CDC Releases Hidden COVID-19 Vaccine Injury Reports
Cdc releases hidden covid 19 vaccine injury reports – CDC Releases Hidden COVID-19 Vaccine Injury Reports: The news has sent shockwaves through the medical community and sparked heated debates about vaccine safety and transparency. The alleged “hidden” reports, said to contain details of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination, have fueled concerns about potential risks and raised questions about the CDC’s data collection and reporting practices.
This discovery has prompted a critical examination of the CDC’s role in vaccine safety monitoring and the importance of open access to crucial data. The allegations have also highlighted the delicate balance between protecting public health and safeguarding individual rights, as well as the potential impact on public trust in vaccines.
Data Transparency and Accessibility
In the realm of public health, data transparency is paramount. Open and accessible data empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, builds trust in public health institutions, and facilitates independent research and analysis. When it comes to vaccine safety data, transparency is particularly crucial.
Challenges and Benefits of Making Vaccine Safety Data Publicly Accessible
Making vaccine safety data publicly accessible presents both challenges and benefits.
The CDC’s release of hidden COVID-19 vaccine injury reports is a concerning development, especially given the ongoing debate surrounding vaccine safety. While we focus on the potential risks of vaccines, it’s important to remember that space exploration continues to push boundaries, like the upcoming Boeing Starliner launch which will bring new cargo and scientific experiments to the International Space Station.
This event reminds us that despite challenges, human ingenuity and innovation continue to drive us forward, just as we need to continue to research and understand the potential risks and benefits of vaccines.
- Challenges:
- Privacy Concerns:Ensuring the protection of individual patient data is paramount. Balancing transparency with privacy requires careful consideration of data anonymization and security measures.
- Data Complexity:Vaccine safety data can be complex and requires specialized knowledge to interpret. Making raw data accessible without adequate context or analysis could lead to misinterpretations and public confusion.
- Misinterpretation and Misuse:The potential for misuse of data, such as selective reporting or cherry-picking data to support preconceived notions, is a concern.
- Benefits:
- Increased Trust:Transparency fosters trust in public health institutions by demonstrating accountability and openness.
- Enhanced Public Health Decision-Making:Accessible data empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, and it provides valuable information for policymakers and researchers.
- Improved Vaccine Safety Monitoring:Open access to data allows for independent analysis and scrutiny of vaccine safety, potentially leading to earlier detection of safety signals and more effective monitoring systems.
Examples of Other Countries’ Approaches to Vaccine Safety Data Transparency
Several countries have implemented different approaches to vaccine safety data transparency.
- European Union:The European Medicines Agency (EMA) publishes summaries of safety reports for all vaccines authorized in the EU, including detailed information on suspected adverse events.
- United States:The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) maintains the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), a database of reports of adverse events following vaccination. VAERS data is publicly available, but it’s important to note that it is not a system for determining causality.
- United Kingdom:The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) publishes monthly safety reports for all vaccines authorized in the UK, including detailed information on suspected adverse events.
Vaccine Safety and Public Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the critical role of vaccines in safeguarding public health. While vaccines offer substantial protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and benefits associated with them. Informed consent plays a vital role in vaccination decisions, and ethical considerations must guide the development, distribution, and use of vaccines.
Risks and Benefits of COVID-19 Vaccination
Weighing the risks and benefits of COVID-19 vaccination is essential for making informed decisions. The benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks for most individuals.
The CDC releasing hidden COVID-19 vaccine injury reports is a serious issue that raises concerns about transparency and accountability. It’s important to remember that healthcare systems are complex, and understanding the intricacies of programs like Medicaid is crucial. For instance, did you know that there are 10 things to know about Medicaid managed care that can impact individuals’ access to care?
This knowledge is vital when evaluating the potential consequences of vaccine-related injuries and advocating for better healthcare practices.
- Benefits:
- Reduced risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death: Vaccines significantly reduce the likelihood of developing severe COVID-19, requiring hospitalization, or dying from the disease.
