Census Map Shows Dramatic California Exodus
Census Map Shows Dramatic California Exodus, a stark visual representation of a demographic shift that’s reshaping the Golden State. The map reveals a significant population decline, particularly in key counties, prompting questions about the driving forces behind this exodus and its potential impact on California’s future.
The exodus is a complex phenomenon with roots in economic, social, and political factors. The high cost of living, housing affordability crisis, and limited job opportunities are among the economic pressures driving Californians away. Additionally, taxes, regulations, and cultural trends play a role in the decision-making process for many.
Understanding the motivations behind this exodus is crucial to addressing its consequences and exploring potential solutions.
The Exodus Phenomenon
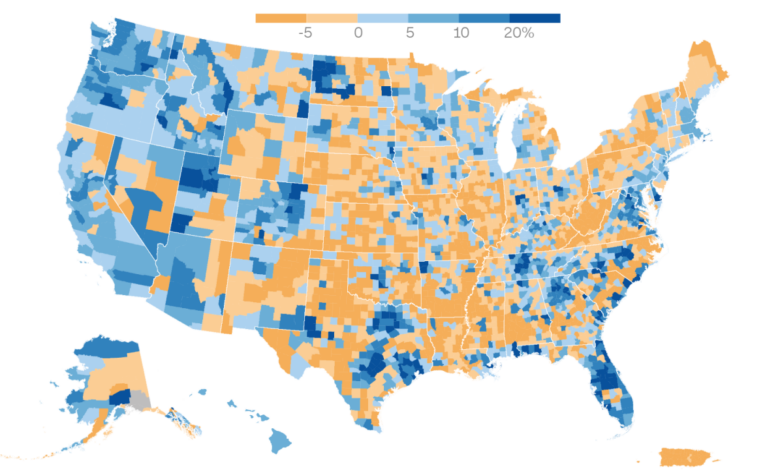
The recent census map paints a stark picture of the California exodus, revealing a significant shift in population dynamics within the state. The map, a visual representation of population changes, highlights the areas experiencing population losses, providing valuable insights into the reasons behind this demographic shift.
Demographic Shifts Revealed by the Map
The census map reveals a clear trend of population decline in several California counties, particularly in the northern and central regions. The map showcases the areas experiencing the most significant population losses, shedding light on the underlying factors driving this exodus.
Counties Experiencing the Most Significant Population Losses
The census map pinpoints the counties experiencing the most significant population losses, highlighting the magnitude of the exodus. The map illustrates the geographical distribution of population decline, revealing the areas most affected by this trend.
- Counties in Northern California:Several counties in Northern California, including Siskiyou, Modoc, and Lassen, have experienced significant population declines. These counties have historically relied on agriculture and resource extraction, which have been impacted by economic changes and environmental factors.
- Counties in Central California:Counties in Central California, such as Madera, Merced, and Tulare, have also witnessed notable population losses. These counties have experienced challenges related to agriculture, water scarcity, and economic opportunities.
Historical Context of Population Movements in California
The current exodus is not an isolated event; it is part of a broader historical context of population movements in California. The state has experienced waves of migration and population shifts throughout its history, driven by various factors, including economic opportunities, technological advancements, and social trends.
Driving Forces Behind the Exodus: Census Map Shows Dramatic California Exodus
California’s population decline, often referred to as the “California Exodus,” is a complex phenomenon driven by a confluence of factors. This trend has been particularly pronounced in recent years, prompting many to question the reasons behind this demographic shift. Understanding the underlying forces driving this exodus is crucial for comprehending the changing landscape of California and its implications for the future.
Economic Factors
The high cost of living in California, particularly in major metropolitan areas, is a primary driver of the exodus. Housing affordability has become a major concern, with median home prices significantly exceeding the national average. The soaring cost of housing is fueled by a combination of factors, including limited housing supply, high demand, and a robust real estate market.
This affordability crisis disproportionately impacts lower- and middle-income households, forcing many to seek more affordable housing options in other states.Furthermore, California’s tax structure, including high income and property taxes, can be a deterrent for some individuals and businesses. The state’s progressive tax system, while designed to generate revenue for public services, can be perceived as burdensome by high earners, particularly those in the technology and finance sectors.
This perception can lead to outmigration, as individuals and businesses seek lower tax burdens in other states.
“California’s high cost of living, particularly housing costs, is a major factor driving the exodus. The state’s tax structure, including high income and property taxes, also plays a role.”
The recent census map showing a dramatic California exodus is making headlines, and it’s got me wondering if the political landscape is shifting too. It’s interesting to note that just as these population trends emerge, we’re seeing a veteran politician like longtime Democrat senator announces she wont seek another term decide to step aside.
Could this be a sign of changing times, or just a coincidence? Only time will tell how these events will shape California’s future.
Social and Political Factors, Census map shows dramatic california exodus
Social and political factors also contribute to the California exodus. California is known for its progressive policies and liberal values, which can be appealing to some but also a deterrent to others. For example, the state’s stringent environmental regulations, while intended to protect the environment, can be seen as burdensome by some businesses.
