Doctors Worldwide Urge Vaccine Pause: Is It Time to Stop the Shots?
Doctors around the world say its time to stop the shots – Doctors around the world say it’s time to stop the shots. This bold statement, echoing across social media and online platforms, has sparked heated debate and raised serious concerns about vaccine safety and efficacy. But who are these doctors? What are their credentials?
And what specific vaccines are they calling for a halt to?
The claim that a significant number of doctors are advocating for a vaccine pause is a complex issue that requires careful examination. It’s crucial to understand the origins of this statement, the motivations behind it, and the scientific evidence that supports or contradicts its claims.
This investigation delves into the heart of the controversy, exploring the demographics and expertise of the doctors making this statement, the vaccines in question, and the potential consequences of widespread vaccine hesitancy.
Examining the “Doctors”
It’s crucial to critically evaluate the claims made by those advocating against COVID-19 vaccines, especially when they present themselves as medical professionals. Understanding the demographics, credentials, and perspectives of these individuals is essential to discerning the validity of their arguments.
Demographics and Backgrounds
While there’s no single profile for doctors who oppose vaccines, some patterns emerge. A significant proportion of these individuals tend to be older, with established careers and a strong sense of independence. Many have practiced in fields outside of infectious disease, potentially leading to different perspectives on the nature of pandemics and vaccine development.
Some may be drawn to alternative medicine or hold strong anti-establishment views, which can influence their stance on vaccines.
Credentials and Areas of Expertise
It’s important to examine the credentials and areas of expertise of these doctors. While some may hold legitimate medical degrees, their expertise may not necessarily lie in infectious disease, immunology, or public health. Some may have limited experience in research or clinical trials, which are essential for understanding the complexities of vaccine development and efficacy.
Comparison with Broader Medical Consensus
The overwhelming consensus within the broader medical community is that COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective. Leading health organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) all endorse vaccination.
It’s a wild time out there, folks. Doctors around the world are calling for a halt to the shots, and meanwhile, the House just passed a bill to compel the Biden administration to publish inflationary estimates of executive actions, a move that could shed light on the economic impact of recent policies.
It’s all so confusing, but one thing’s for sure: the future is uncertain, and it’s more important than ever to stay informed about the decisions being made that affect our lives. We need to trust our gut, listen to our doctors, and demand transparency from our leaders.
These organizations rely on rigorous scientific evidence, extensive research, and data from millions of vaccinated individuals.
The “Shots” in Question
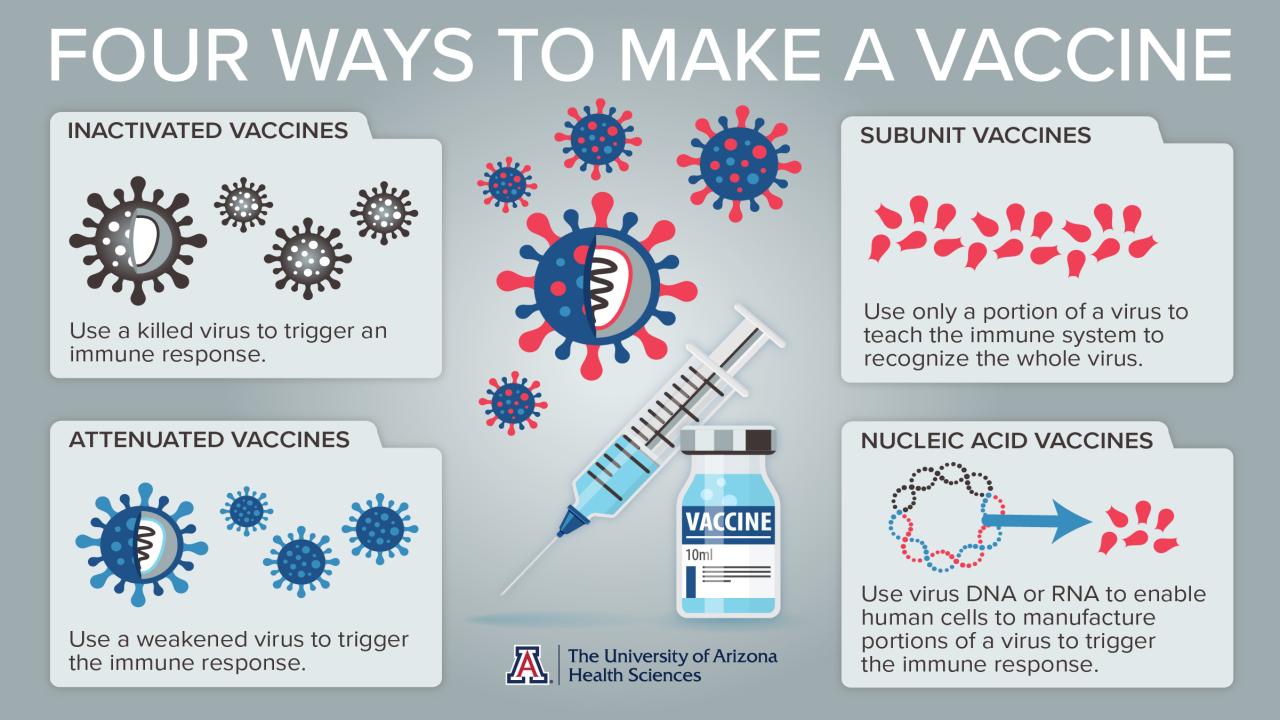
The statement “it’s time to stop the shots” is a broad generalization that often refers to various vaccines, particularly those developed to prevent infectious diseases like COVID-19, measles, mumps, rubella, and influenza. It’s crucial to understand the specific vaccines being targeted by this statement and evaluate the scientific evidence behind them.