- Protection against long COVID: Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of developing long COVID, a condition characterized by lingering symptoms after an initial infection.
- Reduced transmission: Vaccines can help reduce the spread of COVID-19, protecting vulnerable individuals who cannot be vaccinated.
- Return to normalcy: Vaccination allows individuals to return to pre-pandemic activities, such as attending social gatherings, traveling, and working in person.
- Risks:
- Mild side effects: Common side effects after vaccination include pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, and chills. These side effects are generally mild and temporary.
- Rare serious side effects: Some individuals may experience rare but serious side effects, such as myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) or pericarditis (inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart). These side effects are more common in younger males, and the risk is generally low.
- Allergic reactions: While rare, allergic reactions to vaccine components are possible. Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions should consult with their healthcare provider before vaccination.
Informed Consent in Vaccination Decisions
Informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical healthcare practices, including vaccination. Individuals have the right to make informed decisions about their health, and this right extends to vaccination.
Informed consent requires that individuals understand the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives to vaccination before making a decision.
The CDC releasing hidden COVID-19 vaccine injury reports is a serious concern, and it raises questions about transparency and accountability. It’s important to remember that even with the best intentions, data can be misinterpreted or hidden, leading to a lack of trust.
This reminds me of how crucial it is to have the right tech to manage employee data and ensure transparency, as outlined in this article on curbing turnover: want to curb turnover the right tech can help. Just as we need accurate information to make informed decisions about our health, we also need reliable data to make sound decisions about our workforce.
Ultimately, both scenarios highlight the importance of open communication and access to reliable information.
- Essential components of informed consent include:
- Clear and accurate information: Individuals should receive comprehensive and understandable information about the vaccine, including its benefits, risks, and potential side effects.
- Opportunity for questions: Individuals should be given the opportunity to ask questions and receive clear answers from healthcare providers.
- Voluntary decision-making: Individuals should be free to make their own decisions about vaccination without coercion or pressure.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Vaccine Safety and Public Health
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of vaccines while protecting public health.
- Transparency and accountability: Vaccine development, testing, and distribution processes should be transparent and accountable to the public. This includes sharing data on vaccine safety and efficacy, as well as addressing concerns and questions.
