CDC Spreads False Info on COVID-19 Vaccine Safety
Cdc spreads false information about covid 19 vaccine safety monitoring – CDC Spreads False Info on COVID-19 Vaccine Safety: a claim that has sparked heated debate and raised concerns about the reliability of public health information. This accusation, often circulating online, alleges that the CDC is misrepresenting data or downplaying potential risks associated with COVID-19 vaccines.
While the CDC plays a crucial role in vaccine safety monitoring, the claim of deliberate misinformation raises serious questions about public trust and the scientific process.
It’s important to dissect these claims and examine the evidence. The CDC employs various surveillance systems, including the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), to track potential vaccine side effects. While VAERS is a valuable tool, it’s essential to understand its limitations.
The system relies on self-reporting, which can be prone to bias and inaccurate information. Additionally, a correlation between a vaccine and a health event does not necessarily mean the vaccine caused it.
CDC’s Vaccine Safety Monitoring System
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a critical role in ensuring the safety of vaccines, a vital component of public health. To achieve this, the CDC employs a robust vaccine safety monitoring system that includes various surveillance programs and data analysis techniques.
It’s becoming increasingly clear that the CDC has been spreading misinformation about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccines, and their lack of transparency is alarming. It’s hard to ignore the parallels to the claims made by Dr. Scott Atlas, a former White House advisor, who says Twitter’s censorship of COVID-19 information led to loss of life.
Both instances highlight the dangers of suppressing dissenting voices and the potential for harm when government agencies prioritize narrative over truth.
The CDC’s Role in Vaccine Safety Monitoring
The CDC’s primary responsibility in vaccine safety monitoring is to detect, investigate, and prevent potential safety issues associated with vaccines. This involves collecting and analyzing data from multiple sources, including healthcare providers, vaccine manufacturers, and the public, to identify any unusual patterns or adverse events that may be linked to vaccines.
The CDC also works to communicate its findings to healthcare professionals, the public, and policymakers, ensuring transparency and promoting informed decision-making.
Surveillance Systems Used by the CDC
The CDC utilizes a variety of surveillance systems to monitor vaccine safety. These systems are designed to capture different types of data and provide insights into potential safety concerns. Some key systems include:
- Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS):This is a passive surveillance system that relies on voluntary reports of suspected adverse events following vaccination. Healthcare providers, vaccine manufacturers, and individuals can submit reports to VAERS, which helps identify potential safety signals.
- The Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD):This is an active surveillance system that collects data from healthcare providers who are part of a network of large healthcare organizations. The VSD allows for more in-depth analysis of potential vaccine safety issues by comparing vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals within the network.
- Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project (CISA):This program investigates specific safety concerns about vaccines, often focusing on potential long-term effects. CISA uses a combination of data sources, including VAERS, VSD, and other databases, to conduct detailed analyses.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The CDC employs sophisticated data analysis techniques to identify patterns and trends in vaccine safety data. These techniques include:
- Statistical analysis:This involves using statistical methods to determine if there is a statistically significant association between vaccination and adverse events.
- Signal detection:This involves identifying unusual patterns in data that may suggest a potential safety concern.
- Case-control studies:These studies compare individuals who have experienced an adverse event to individuals who have not, to determine if there is a relationship between vaccination and the event.
The CDC’s vaccine safety monitoring system is a vital component of public health, ensuring that vaccines are safe and effective. By collecting and analyzing data from multiple sources, the CDC can identify potential safety issues, investigate them thoroughly, and take appropriate actions to protect public health.