Additionally, cultural trends, such as the increasing diversity of the state’s population, can lead to a sense of cultural shift for some residents.
“California’s progressive policies and liberal values, while appealing to some, can also be a deterrent to others.”
Motivations of Different Demographic Groups
The motivations for leaving California vary among different demographic groups. Younger adults, particularly those with families, may be driven by the desire for more affordable housing and better educational opportunities for their children. Retirees may seek lower taxes and a more relaxed lifestyle in other states.
High-income earners, particularly in the technology and finance sectors, may be attracted by lower taxes and a more business-friendly environment in other states.
“The motivations for leaving California vary among different demographic groups, including younger adults, retirees, and high-income earners.”
The Impact of the Exodus on California
The exodus of residents from California, driven by factors like high cost of living, taxes, and political climate, is having a profound impact on the state’s economy, social fabric, and future. While the exodus presents challenges, it also offers opportunities for California to re-evaluate its policies and priorities.
Economic Consequences
The population decline in California is leading to a shrinking workforce, which can impact economic growth and job creation. This can be particularly challenging for industries that rely on a large labor pool, such as technology, healthcare, and manufacturing. Additionally, the exodus is affecting the housing market, with some areas experiencing a decline in property values and rental rates.
This can impact local economies and property taxes, which are a significant source of revenue for the state. The exodus also reduces the state’s tax base, leading to lower revenues. This can strain public services and make it more difficult to fund essential programs.
Social and Political Implications
The exodus is changing the demographics of California, with a decline in the number of younger residents and an increase in the proportion of older residents. This shift in demographics can affect voting patterns and political priorities. The exodus is also affecting the provision of public services.
As the population declines, there may be fewer resources available for schools, hospitals, and other public services. This can lead to challenges in meeting the needs of a shrinking population and could exacerbate existing inequalities.
The census map showing a dramatic California exodus is a stark reminder of the challenges facing the state. It’s not just high housing costs that are driving people away, but also a sense of uncertainty in the economy. This is especially concerning considering news from Wells Fargo, which is warning customers of incorrect balances or missing transactions , potentially adding another layer of financial stress for residents already considering leaving.
Whether it’s the cost of living or financial instability, it seems the Golden State is losing its shine for many.
Long-Term Effects
The exodus could have long-term consequences for California’s economy and social fabric. The decline in population could lead to a decrease in economic growth and a decline in the state’s overall competitiveness. The exodus could also exacerbate social inequalities, with some communities disproportionately affected by the loss of residents and resources.
Strategies to Address the Exodus
California is implementing a number of strategies to address the exodus and its consequences. These strategies include:
- Investing in Affordable Housing:The state is investing in programs to create more affordable housing options for residents. This includes expanding the supply of affordable rental units and providing subsidies to help people purchase homes.
- Reducing the Cost of Living:The state is exploring ways to reduce the cost of living, such as lowering taxes and providing tax credits to low- and middle-income residents.
- Improving Public Services:The state is investing in programs to improve public services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. This includes increasing funding for schools, hospitals, and transportation systems.
- Promoting Economic Growth:The state is implementing policies to promote economic growth and job creation. This includes investing in research and development, supporting small businesses, and attracting new industries to California.
Destination States and Their Experiences
The California exodus has not only impacted the Golden State but has also significantly influenced the demographic landscapes of several destination states. These states, often considered more affordable or offering a different lifestyle, have experienced a surge in new residents from California, bringing both opportunities and challenges.
Top Destination States
The top states receiving migrants from California are primarily located in the South and the Mountain West, driven by factors like lower cost of living, favorable tax policies, and attractive climate. These states include:
- Texas: With a booming economy and a business-friendly environment, Texas has become a major draw for Californians. Its low cost of living, particularly in housing, is a significant attraction.
- Arizona: Arizona’s warm climate, low taxes, and growing job market have made it a popular destination for Californians seeking a more affordable lifestyle.
- Nevada: Nevada’s low taxes, gambling industry, and booming tourism sector have attracted many Californians, particularly to the Las Vegas metropolitan area.
- Idaho: Idaho’s natural beauty, affordable housing, and conservative political climate have appealed to Californians seeking a change of pace.
- Oregon: While Oregon has a higher cost of living than some other destination states, its natural beauty, progressive policies, and tech industry have attracted many Californians.
Economic and Social Environments
The economic and social environments of these destination states vary significantly.
- Texas: Texas boasts a robust economy, with major industries including energy, technology, and healthcare. Its low cost of living and business-friendly policies attract many entrepreneurs and businesses.
- Arizona: Arizona’s economy is driven by tourism, manufacturing, and technology. Its low cost of living and growing job market make it attractive for retirees and young professionals.
- Nevada: Nevada’s economy is heavily reliant on tourism and gambling. Its low taxes and booming tourism sector attract many service workers and entertainment professionals.
