
Crude Realities: Decoding OPECs Oil Pricing, Barrel Sizes, and Global Rankings
Crude realities decoding opecs oil pricing barrel sizes and global rankings – Crude Realities: Decoding OPEC’s Oil Pricing, Barrel Sizes, and Global Rankings sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The world of oil is a complex one, where global economics, geopolitics, and technological advancements constantly intertwine.
At the heart of this complex web lies OPEC, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, which wields significant influence over the global oil market.
This exploration delves into the intricate mechanisms by which OPEC sets oil prices, the historical evolution of its influence, and the various strategies it employs to control the market. We will unravel the mysteries of barrel sizes, their historical origins, and their impact on pricing and transportation.
Furthermore, we’ll take a look at the global oil production landscape, ranking the top producers and examining the factors driving their production levels. Ultimately, we’ll delve into the far-reaching impact of oil pricing on global economies, analyzing its influence on various industries and highlighting countries significantly impacted by oil price fluctuations.
The Global Oil Market
The global oil market is a complex and dynamic system, driven by a multitude of factors including supply and demand, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. One of the key players in this market is the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), a cartel of oil-producing nations that plays a significant role in shaping global oil prices.
OPEC’s Role in Global Oil Pricing
OPEC’s primary objective is to coordinate and unify petroleum policies among its member countries, ensuring the stabilization of oil markets to secure an efficient, economic, and regular supply of petroleum to consumers. The organization achieves this by setting production quotas for its members, aiming to influence the global supply of crude oil and, consequently, impact prices.
This control over supply allows OPEC to exert significant influence on the global oil market, impacting prices and impacting global economies.
Trying to understand the complexities of OPEC’s oil pricing and global rankings is like navigating a labyrinth of barrels and market forces. It’s a world where the smallest change in supply or demand can have a ripple effect across the globe.
And then you have the news about 9 boxes of biden documents taken from boston office not reviewed for classified materials , which, while seemingly unrelated, serves as a reminder that even the most powerful figures can be caught in the crosshairs of unforeseen events.
The intricate dance between political maneuvering and global oil production continues, and the world watches with bated breath.
OPEC’s Influence Throughout History
OPEC’s influence on the global oil market has evolved significantly throughout its history. In the 1970s, OPEC’s power reached its peak during the oil crises, when it successfully imposed an oil embargo on Western nations, leading to a dramatic surge in oil prices.
However, OPEC’s influence has waned since then, as the emergence of new oil producers and alternative energy sources has reduced its market share and control.
OPEC’s Methods to Control Oil Prices
OPEC employs various methods to control oil prices. One of the most common is setting production quotas for its members, aiming to influence the global supply of crude oil and, consequently, impact prices. Another strategy is to coordinate price increases or reductions among its members, ensuring a united front in the market.
Furthermore, OPEC can influence oil prices by strategically releasing or withholding oil reserves from the market, further impacting supply and demand dynamics.
Recent Events Impacting OPEC’s Strategies
Recent events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the ongoing war in Ukraine, have significantly impacted OPEC’s strategies. The pandemic led to a sharp decline in global oil demand, forcing OPEC to reduce production to stabilize prices. The war in Ukraine, on the other hand, has created uncertainty and volatility in the market, leading to a surge in oil prices.
In response to these challenges, OPEC has been forced to adapt its strategies, adjusting production quotas and engaging in negotiations with other oil-producing countries to ensure market stability.
Decoding OPEC’s Pricing Mechanisms
OPEC, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, wields significant influence over global oil prices. Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind OPEC’s pricing decisions is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the global oil market.
Factors Influencing OPEC’s Pricing Decisions
OPEC’s pricing decisions are a complex interplay of various factors. The organization carefully considers these factors to achieve its objectives, which primarily involve ensuring stable oil prices that are fair to both producers and consumers.
- Global Demand:OPEC closely monitors global oil demand, which is influenced by economic growth, industrial activity, and consumer behavior. Higher demand typically leads to higher prices, while lower demand can push prices down.
