
Coronavirus Declared US Public Health Emergency
Coronavirus declared public health emergency in us – Coronavirus Declared US Public Health Emergency: In early 2020, the world watched as the novel coronavirus, COVID-19, rapidly spread across the globe. The United States, initially hesitant, eventually declared a public health emergency in response to the escalating crisis.
This declaration, a pivotal moment in the nation’s history, marked a shift in the government’s approach to the pandemic and triggered a cascade of actions aimed at mitigating the spread and impact of the virus.
The declaration, issued by the Department of Health and Human Services, officially recognized the severity of the situation and empowered federal agencies to allocate resources and implement measures to combat the virus. This included mobilizing healthcare professionals, securing medical supplies, and coordinating research efforts to develop vaccines and treatments.
The declaration also paved the way for unprecedented social distancing measures, school closures, and business restrictions, all aimed at slowing the spread of the virus and preventing overwhelming the healthcare system.
The Declaration of a Public Health Emergency

The declaration of a public health emergency in the United States for the coronavirus was a significant step in the nation’s response to the rapidly evolving pandemic. It signaled the seriousness of the situation and triggered a range of actions aimed at mitigating the spread of the virus and protecting public health.
The declaration of the coronavirus as a public health emergency in the US was a stark reminder of the fragility of our well-being. It made me think about how easily things can change, and how important it is to fight for the rights we hold dear.
It’s fascinating to consider that america almost took a different path toward abortion rights , a path that could have impacted the lives of millions. Just like with the pandemic, we’re constantly learning and adapting, and the fight for our rights never truly ends.
The Declaration’s Significance
The declaration of a public health emergency empowered the US government to allocate resources, expedite research and development, and implement measures to control the outbreak. It also served as a crucial signal to the public, emphasizing the need for vigilance, adherence to public health guidelines, and cooperation in combating the pandemic.
Details of the Declaration
The US Secretary of Health and Human Services, Alex Azar, declared a public health emergency on January 31, 2020, under the authority of the Public Health Service Act. This declaration was made in response to the growing threat posed by the novel coronavirus, known as SARS-CoV-2, which had been identified as a public health emergency of international concern by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Factors Leading to the Declaration
Several factors contributed to the declaration of a public health emergency, including:* Rapid spread of the virus:The virus was spreading rapidly in China and other countries, raising concerns about its potential to become a global pandemic.
Limited understanding of the virus
At the time, there was limited knowledge about the virus’s transmission, severity, and potential for treatment.
Concerns about the US healthcare system
The declaration acknowledged the potential strain the outbreak could place on the US healthcare system, with concerns about resource availability and capacity.
Need for coordinated response
The declaration aimed to facilitate a coordinated response across federal, state, and local levels, leveraging resources and expertise to effectively address the outbreak.
Impact of the Declaration: Coronavirus Declared Public Health Emergency In Us
The declaration of a public health emergency in the US due to the coronavirus pandemic had immediate and far-reaching consequences for the nation. It signaled a shift in the government’s approach to the crisis, leading to the implementation of various measures aimed at mitigating the spread of the virus and protecting public health.
The US declared a public health emergency in response to the rapidly spreading coronavirus, but it seems some politicians aren’t taking the situation as seriously as they should. President Trump, despite the risks, says he will continue to hold outdoor rallies , potentially putting his supporters and the general public at risk.
This decision raises serious questions about his commitment to public health and safety, especially during a time when responsible action is crucial to curb the spread of the virus.
Impact on Healthcare
The declaration significantly impacted the US healthcare system. It triggered a surge in demand for medical resources, including personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilators, and hospital beds. The declaration also facilitated the rapid mobilization of healthcare professionals and the allocation of federal funds to support hospitals and research efforts.
Impact on Education
The declaration led to widespread school closures across the country. Educational institutions transitioned to remote learning models, disrupting traditional classroom settings and presenting new challenges for students, teachers, and families.
Impact on the Economy
The declaration had a profound impact on the US economy. Business closures, travel restrictions, and social distancing measures resulted in significant economic disruptions, leading to widespread job losses and a decline in economic activity. The government implemented various economic relief programs, such as the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), to mitigate the economic fallout.
