Democrats Use Coronavirus Stimulus to Expand Government
Democrats are using coronavirus stimulus as opportunity to push their big government agenda, a claim that has sparked intense debate. This argument centers on the idea that the massive government spending package, designed to address the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic, is being used as a tool to expand government programs and influence.
Critics argue that this approach will lead to increased government control and a larger, more intrusive bureaucracy. The debate hinges on the role of government in a crisis and the potential long-term consequences of increased government spending.
The stimulus package, one of the largest in American history, has been a focal point for political and economic discussions. Supporters of the package emphasize the need for government intervention to prevent a deeper economic crisis and protect vulnerable populations.
They point to programs like enhanced unemployment benefits, direct payments to individuals, and support for businesses as essential for economic recovery. Opponents, however, argue that the package is an overreach of government power and will ultimately lead to higher taxes and inflation.
They worry that the expanded government programs will become permanent, creating a larger, more expensive government bureaucracy.
The Context of the Claim

The claim that Democrats are using the coronavirus stimulus as an opportunity to push their big government agenda is a common one, particularly among conservative circles. This claim often emerges during periods of significant government intervention in the economy, particularly when such interventions are driven by a perceived need to address a crisis.
It’s important to understand the historical context of government intervention during crises and the political climate surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic to assess the validity of this claim. The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the global economy, leading to widespread unemployment, business closures, and a significant decline in economic activity.
Governments around the world responded with a range of measures, including stimulus packages, loan programs, and direct payments to individuals and businesses. These measures were intended to mitigate the economic fallout of the pandemic and support individuals and businesses during a period of unprecedented uncertainty.
Government Intervention During Crises: A Historical Perspective
Government intervention in the economy during crises is not a new phenomenon. Historically, governments have played a role in stabilizing the economy during periods of recession or war. For example, the United States government played a significant role in the economy during the Great Depression, implementing programs such as the New Deal to provide relief and stimulate economic growth.
The role of government in the economy has evolved over time, and the level of government intervention has varied depending on the specific circumstances and political climate. However, it is clear that government intervention during crises has been a recurring theme throughout history.
The Political Climate Surrounding the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has also had a significant impact on the political landscape, leading to heightened political polarization and a debate over the appropriate level of government intervention. The pandemic has exacerbated existing political divisions, with different political parties advocating for different approaches to addressing the crisis.
This debate has been particularly evident in the United States, where the two major political parties have adopted contrasting views on the role of government in addressing the pandemic. Democrats have generally supported a more active role for government in providing economic relief and public health measures, while Republicans have tended to favor a more limited government approach.
Comparing and Contrasting Previous Stimulus Packages with the COVID-19 Relief Measures, Democrats are using coronavirus stimulus as opportunity to push their big government agenda
The COVID-19 relief measures are not the first time the United States government has implemented stimulus packages to address an economic crisis. Previous stimulus packages, such as the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, were enacted in response to the Great Recession.
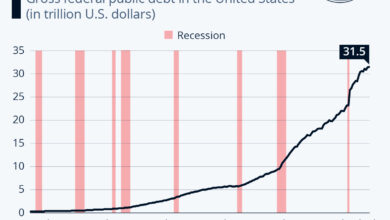
However, the COVID-19 relief measures are unprecedented in their scale and scope. The CARES Act, the first major COVID-19 relief package, provided over \$2 trillion in economic relief, including direct payments to individuals, loans to businesses, and funding for unemployment benefits.
Subsequent relief packages, such as the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021, have continued to provide significant economic support. The COVID-19 relief measures have been the subject of much debate, with some arguing that they are necessary to prevent a deeper economic downturn, while others argue that they are too expensive and will lead to higher levels of government debt.
It is important to note that the long-term economic impact of these measures is still uncertain.
Analysis of Stimulus Measures
The 2020 CARES Act, enacted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, provided trillions of dollars in economic relief, but some argue certain provisions promote “big government” by expanding government programs and interventions. This section examines specific measures within the stimulus package and their potential implications for government size and influence.
Expansion of Unemployment Benefits
The CARES Act significantly expanded unemployment benefits, providing an additional $600 per week on top of regular state benefits. This measure was intended to provide immediate relief to workers who lost their jobs due to the pandemic, but it also led to an unprecedented increase in government spending on unemployment insurance.
- The expanded unemployment benefits were initially scheduled to expire in July 2020, but were extended several times, most recently through September 2021. This extended period of enhanced benefits raised concerns about disincentivizing work and contributing to labor shortages.
- Critics argue that the expanded benefits, coupled with the federal government’s role in setting unemployment benefit levels, represented a significant expansion of government influence in the labor market.
Increased Government Spending on Healthcare
The CARES Act allocated billions of dollars to support healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and nursing homes. This funding was intended to help these providers cope with the surge in COVID-19 patients and to ensure access to testing and treatment.
- The stimulus package also included funding for the development and distribution of vaccines and treatments for COVID-19. This represents a significant government investment in the pharmaceutical industry and public health infrastructure.
- Critics argue that this increased government spending on healthcare reflects a shift towards a more centralized and government-controlled healthcare system, potentially leading to greater government influence over healthcare decisions.
Bailouts for Businesses
The CARES Act included a variety of programs designed to provide financial assistance to businesses impacted by the pandemic. This included loans, grants, and tax credits for small businesses, as well as loans and guarantees for larger corporations.
