially in rural areas.
- Range anxiety:Many consumers are concerned about the limited range of EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Battery recycling:The disposal and recycling of EV batteries pose environmental challenges.
Despite these challenges, the EV market also presents significant opportunities:
- Growing consumer demand:Consumer interest in EVs is steadily increasing, driven by factors such as environmental concerns, fuel savings, and technological advancements.
- Government support:Governments around the world are providing incentives to promote EV adoption, such as tax credits, subsidies, and charging infrastructure investments.
- Innovation in battery technology:Continued advancements in battery technology are expected to further improve range, reduce costs, and enhance charging speeds.
- Integration with smart grids:EVs can play a role in the transition to a more sustainable energy system by integrating with smart grids and providing energy storage capabilities.
| Challenge | Opportunity |
|---|---|
| High upfront cost | Government incentives, economies of scale, and declining battery costs |
| Limited charging infrastructure | Public and private investments in charging infrastructure, development of wireless charging technologies |
| Range anxiety | Advancements in battery technology, expansion of charging infrastructure, development of range-extending technologies |
| Battery recycling | Innovation in battery recycling technologies, development of circular economy models for battery materials |
Closure
The future of the electric vehicle market is a complex and evolving landscape. While the FreedomWorks economist’s prediction of a “flop” may be a dramatic statement, it underscores the challenges that remain in achieving widespread EV adoption. However, the industry is rapidly evolving, with advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and manufacturing costs constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Ultimately, the success of electric vehicles will depend on a confluence of factors, including consumer demand, government policies, and technological innovation. The debate is far from over, and the journey toward a truly sustainable automotive future is just beginning.