Public Health Response
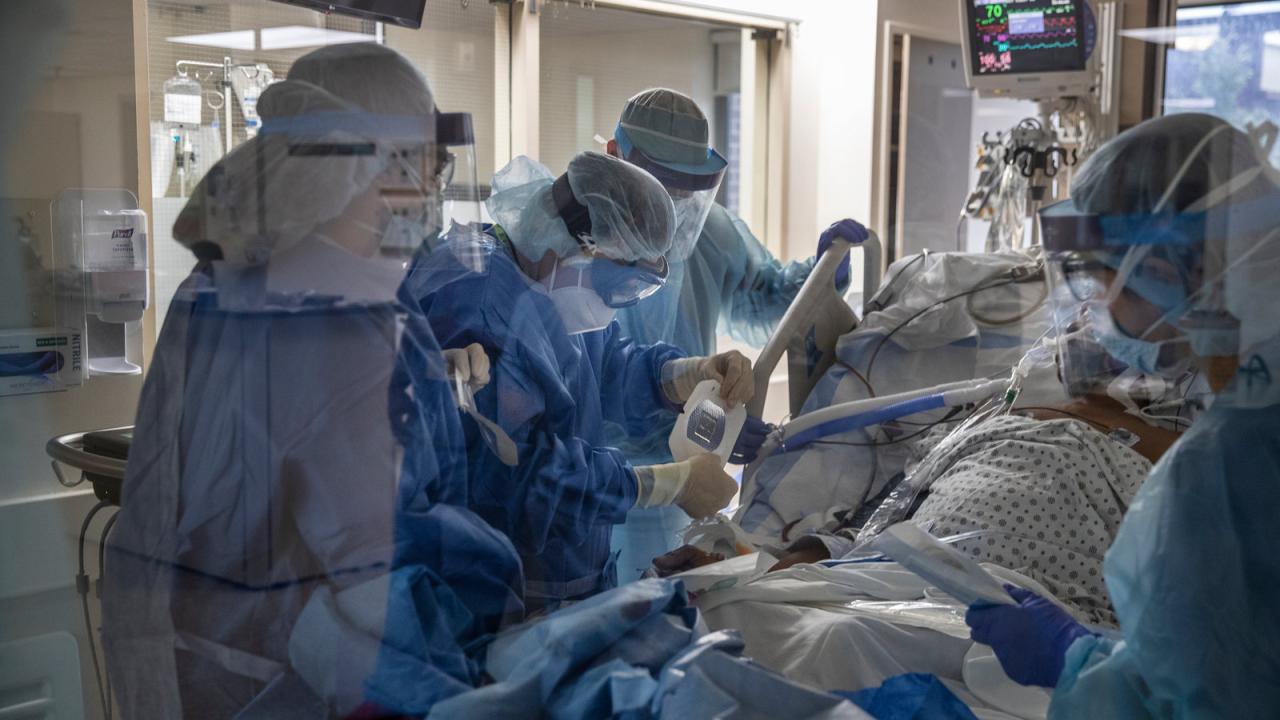
The declaration of a public health emergency in the United States due to the coronavirus outbreak triggered a multifaceted public health response aimed at mitigating the spread of the virus and protecting the population. Public health officials at all levels, from local to federal, implemented a range of strategies and initiatives, guided by scientific evidence and public health principles.
The Role of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
The CDC, as the nation’s leading public health agency, played a pivotal role in coordinating the public health response to the coronavirus outbreak. The agency’s expertise in infectious disease surveillance, outbreak investigation, and public health communication proved invaluable in guiding the nation’s efforts.
The declaration of the coronavirus as a public health emergency in the US brought about a surge in demand for apps related to health, safety, and information. This highlighted the need for a streamlined and efficient App Store, one that doesn’t harbor outdated or unsupported apps.
A clean App Store, as suggested in this article why apple needs to evict old and unsupported app store apps , would ensure users can easily access the latest and most relevant tools during times of crisis, like the pandemic, without being bogged down by outdated and potentially insecure apps.
In a time of uncertainty, a reliable and up-to-date app ecosystem is crucial, and Apple needs to take proactive steps to ensure this.
- Surveillance and Data Collection:The CDC established robust surveillance systems to track the spread of the virus, monitor disease trends, and identify emerging patterns. This data was crucial for understanding the virus’s behavior and informing public health decisions.
- Outbreak Investigation and Response:The CDC deployed teams of epidemiologists and other public health professionals to investigate outbreaks, trace contacts, and identify potential sources of transmission. This work helped to contain the spread of the virus and prevent further outbreaks.
- Guidance and Recommendations:The CDC issued a series of guidelines and recommendations for individuals, communities, and healthcare providers to mitigate the spread of the virus. These recommendations included social distancing, handwashing, wearing masks, and staying home when sick.
- Research and Development:The CDC supported research efforts to develop vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tests for COVID-19. This research was essential for improving the nation’s ability to prevent and treat the disease.
Key Public Health Messages and Recommendations
The public health response to the coronavirus outbreak relied heavily on effective communication to educate the public about the virus, its transmission, and ways to protect themselves. Public health officials emphasized key messages and recommendations that aimed to empower individuals to take proactive steps to prevent the spread of the virus.
- Social Distancing:Maintaining physical distance from others was a critical measure to reduce the risk of transmission. This involved avoiding crowded places, maintaining a distance of at least six feet from others, and limiting social gatherings.
