Chinas Coronavirus Numbers Dont Add Up, and the White House Doubts Them
Chinas coronavirus numbers dont add up and the white house doesnt believe them – China’s coronavirus numbers don’t add up, and the White House doesn’t believe them. This has become a major point of contention, raising questions about transparency and trust in the face of a global pandemic. While China claims to have successfully contained the virus, many experts and governments around the world remain skeptical, citing inconsistencies in reported data and concerns about potential underreporting.
This skepticism has fueled tensions between China and the United States, with the White House expressing doubts about the reliability of China’s numbers and calling for greater transparency.
The discrepancies between China’s reported data and estimates from other sources have led to a debate about the true extent of the pandemic in China. Some experts believe that the actual number of cases and deaths may be significantly higher than what has been officially reported.
The lack of reliable data makes it difficult to assess the effectiveness of China’s containment measures and to predict the potential for future outbreaks. This uncertainty has also hampered global efforts to coordinate pandemic response strategies, as countries rely on accurate data to make informed decisions about travel restrictions, resource allocation, and vaccine development.
Transparency and Accuracy of China’s COVID-19 Data
The accuracy and transparency of China’s official COVID-19 data have been a subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny since the early days of the pandemic. While China has been lauded for its swift and decisive actions in containing the initial outbreak, concerns have been raised about the reliability of its reported case numbers, fueling suspicions of underreporting and a lack of transparency.The discrepancies between China’s official data and estimates from other sources have led to skepticism about the true extent of the pandemic in the country.
These discrepancies have raised questions about the reliability of China’s data and its potential impact on global pandemic response efforts.
Potential Reasons for Discrepancies
Several factors may contribute to the discrepancies between China’s reported data and estimates from other sources. * Changes in Testing and Reporting Criteria:China has adjusted its testing and reporting criteria throughout the pandemic, potentially impacting the number of cases reported.
Focus on Asymptomatic Cases
China’s emphasis on identifying and isolating asymptomatic cases might lead to an underestimation of overall cases, as many asymptomatic individuals may not be tested or reported.
Data Collection and Reporting System
China’s data collection and reporting system may not be as robust as those in other countries, leading to potential inaccuracies and underreporting.
Political Considerations
Concerns about the potential impact of reporting high case numbers on public morale and the economy may influence China’s reporting practices.
Examples of Questioned Data
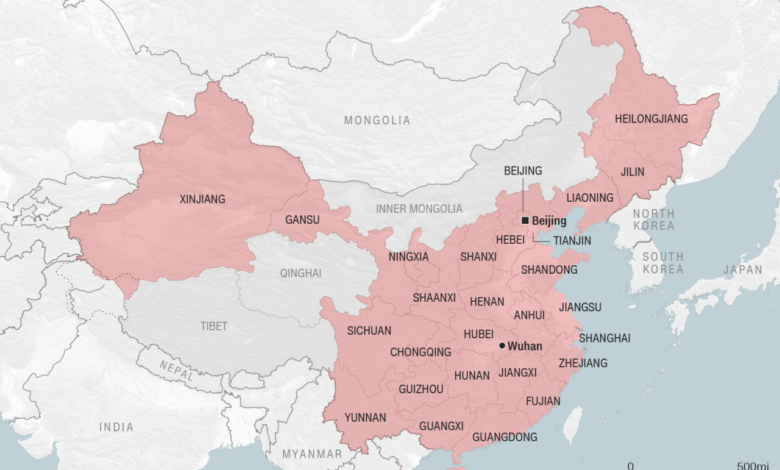
There have been several instances where China’s COVID-19 data has been questioned or disputed.* Early Stages of the Pandemic:In the early stages of the pandemic, China’s reported case numbers were significantly lower than estimates from other sources, particularly in Wuhan, the epicenter of the outbreak.
It’s hard to ignore the inconsistencies in China’s COVID-19 reporting, and the White House’s skepticism is understandable. While the world grapples with the pandemic’s impact, it’s interesting to see how political controversies like the one detailed in a New Book Explores Clinton-Lynch Tarmac Meeting can sometimes overshadow global health concerns.