Understanding the Claims of False Information: Cdc Spreads False Information About Covid 19 Vaccine Safety Monitoring

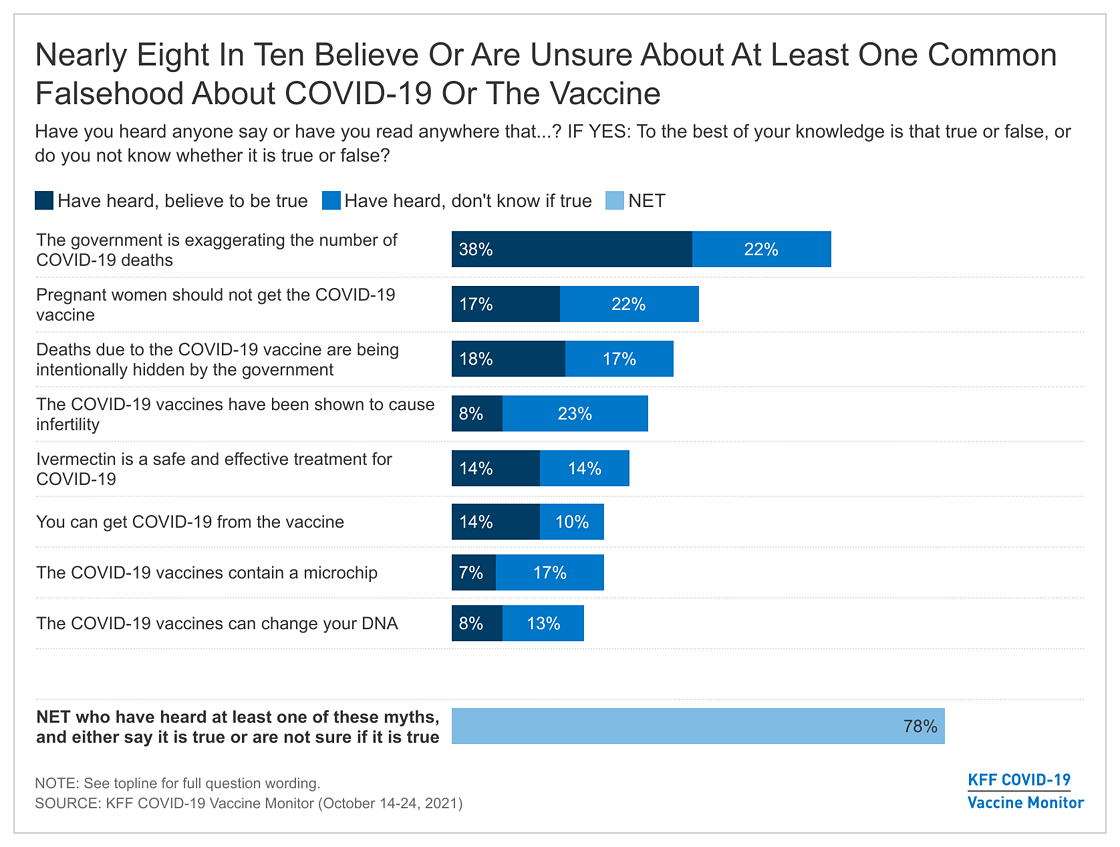
The claims that the CDC spreads false information about COVID-19 vaccine safety are a serious concern, as they can undermine public trust in vaccines and potentially lead to vaccine hesitancy. It’s crucial to critically examine these claims and evaluate their validity.
Claims of False Information
The claims of false information regarding COVID-19 vaccine safety often revolve around allegations that the CDC downplays or hides adverse effects of the vaccines. Some common claims include:
- The CDC is not transparent about vaccine side effects.
- The CDC is suppressing data on vaccine-related deaths.
- The CDC is manipulating data to make vaccines appear safer than they are.
It’s important to understand the context and evidence behind these claims. While some individuals may experience adverse reactions after receiving a vaccine, it’s crucial to distinguish between rare side effects and claims of widespread manipulation or suppression of data.
Evidence and Sources
Many claims of false information about COVID-19 vaccine safety originate from social media, blogs, and websites that promote anti-vaccine sentiment. These sources often lack scientific rigor and rely on anecdotal evidence or misinterpretations of data. For example, some websites may cherry-pick data points to support their claims, ignoring the broader context and statistical significance.
