
Despite Soft Landing Predictions, Some Economists See Warning Signs
Despite soft landing predictions some economists see warning signs flashing red – Despite soft landing predictions, some economists see warning signs flashing red, casting a shadow of doubt on the rosy economic outlook. While many experts anticipate a smooth transition from high inflation to a more stable economic landscape, others are raising concerns about potential risks lurking beneath the surface.
This tension between optimism and caution stems from a complex interplay of factors, including rising interest rates, persistent inflation, and a global economic landscape marked by uncertainty. As the Federal Reserve continues to tighten monetary policy, the impact on consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic growth remains a subject of intense debate.
The labor market, while robust, is also showing signs of cooling, raising questions about its ability to sustain the current level of economic activity.
The “Soft Landing” Narrative
The current economic narrative revolves around the possibility of a “soft landing”a scenario where the Federal Reserve successfully steers the US economy away from a recession while bringing inflation under control. This optimistic outlook has gained traction in recent months, fueled by a combination of factors and supported by key economic indicators.
Factors Contributing to the “Soft Landing” Outlook
Several factors contribute to the current optimism surrounding a potential soft landing. These include:
- The resilient US labor market, with unemployment remaining low and job openings remaining high, suggests that the economy is still strong and can withstand higher interest rates.
- Consumer spending, while showing signs of slowing, remains robust, supported by strong employment and a healthy savings rate.
- Inflation has begun to moderate, with core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, showing signs of easing.
- The Federal Reserve has signaled a potential pause in its interest rate hikes, suggesting a more cautious approach to further tightening monetary policy.
Key Economic Indicators Supporting the “Soft Landing” Prediction
Several key economic indicators are being closely watched to assess the likelihood of a soft landing. These include:
- Inflation:The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index are closely monitored for signs of easing inflation. Recent data shows that inflation has begun to moderate, but it remains above the Fed’s target of 2%.
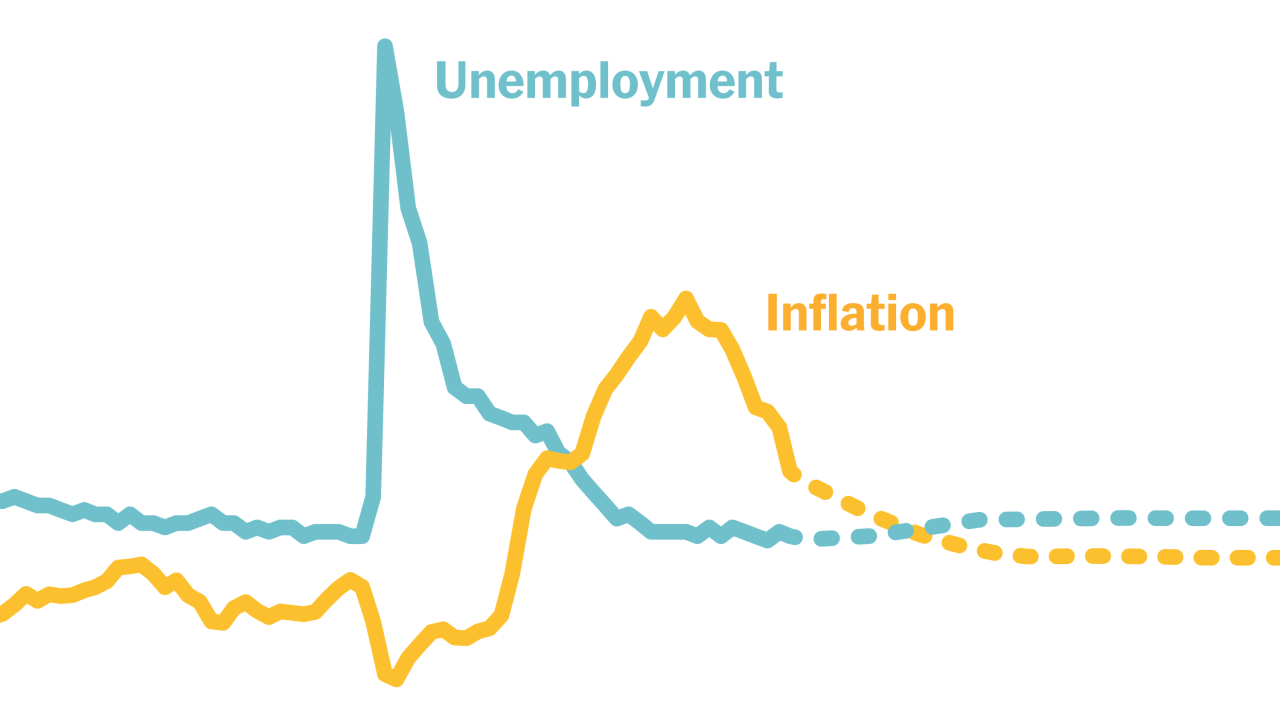
- Unemployment:The unemployment rate is a key indicator of labor market health. The unemployment rate has remained low, suggesting that the economy is still strong and can withstand higher interest rates.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP):GDP growth is a measure of the overall health of the economy. Recent data suggests that the economy is still growing, although at a slower pace.