Ultimately, though, the accuracy of China’s data remains a crucial factor in effectively addressing the pandemic’s global spread.
Hubei Province
Data from Hubei Province, where Wuhan is located, showed a sudden drop in reported cases in February 2020, raising questions about the accuracy of the data.
Zero-COVID Policy
The White House’s skepticism towards China’s coronavirus numbers is understandable, given the ongoing tensions between the two nations. It’s a reminder that even amidst a global pandemic, political maneuvering continues. Meanwhile, the Trump Campaign Fires Back After Obama Claims Economic Boom Credit highlights how quickly the focus can shift from a global crisis to domestic politics.
It’s a reminder that even amidst a global crisis, political maneuvering continues.
China’s strict “zero-COVID” policy, which aims to eliminate all cases through widespread testing, lockdowns, and quarantine measures, has led to criticism that the policy has resulted in underreporting of cases.
Impact of Underreporting on Global Response
Underreporting of COVID-19 cases in China could have significant implications for global pandemic response efforts.* Accurate Pandemic Assessment:Accurate data is crucial for understanding the true scale of the pandemic and making informed decisions about public health measures.
Global Spread
Underreporting in one country can lead to an underestimation of the pandemic’s global spread, potentially delaying or hindering effective response efforts.
The White House’s skepticism about China’s COVID-19 numbers is understandable, given the country’s history of opaque reporting. Meanwhile, the news that Border Patrol will deploy elite tactical agents in sanctuary cities raises questions about the administration’s priorities. While focusing on immigration, it seems the administration is still struggling to get a handle on the global pandemic and its implications for national security.
Development of Vaccines and Treatments
Accurate data on the prevalence and characteristics of the virus is essential for the development of effective vaccines and treatments.
The White House’s Position on China’s COVID-19 Data
The White House has expressed significant skepticism regarding the reliability of China’s COVID-19 data, raising concerns about transparency and accuracy. This stance has had notable implications for bilateral relations and international cooperation, as well as influencing public trust and perceptions of the pandemic.
The White House’s Stance on Data Reliability
The White House has consistently voiced concerns about the transparency and accuracy of China’s COVID-19 data. These concerns stem from a perceived lack of information sharing and potential underreporting of cases, particularly in the early stages of the pandemic. This skepticism has been expressed through various statements and actions.
Statements and Actions Expressing Skepticism, Chinas coronavirus numbers dont add up and the white house doesnt believe them
- In 2020, then-President Donald Trump repeatedly criticized China’s handling of the pandemic, accusing the country of withholding information and downplaying the severity of the virus.
- The Trump administration also imposed travel restrictions on China, citing concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
- The Biden administration has continued to express concerns about China’s data transparency, calling for greater cooperation and information sharing.
- The White House has also pointed to discrepancies between China’s official figures and estimates from independent sources, further fueling skepticism.
Implications for Bilateral Relations and International Cooperation
The White House’s stance on China’s COVID-19 data has significantly impacted bilateral relations and international cooperation. The lack of trust and transparency has strained diplomatic ties, hindering collaborative efforts to address the pandemic.
Impact on Public Trust and Perceptions of the Pandemic
The White House’s skepticism has also influenced public trust and perceptions of the pandemic. Public distrust in China’s data can lead to skepticism about the global response to the virus, potentially hindering public health efforts and hindering global cooperation.
International Perspectives on China’s COVID-19 Data: Chinas Coronavirus Numbers Dont Add Up And The White House Doesnt Believe Them
The transparency and accuracy of China’s COVID-19 data have been a subject of intense scrutiny and debate globally. Different countries and international organizations hold diverse views on the reliability of China’s reported figures, influenced by a complex interplay of political considerations, scientific assessments, and national interests.
Comparative Analysis of International Perspectives
The international community’s response to China’s COVID-19 data has been characterized by a spectrum of opinions, ranging from cautious skepticism to outright criticism.
- The World Health Organization (WHO), while acknowledging the challenges in data collection and reporting, has generally maintained a cautious stance, emphasizing the need for collaboration and transparency. The WHO has consistently called for China to share more detailed data and information to facilitate a better understanding of the pandemic’s evolution.