Analyzing the Credibility and Reliability of Sources
When evaluating claims about vaccine safety, it’s essential to consider the source of the information.
It’s frustrating to see the CDC spreading misinformation about COVID-19 vaccine safety monitoring, especially when it comes to the long-term effects. While the focus is on vaccine safety, it’s important to remember that energy independence is also crucial. The recent shift in the GOP-led House panels to focus on domestic energy production, as highlighted in this article gop led house panels shift gears goes full throttle for domestic energy production , is a positive step, but we shouldn’t lose sight of the need for transparency and accurate information regarding vaccine safety.
- Reputable Sources:Look for information from credible sources like the CDC, the World Health Organization (WHO), and reputable medical journals. These organizations employ experts in vaccine safety and rely on rigorous scientific methods.
- Scientific Rigor:Evaluate whether the information is based on peer-reviewed research and scientific evidence.
- Bias and Agenda:Be aware of potential biases or agendas that might influence the information presented.
It’s also crucial to be cautious of information that lacks clear evidence or relies on anecdotal experiences. While individual experiences can be valid, they do not necessarily represent the broader picture.
Examining the Scientific Evidence
The safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines have been rigorously studied and evaluated by numerous scientific organizations worldwide. A vast body of evidence supports their effectiveness in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19. This section delves into the scientific evidence, comparing and contrasting findings from various reputable sources and highlighting the potential risks and benefits associated with vaccination.
Safety and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines
Numerous large-scale clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. These trials involved tens of thousands of participants, with rigorous data collection and analysis. The results consistently show that the vaccines are highly effective in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19.
“The vaccines have been shown to be safe and effective in preventing COVID-19 illness, including severe disease, hospitalization, and death.”
CDC
Comparison of Findings from Reputable Organizations
The CDC, the World Health Organization (WHO), and other leading health organizations have conducted extensive reviews of the available scientific evidence. Their findings consistently demonstrate the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. While there may be minor variations in specific recommendations or data interpretations, the overall consensus is clear: COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective.
“The WHO recommends COVID-19 vaccination for all eligible individuals, regardless of their previous infection status.”
WHO
Potential Risks and Benefits of COVID-19 Vaccination
Like any medical intervention, COVID-19 vaccines carry potential risks and benefits. The benefits of vaccination, however, significantly outweigh the risks.
- Benefits:
- Reduced risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19
- Reduced risk of long COVID
- Protection for individuals and communities
- Contribution to herd immunity
- Risks:
- Mild side effects, such as pain at the injection site, fatigue, and headache
- Rare serious side effects, such as allergic reactions
It’s crucial to note that the vast majority of individuals experience only mild side effects after vaccination, and serious side effects are extremely rare. The CDC and other health organizations closely monitor vaccine safety and provide updated information and recommendations.
Addressing Misinformation and Disinformation
The spread of misinformation and disinformation about vaccine safety is a significant public health concern. It can undermine trust in vaccines and lead to vaccine hesitancy, ultimately impacting public health efforts to control infectious diseases. Understanding the strategies used to spread misinformation and how to combat it is crucial.
Strategies for Spreading Misinformation, Cdc spreads false information about covid 19 vaccine safety monitoring
Misinformation about vaccine safety often spreads through a variety of channels, utilizing specific strategies to gain traction. These strategies are designed to exploit human biases and vulnerabilities, making it crucial to understand them to effectively counter them.
- Appealing to Emotion:Misinformation often plays on fear, anger, or distrust. For example, claims that vaccines cause autism are emotionally charged and resonate with parents concerned about their children’s well-being.
- Cherry-Picking Data:Misinformation often presents isolated or out-of-context data to support a biased narrative. For instance, highlighting rare side effects without considering the overall benefits of vaccination can create a false sense of risk.
- Using Conspiracy Theories:Misinformation often weaves narratives that suggest hidden agendas or conspiracies, often blaming powerful institutions or individuals for spreading misinformation. This approach fosters distrust and makes it difficult to separate truth from fiction.