- Global Supply:OPEC also analyzes global oil supply, including production levels from both OPEC and non-OPEC countries. A surplus in supply can put downward pressure on prices, while a shortage can drive prices up.
- Inventory Levels:OPEC monitors global oil inventories, which serve as a buffer against supply disruptions. High inventory levels can indicate a surplus, while low levels can signal a potential shortage.
- Geopolitical Factors:Political instability, conflicts, and sanctions in oil-producing regions can significantly impact supply and prices. For instance, geopolitical tensions in the Middle East have historically led to oil price spikes.
- Economic Conditions:Global economic conditions, such as interest rates, inflation, and currency exchange rates, can influence oil demand and prices. For example, a weakening global economy can reduce demand for oil, leading to lower prices.
- Technological Advancements:Technological advancements in oil extraction, refining, and alternative energy sources can impact both supply and demand. For instance, the development of shale oil production in the United States has increased global supply and put downward pressure on prices.
- Member Country Interests:OPEC’s pricing decisions are also influenced by the individual interests of its member countries. Each country has its own production capacity, economic needs, and political considerations, which can impact its stance on pricing strategies.
Impact of Global Demand and Supply Dynamics
Global demand and supply dynamics play a pivotal role in shaping OPEC’s pricing decisions. When demand exceeds supply, OPEC may increase production to meet the shortfall, potentially leading to higher prices. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, OPEC may reduce production to stabilize prices, which can prevent a price crash.
“OPEC’s pricing decisions are often driven by a delicate balance between maintaining market share and ensuring stable oil prices.”
Role of Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical factors can significantly influence OPEC’s pricing strategies. For instance, during periods of political instability or conflict in oil-producing regions, OPEC may choose to increase production to offset supply disruptions and prevent price spikes. However, in other cases, geopolitical tensions can lead to reduced production and higher prices, as seen during the 1973 oil crisis.
OPEC’s Pricing Strategies Over the Past Decade
| Year | Pricing Strategy | Key Factors | Impact on Oil Prices |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Production Increase | Rising global demand, increasing shale oil production | Oil prices remained relatively stable |
| 2014 | Production Freeze | Declining oil prices, geopolitical tensions | Oil prices declined sharply |
| 2015 | Production Cuts | Persistent low oil prices, global economic slowdown | Oil prices stabilized but remained low |
| 2016 | Production Cuts | Continued low oil prices, global economic uncertainty | Oil prices gradually increased |
| 2017 | Production Cuts | Improving global economic conditions, increasing demand | Oil prices rose significantly |
| 2018 | Production Increases | Strong global economic growth, rising demand | Oil prices remained relatively stable |
| 2019 | Production Cuts | Slowing global economic growth, trade tensions | Oil prices declined |
| 2020 | Production Cuts | COVID-19 pandemic, sharp decline in demand | Oil prices crashed to record lows |
| 2021 | Gradual Production Increases | Post-pandemic economic recovery, rising demand | Oil prices surged to multi-year highs |
| 2022 | Production Cuts | Geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions | Oil prices reached record highs |
The Importance of Barrel Sizes

The oil industry operates on a global scale, with production, transportation, and consumption occurring across continents. Understanding the different barrel sizes used in this industry is crucial for comprehending oil pricing and trade dynamics. These varying barrel sizes have historical roots and significantly impact how oil is priced and transported.
Historical Origins of Barrel Sizes
The use of barrels in the oil industry dates back to the early days of oil extraction in the 19th century. At that time, barrels were used to store and transport oil, and the size of the barrels varied depending on the region and the type of oil being produced.
- The most common barrel size used in the oil industry is the 42-gallon barrel, which originated in the United States. This size was standardized in the early 20th century and became the benchmark for oil pricing.
- In Europe, the 159-liter barrelwas commonly used. This barrel size, also known as the “UK barrel”, was slightly larger than the 42-gallon barrel. However, the 42-gallon barrel eventually became the global standard, and the UK barrel is now rarely used.
- Other barrel sizes, such as the “petroleum barrel”(40 gallons) and the “oil barrel”(36 gallons), were also used in the past, but these sizes have largely been phased out.