The vast majority of vaccines currently available have undergone rigorous scientific testing and evaluation to ensure their safety and efficacy. These vaccines work by introducing a weakened or inactive version of the virus or bacteria, or a specific protein from the pathogen, into the body.
This triggers the immune system to produce antibodies that can fight off the real pathogen if encountered later.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Vaccine Safety and Efficacy
The safety and efficacy of vaccines are determined through a multi-stage process involving extensive clinical trials and ongoing surveillance.
- Clinical Trials:Vaccines undergo rigorous testing in multiple phases, starting with small groups of volunteers and progressively expanding to larger populations. These trials aim to assess the vaccine’s effectiveness in preventing the disease, its safety profile, and the optimal dosage.
- Post-Market Surveillance:Even after a vaccine is approved and available to the public, ongoing monitoring systems track its safety and effectiveness. These systems collect data on adverse events and vaccine effectiveness, allowing for ongoing assessment and adjustments as needed.
- Independent Review:Scientific institutions and regulatory bodies like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) review the data from clinical trials and post-market surveillance to ensure the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
Risks and Benefits of Vaccination
Every medical intervention carries potential risks and benefits. It’s essential to weigh these factors when making decisions about vaccination.
- Benefits of Vaccination:Vaccines have dramatically reduced the incidence and severity of preventable diseases worldwide. For example, the widespread use of the measles vaccine has led to a significant decline in measles cases, making it a rare disease in many countries.
Vaccines also contribute to herd immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical conditions or age.
- Risks of Vaccination:While rare, some individuals may experience mild side effects like soreness at the injection site, fever, or fatigue. These side effects are typically mild and short-lived. Serious adverse events following vaccination are extremely uncommon and are carefully monitored by health authorities.
- Risks of Non-Vaccination:The risks of not getting vaccinated are far greater than the risks of getting vaccinated. Unvaccinated individuals are at a significantly higher risk of contracting and spreading preventable diseases, potentially leading to serious complications, hospitalization, and even death.
Public Health Implications
Vaccine hesitancy and refusal can have significant consequences for public health, impacting disease transmission and the effectiveness of public health interventions. This section explores the potential consequences of widespread vaccine hesitancy and refusal, emphasizing the role of misinformation and distrust in undermining public health efforts.
Impact on Herd Immunity
Herd immunity is a crucial concept in public health, referring to the indirect protection from disease that occurs when a large percentage of the population is immune. When a sufficient proportion of individuals are immune, it becomes difficult for a disease to spread, protecting those who are not immune, such as infants, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems.
Vaccine hesitancy and refusal can significantly undermine herd immunity by reducing the proportion of the population that is immune. This can lead to outbreaks and resurgence of preventable diseases, putting vulnerable populations at risk.
Disease Transmission
When vaccine coverage is low, diseases can spread more easily, leading to increased rates of infection, hospitalizations, and deaths. For example, the measles, a highly contagious disease, has seen a resurgence in recent years due to declining vaccination rates. In 2019, the United States experienced the highest number of measles cases in 25 years, with outbreaks occurring in several states.
This resurgence highlighted the dangers of vaccine hesitancy and the importance of high vaccination coverage.
Misinformation and Distrust
Misinformation and distrust in public health institutions and experts can significantly contribute to vaccine hesitancy. The spread of misinformation, often through social media and other online platforms, can create fear and confusion about vaccines, leading individuals to make decisions based on inaccurate or incomplete information.Distrust in public health institutions can stem from a variety of factors, including past controversies, lack of transparency, and perceived conflicts of interest.
When people distrust public health institutions, they may be less likely to believe in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines, leading to lower vaccination rates.
Ethical Considerations
The promotion or spread of the statement “It’s time to stop the shots” carries significant ethical implications. This statement, often used to express opposition to vaccines, can have a profound impact on individual health, community well-being, and the public’s trust in healthcare professionals.
Potential Harm to Individuals and Communities
The spread of misinformation about vaccines can lead to a decline in vaccination rates, increasing the risk of preventable diseases. This can have severe consequences for individuals and communities, particularly vulnerable populations like children, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems.
It’s been a whirlwind of conflicting information lately, with doctors around the world speaking out against certain medical interventions. While this is happening, it’s interesting to see the impact of leadership changes on organizations like Project Veritas, which recently lost hundreds of thousands of followers following James O’Keefe’s exit.
project veritas loses hundreds of thousands of followers following james okeefes exit. It makes you wonder, what will the future hold for those advocating for alternative viewpoints, and how will this impact the ongoing debate surrounding the “shots” that are at the heart of so much controversy?