- The United States, under the Trump administration, was particularly vocal in its criticism of China’s data, alleging underreporting and a lack of transparency. This stance was largely driven by political tensions and the desire to hold China accountable for the pandemic’s global spread.
- The European Union, while expressing concerns about data accuracy, has adopted a more diplomatic approach, urging China to improve its data collection and reporting practices. The EU has also emphasized the importance of international collaboration and information sharing to effectively combat the pandemic.
- Several countries in Asia, particularly those with close economic ties to China, have generally been more hesitant to publicly criticize China’s data, often citing the need for regional solidarity and cooperation.
Potential Biases and Political Considerations
The varying perspectives on China’s COVID-19 data are often influenced by a complex interplay of political considerations, national interests, and geopolitical dynamics.
- The US, for example, has been highly critical of China’s handling of the pandemic, viewing it as a potential strategic rival and seeking to undermine its international standing. This has led to a more confrontational approach in questioning China’s data and demanding greater transparency.
- Conversely, some countries in Asia, particularly those reliant on China for economic and trade relations, have been more reluctant to criticize China’s data, fearing potential economic repercussions or strained relations.
- The WHO, as an international organization, has a vested interest in fostering collaboration and information sharing among member states. This has led to a more conciliatory approach, seeking to work with China to improve its data reporting practices rather than engage in public criticism.
Impact on Global Pandemic Response Strategies
Varying interpretations of China’s COVID-19 data have had significant implications for global pandemic response strategies.
- The lack of reliable data from China has made it difficult to accurately assess the global spread of the virus and develop effective containment measures.
- Disagreements over the accuracy of China’s data have also contributed to mistrust and skepticism among countries, hindering international cooperation and information sharing.
- Some countries have adopted stricter travel restrictions and quarantine measures based on their own assessments of the situation in China, even in the absence of complete and accurate data.
Consequences of Differing Perspectives
The divergence in perspectives on China’s COVID-19 data has raised concerns about the potential for:
- Reduced international collaboration and information sharing, hampering efforts to effectively combat the pandemic.
- Increased geopolitical tensions and mistrust, further complicating global efforts to address the pandemic.
- Misallocation of resources and ineffective pandemic response strategies due to inaccurate or incomplete data.
The Role of Independent Verification
In the face of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the accuracy and transparency of data reported by countries, particularly China, have become critical concerns. Independent verification plays a crucial role in assessing the reliability of reported data and ensuring public trust.
Independent verification refers to the process of examining and evaluating data by external and impartial entities to determine its accuracy and completeness. It is essential for establishing credibility and accountability, especially in situations where there are concerns about potential biases or manipulation of data.
Challenges and Limitations of Independent Verification
Independent verification of China’s COVID-19 data faces significant challenges. The Chinese government has been criticized for its lack of transparency and its control over information flow.
- Limited Access to Data:Independent verifiers often face difficulties obtaining comprehensive and reliable data from the Chinese government. This lack of access can hinder their ability to conduct thorough assessments.
- Lack of Collaboration:The Chinese government’s reluctance to collaborate with international organizations and independent researchers further complicates verification efforts.
- Language and Cultural Barriers:Language and cultural differences can create communication barriers and make it challenging to interpret data accurately.
- Political Considerations:Political sensitivities surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic can influence the willingness of the Chinese government to cooperate with independent verification efforts.
Methods and Effectiveness of Independent Verification
Despite these challenges, various methods have been employed to independently verify China’s COVID-19 data. These methods include:
- Satellite Imagery Analysis:Analyzing satellite images to assess the scale of construction activities related to hospitals and crematoriums can provide insights into the potential number of COVID-19 cases.
- Social Media Monitoring:Monitoring social media platforms for mentions of COVID-19 symptoms, hospital visits, and related s can offer clues about the spread of the virus.
- Data Comparison:Comparing China’s reported data with data from neighboring countries and international organizations can help identify discrepancies and potential inconsistencies.
- Statistical Modeling:Utilizing statistical models based on population demographics and mobility patterns can provide estimates of the actual number of cases.