Impact of Barrel Sizes on Oil Pricing and Transportation
The different barrel sizes used in the oil industry can have a significant impact on oil pricing and transportation.
The world of oil is a complex one, with OPEC’s pricing strategies, barrel sizes, and global rankings all playing a crucial role. But while we’re decoding these crude realities, it’s worth noting that the US is also looking to refine its own economic landscape.
The USDA’s proposed new rule for “Product of USA” food labels could have a significant impact on American agriculture and trade, ultimately influencing the global market for commodities like oil. Ultimately, understanding the interplay of these diverse economic forces is key to navigating the complexities of our interconnected world.
- Pricing:Oil is typically priced per barrel, and the size of the barrel can influence the price. For example, if oil is priced at $100 per barrel, the price per gallon will be higher for a 42-gallon barrel than for a 36-gallon barrel.
This difference in pricing can be important for producers, refiners, and consumers.
- Transportation:The size of the barrel can also affect transportation costs. Larger barrels are generally more efficient to transport than smaller barrels, as they require fewer containers and less handling. However, larger barrels may be more difficult to handle in certain situations, such as when loading and unloading ships.
Visual Representation of Barrel Sizes and Oil Prices
[Here you would insert a visual representation, like a graph or chart, showing the relationship between barrel sizes and oil prices. This could be a bar chart comparing prices per gallon for different barrel sizes, or a line graph showing how oil prices fluctuate based on different barrel sizes.]
Global Oil Production and Rankings
The global oil market is a complex and dynamic system, influenced by a multitude of factors, including production levels, demand patterns, and geopolitical events. Understanding the major oil producers and their production methods is crucial for comprehending the global energy landscape.
Global Oil Production Ranking
This section presents a ranking of the top 10 oil-producing countries based on their annual production figures. The ranking provides insights into the global distribution of oil production and the dominant players in the market.
| Rank | Country | Production (Million Barrels/Day) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | 12.4 |
| 2 | Saudi Arabia | 10.0 |
| 3 | Russia | 10.0 |
| 4 | Canada | 4.9 |
| 5 | China | 4.1 |
| 6 | Iraq | 3.9 |
| 7 | United Arab Emirates | 3.4 |
| 8 | Iran | 2.8 |
| 9 | Brazil | 2.8 |
| 10 | Kuwait | 2.7 |
Factors Driving Oil Production Levels
Several factors influence the oil production levels of countries, including:
- Geological Resources:The presence of vast oil reserves is a fundamental prerequisite for significant oil production. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Russia possess abundant oil reserves, enabling them to produce large quantities.
- Technological Advancements:Technological innovations in oil extraction and refining processes have played a crucial role in boosting production levels. For example, advancements in hydraulic fracturing (“fracking”) have unlocked previously inaccessible oil reserves in the United States, leading to a surge in production.
- Government Policies:Government policies, including tax incentives, subsidies, and regulations, can significantly impact oil production. Countries may incentivize oil exploration and production through tax breaks and subsidies, while regulations can influence environmental and safety standards.
- Global Demand:Global demand for oil is a major driver of production levels. When global demand is high, countries may increase production to meet the demand, leading to higher prices. Conversely, a decline in global demand can result in reduced production and lower prices.
- Geopolitical Factors:Geopolitical factors, such as political stability, international relations, and conflicts, can impact oil production. Political instability or conflicts in oil-producing regions can disrupt production and lead to price fluctuations.
Methods of Oil Extraction and Refining
Oil-producing countries employ various methods to extract and refine oil, each with its own environmental and economic implications.
- Conventional Oil Extraction:This method involves drilling into underground reservoirs and pumping oil to the surface. It is the most common method, but it can be energy-intensive and have environmental impacts, such as greenhouse gas emissions and habitat destruction.
- Unconventional Oil Extraction:This includes methods like hydraulic fracturing (“fracking”) and oil sands extraction. These methods are often more complex and require specialized technologies, but they have also raised concerns about environmental impacts, such as water contamination and habitat destruction.
- Oil Refining:After extraction, crude oil is transported to refineries where it is processed into various petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel, and kerosene. Refineries use complex processes involving distillation, cracking, and blending to transform crude oil into usable products.
