
Dollars Dominance Wanes: Efforts to Protect Us Intensify
As efforts to protect us intensify amid global shift from dollar takes center stage, the world’s financial landscape is undergoing a seismic shift. The US dollar, long the dominant currency, is facing unprecedented challenges. Rising US debt and inflation, geopolitical tensions, and the emergence of alternative currencies and financial systems are all contributing to this change.
This shift has profound implications for international trade, investment, and the global economy as a whole.
The US government and institutions are taking steps to maintain the dollar’s dominance, but the effectiveness of these measures remains to be seen. The rise of alternative currencies, such as the Chinese yuan and the euro, and the development of alternative financial systems, like the BRICS New Development Bank, are posing significant challenges to the dollar’s supremacy.
The Global Shift Away from the Dollar
The US dollar has reigned supreme in the global financial system for decades, serving as the primary reserve currency and the dominant medium of exchange for international trade and investment. This dominance has provided the United States with significant economic and geopolitical advantages.
However, recent years have witnessed a growing trend of countries and institutions moving away from the dollar, leading to a potential shift in the global financial landscape.
It’s a strange world we live in, where efforts to protect us intensify amid a global shift from the dollar, while simultaneously, we’re being warned about a powerful storm system brewing. The federal agency issues warnings over powerful storm system and the potential for widespread damage, reminding us that even amidst financial upheaval, nature’s forces can be equally disruptive.
As we navigate these uncertain times, it’s clear that our focus needs to be on both safeguarding our financial well-being and preparing for the unpredictable forces of nature.
Factors Driving the Shift Away from the Dollar
The decline of the US dollar’s dominance is driven by a confluence of factors, each contributing to a growing desire for alternatives.
- Rising US Debt and Inflation: The United States has accumulated a massive national debt, which has been exacerbated by years of fiscal deficits and expansive monetary policy. This has led to concerns about the sustainability of the dollar’s value and its ability to maintain its purchasing power.
Furthermore, rising inflation in the US has eroded the dollar’s value, making it less attractive for foreign investors and businesses.
- Geopolitical Tensions and Sanctions: The US has increasingly used its financial dominance to impose sanctions on other countries, particularly those perceived as adversaries. This has created a sense of vulnerability for countries reliant on the dollar system, prompting them to seek alternative currencies and payment mechanisms.
The use of sanctions has also raised concerns about the politicalization of the dollar, further eroding its appeal.
- Emergence of Alternative Currencies and Financial Systems: The rise of new financial technologies and the emergence of alternative currencies, such as cryptocurrencies and digital assets, have presented viable alternatives to the dollar-centric system. Countries like China are actively promoting the use of their own currencies in international trade and are developing alternative financial infrastructure, such as the Belt and Road Initiative.
Efforts to Protect the Dollar’s Dominance: Efforts To Protect Us Intensify Amid Global Shift From Dollar
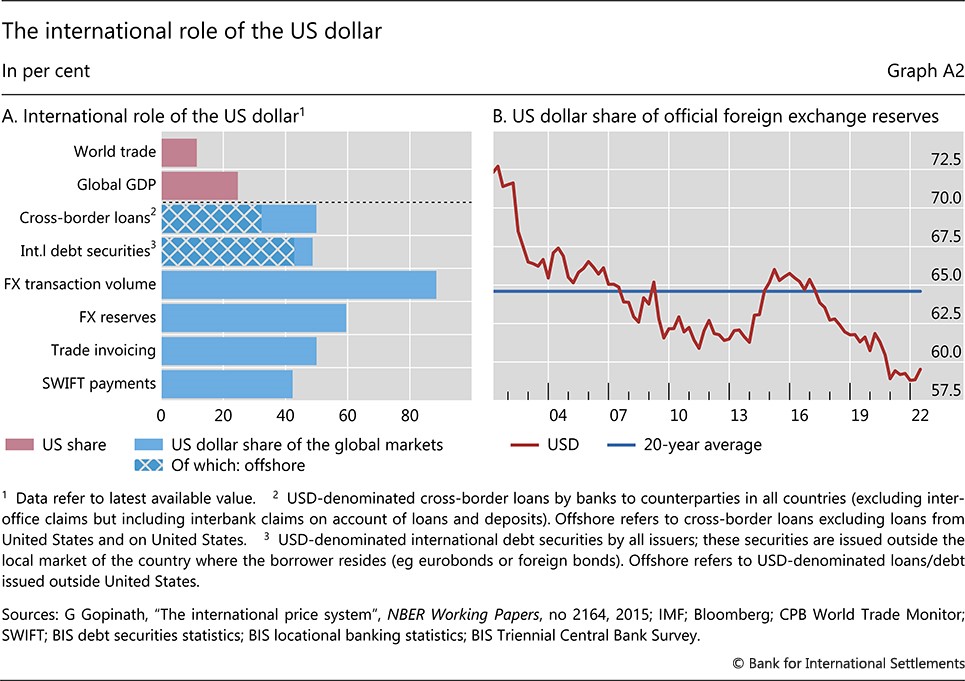
The United States, recognizing the potential challenges to the dollar’s global dominance, has initiated various measures to safeguard its position. These efforts aim to bolster the US economy, promote the dollar’s usage in international trade, and deter actions that could undermine its supremacy.
