Consumer Confidence Plummets as Economy Weakens Further
Consumer confidence plummets as the economy weakens further, casting a shadow over the once-optimistic economic landscape. This decline in sentiment, a barometer of consumer spending, reflects a growing unease about the future. As inflation soars and interest rates rise, consumers are tightening their belts, leading to a ripple effect across industries.
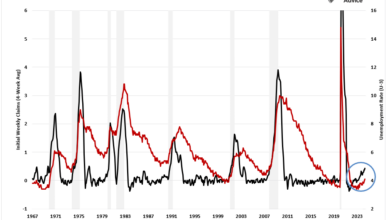
The labor market, once a beacon of strength, is now showing signs of strain, with job growth slowing and unemployment rising. These economic headwinds are creating a perfect storm, threatening to derail the fragile economic recovery.
The impact of this weakening economy on consumer spending is already being felt. Consumers are delaying major purchases, opting for cheaper alternatives, and cutting back on discretionary spending. This shift in behavior is putting pressure on businesses, forcing them to adjust their strategies and brace for a potential downturn.
The implications of this trend are far-reaching, potentially leading to a downward spiral in consumer confidence and economic activity.
Economic Indicators and Consumer Confidence
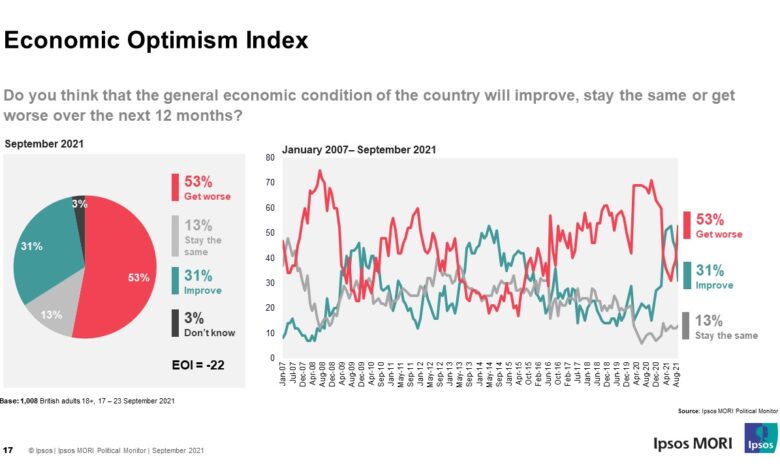
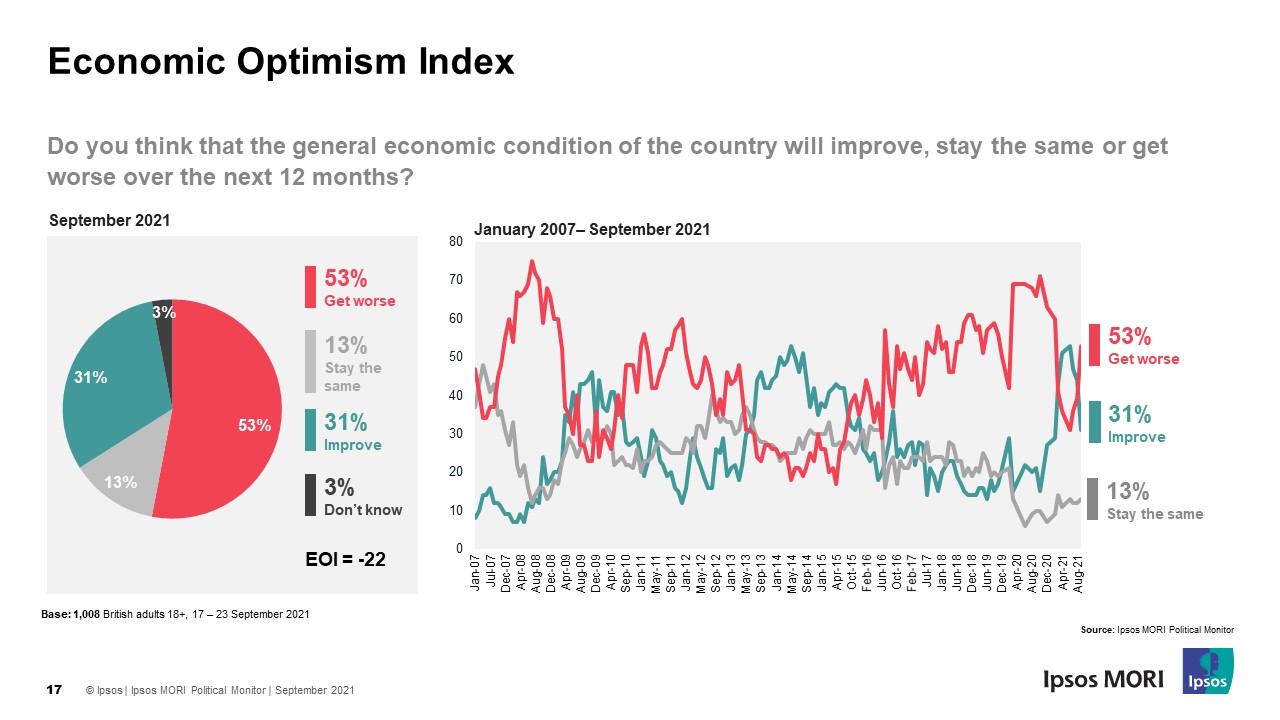
Consumer confidence, a measure of how optimistic consumers are about the economy, is a crucial indicator of economic health. It directly influences spending patterns, which drive economic growth. When consumers are confident, they are more likely to spend money, leading to increased demand for goods and services, thus boosting economic activity.
Conversely, low consumer confidence can lead to a decline in spending, potentially causing a recession.
Key Economic Indicators Influencing Consumer Sentiment
Several key economic indicators directly impact consumer sentiment and confidence. Understanding these indicators helps analyze current economic trends and predict future economic performance.
- Unemployment Rate:A low unemployment rate signifies a strong labor market, boosting consumer confidence. Job security provides financial stability and encourages spending. Conversely, a high unemployment rate can lead to job insecurity and reduced spending.