- Interest Rates:The Federal Reserve’s target range for the federal funds rate is a key indicator of monetary policy. The Fed has been raising interest rates to combat inflation, but recent data suggests that the Fed may be nearing the end of its rate hike cycle.
Warning Signs and Potential Risks

While many economists are optimistic about a soft landing, some are raising concerns about potential warning signs that could derail the economic recovery. These warning signs highlight the inherent uncertainties and risks associated with the current economic landscape.
Potential Risks to a Soft Landing
Several factors could pose significant risks to a soft landing scenario.
- Inflation Persistence:Despite recent declines, inflation remains stubbornly high in many countries. If inflation proves to be more persistent than expected, central banks may need to maintain or even increase interest rates for longer, potentially leading to a recession.
- Geopolitical Tensions:Ongoing geopolitical tensions, such as the war in Ukraine and the rising tensions between the US and China, create uncertainty and volatility in global markets. These tensions can disrupt supply chains, raise energy prices, and further fuel inflation.
- Consumer Spending Slowdown:As interest rates rise, consumers may cut back on spending, leading to a decline in economic activity. This is particularly concerning given that consumer spending accounts for a significant portion of economic growth in many countries.
- Labor Market Tightness:The labor market remains tight, with low unemployment and high job openings. While this is generally positive, it can lead to wage inflation, which can further fuel price increases. Additionally, if companies start laying off workers due to economic slowdown, it could create a vicious cycle of declining demand and further economic contraction.
While some economists predict a soft landing, others are seeing red flags pop up. The global economy is facing a perfect storm of challenges, from inflation and rising interest rates to the war in Ukraine and the ongoing pandemic. And adding fuel to the fire, a recent doctor calls for withdrawal of Pfizer Moderna COVID-19 vaccines following new research , which has raised concerns about the long-term health effects of these vaccines.
With so many uncertainties looming, it’s clear that we’re in for a bumpy ride in the coming months.
- Financial Market Volatility:Rising interest rates and global economic uncertainty can lead to volatility in financial markets. This volatility can impact businesses and consumers, making it more difficult to plan and invest for the future.
Contrasting Viewpoints
The current economic situation is characterized by a divergence of viewpoints.
- Optimistic View:Proponents of a soft landing argue that inflation is gradually cooling down, the labor market remains strong, and consumer spending is resilient. They believe that central banks will be able to manage interest rates effectively to avoid a recession.
- Pessimistic View:Critics of the soft landing narrative point to the persistent inflation, rising interest rates, and potential for a consumer spending slowdown. They argue that the economic risks are significant and a recession is a real possibility.
Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation remains a significant concern for the global economy, impacting consumer purchasing power and business operations. The Federal Reserve’s approach to managing interest rates plays a crucial role in mitigating inflation’s effects.
Current Inflation Rates and Economic Impact
Inflation, measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), has been persistently high in recent years. The CPI increased by 6.4% in January 2023, indicating that prices are rising at a faster pace than in the previous year. This high inflation erodes the purchasing power of consumers, as their incomes do not keep pace with the rising cost of goods and services.
