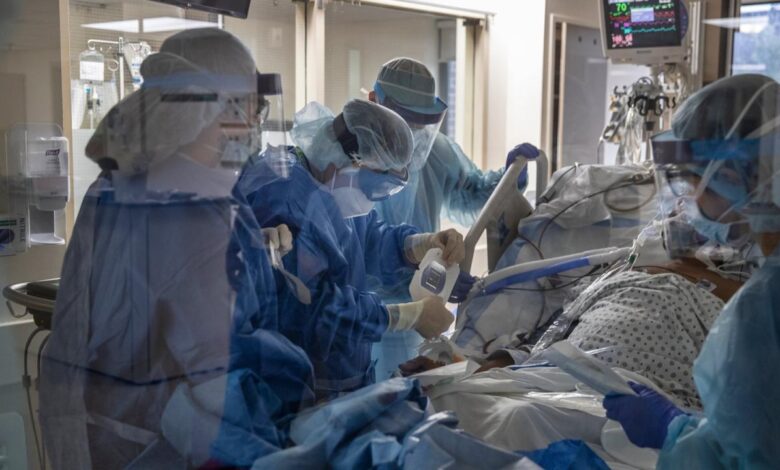
COVID-19 Pandemic Hospital Infections Surge, Raising Concerns
Covid 19 pandemic has brought a life threatening infection spike in hospitals raising serious concerns – COVID-19 pandemic has brought a life threatening infection spike in hospitals raising serious concerns, pushing healthcare systems to their breaking point. The surge in hospitalizations, fueled by the highly contagious nature of the virus, has strained resources, leading to staff shortages, bed capacity limitations, and an unprecedented burden on healthcare workers. The pandemic has not only impacted the physical health of patients but also their mental well-being, as isolation and limited access to non-COVID-related care have taken a toll.
The severity of COVID-19 infections varies widely, with factors like age, underlying health conditions, and the specific virus variant playing significant roles. While vaccines have proven effective in mitigating the severity of the disease, the emergence of new variants and vaccine hesitancy continue to pose challenges. The long-term effects of COVID-19, known as Long COVID, have further complicated the situation, leaving many individuals with debilitating symptoms and impacting healthcare systems worldwide.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Hospital Systems
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on hospital systems worldwide, placing immense strain on resources and forcing healthcare professionals to adapt to unprecedented challenges.
Surge in Hospitalizations
The highly contagious nature of COVID-19 resulted in a rapid surge in hospitalizations, overwhelming healthcare systems in many countries. The initial wave of the pandemic, in particular, saw a dramatic increase in the number of patients requiring critical care, leading to a shortage of beds and ventilators. The Delta and Omicron variants, with their increased transmissibility, further exacerbated the situation, leading to new peaks in hospitalizations.
Strain on Hospital Resources
The surge in hospitalizations put immense strain on hospital resources, including staff, beds, and equipment.
- Staff Shortages: The pandemic led to a significant shortage of healthcare workers, as many were infected with COVID-19 or had to isolate due to exposure. This shortage further strained the already overworked staff, leading to burnout and exhaustion.
- Bed Capacity Limitations: Hospitals quickly reached their bed capacity, leading to the use of overflow facilities and the conversion of other spaces into makeshift wards. This resulted in a decrease in the quality of care and an increase in wait times for patients.
- Equipment Shortages: The demand for ventilators, personal protective equipment (PPE), and other medical supplies far exceeded the available supply, leading to shortages and rationing.
Impact on Healthcare Workers
The pandemic has had a significant impact on healthcare workers, both physically and emotionally.
It’s hard to believe that while hospitals are struggling with a life-threatening spike in COVID-19 infections, we’re also dealing with the news that Donald Trump has filed a motion seeking to prevent the Department of Justice from accessing records at Mar-a-Lago until a special master is appointed. This move is just another reminder that even in the face of a global pandemic, we can’t escape the political drama that seems to be a constant in our lives.
With so much uncertainty and stress, it’s more important than ever to focus on the things we can control, like staying safe and healthy during this challenging time.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Healthcare workers were at a higher risk of contracting COVID-19 due to their constant exposure to infected patients. This risk, coupled with the fear of transmitting the virus to their families, created significant anxiety and stress.
- Emotional Toll: Witnessing the suffering of patients, dealing with the loss of colleagues, and facing the constant threat of infection took a heavy emotional toll on healthcare workers. Many experienced burnout, anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
- Long-Term Health Consequences: Some healthcare workers have experienced long-term health consequences from COVID-19, including fatigue, shortness of breath, and cognitive impairment. These long-term effects can further exacerbate the emotional and physical strain on healthcare workers.