- Inflation Rate:Rising inflation erodes purchasing power, making consumers less confident about their ability to afford essential goods and services. This can lead to a decline in consumer spending and economic growth.
- Interest Rates:High interest rates increase borrowing costs, discouraging consumers from taking on debt for major purchases like homes or cars. This can dampen consumer spending and economic growth.
- Housing Market:The housing market’s performance, including home prices and mortgage rates, significantly influences consumer sentiment. A robust housing market, with rising home values, boosts consumer confidence, while a weak housing market can lead to uncertainty and reduced spending.
- Stock Market Performance:The stock market’s performance reflects investor confidence in the economy. A strong stock market can boost consumer confidence, as it indicates economic growth and potential for investment gains.
Impact of Rising Inflation and Interest Rates
Rising inflation and interest rates can significantly impact consumer confidence. Inflation erodes purchasing power, making consumers less confident about their ability to afford essential goods and services. This can lead to a decline in consumer spending and economic growth. High interest rates increase borrowing costs, discouraging consumers from taking on debt for major purchases like homes or cars.
This can further dampen consumer spending and economic growth.For example, during the 1970s, high inflation and interest rates led to a period of economic stagnation known as stagflation. Consumers became hesitant to spend due to the eroding value of their money and the high cost of borrowing.
This led to a decline in consumer spending and economic growth.
Labor Market and Consumer Spending
The labor market plays a crucial role in consumer spending and confidence. A strong labor market, characterized by low unemployment and wage growth, provides consumers with job security and financial stability. This encourages spending, leading to increased demand for goods and services.