- Handwashing:Frequent handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds was emphasized as a simple yet effective way to remove the virus from hands. Hand sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol could be used as an alternative when soap and water were not readily available.
- Face Masks:Wearing face masks in public settings became a widespread recommendation to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets. This measure was particularly important in situations where social distancing was difficult to maintain.
- Staying Home When Sick:Individuals were encouraged to stay home if they were experiencing symptoms of COVID-19, such as fever, cough, or shortness of breath. This helped to prevent the spread of the virus to others.
- Vaccination:Once COVID-19 vaccines became available, public health officials strongly encouraged vaccination as the most effective way to prevent serious illness, hospitalization, and death.
Social and Economic Implications

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on American society, leaving a lasting mark on its social fabric and economic landscape. The virus’s spread has not only disrupted daily life but also amplified existing inequalities, exposing vulnerabilities in the nation’s social safety net and economic systems.
Impact on Different Demographics
The pandemic’s effects have been unevenly distributed across different demographics, highlighting the disparities in access to healthcare, resources, and social support systems. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, individuals with underlying health conditions, and racial and ethnic minorities, have disproportionately suffered from the health and economic consequences of the virus.
- Elderly Population:The elderly are at a higher risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19. The pandemic has exacerbated social isolation among seniors, leading to increased mental health issues and reduced access to essential services.
- Individuals with Underlying Health Conditions:Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses, are more susceptible to severe COVID-19 infections. The pandemic has highlighted the need for improved access to healthcare and preventative care for these vulnerable groups.
- Racial and Ethnic Minorities:Racial and ethnic minorities have experienced higher rates of COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. These disparities are rooted in systemic inequities, including limited access to healthcare, higher rates of poverty, and essential worker roles with greater exposure to the virus.
Impact on Businesses and Industries
The pandemic has significantly disrupted businesses and industries across the US, leading to widespread job losses, business closures, and supply chain disruptions. The impact has been particularly severe in sectors heavily reliant on in-person interaction, such as hospitality, retail, and travel.
- Hospitality Industry:Restaurants, hotels, and entertainment venues have faced severe restrictions and closures, resulting in significant job losses and revenue declines. The pandemic has accelerated the shift towards online ordering and delivery services, creating opportunities for businesses that can adapt to these trends.
- Retail Industry:Non-essential retail businesses experienced temporary closures and a shift towards online shopping. The pandemic has accelerated the growth of e-commerce and the adoption of digital technologies by retailers.
- Travel Industry:The travel industry has been among the hardest hit, with travel restrictions, flight cancellations, and reduced demand significantly impacting airlines, hotels, and tourism-related businesses. The industry is expected to recover gradually as travel restrictions ease and consumer confidence returns.
Economic Impact and Recovery
The pandemic has triggered a severe economic recession, with widespread job losses, business closures, and a decline in consumer spending. The government has implemented various economic stimulus measures, including unemployment benefits, loan programs, and tax relief, to mitigate the impact of the pandemic.
- Job Losses and Unemployment:The pandemic led to a sharp increase in unemployment, with millions of Americans losing their jobs due to business closures and economic slowdown. The unemployment rate reached record highs in the spring of 2020, but has since declined as businesses reopen and the economy recovers.
- Business Closures:Many businesses, particularly small businesses, have been forced to close due to the pandemic’s economic impact. The pandemic has highlighted the importance of government support for small businesses and the need for greater flexibility in the regulatory environment.
- Economic Recovery:The US economy has begun to recover from the pandemic-induced recession, but the recovery is uneven and faces challenges, including supply chain disruptions, inflation, and labor shortages. The long-term impact of the pandemic on the economy remains uncertain.
International Cooperation and Response
The global response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been a testament to the importance of international cooperation. The sheer scale and speed of the virus’s spread demanded a coordinated effort from countries around the world, involving the sharing of information, resources, and expertise.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations played a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to combat the pandemic. The World Health Organization (WHO), in particular, emerged as a central hub for information sharing, providing guidance on public health measures, and coordinating the global response.
- The WHO declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) on January 30, 2020, signaling the urgency of the situation and the need for global action.
- The organization provided technical guidance to countries on testing, treatment, and prevention strategies, including the development and deployment of vaccines.
- The WHO also facilitated the sharing of knowledge and resources, connecting experts and researchers worldwide to accelerate research and development efforts.
Other international organizations, such as the United Nations (UN) and the World Bank, also contributed to the global response. The UN provided humanitarian assistance to countries struggling with the pandemic, while the World Bank offered financial support to help countries strengthen their health systems and mitigate the economic impact of the crisis.