The Nature of COVID-19 Infections
COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has had a profound impact on global health and society. Understanding the nature of COVID-19 infections is crucial for effective prevention, treatment, and management. This section delves into the symptoms, severity, and long-term effects of COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a life-threatening infection spike in hospitals, raising serious concerns about our healthcare system’s capacity. While we grapple with this crisis, the news that border patrol chief says no consequences are driving border crisis adds another layer of complexity. This situation further strains our resources and makes it even harder to combat the pandemic’s effects, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach to both healthcare and border security.
Symptoms and Severity of COVID-19 Infections
COVID-19 presents a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and the severity can vary significantly among individuals. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, muscle aches, headache, sore throat, congestion, and loss of taste or smell. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. In severe cases, COVID-19 can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure, and even death.
Factors Contributing to Severity of COVID-19 Infections
The severity of COVID-19 infections is influenced by several factors:
Age
Older adults are more susceptible to severe COVID-19 illness and complications. The immune system weakens with age, making it harder to fight off infections.
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a life-threatening infection spike in hospitals, raising serious concerns about the strain on healthcare systems. While we grapple with this health crisis, political tensions continue to simmer, as seen in the recent news about Biden responding to Trump’s declassification order claims. It’s crucial that we remember the severity of the pandemic and focus on finding solutions that address both the immediate health concerns and the long-term consequences of this global event.
Underlying Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, chronic lung disease, kidney disease, and obesity, are at increased risk of severe COVID-19. These conditions can compromise the immune system and make the body more vulnerable to the virus.
Variant Type
The emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, such as Alpha, Delta, and Omicron, has raised concerns about their transmissibility, severity, and ability to evade immunity. Some variants are more transmissible or cause more severe illness than others.
Long-Term Effects of COVID-19 (Long COVID)
A significant proportion of individuals who have recovered from COVID-19 experience long-term effects, collectively known as Long COVID. These effects can persist for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
Symptoms of Long COVID
Symptoms of Long COVID are diverse and can affect various organ systems. Common symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, brain fog, headache, joint pain, muscle aches, anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.
Impact of Long COVID on Individuals and Healthcare Systems
Long COVID has a significant impact on individuals, affecting their physical and mental health, quality of life, and ability to work. It also poses a challenge to healthcare systems, leading to increased demand for medical services and long-term care.