Impact of Independent Verification on Transparency and Accountability
Independent verification plays a crucial role in promoting transparency and accountability by:
- Enhancing Trust:Independent verification can help build trust in the reported data by providing external validation and reducing concerns about potential manipulation.
- Improving Data Quality:The process of verification can lead to improvements in data collection, reporting, and analysis, ultimately enhancing the accuracy and reliability of data.
- Holding Governments Accountable:Independent verification can expose inconsistencies or inaccuracies in reported data, holding governments accountable for their actions and promoting transparency.
Impact on Public Health and Global Response
The accuracy and completeness of data are paramount to effective public health responses, particularly during pandemics. Inaccurate or incomplete data about the spread and severity of a disease can have profound consequences, impacting the effectiveness of pandemic response strategies and potentially leading to worse health outcomes.
Consequences of Inaccurate Data on Public Health
Inaccurate or incomplete data can significantly hinder pandemic response efforts. It can lead to:* Misallocation of resources:Incorrect data about the prevalence and severity of a disease can result in the misallocation of resources, such as medical supplies, personnel, and funding. This can leave vulnerable populations underserved and exacerbate health disparities.
Ineffective interventions
Based on inaccurate data, public health officials might implement ineffective or inappropriate interventions, such as lockdowns or travel restrictions, that fail to achieve their intended goals or even worsen the situation.
Delayed response
Inaccurate data can delay the identification and containment of a disease outbreak, allowing it to spread further and potentially leading to more severe consequences.
Public mistrust
If data is perceived as unreliable or manipulated, it can erode public trust in official information and make it harder to implement effective public health measures.
Misinformation and rumors
Inaccurate data can create a vacuum for misinformation and rumors to spread, leading to public panic and confusion.
Impact on Global Preparedness and Resource Allocation
Inaccurate data about the spread of a disease can significantly impact global preparedness and resource allocation. * International coordination:Accurate data is crucial for international coordination efforts to contain a pandemic. If countries have differing or inaccurate data, it can lead to conflicting policies and strategies, hindering global cooperation.
Resource allocation
International organizations and donor agencies rely on accurate data to allocate resources effectively to countries in need. Inaccurate data can lead to resources being directed to areas where they are not needed or away from areas that require them.
Vaccine and treatment development
Accurate data about the prevalence, severity, and characteristics of a disease are essential for developing and deploying effective vaccines and treatments.
Implications for Vaccine and Treatment Development
Accurate data about the disease, including its prevalence, severity, and mutations, are crucial for developing effective vaccines and treatments. * Clinical trials:Inaccurate data can lead to biased or inconclusive results in clinical trials, delaying the development of effective vaccines and treatments.
Production and distribution
Accurate data about the projected demand for vaccines and treatments is crucial for ensuring timely production and distribution to those who need them.
Targeting interventions
Accurate data about the characteristics of a disease can help researchers target interventions more effectively, such as developing vaccines that are tailored to specific strains or populations.
Examples of Inaccurate Data Affecting Pandemic Response
Several examples illustrate how inaccurate data can negatively impact pandemic response strategies:* Early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic:In the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, China’s reported case numbers were significantly lower than what was estimated by international experts, raising concerns about data transparency and accuracy.
This lack of reliable data hindered global preparedness and resource allocation.
H1N1 pandemic
During the H1N1 pandemic, some countries initially underreported cases, leading to a delayed response and an underestimation of the true scale of the outbreak. This contributed to the widespread panic and disruption that characterized the pandemic.
Ebola outbreak
In the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, inaccurate data about the number of cases and deaths hampered response efforts and led to a slower containment of the epidemic.
Concluding Remarks
The controversy surrounding China’s coronavirus numbers highlights the importance of transparency and accountability in global health emergencies. While China has taken steps to improve its data reporting, concerns remain about the accuracy and completeness of its data. The White House’s skepticism, coupled with the lack of independent verification, has further complicated the situation.
Moving forward, it is crucial for all countries to prioritize data transparency and collaboration to ensure an effective and coordinated global response to future pandemics.