- Idaho: Idaho’s economy is largely driven by agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing. Its low cost of living and natural beauty attract retirees and outdoor enthusiasts.
- Oregon: Oregon’s economy is driven by technology, manufacturing, and agriculture. Its progressive policies and natural beauty attract many tech workers and environmentalists.
Challenges and Opportunities
The influx of Californians presents both challenges and opportunities for destination states.
The recent census map showing a dramatic California exodus has sparked a lot of debate. Some attribute it to high cost of living, while others point to political and social changes. Interestingly, this trend comes at a time when the House GOP is introducing a “Parents Bill of Rights” – house gop introduces parents bill of rights speaker mccarthy promises action on historic milestone – which could further influence families’ decisions about where to live.
It’ll be interesting to see how this legislation impacts the ongoing exodus from California.
- Challenges:
- Housing Market Pressures: The influx of Californians can put pressure on housing markets, leading to rising prices and reduced affordability for existing residents.
- Infrastructure Strain: The influx of new residents can strain existing infrastructure, such as roads, schools, and public services.
- Social and Cultural Shifts: The influx of Californians can bring changes to the social and cultural landscape of destination states, potentially leading to conflicts over values and priorities.
- Opportunities:
- Economic Growth: The influx of Californians can bring new businesses, investments, and jobs to destination states.
- Increased Diversity: The influx of Californians can increase the diversity of destination states, enriching their cultural and social landscapes.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Californians often bring with them innovative ideas and entrepreneurial spirit, which can contribute to the growth of destination states.
Impact on National Demographic Landscape
The California exodus is significantly impacting the national demographic landscape.
- Shifting Population Centers: The exodus is contributing to a shift in population centers from the West Coast to the South and Mountain West.
- Political Implications: The influx of Californians, often with liberal political leanings, can influence the political landscape of destination states, potentially shifting their political affiliations.
- Cultural Exchange: The migration of Californians to other states fosters cultural exchange, bringing new ideas, perspectives, and traditions to destination states.
Perspectives and Opinions on the Exodus
The California exodus has sparked a diverse range of opinions and perspectives, from those who have left the state to those who have chosen to stay, and from experts who analyze the phenomenon to policymakers who grapple with its implications.
Understanding these perspectives is crucial to comprehending the complex factors driving the exodus and its potential impact on California and its destination states.
Perspectives of Californians Who Have Left
Californians who have left the state offer a variety of reasons for their departure, often citing a combination of factors.
- High Cost of Living:Many cite the high cost of housing, taxes, and other living expenses as a primary reason for leaving. They often seek more affordable options in other states.
- Political Climate:Some express dissatisfaction with the state’s political climate, including policies they perceive as unfavorable.
- Quality of Life:Others prioritize factors like lower crime rates, better access to nature, and a slower pace of life, which they find more appealing in other states.
- Career Opportunities:Some individuals relocate for career opportunities, particularly in industries where growth is more pronounced in other states.
Perspectives of Californians Who Have Stayed
Those who have chosen to stay in California often express a deep love for the state, highlighting its unique advantages.
- Cultural Diversity and Opportunities:They appreciate the state’s cultural richness, diverse communities, and abundant opportunities in various fields.
- Climate and Lifestyle:Many cherish California’s climate, beaches, and outdoor recreation opportunities.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship:They value the state’s role as a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship, with thriving industries like technology and entertainment.
- Strong Economy and Job Market:California’s strong economy and robust job market offer opportunities for career advancement and financial stability.
Perspectives of Experts and Policymakers
Experts and policymakers offer a range of insights into the exodus, its causes, and its potential implications.
- Economic Factors:Some experts emphasize the role of economic factors, including the high cost of living and the changing nature of the economy, in driving the exodus.
- Social and Political Factors:Others highlight the influence of social and political factors, such as dissatisfaction with government policies and concerns about social issues.
- Demographic Trends:Policymakers analyze demographic trends, including the aging population and the growing demand for affordable housing, to understand the exodus’s impact.
- Impact on California and Destination States:Experts study the effects of the exodus on California’s economy, housing market, and demographics, as well as the implications for destination states.
Comparison of Living in California vs. Destination States
| Factor | California | Destination States (e.g., Texas, Arizona, Nevada) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost of Living | High | Generally Lower |
| Housing Costs | Very High | Lower, but Increasing in Some Areas |
| Taxes | High | Generally Lower |
| Climate | Mild, Mediterranean | Vary Widely (e.g., Desert, Hot, Humid) |
| Job Market | Strong, Diverse | Growing in Some Industries, but Can Be Less Diverse |
| Quality of Life | Subjective, Varies by Location | Subjective, Varies by Location |
Closing Notes
The California exodus is a multifaceted story that highlights the challenges and opportunities facing the state. As Californians continue to seek new horizons, the economic, social, and political landscape of the state is undergoing a transformation. The exodus serves as a wake-up call for California to address its underlying issues and explore innovative strategies to attract and retain residents while adapting to the changing demographic landscape.