Strengthening the US Economy
A robust US economy is crucial for maintaining the dollar’s allure. The government’s economic policies, including fiscal and monetary measures, are designed to foster growth, create jobs, and control inflation. These efforts aim to maintain investor confidence and strengthen the US economy’s attractiveness.
For instance, the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies play a significant role in managing inflation and influencing the value of the dollar.
Promoting the Use of the Dollar in International Trade
The US government actively promotes the use of the dollar in international trade. This involves encouraging countries to denominate their trade transactions in dollars, fostering the use of the dollar in international financial markets, and facilitating the settlement of international payments in dollars.
By increasing the demand for the dollar in global trade, the US aims to reinforce its dominance.
Imposing Sanctions on Countries that Challenge the Dollar’s Dominance
The US has employed sanctions as a tool to deter countries from challenging the dollar’s dominance. These sanctions can target individuals, businesses, or even entire economies, aiming to discourage alternative currency systems or financial arrangements. By imposing costs on countries that attempt to bypass the dollar, the US seeks to maintain its financial influence.
Alternative Currencies and Financial Systems
The global shift away from the dollar has spurred the rise of alternative currencies and financial systems, potentially reshaping the global financial landscape. These alternatives present both opportunities and challenges, as they seek to challenge the dollar’s long-standing dominance.
The Rise of Alternative Currencies
The emergence of alternative currencies is a direct response to the perceived limitations of the dollar-centric system. These alternatives offer a potential path towards greater economic independence and reduced reliance on the US dollar.
- The Chinese Yuan: As the world’s second-largest economy, China has been actively promoting the international use of its currency, the yuan. The yuan’s increasing use in international trade and financial transactions, particularly with countries participating in the Belt and Road Initiative, is a significant challenge to the dollar’s dominance.
It’s a wild time out there, with the global shift away from the dollar causing ripples in everything from trade to security. Amidst this upheaval, news of longtime democrat senator announces she wont seek another term adds another layer of uncertainty.
Will her absence leave a void in the efforts to protect us, or will it pave the way for a new generation of leaders to navigate this complex landscape?
For example, the yuan’s share in global foreign exchange reserves has been steadily increasing, and China has been working to establish yuan-denominated trading platforms and financial institutions.
- The Euro: The euro, the official currency of the Eurozone, has emerged as a strong competitor to the dollar. Its adoption by 19 European countries has created a large economic bloc with a significant influence on global trade and finance. The euro’s stability and the Eurozone’s economic size make it a viable alternative to the dollar for international transactions.
- Cryptocurrencies: The rise of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, has introduced a decentralized and digital alternative to traditional fiat currencies. While still in their early stages of development, cryptocurrencies have the potential to disrupt the existing financial system by offering a more transparent and efficient way to conduct transactions.
However, their volatility and lack of regulatory clarity pose significant challenges to their widespread adoption.
Alternative Financial Systems
Beyond individual currencies, the development of alternative financial systems is another key aspect of the shift away from the dollar. These systems aim to provide alternative platforms for trade, investment, and development, reducing reliance on institutions dominated by the US dollar.