Businesses also face challenges, as rising input costs can reduce profit margins and potentially lead to price increases for consumers.
The Federal Reserve’s Approach to Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve (Fed) uses interest rates as a primary tool to manage inflation. By increasing interest rates, the Fed makes it more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money, leading to reduced spending and potentially lower inflation. The Fed’s approach to managing interest rates is influenced by several factors, including the current inflation rate, economic growth, and the overall state of the labor market.
Despite soft landing predictions, some economists see warning signs flashing red. The recent California storm that left a dozen dead and more than 100,000 without power is a stark reminder of the fragility of our infrastructure and the potential for unexpected disruptions.
These events, while localized, can ripple through the economy and further complicate the already uncertain economic landscape.
In response to persistent inflation, the Fed has been raising interest rates in recent months. The target federal funds rate, which is the rate at which banks lend to each other, has increased from near zero in early 2022 to over 4% in early 2023.
Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Consumer Spending and Business Investment
Rising interest rates can have a significant impact on consumer spending and business investment. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for consumers, potentially leading to reduced spending on durable goods, such as cars and homes. Businesses also face higher borrowing costs, which can discourage investment in new equipment, expansion, or hiring.
This can lead to slower economic growth and potentially even a recession.
Labor Market Dynamics
The labor market remains a key indicator of the overall health of the economy, providing insights into the strength of consumer demand, wage pressures, and potential inflation risks. Examining the current state of the labor market, including unemployment rates and job growth, helps us understand the economic landscape and its implications for the future.
Unemployment Rates and Job Growth
The unemployment rate, a crucial metric of labor market health, reflects the percentage of the labor force actively seeking employment but unable to find it. A low unemployment rate typically signals a robust economy with strong demand for workers. Conversely, a high unemployment rate indicates a weak economy with limited job opportunities.
Job growth, measured by the change in the number of employed individuals, reflects the rate at which new jobs are being created in the economy. A positive job growth rate indicates an expanding economy, while a negative rate suggests a contracting economy.
Impact of Labor Market Conditions on Inflation and Economic Growth
A tight labor market, characterized by low unemployment and strong job growth, can exert upward pressure on wages. This is because employers face intense competition for qualified workers, leading them to offer higher salaries and benefits to attract and retain talent.
Increased wage growth can contribute to inflation, as businesses pass on higher labor costs to consumers through increased prices. However, a tight labor market can also stimulate economic growth. With more people employed and earning higher wages, consumer spending increases, boosting demand for goods and services.
This, in turn, can lead to higher business investment and economic expansion.
Wage Growth and Inflation
The relationship between wage growth and inflation is complex and can vary depending on several factors, including the level of unemployment, productivity growth, and the overall supply and demand dynamics in the economy. In a scenario where wage growth outpaces productivity growth, businesses may face pressure to raise prices to maintain profitability.
This can contribute to a cycle of rising inflation. However, if productivity growth keeps pace with wage growth, businesses can absorb higher labor costs without significantly impacting prices. In such a scenario, wage growth can support economic growth without fueling inflation.
“The relationship between wage growth and inflation is complex and can vary depending on several factors, including the level of unemployment, productivity growth, and the overall supply and demand dynamics in the economy.”
Global Economic Factors
The U.S. economy is not an isolated island; it’s deeply interconnected with the global economy. Global economic conditions, international trade, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical risks significantly impact the U.S. economic outlook. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the current economic landscape and anticipating potential challenges.
Impact of Global Economic Conditions
The health of the global economy directly influences the U.S. economy. When global economic growth is strong, U.S. businesses benefit from increased demand for their goods and services in foreign markets. Conversely, a global economic slowdown can lead to reduced exports, lower investment, and slower U.S.
growth. For example, the 2008 global financial crisis significantly impacted the U.S. economy, leading to a recession and a sharp decline in economic activity.
Role of International Trade and Supply Chain Disruptions
International trade plays a vital role in the U.S. economy, facilitating the exchange of goods and services with other countries. However, recent years have witnessed disruptions in global supply chains due to factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and natural disasters.