Conversely, a weak labor market, with high unemployment and stagnant wages, can lead to job insecurity and reduced spending.For example, during the Great Recession of 2008-2009, the unemployment rate soared, leading to a significant decline in consumer spending. As businesses cut jobs and wages stagnated, consumers became hesitant to spend, contributing to the economic downturn.
Impact of Weakening Economy on Consumer Spending: Consumer Confidence Plummets As The Economy Weakens Further
A weakening economy has a significant impact on consumer spending patterns. As economic uncertainty rises, consumers tend to become more cautious with their money, leading to a decline in overall spending. This behavior is driven by several factors, including concerns about job security, rising inflation, and a decrease in disposable income.
Industries and Sectors Most Vulnerable to Declining Consumer Confidence
Industries and sectors heavily reliant on discretionary spending are most vulnerable to declining consumer confidence. These sectors include:
- Retail:Consumers may delay purchases of non-essential items, such as clothing, electronics, and furniture, when they feel economically insecure.
- Tourism and Hospitality:Travel and leisure activities are often the first to be cut back during economic downturns as consumers prioritize essential expenses.
- Automotive:New car purchases are a major discretionary expense, and consumers may choose to delay or postpone buying a new vehicle if they are concerned about their financial stability.
Implications of Reduced Consumer Spending on Business Revenue and Economic Growth
Reduced consumer spending has significant implications for businesses and the overall economy.
It’s a tough time to be a consumer. With inflation soaring and job security feeling shaky, confidence is plummeting. And things might get even worse. The Supreme Court ruling could soon make gun safety laws even weaker, potentially leading to increased violence and fear , which could further erode consumer confidence and put a strain on the already fragile economy.
- Decreased Business Revenue:Businesses in vulnerable sectors experience a decline in sales, leading to reduced revenue and potential profit losses.
- Slower Economic Growth:Consumer spending accounts for a large portion of economic activity. A decrease in spending can lead to a slowdown in economic growth, potentially causing job losses and further reducing consumer confidence.
Potential for a Downward Spiral in Consumer Confidence and Economic Activity, Consumer confidence plummets as the economy weakens further
A decline in consumer confidence can create a downward spiral in economic activity.
- Job Losses:As businesses struggle with reduced revenue, they may be forced to lay off employees, further increasing unemployment and fueling consumer anxiety.
- Reduced Investment:Businesses may become hesitant to invest in expansion or new projects due to uncertainty about future demand. This can lead to a further slowdown in economic growth.
Consumer Sentiment and Market Volatility
Consumer sentiment and stock market performance are intricately intertwined, reflecting a dynamic relationship that influences investor behavior and market volatility. As consumer confidence dips, it often signals a potential economic downturn, impacting investor sentiment and driving market fluctuations.
Impact of Declining Consumer Sentiment on Investor Behavior and Market Volatility
A decline in consumer confidence often translates to a pessimistic outlook among investors. This pessimism stems from the belief that a weakening economy will negatively impact corporate earnings, leading to decreased stock prices. Investors, anticipating a potential market downturn, may adopt a more cautious approach, reducing their exposure to riskier assets like stocks.
It’s hard to shake the feeling that the ground is shifting beneath our feet. Consumer confidence is plummeting as the economy weakens further, leaving many of us feeling anxious and uncertain about the future. And then there’s the news, which feels like a constant barrage of bad news.
Just last week, america had 3 simultaneous shootings on wednesday less than 2 weeks after uvalde , a stark reminder of the violence that plagues our society. It’s enough to make you want to pull the covers over your head and ignore everything, but we can’t.
We need to stay informed, engaged, and hopeful, even when it feels impossible.
This shift in investor behavior can trigger a sell-off, further exacerbating market volatility.
Potential for a “Flight to Safety”
As investors become risk-averse, they often seek refuge in more stable assets, known as a “flight to safety.” This typically involves shifting investments from stocks to bonds, gold, or other safe-haven assets perceived to be less vulnerable to economic downturns.