- The BRICS New Development Bank: Established by Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, the BRICS New Development Bank (NDB) aims to provide an alternative source of financing for infrastructure and development projects in emerging markets. The NDB offers a platform for member countries to collaborate on development initiatives without relying on the World Bank or other institutions heavily influenced by the US.
- The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB): The AIIB, founded by China and supported by several Asian countries, focuses on infrastructure development projects in Asia. The AIIB’s establishment reflects the growing economic power and influence of Asia, offering an alternative to traditional Western-dominated institutions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternative Systems
The shift towards alternative currencies and financial systems presents both advantages and disadvantages, impacting the global financial landscape.
- Advantages:
- Reduced Reliance on the Dollar: Alternative currencies and financial systems offer a path towards greater economic independence, reducing reliance on the US dollar and its associated geopolitical influence. This can provide greater flexibility and control over economic policies.
- Increased Trade and Investment Opportunities: Alternative systems can facilitate trade and investment between countries that may not be fully integrated into the dollar-based system, opening up new opportunities for economic growth and development.
- Innovation and Competition: The emergence of alternative currencies and financial systems can foster innovation and competition within the global financial system, potentially leading to greater efficiency and better services.
- Disadvantages:
- Volatility and Risk: Alternative currencies and financial systems may be subject to greater volatility and risk, particularly in their early stages of development. This can create uncertainty and instability for businesses and investors.
- Lack of Liquidity and Scalability: Alternative systems may lack the liquidity and scalability of the existing dollar-based system, limiting their ability to handle large-scale transactions and financial flows.
- Regulatory Challenges: The development and adoption of alternative currencies and financial systems pose significant regulatory challenges, requiring international cooperation and coordination to ensure stability and prevent abuse.
Implications for International Trade and Investment
The global shift away from the dollar is likely to have a significant impact on international trade and investment patterns. As the world moves towards a multipolar currency system, businesses and investors need to adapt to a more complex and dynamic environment.
This shift presents both opportunities and risks for different countries and regions.
Impact on Trade Patterns
The dollar’s dominance has facilitated international trade for decades, providing a stable and widely accepted medium of exchange. However, as other currencies gain prominence, trade patterns may change. For example, countries that are heavily reliant on the dollar for their exports may face increased costs or volatility in their earnings.
Conversely, countries that are less reliant on the dollar may see their exports become more competitive.
It’s a crazy time, isn’t it? With the global shift away from the dollar, efforts to protect us intensify, but then you see news like evacuations ordered as federal agency warns California at high risk of catastrophic flooding and you realize that protecting ourselves from natural disasters is just as crucial as protecting our financial futures.
We need to be prepared on all fronts, especially as the world becomes more unpredictable.
- Increased use of alternative currencies:As the dollar’s dominance wanes, businesses may increasingly use other currencies for international transactions, such as the euro, yuan, or even regional currencies like the ASEAN currency basket. This could lead to a more diverse and fragmented trade landscape, with different regions using different currencies for their transactions.
For example, the increasing use of the yuan in trade between China and its trading partners is already impacting global trade patterns.
- Potential for trade disputes:The shift away from the dollar could lead to increased trade disputes as countries compete for market share and influence. For example, the US could retaliate against countries that move away from the dollar by imposing tariffs or other trade restrictions.
The rise of alternative currencies could also create challenges in enforcing contracts and resolving disputes, leading to greater uncertainty and risk for businesses.
Impact on Investment Patterns
The shift away from the dollar could also lead to changes in investment patterns. Investors may become more hesitant to invest in countries that are heavily reliant on the dollar, as the value of their investments could be affected by currency fluctuations.
Conversely, investors may become more interested in countries that are diversifying their currency reserves and developing alternative financial systems.
- Diversification of investment portfolios:Investors may seek to diversify their investment portfolios by investing in assets denominated in different currencies, such as the euro, yuan, or other emerging market currencies. This could lead to increased capital flows to countries that are developing alternative financial systems.
- Potential for capital flight:Countries that are heavily reliant on the dollar may experience capital flight as investors seek to move their assets to safer havens. This could lead to economic instability and currency depreciation, further exacerbating the impact of the global shift from the dollar.
Adaptation Strategies for Businesses and Investors
Businesses and investors need to adapt to the changing currency landscape by:
- Diversifying their currency exposures:Businesses can hedge against currency risk by diversifying their operations and sourcing materials from countries with different currencies. Investors can diversify their portfolios by investing in assets denominated in different currencies.