- Equity and access: Vaccines should be accessible to all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status, location, or other factors. This requires addressing disparities in access and ensuring equitable distribution.
- Respect for individual autonomy: Individuals should be empowered to make informed decisions about vaccination based on their own values and beliefs. This includes respecting their right to refuse vaccination, while also providing accurate information and addressing concerns.
- Public trust and communication: Maintaining public trust in vaccines is essential for ensuring high vaccination rates and protecting public health. This requires clear, accurate, and consistent communication from public health officials and healthcare providers.
Potential Impact on Vaccine Hesitancy
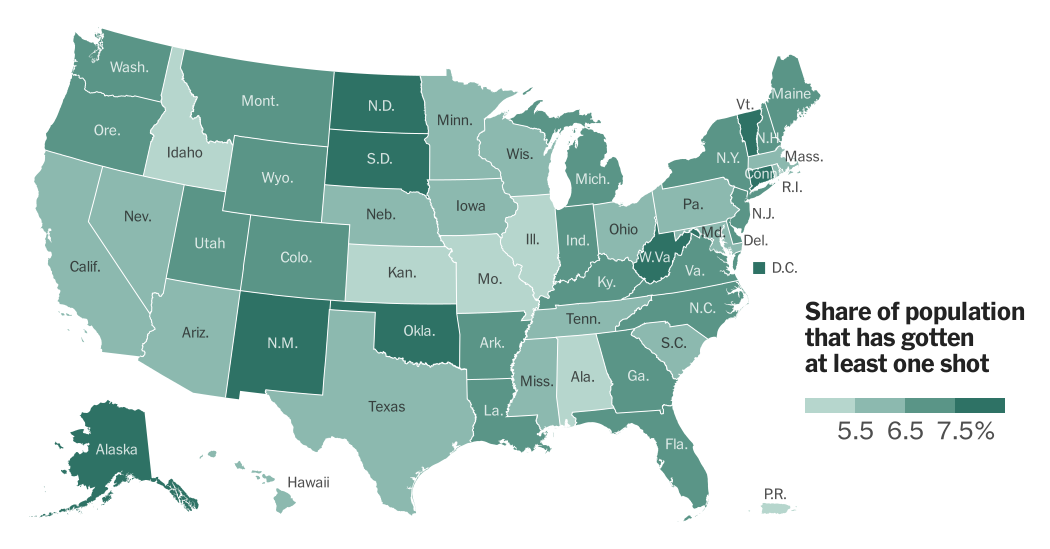
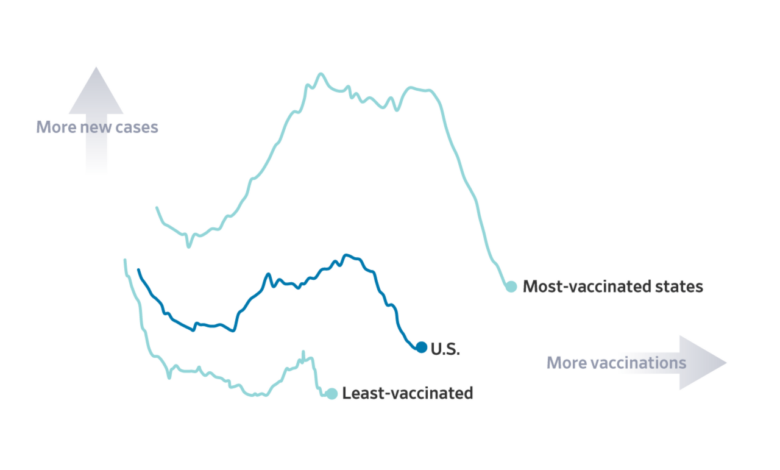
The alleged release of hidden COVID-19 vaccine injury reports could have a significant impact on vaccine hesitancy, potentially eroding public trust in vaccines and hindering vaccination efforts. It is crucial to analyze the potential consequences and develop strategies to mitigate these effects.
Impact on Vaccine Hesitancy
The revelation of hidden vaccine injury reports, if true, could fuel existing concerns about vaccine safety and exacerbate vaccine hesitancy. Individuals who were already skeptical about vaccines might interpret this as evidence of a cover-up, reinforcing their belief that vaccines are dangerous.
This could lead to a decrease in vaccine uptake, potentially jeopardizing herd immunity and increasing the risk of outbreaks.
Strategies to Address Vaccine Hesitancy
Addressing vaccine hesitancy requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on restoring public trust and providing accurate information. Here are some potential strategies:
- Transparency and Open Communication:Public health agencies should be transparent about vaccine safety data, including any potential risks and benefits. This includes proactively disclosing any adverse events associated with vaccines and providing clear explanations for how these events are monitored and investigated.
- Engaging with Communities:Public health officials should engage with communities, particularly those with high levels of vaccine hesitancy, to address concerns and build trust. This can be done through community forums, town hall meetings, and social media platforms.
- Promoting Accurate Information:Efforts should be made to counter misinformation and promote accurate information about vaccines. This includes partnering with credible sources of information, such as medical professionals, scientific organizations, and trusted community leaders.
- Addressing Misconceptions:Public health campaigns should address common misconceptions about vaccines, providing evidence-based information to debunk myths and dispel false claims.
Importance of Accurate and Reliable Information, Cdc releases hidden covid 19 vaccine injury reports
Accurate and reliable information about vaccine safety is crucial for building public trust and promoting vaccine acceptance. Individuals should be able to access credible sources of information that provide a balanced and objective assessment of vaccine risks and benefits.
Misinformation and conspiracy theories can spread rapidly, undermining public health efforts and creating unnecessary fear and distrust.