The Role of Public Health Measures: Covid 19 Pandemic Has Brought A Life Threatening Infection Spike In Hospitals Raising Serious Concerns
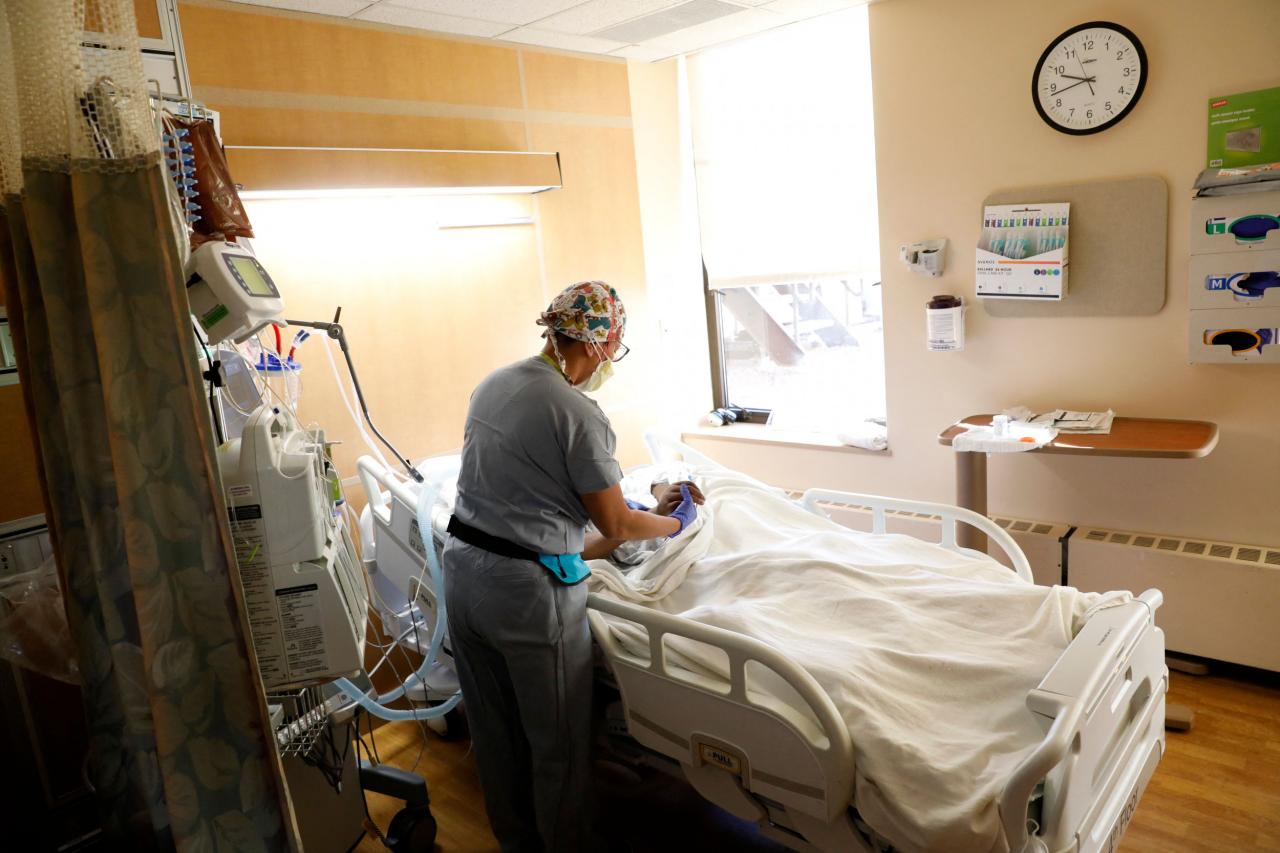
Public health measures have been crucial in mitigating the spread of COVID-19, and their impact on hospital systems has been significant. These measures include vaccination, masking, and social distancing, each playing a distinct role in reducing transmission and protecting vulnerable populations.
Effectiveness of Public Health Measures, Covid 19 pandemic has brought a life threatening infection spike in hospitals raising serious concerns
Vaccination, masking, and social distancing have been proven effective in reducing COVID-19 transmission and severity.
- Vaccination: Vaccines significantly reduce the risk of infection, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19. Studies have shown that vaccinated individuals are less likely to contract the virus and, if they do, experience milder symptoms. For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine were 95% effective in preventing symptomatic COVID-19.
- Masking: Wearing masks, especially in indoor settings, reduces the spread of respiratory droplets that can carry the virus. Studies have demonstrated that mask-wearing significantly reduces the transmission of COVID-19, particularly in high-risk environments like healthcare facilities.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance from others minimizes the chances of coming into contact with infected individuals. Social distancing measures, such as limiting gatherings and promoting remote work, have been effective in reducing community transmission.
Challenges in Implementing and Maintaining Public Health Measures
Implementing and maintaining public health measures face several challenges, including:
- Public Compliance: Ensuring widespread compliance with public health recommendations is crucial for their effectiveness. However, public compliance can be influenced by factors such as individual beliefs, perceptions of risk, and economic considerations. For instance, some individuals may resist mask mandates due to concerns about personal liberty or the inconvenience of wearing a mask.
- Economic Considerations: Public health measures can have significant economic impacts, particularly on businesses and industries that rely on face-to-face interactions. Restrictions on gatherings and travel can lead to job losses and business closures. Balancing public health needs with economic considerations is a complex challenge that requires careful policy decisions.
Impact on Hospitalizations and Healthcare Systems
Public health measures have had a significant impact on hospitalizations and the overall burden on healthcare systems.
- Reduced Hospitalizations: The widespread adoption of vaccination, masking, and social distancing has contributed to a decrease in COVID-19 hospitalizations. Studies have shown a strong correlation between vaccination rates and lower hospitalization rates.
- Reduced Strain on Healthcare Systems: By reducing the number of COVID-19 cases, these measures have alleviated the strain on healthcare systems. This has allowed hospitals to focus on other critical medical needs and prevent overwhelming healthcare resources.