- Spreading False Expertise:Misinformation often relies on individuals claiming expertise without proper qualifications or evidence to support their claims. This can create an illusion of credibility and mislead people into believing false information.
Role of Social Media and Online Platforms
Social media and online platforms have significantly contributed to the spread of misinformation. Their algorithms, designed to keep users engaged, can amplify false content by prioritizing virality over accuracy.
- Echo Chambers:Social media algorithms often create echo chambers where users are primarily exposed to information that confirms their existing beliefs, reinforcing misinformation and hindering exposure to accurate information.
- Viral Spread:The ease with which misinformation can be shared and spread through social media platforms makes it difficult to control its reach. False claims can quickly go viral, reaching a large audience before they can be debunked.
- Lack of Fact-Checking:Many online platforms lack robust mechanisms for fact-checking and removing false content. This allows misinformation to persist and spread unchecked, further contributing to the problem.
Combating Misinformation
Recognizing the challenges posed by misinformation, various organizations and individuals are actively working to combat it. Their efforts focus on promoting accurate information, debunking false claims, and building trust in reliable sources.
It’s disheartening to see the CDC spreading misinformation about the COVID-19 vaccine’s safety monitoring. It’s reminiscent of the “Russia hoax” narrative, which, as this article points out, was a fabricated story used to discredit a political opponent. The CDC’s actions raise serious concerns about transparency and the integrity of public health information, especially when it comes to something as important as vaccine safety.
- Fact-Checking Organizations:Fact-checking organizations like Snopes, PolitiFact, and FactCheck.org play a crucial role in verifying information and debunking false claims. They use evidence-based research to assess the accuracy of information and provide clear explanations to the public.
- Social Media Platforms:Social media platforms are increasingly implementing measures to combat misinformation. This includes flagging false content, promoting accurate information, and partnering with fact-checking organizations to verify information.
- Public Health Agencies:Public health agencies like the CDC and WHO are actively working to counter misinformation by providing accurate information about vaccines and diseases. They use various communication channels, including websites, social media, and public outreach programs, to reach diverse audiences.
- Media Literacy Education:Promoting media literacy is essential to empower individuals to critically evaluate information and identify misinformation. Educational programs can teach people how to recognize biases, evaluate sources, and verify information before sharing it.
Impact on Public Health

The spread of misinformation about COVID-19 vaccine safety can have devastating consequences for public health. Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by false information, can lead to lower vaccination rates, putting individuals and communities at risk of preventable diseases.
The Importance of Public Trust
Trust in scientific institutions like the CDC is crucial for effective public health interventions. When the public loses trust in these institutions, it can be difficult to promote evidence-based practices, such as vaccination.
“Public trust is the foundation of public health. When people trust their health authorities, they are more likely to follow their recommendations, which can lead to better health outcomes.”Dr. Anthony Fauci, Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
The Role of Communication and Transparency
Clear, accurate, and transparent communication is essential for building trust and promoting vaccine uptake. Public health officials must actively engage with the public, address concerns, and provide reliable information.
- Open and Honest Communication:Public health officials should be transparent about the risks and benefits of vaccines, acknowledging uncertainties and addressing concerns openly.
- Engaging with Communities:Reaching out to diverse communities and addressing their specific concerns and needs is crucial for building trust and promoting vaccine uptake.
- Utilizing Multiple Channels:Public health officials should utilize various communication channels, including traditional media, social media, and community outreach programs, to reach diverse audiences.
End of Discussion
Navigating the complex world of vaccine safety requires critical thinking and a reliance on credible sources. While it’s essential to be vigilant about potential risks, it’s equally important to avoid spreading misinformation that can undermine public health efforts. The CDC’s role in vaccine safety monitoring is crucial, and it’s vital to engage in constructive dialogue about its practices and data analysis.
Ultimately, fostering a culture of transparency and open communication is essential for building trust and promoting informed decision-making regarding public health.