Summary: Cdc Releases Hidden Covid 19 Vaccine Injury Reports
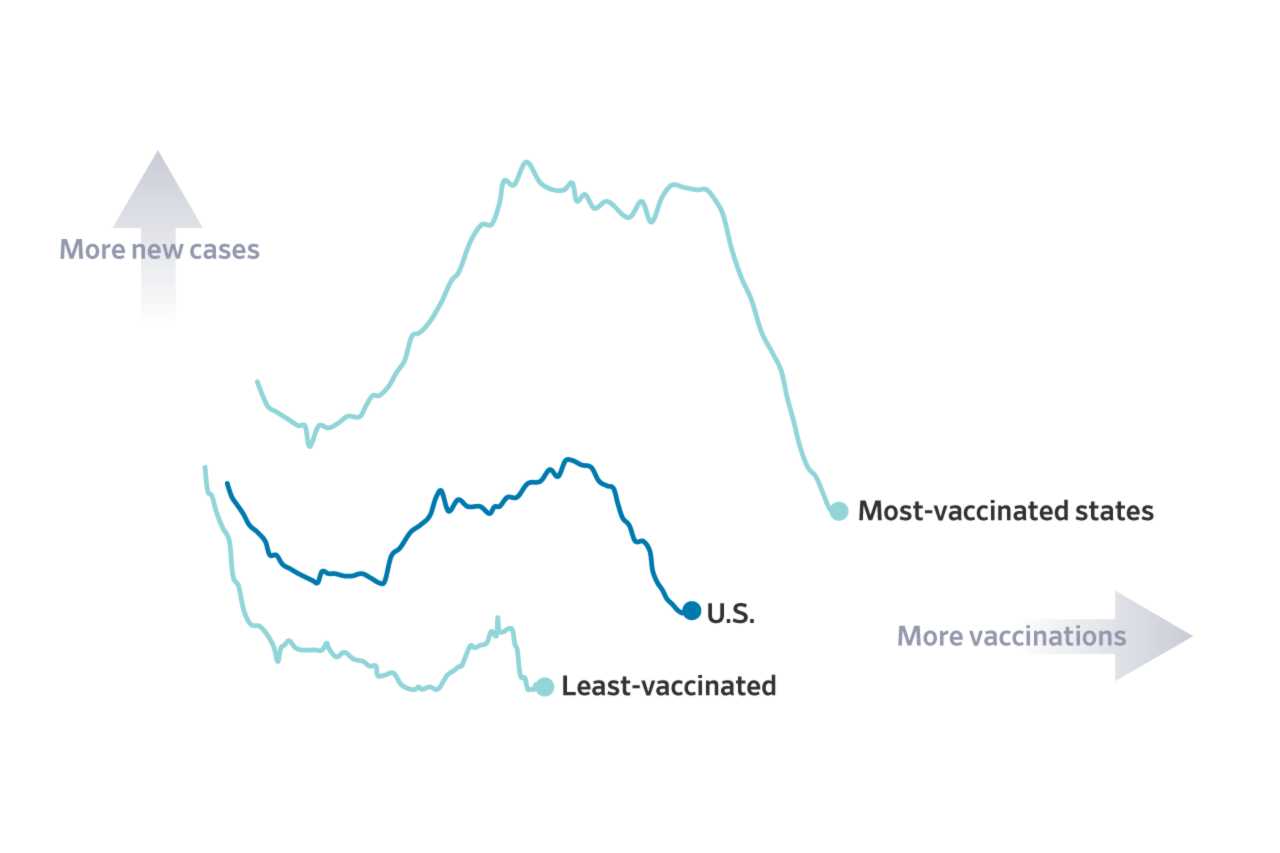
The revelation of these alleged “hidden” reports underscores the need for a transparent and accountable approach to vaccine safety data. It’s essential that the CDC, and other health authorities, prioritize open access to data, foster public trust through honest communication, and address concerns about vaccine safety in a comprehensive and transparent manner.
Only then can we navigate the complex landscape of vaccine hesitancy and ensure that informed decisions are made about our health and well-being.