These disruptions have led to shortages, price increases, and delays in production and delivery, impacting U.S. businesses and consumers. For example, the pandemic-induced lockdowns in China, a major manufacturing hub, caused significant disruptions in global supply chains, impacting the availability and cost of various goods in the U.S.
While many economists predict a soft landing, others are waving red flags, warning of a potential economic storm. This worry isn’t unfounded, considering that your living standards have declined dramatically in recent years. The rising cost of living and stagnant wages are a stark reminder that even with a soft landing, the journey back to economic stability could be bumpy and fraught with challenges.
Potential Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical risks, such as international conflicts, trade wars, and political instability, can significantly impact the global economy. These risks can disrupt trade flows, increase uncertainty, and lead to market volatility. For example, the ongoing war in Ukraine has disrupted global energy markets, leading to higher energy prices and inflation.
Additionally, the escalating tensions between the U.S. and China over trade and technology have created uncertainty and potential risks for businesses operating in both countries.
Policy Responses and Potential Solutions: Despite Soft Landing Predictions Some Economists See Warning Signs Flashing Red
The possibility of a soft landing hinges on the ability of policymakers to navigate the delicate balance between taming inflation and maintaining economic growth. Both the government and the Federal Reserve have a range of tools at their disposal to address the economic challenges.
The effectiveness of these policies in achieving a soft landing is a subject of ongoing debate among economists. Different economic scenarios, each with its own set of risks and opportunities, will necessitate tailored policy responses.
Government Policy Responses
Government policy responses are aimed at mitigating the negative impacts of inflation and supporting economic growth.
- Fiscal Policy:The government can use fiscal policy to influence aggregate demand through changes in government spending and taxation. For example, increasing government spending on infrastructure projects or reducing taxes can stimulate economic activity. Conversely, reducing government spending or raising taxes can dampen demand and help control inflation.
- Targeted Support:The government can implement targeted programs to provide relief to vulnerable households and businesses affected by inflation. For instance, providing subsidies for energy costs or expanding access to food assistance can help alleviate the burden of rising prices.
Federal Reserve Policy Responses, Despite soft landing predictions some economists see warning signs flashing red
The Federal Reserve, as the central bank of the United States, plays a crucial role in managing inflation and interest rates.
- Monetary Policy:The Fed’s primary tool for controlling inflation is monetary policy, which involves adjusting interest rates and the money supply. Raising interest rates makes borrowing more expensive, which can slow down economic activity and reduce inflationary pressures. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate borrowing and economic growth.
- Quantitative Easing:In extraordinary circumstances, the Fed can use quantitative easing (QE) to inject liquidity into the financial system by purchasing government bonds or other assets. This can lower long-term interest rates and stimulate borrowing and investment.
Effectiveness of Policy Tools
The effectiveness of different policy tools in achieving a soft landing depends on a variety of factors, including the severity of inflation, the state of the economy, and the expectations of market participants.
- Monetary Policy:While raising interest rates is generally effective in controlling inflation, it can also slow down economic growth. The Fed faces a delicate balancing act in adjusting interest rates to achieve a soft landing.
- Fiscal Policy:The effectiveness of fiscal policy depends on the timing and the nature of the government’s interventions. In some cases, fiscal policy can be a powerful tool for stimulating economic activity, but it can also contribute to inflation if not carefully managed.
Alternative Economic Scenarios
The economic outlook is uncertain, and a range of alternative scenarios are possible.
- Persistent Inflation:If inflation remains stubbornly high, the Fed may need to continue raising interest rates aggressively, potentially leading to a recession.
- Recession:If the economy weakens significantly, the Fed may need to cut interest rates to stimulate growth, which could lead to higher inflation.
- Stagflation:A scenario of both high inflation and slow economic growth, known as stagflation, would pose a significant challenge for policymakers.
Final Review

The economic landscape is a dynamic and unpredictable terrain. While the prospect of a soft landing remains a possibility, the presence of warning signs underscores the need for vigilance and adaptability. As we navigate this period of economic transition, careful monitoring of key economic indicators, coupled with informed policy responses, will be crucial in mitigating potential risks and ensuring a sustainable path toward economic stability.