Environmental and Economic Impacts of Oil Production, Crude realities decoding opecs oil pricing barrel sizes and global rankings
Oil production has significant environmental and economic impacts on countries and the global community.
Understanding the intricacies of OPEC’s oil pricing, from barrel sizes to global rankings, can feel like deciphering a complex code. But it’s a code that impacts our daily lives, especially when you consider how the rising cost of oil fuels inflation.
That’s why news like millions of Americans getting bigger Social Security payments as the cost of living adjustment kicks in is so important. It’s a reminder that even as we grapple with global energy dynamics, there are measures being taken to alleviate some of the pressure on everyday Americans.
- Environmental Impacts:Oil production can contribute to air pollution, water contamination, and habitat destruction. The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Oil spills and leaks can have devastating impacts on ecosystems and wildlife.
- Economic Impacts:Oil production can be a major driver of economic growth, creating jobs and generating revenue for governments. However, it can also lead to economic dependence on oil exports, making countries vulnerable to price fluctuations. The environmental costs of oil production, such as cleanup and remediation, can also have significant economic implications.
Crude Realities
The price of oil is a critical factor in the global economy. Fluctuations in oil prices can have a significant impact on countries, industries, and individuals worldwide. Understanding how oil price changes affect the global economy is crucial for investors, policymakers, and consumers alike.
The Impact of Oil Price Fluctuations on Global Economies
Oil price volatility can have both positive and negative consequences for different economies. When oil prices rise, it can lead to higher inflation, as businesses pass on increased costs to consumers. This can also reduce consumer spending, as households have less disposable income.
On the other hand, high oil prices can benefit oil-producing countries, as they receive higher revenues from oil exports. These revenues can be used to fund infrastructure projects, social programs, and economic development.
Economic Consequences of High and Low Oil Prices
High oil prices can lead to:
- Increased inflation: As businesses pass on higher costs to consumers, the overall price level in the economy increases.
- Reduced consumer spending: Households have less disposable income, leading to a decrease in consumer demand for goods and services.
- Economic slowdown: The combination of higher inflation and reduced consumer spending can lead to a slowdown in economic growth.
- Increased government spending: Governments may need to increase spending on social programs and subsidies to help households cope with higher energy costs.
- Currency appreciation: Oil-producing countries may see their currencies appreciate as they receive higher revenues from oil exports.
Low oil prices can lead to:
- Lower inflation: Businesses may reduce prices to remain competitive, leading to a decrease in the overall price level.
- Increased consumer spending: Households have more disposable income, leading to an increase in consumer demand for goods and services.
- Economic growth: The combination of lower inflation and increased consumer spending can lead to faster economic growth.
- Reduced government spending: Governments may need to reduce spending on social programs and subsidies as energy costs decrease.
- Currency depreciation: Oil-producing countries may see their currencies depreciate as they receive lower revenues from oil exports.
Industries Most Affected by Oil Price Volatility
The industries most affected by oil price volatility include:
- Transportation: The transportation sector is a major consumer of oil, and fluctuations in oil prices can significantly impact transportation costs. Airlines, trucking companies, and shipping companies are particularly vulnerable to oil price changes.
- Manufacturing: Many manufacturing industries rely on oil-based inputs, such as plastics and chemicals. Higher oil prices can lead to higher production costs and reduced profits.
- Energy: Oil and gas companies are directly affected by oil price fluctuations. Higher oil prices can lead to higher profits, while lower oil prices can lead to reduced profits and even losses.
- Agriculture: The agriculture sector relies on oil-based inputs, such as fertilizers and pesticides. Higher oil prices can lead to higher production costs and reduced profits.
- Tourism: The tourism industry is affected by oil prices as higher prices can lead to higher transportation costs, which can discourage travel.
Examples of Countries Significantly Impacted by Oil Price Changes
Several countries have been significantly impacted by oil price changes. For example,
- Saudi Arabia, a major oil producer, has seen its economy boom during periods of high oil prices. However, low oil prices have led to budget deficits and economic challenges.