Future Considerations
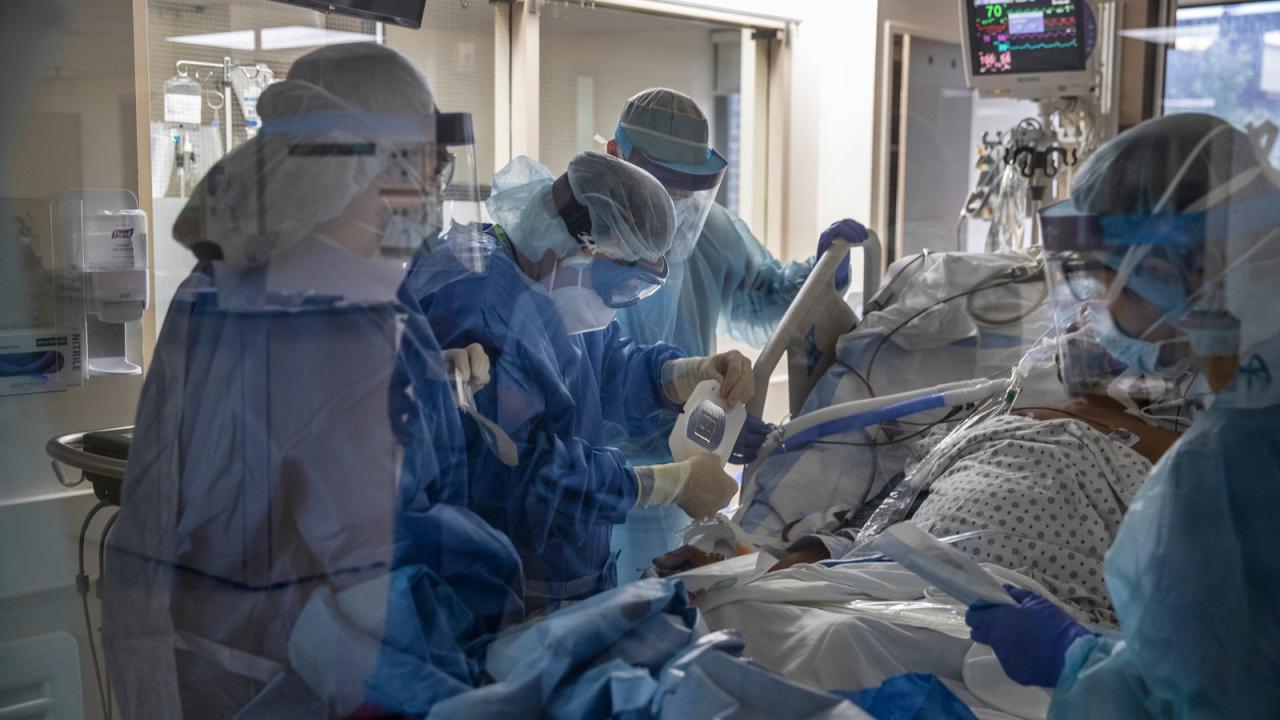
The COVID-19 pandemic has undoubtedly left an indelible mark on global healthcare systems. While the initial surge of infections has subsided in many regions, the virus continues to evolve, posing a persistent threat. As we navigate the long-term implications of the pandemic, it is crucial to consider the potential for future waves of infections and their impact on hospital systems.
This necessitates a proactive approach that encompasses ongoing research, robust preparedness strategies, and continuous public health vigilance.
The Potential for Future COVID-19 Waves
The emergence of new variants, such as Omicron, has demonstrated the virus’s capacity for rapid evolution. These variants can exhibit increased transmissibility, immune evasion, or altered disease severity, potentially leading to new surges in infections. The ongoing emergence of new variants underscores the need for ongoing surveillance and genomic sequencing to track viral evolution and identify potential threats.
The Importance of Ongoing Research and Development
The development of effective vaccines and treatments has been instrumental in mitigating the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, ongoing research and development remain crucial for addressing emerging challenges. This includes:
- Developing broader-spectrum vaccines that offer protection against multiple variants.
- Exploring novel antiviral therapies that can effectively target emerging variants.
- Conducting research on long-term health consequences associated with COVID-19 infection.
The rapid development of vaccines and treatments during the pandemic serves as a testament to the power of scientific collaboration and innovation. Continued investment in research is essential for staying ahead of the virus and developing new strategies to combat future waves.
The Role of Preparedness and Planning
Effective preparedness and planning are critical for mitigating the impact of future COVID-19 outbreaks and ensuring healthcare system resilience. This involves:
- Maintaining adequate supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilators, and other essential medical supplies.
- Strengthening surge capacity in hospitals by increasing bed availability and staffing levels.
- Developing robust public health communication strategies to effectively inform the public about the evolving situation and recommended preventive measures.
- Establishing clear protocols for managing patient flow and prioritizing care during periods of high demand.
Effective preparedness requires a multi-pronged approach that encompasses collaboration among healthcare providers, public health officials, and policymakers. Lessons learned from the initial stages of the pandemic can inform strategies for future outbreaks, ensuring that healthcare systems are better equipped to respond effectively.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the fragility of our healthcare systems and the importance of preparedness in facing future health crises. Ongoing research and development of treatments and vaccines remain crucial, along with public health measures like vaccination, masking, and social distancing. As we navigate the ongoing pandemic, it is essential to remember the resilience of healthcare workers, the importance of community support, and the need for continued vigilance in mitigating the spread of this virus.