With consumer confidence plummeting as the economy weakens further, businesses are facing a new reality. Many companies are reevaluating their office spaces and exploring ways to adapt to the rise of remote work. Check out this insightful article on council post three ways to transform your commercial office space in response to remote work for some innovative ideas on how to transform your office space into a more collaborative and flexible environment.
These changes are essential for businesses to remain competitive and attract talent in a challenging economic landscape.
This influx of demand for safe-haven assets can drive their prices up, while simultaneously pushing stock prices down, further amplifying market volatility.
Key Indicators of a Shift in Market Sentiment Driven by Consumer Confidence
Several key indicators signal a shift in market sentiment driven by consumer confidence. These include:
- Consumer Confidence Index (CCI):This widely-tracked index measures consumer sentiment based on surveys regarding their perceptions of the economy, employment, and personal finances. A decline in the CCI often indicates a weakening consumer outlook, which can trigger a sell-off in the stock market.
- Retail Sales:A decline in retail sales can signal a decrease in consumer spending, reflecting a weakening economy and potentially impacting corporate earnings. This can lead to a decline in stock prices, as investors anticipate reduced profitability for companies.
- Unemployment Rate:An increase in the unemployment rate indicates a weakening labor market, which can erode consumer confidence and lead to reduced spending. This, in turn, can negatively impact corporate earnings and trigger a decline in stock prices.
Government Policies and Consumer Confidence
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping consumer confidence and influencing economic activity. Consumers often base their spending decisions on their perception of the current and future economic outlook, which is heavily influenced by government actions.
Fiscal and Monetary Policies
Fiscal and monetary policies are the primary tools governments use to manage the economy. Fiscal policy involves government spending and taxation, while monetary policy focuses on controlling the money supply and interest rates. These policies can significantly impact consumer confidence by influencing factors such as employment, income, and inflation.
Effectiveness of Fiscal and Monetary Policies
The effectiveness of fiscal and monetary policies in mitigating the effects of economic weakness varies depending on several factors, including the severity of the downturn, the structure of the economy, and the credibility of the government’s policies.
- Expansionary fiscal policy, such as increased government spending or tax cuts, can stimulate demand and boost economic growth. However, it can also lead to higher government debt and inflation if not implemented effectively.
- Expansionary monetary policy, such as lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply, can encourage borrowing and investment, leading to higher economic activity. However, it can also contribute to asset bubbles and inflation if not carefully managed.
Policy Interventions to Boost Consumer Confidence
Governments can implement various policy interventions to boost consumer confidence and stimulate economic growth. These interventions can include:
- Targeted tax cutsfor low- and middle-income households can increase disposable income and stimulate consumer spending.
- Investing in infrastructurecan create jobs and improve productivity, leading to long-term economic growth and increased consumer confidence.
- Providing subsidies or grantsto businesses can encourage investment and job creation, ultimately benefiting consumers.
- Strengthening social safety nets, such as unemployment insurance and food assistance, can provide a safety net for consumers during economic downturns, reducing anxiety and boosting confidence.
Comparative Approaches of Different Governments
Different governments adopt different approaches to addressing economic challenges, based on their political ideologies and economic circumstances.
Examples of Different Approaches
- Keynesian economics, often adopted by left-leaning governments, emphasizes government intervention to stimulate demand and stabilize the economy. This approach typically involves increased government spending and tax cuts during economic downturns.
- Monetarist economics, favored by right-leaning governments, emphasizes controlling the money supply to stabilize the economy. This approach typically involves limiting government spending and relying on market forces to drive economic growth.
Final Summary
The current economic climate is a complex and challenging one. The decline in consumer confidence, coupled with a weakening economy, presents a formidable obstacle to sustained economic growth. The government must take decisive action to address these challenges, implementing policies that stimulate consumer spending, boost business confidence, and create a more stable economic environment.
It is only through a concerted effort that we can navigate these turbulent waters and chart a course towards a brighter economic future.