- Venezuela, another major oil producer, has been heavily impacted by the decline in oil prices in recent years. The country’s economy has contracted significantly, and its currency has depreciated sharply.
- The United States, a major oil consumer, has seen its economy grow during periods of low oil prices. However, high oil prices have led to higher inflation and reduced consumer spending.
- China, a major importer of oil, has seen its economy grow rapidly during periods of low oil prices. However, high oil prices have led to higher transportation costs and reduced industrial output.
Future Trends in the Global Oil Market: Crude Realities Decoding Opecs Oil Pricing Barrel Sizes And Global Rankings
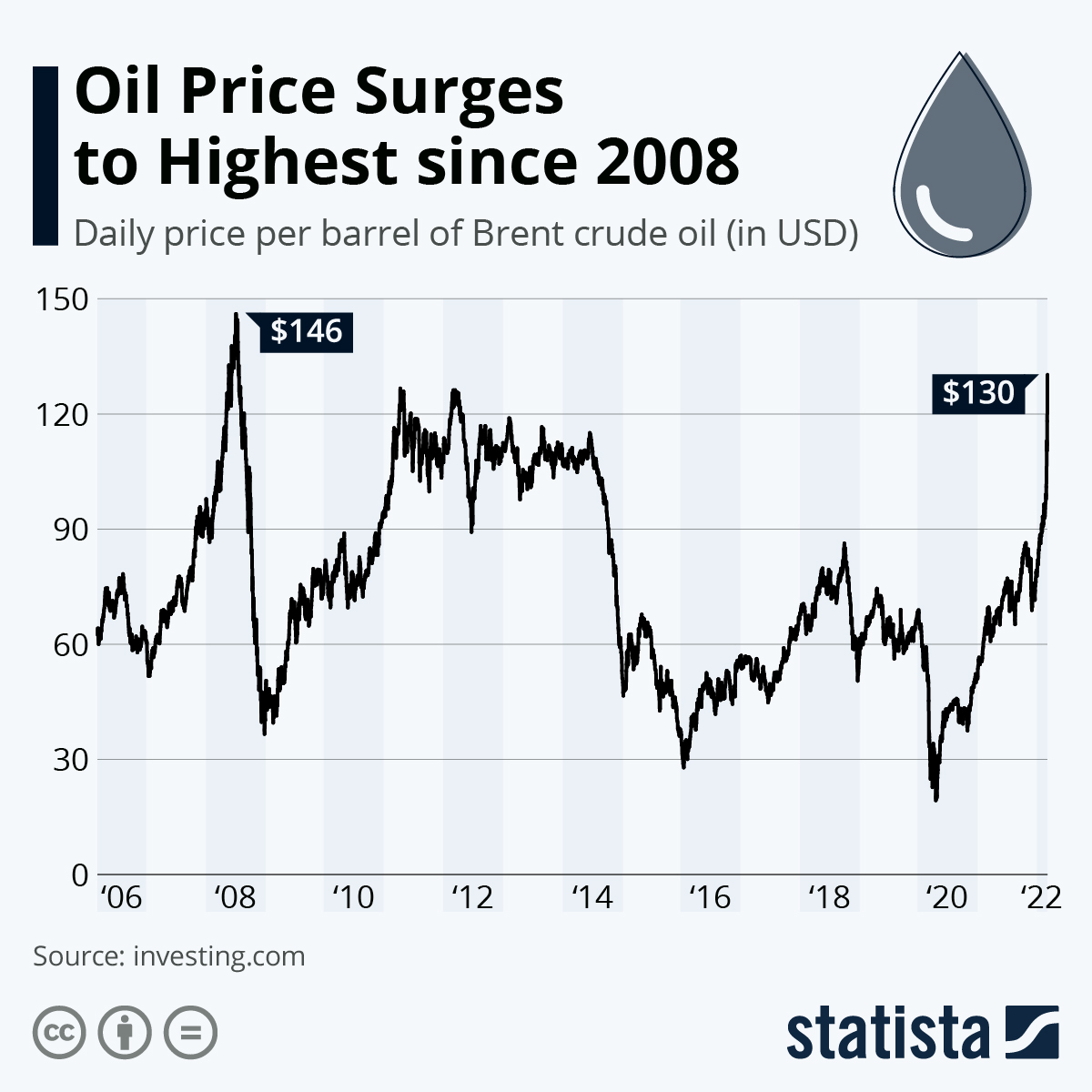
The global oil market is a complex and dynamic system influenced by a multitude of factors, including geopolitical events, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. Understanding these forces is crucial for predicting future trends and their potential impact on oil prices, production, and consumption.