- Increased Risk of Disease Outbreaks:Lower vaccination rates can lead to a resurgence of diseases like measles, mumps, and rubella, which were once considered eradicated or nearly eradicated. Outbreaks can overwhelm healthcare systems, lead to hospitalizations, and even death.
- Impact on Herd Immunity:Vaccines work by protecting not only the vaccinated individual but also those around them who are unable to be vaccinated. This is known as herd immunity. When vaccination rates decline, herd immunity weakens, making it easier for diseases to spread.
It’s a strange world we live in, where doctors around the world are calling for an end to the shots, yet in some places, parents are even being blocked from protecting their children. A recent case in point is a state supreme court blocking a mother from vaccinating her children against COVID-19.
It seems the tide is turning, but not without some serious bumps along the way.
- Disproportionate Impact on Vulnerable Populations:Lower vaccination rates can disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, such as infants, the elderly, and people with underlying health conditions. These individuals may be unable to receive vaccines due to age or medical reasons, making them more susceptible to serious illness.
Responsibility of Healthcare Professionals and Public Figures
Healthcare professionals and public figures have a crucial responsibility to communicate accurate and evidence-based information about vaccines. Their statements can have a significant impact on public perception and behavior.
“Healthcare professionals have a responsibility to provide patients with accurate information about vaccines and to address their concerns in a compassionate and respectful manner.”
The World Health Organization
- Maintaining Public Trust:Spreading misinformation can erode public trust in healthcare professionals and institutions. This can lead to a decline in vaccination rates and a reluctance to seek medical care.
- Promoting Evidence-Based Decision-Making:Healthcare professionals and public figures should promote evidence-based decision-making about vaccines. This involves providing accurate information about the benefits and risks of vaccines, and addressing concerns based on scientific evidence.
- Combating Misinformation:It is crucial to combat misinformation about vaccines through education and outreach. Healthcare professionals and public figures can play a vital role in this effort by providing accurate information and debunking myths and conspiracy theories.
Alternative Perspectives
The call to “stop the shots” is a complex issue with a wide range of perspectives. It’s crucial to consider diverse viewpoints to understand the nuances of this debate and the potential implications for public health. This section explores the views of medical experts, public health officials, vaccine advocates, and individuals impacted by vaccine hesitancy.
Perspectives of Medical Experts and Public Health Officials
The overwhelming majority of medical experts and public health officials worldwide support vaccination as a safe and effective way to prevent infectious diseases. They cite extensive scientific evidence demonstrating the efficacy and safety of vaccines in protecting individuals and communities from preventable diseases.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasize the importance of vaccination as a cornerstone of public health, promoting herd immunity and protecting vulnerable populations.
- Medical experts highlight the rigorous testing and regulatory processes that vaccines undergo before being made available to the public, ensuring their safety and effectiveness.
- They emphasize the potential consequences of vaccine hesitancy, including outbreaks of preventable diseases and increased strain on healthcare systems.
Views of Vaccine Advocates
Vaccine advocates often share personal experiences or stories of individuals who have benefited from vaccination, highlighting the life-saving potential of these interventions.
- They often cite the dramatic reduction in disease incidence and mortality rates attributed to vaccination programs.
- They argue that vaccination not only protects individuals but also contributes to the collective well-being of society by reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
- Vaccine advocates may also emphasize the ethical responsibility to protect vulnerable individuals, such as infants and those with compromised immune systems, by achieving high vaccination rates.
Experiences and Concerns of Individuals Impacted by Vaccine Hesitancy
While the scientific evidence overwhelmingly supports the safety and efficacy of vaccines, some individuals remain hesitant or resistant to vaccination.
- Concerns about vaccine safety, side effects, and the potential for long-term health consequences are often cited as reasons for vaccine hesitancy.
- Some individuals may be influenced by misinformation or distrust in healthcare institutions and authorities.
- Others may have personal experiences or beliefs that shape their views on vaccination.
The Role of Communication and Trust, Doctors around the world say its time to stop the shots
Effective communication and building trust are essential in addressing vaccine hesitancy. Open and transparent dialogue, based on credible information and evidence, can help to address concerns and foster informed decision-making.
- Healthcare providers play a critical role in providing accurate information and answering questions about vaccines.
- Community-based initiatives and public health campaigns can help to promote vaccine confidence and address misinformation.
- Engaging with individuals who have concerns and listening to their perspectives can help to build trust and foster understanding.
Closing Notes: Doctors Around The World Say Its Time To Stop The Shots
The debate surrounding the “doctors around the world” statement highlights the crucial role of accurate information and scientific evidence in public health decision-making. While the statement may resonate with some due to concerns about vaccine safety or individual experiences, it’s essential to rely on credible sources and evidence-based information when navigating complex health issues.
Ultimately, promoting open dialogue, critical thinking, and informed decision-making is crucial in ensuring the health and well-being of individuals and communities.