Impact on Global Health Security and International Relations
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the interconnectedness of global health security and international relations. The rapid spread of the virus across borders underscored the importance of international cooperation in addressing global health threats.
- The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global health systems, including inadequate surveillance and response capabilities in many countries.
- The pandemic also strained international relations, with countries imposing travel restrictions and trade barriers to contain the spread of the virus. This, in turn, disrupted global supply chains and economies.
- The pandemic has led to a renewed focus on strengthening global health security, with countries working together to build more resilient health systems and improve pandemic preparedness.
The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of equitable access to vaccines and treatments, with calls for greater cooperation to ensure that all countries have access to the tools needed to combat the virus.
Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the US public health system and emergency preparedness infrastructure, highlighting the need for significant improvements. By analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of the response, valuable lessons can be gleaned to guide future preparedness efforts and ensure a more effective and resilient response to future public health emergencies.
Lessons Learned from the US Response to COVID-19, Coronavirus declared public health emergency in us
The US response to the COVID-19 pandemic revealed critical areas for improvement in public health preparedness.
- Early Detection and Response:The initial response to the pandemic was hampered by delays in testing and a lack of coordination among federal, state, and local agencies. This led to a slow and uneven response, allowing the virus to spread rapidly.
- Supply Chain Issues:Shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilators, and other essential medical supplies were widespread, highlighting the need for a robust and responsive supply chain.
- Communication and Public Trust:Inconsistent and conflicting messaging from public health officials eroded public trust and led to confusion and hesitancy in adopting public health recommendations.
- Social and Economic Disparities:The pandemic disproportionately impacted marginalized communities, exposing deep-seated social and economic inequalities that exacerbated the health crisis.
- Data Collection and Analysis:The lack of a centralized and comprehensive data system hindered the ability to track the spread of the virus, understand its impact, and develop effective public health interventions.
- Mental Health Impacts:The pandemic’s social isolation, economic hardship, and fear significantly impacted mental health, highlighting the need for increased mental health services and support.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Public Health System and Emergency Preparedness Measures
The US public health system and emergency preparedness measures have both strengths and weaknesses that were exposed during the pandemic.
- Strengths:
- Existing Infrastructure:The US has a well-established public health infrastructure, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and state and local health departments, which played a vital role in coordinating the response.
- Research and Development:The US has a robust research and development ecosystem that enabled the rapid development of vaccines and treatments.
- Innovation and Adaptability:The pandemic spurred innovation in areas such as telehealth, remote work, and digital contact tracing, demonstrating the US’s capacity for adaptation.
- Weaknesses:
- Funding and Staffing:Public health agencies have faced chronic underfunding and staffing shortages, limiting their capacity to respond effectively to public health emergencies.
- Coordination and Communication:The pandemic exposed weaknesses in interagency coordination and communication, leading to delays and inconsistencies in the response.
- Data Systems and Surveillance:The lack of a comprehensive and centralized data system hindered the ability to track the virus, monitor its impact, and develop effective interventions.
- Preparedness for Pandemic Threats:The US was not adequately prepared for a pandemic of this magnitude, lacking sufficient stockpiles of essential medical supplies and a robust system for rapid testing and contact tracing.
Recommendations for Improving Future Preparedness
The COVID-19 pandemic provides valuable lessons for improving future preparedness for public health emergencies.
- Strengthen Public Health Infrastructure:Increase funding for public health agencies to enhance their capacity for surveillance, disease investigation, and response.
- Improve Coordination and Communication:Establish clear lines of communication and coordination among federal, state, and local agencies to ensure a unified and effective response.
- Develop a Robust Supply Chain:Create a national stockpile of essential medical supplies and develop a more resilient supply chain to ensure access to critical resources during emergencies.
- Invest in Data Systems and Surveillance:Develop a comprehensive and centralized data system to track disease outbreaks, monitor the effectiveness of interventions, and inform public health decisions.
- Address Social and Economic Disparities:Implement policies to reduce social and economic inequalities, which disproportionately impact marginalized communities during public health emergencies.
- Strengthen Mental Health Services:Expand access to mental health services and support to address the psychological impacts of public health emergencies.
- Promote Public Trust:Establish clear and consistent communication channels to build public trust and encourage adherence to public health recommendations.
- Invest in Pandemic Research and Development:Support ongoing research into emerging infectious diseases and develop strategies for rapid vaccine and treatment development.
Closing Notes
The declaration of a public health emergency in the US was a crucial step in addressing the COVID-19 pandemic. It allowed the government to mobilize resources and implement measures that ultimately helped to slow the spread of the virus and save lives.
The experience has also highlighted the importance of robust public health infrastructure, effective communication, and international cooperation in responding to global health emergencies. The lessons learned from this unprecedented crisis will undoubtedly shape the future of public health preparedness and response for years to come.