- The Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) was a popular program that provided forgivable loans to small businesses that retained their employees. This program was widely criticized for its implementation, including concerns about fraud and the distribution of funds to large corporations.
- Critics argue that these bailouts represent a significant expansion of government intervention in the economy, potentially creating moral hazard and distorting market forces.
Arguments for and Against “Big Government”
The debate surrounding government intervention, particularly in the wake of crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, often centers on the concept of “big government.” This debate involves weighing the benefits of government intervention in managing crises against the potential drawbacks of increased government power and spending.
Arguments Supporting Expanded Government Power
The proponents of expanded government intervention during crises argue that government action is essential to mitigate the negative impacts of such events. They emphasize the need for a strong and active government to provide necessary support and resources to individuals, businesses, and the overall economy.
- Economic Stabilization:Government intervention through stimulus packages, loan programs, and unemployment benefits can help stabilize the economy during crises by injecting liquidity, supporting businesses, and providing income support to individuals. This can prevent widespread economic collapse and promote recovery.
- Public Health Measures:Government intervention is crucial in implementing public health measures such as lockdowns, social distancing guidelines, and vaccination programs to control the spread of pandemics and protect public health. These measures may be unpopular, but they are often necessary to prevent widespread illness and death.
- Social Safety Net:A robust social safety net, funded and managed by the government, can provide essential support to vulnerable populations during crises. This includes programs such as food assistance, housing assistance, and healthcare subsidies, which can help individuals and families cope with economic hardship and maintain basic necessities.
Arguments Against Expanded Government Power
Opponents of expanded government intervention argue that such actions can lead to excessive government power, economic inefficiencies, and long-term negative consequences. They emphasize the importance of individual freedom and limited government intervention in the economy.
- Increased Government Power:Critics argue that government intervention during crises can lead to an expansion of government power and control, potentially eroding individual liberties and freedom. This concern is often amplified when emergency powers are granted to the government, which can lead to overreach and abuse.
- Economic Inefficiencies:Critics contend that government spending and regulation can lead to economic inefficiencies and distortions. They argue that government programs are often inefficient, wasteful, and can stifle innovation and economic growth. They also point to the potential for corruption and rent-seeking behavior in government programs.
- Long-Term Consequences:Opponents of expanded government intervention warn of potential long-term consequences, such as increased national debt, inflation, and a decline in economic competitiveness. They argue that excessive government spending can lead to unsustainable debt levels, which can strain future generations and limit economic growth.
Political Perspectives: Democrats Are Using Coronavirus Stimulus As Opportunity To Push Their Big Government Agenda
The COVID-19 stimulus package has been a major point of contention between Democrats and Republicans, with each party highlighting different aspects of the bill and emphasizing its impact on their respective constituents. This political divide is evident in the differing viewpoints on the size and scope of the stimulus, the allocation of funds, and the long-term implications of government intervention in the economy.
Comparative Views on the Stimulus Package
The following table contrasts the perspectives of Democrats and Republicans on the stimulus package:| Feature | Democratic View | Republican View ||—|—|—|| Size and Scope | Favor a larger stimulus package with more extensive aid for individuals, businesses, and state and local governments.
| Support a smaller stimulus package, focusing on targeted relief for specific industries and individuals. || Allocation of Funds | Prioritize direct payments to individuals, unemployment benefits, and aid for state and local governments. | Emphasize support for businesses, particularly small businesses, and tax cuts.
|| Government Intervention | View government intervention as necessary to address the economic crisis and protect vulnerable populations. | Express concerns about government overreach and potential for long-term economic damage. |
Key Arguments of Each Side
The stimulus package has ignited a heated debate, with each side presenting compelling arguments for their positions.| Argument | Democratic Perspective | Republican Perspective ||—|—|—|| Economic Recovery | A robust stimulus is crucial for a swift economic recovery and preventing a deeper recession.
| Government intervention can stifle economic growth and create long-term dependence on government assistance. || Social Safety Net | The stimulus provides a vital safety net for individuals and families struggling financially due to the pandemic. | The stimulus package is overly generous and could discourage work and incentivize dependency.
|| State and Local Governments | Aid for state and local governments is essential to prevent widespread job losses and service cuts. | State and local governments should manage their budgets responsibly and avoid relying on federal bailouts. || Business Support | The stimulus includes measures to support businesses, including loans and tax credits.
| The focus should be on providing targeted assistance to specific industries, such as small businesses, that have been disproportionately affected by the pandemic. |
The Stimulus as a Political Focal Point
The COVID-19 stimulus package has become a focal point for political debate, with both parties using the bill to advance their respective agendas. Democrats have used the package to push for their priorities, such as expanding the social safety net and investing in infrastructure.
Republicans have focused on reducing government spending and promoting economic growth. The debate over the stimulus has also highlighted the broader ideological divide between the two parties, with Democrats emphasizing government intervention and Republicans advocating for free markets.
Summary

The debate over the use of the coronavirus stimulus to expand government power is likely to continue. It raises fundamental questions about the role of government in a crisis and the balance between individual liberty and government intervention. The long-term effects of the stimulus package remain to be seen, but it is clear that it has become a defining issue in the ongoing political and economic discourse.