- Developing new payment mechanisms:Businesses can explore alternative payment mechanisms, such as using blockchain technology or digital currencies, to reduce their reliance on the dollar. This could also help them avoid the costs and delays associated with traditional cross-border payments.
- Monitoring global currency trends:Businesses and investors need to stay informed about global currency trends and the potential impact on their operations and investments. This includes understanding the factors driving currency movements and the implications for their business strategies.
Opportunities and Risks for Different Countries and Regions
The global shift away from the dollar presents both opportunities and risks for different countries and regions.
- Emerging economies:Emerging economies may benefit from the shift away from the dollar, as they can gain access to new markets and attract more foreign investment. However, they also face risks, such as currency volatility and the potential for capital flight.
For example, countries like China and India are actively promoting their currencies as alternatives to the dollar, and they could benefit significantly from the shift.
- Developed economies:Developed economies, such as the US and the Eurozone, may face challenges as their currency dominance diminishes. However, they also have the resources and infrastructure to adapt to the changing landscape. For example, the US can leverage its strong financial system and technology to remain a major player in the global economy.
The Future of the Global Financial System

The global shift away from the dollar, fueled by geopolitical tensions and the rise of alternative currencies, is fundamentally altering the landscape of international finance. This dynamic raises crucial questions about the future of the global financial system and the potential implications for global trade, investment, and economic stability.
Potential Long-Term Implications of the Global Shift from the Dollar
The decline of the dollar’s dominance could have profound and far-reaching consequences for the global economy.
- Increased Volatility:A multipolar system with multiple reserve currencies could lead to greater volatility in exchange rates, making it more challenging for businesses and investors to manage risk. For instance, fluctuations in the value of the Chinese yuan against the US dollar could impact the cost of imports and exports between the two countries.
- Fragmentation of Financial Markets:As countries move away from the dollar, there could be a fragmentation of global financial markets, with different regions developing their own trading and settlement systems. This could make it more difficult for investors to access capital and for businesses to operate across borders.
- Geopolitical Tensions:The shift away from the dollar could exacerbate geopolitical tensions, as countries compete for influence in the global financial system. The recent BRICS summit, where members discussed the creation of a new reserve currency, highlights the potential for geopolitical competition to influence the future of global finance.
Possible Scenarios for the Future of the Global Financial System, Efforts to protect us intensify amid global shift from dollar
The future of the global financial system is uncertain, but several possible scenarios are emerging.
- Multipolar System:One scenario is the emergence of a multipolar system with multiple reserve currencies, such as the dollar, the euro, the yuan, and possibly others. This would create a more balanced global financial system, but it would also increase complexity and volatility.
- New Global Reserve Currency:Another possibility is the emergence of a new global reserve currency, potentially backed by a basket of currencies or a digital asset. This would require significant international cooperation and agreement, but it could offer greater stability and predictability for the global economy.
- Regional Currency Blocs:Alternatively, the global financial system could evolve into a series of regional currency blocs, with each bloc using its own currency for trade and investment within the region. This could lead to increased regionalization of trade and finance, but it could also create barriers to global integration.
Key Challenges and Opportunities Facing the Global Financial System
The global financial system faces several challenges and opportunities as it navigates the transition away from the dollar’s dominance.
- Maintaining Financial Stability:One key challenge is maintaining financial stability in a more volatile and complex global financial system. This will require strong international cooperation and coordination among central banks and regulatory authorities.
- Promoting Inclusive Growth:Another challenge is promoting inclusive growth and ensuring that the benefits of a new global financial system are shared equitably among all countries. This will require addressing issues such as poverty, inequality, and access to financial services.
- Technological Advancements:The rise of digital currencies and blockchain technology presents both opportunities and challenges for the global financial system. These technologies could enhance efficiency and transparency, but they also raise concerns about privacy, security, and regulation.
Conclusion
The future of the global financial system is uncertain. The global shift from the dollar could lead to a multipolar system with multiple reserve currencies or even a new global reserve currency altogether. This shift presents both opportunities and risks for different countries and regions.
It’s a dynamic and complex situation that demands careful analysis and adaptation.