Expert Predictions for Future Oil Prices
Predicting future oil prices is a complex endeavor due to the interplay of various factors, including supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and economic conditions. Experts offer a range of perspectives on future oil price trajectories.
- Some analysts anticipate a gradual increase in oil prices in the coming years, driven by factors such as growing global demand, particularly in emerging economies, and limited investment in new production capacity. They cite the potential for disruptions in oil supply due to geopolitical tensions and the increasing difficulty of extracting oil from unconventional sources as contributing factors.
- Others suggest that oil prices might remain relatively stable or even decline, pointing to factors such as the continued growth of renewable energy sources, technological advancements in energy efficiency, and the potential for increased oil production from new sources.
- A third perspective emphasizes the role of economic uncertainty and global economic growth in shaping future oil prices.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies on Oil Production and Consumption
Technological advancements are transforming the oil and gas industry, impacting both production and consumption.
- Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Techniques:EOR techniques, such as carbon dioxide injection and microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR), aim to extract more oil from existing reservoirs. These technologies are expected to play a significant role in extending the lifespan of existing oil fields and boosting production.
- Fracking:Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, has revolutionized oil and gas production, particularly in the United States. This technology allows for the extraction of oil and gas from previously inaccessible shale formations, leading to increased domestic production and potentially impacting global supply and demand dynamics.
- Oil Sands:Oil sands, a mixture of sand, clay, and bitumen, are another unconventional source of oil. Technologies are being developed to extract bitumen from oil sands, potentially contributing to global oil production.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):The rapid adoption of electric vehicles is expected to significantly reduce demand for gasoline and diesel fuel. This shift in transportation technology could impact oil consumption patterns in the long term.
The Role of Renewable Energy Sources in Shaping the Future of the Oil Market
The growing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, is expected to have a significant impact on the future of the oil market.
- Decreased Oil Demand:As renewable energy sources become more cost-effective and widely adopted, they are likely to displace fossil fuels in electricity generation and other sectors, leading to a decrease in oil demand.
- Shift in Energy Mix:The increasing contribution of renewable energy to the global energy mix will likely result in a shift away from fossil fuels, potentially impacting oil production and pricing.
- Policy Support:Government policies aimed at promoting renewable energy, such as subsidies and carbon pricing mechanisms, are likely to accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels.
Key Milestones in the Evolution of the Global Oil Market
The global oil market has evolved significantly over the past century, marked by key milestones that have shaped its current landscape.
- 19th Century:The discovery of oil in Pennsylvania in 1859 marked the beginning of the modern oil industry.
- Early 20th Century:The development of the internal combustion engine and the rise of the automobile industry led to a surge in oil demand.
- 1960s:The formation of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) in 1960 significantly altered the global oil market dynamics, giving oil-producing nations more control over pricing and production.
- 1970s:The 1973 oil crisis, triggered by an OPEC embargo, highlighted the vulnerability of industrialized nations to oil supply disruptions.
- 1980s-1990s:The oil market experienced periods of both high and low prices, influenced by factors such as geopolitical events, technological advancements, and economic growth.
- 21st Century:The rise of unconventional oil production, the growth of renewable energy sources, and the increasing focus on climate change have introduced new challenges and opportunities for the global oil market.
Final Thoughts

From the complexities of OPEC’s pricing strategies to the diverse world of barrel sizes, this journey through the global oil market reveals a fascinating story of economic power, technological innovation, and geopolitical influence. By understanding the dynamics at play, we gain valuable insights into the forces shaping our energy future and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.






